Prim Algorithm
简介(Introduction)
普里姆算法(\(Prim\) 算法),图论中的一种算法,可在加权连通图里搜索 最小生成树。即由此算法搜索到的边子集所构成的树中,不但包括了连通图里的所有顶点,且其所有边的权值之和亦为最小。
描述(Description)
- \(Prim\) 算法和 \(Dijkstra\) 算法类似,核心思想为 贪心。
- \(Prim\) 算法总是维护最小生成树的一部分。最初,\(Prim\) 算法仅确定 \(1\) 号节点属于最小生成树。
- \(Dijkstra\) 算法和 \(Prim\) 算法区别:
- \(Dijkstra\) 算法遍历寻找的是到源点的最短距离
- \(Prim\) 算法遍历寻找的是到集合的距离(集合外的点连向集合内的点的距离的最小值,如果集合外没有点能连接到集合内,那么距离就是正无穷),并且把这个点加入到集合中。
- \(Prim\) 算法流程:
- 在任一时刻,假设已经确定属于最小生成树的节点集合为 \(T\),剩余节点集合为 \(S\)。
- 找到 \(\large min_{\small {x\in S,y\in T}} \begin{Bmatrix} z \end{Bmatrix}\),即两个端点分别属于集合 \(S,T\) 的权值最小的边,
- 然后将 \(x\) 从集合 \(S\) 中删除,加入到集合 \(T\),并把 \(z\) 累加到答案中
- 类比 \(Dijkstra\) 算法,用一个数组标记节点是否属于 \(T\)。每次从未标记的节点中选出 \(dist\) 值最小的,把它标记(新加入 \(T\)),同时扫描所有出边,更新另一个端点的 \(d\) 值。最后,最小生成树的权值总和就是 \(\sum_{x = 2}^{n}d[x]\)
维护 \(d\) 数组:
- 若 \(x\in S\),则 \(d[x]\) 表示节点 \(x\) 与集合 \(T\) 中的节点之间权值最小的边的权值
- 若 \(x \in T\),则 \(d[x]\) 等于 \(x\) 被加入 \(T\) 时选出最小边的权值
时间复杂度:\(O(n^2)\)
示例(Example)
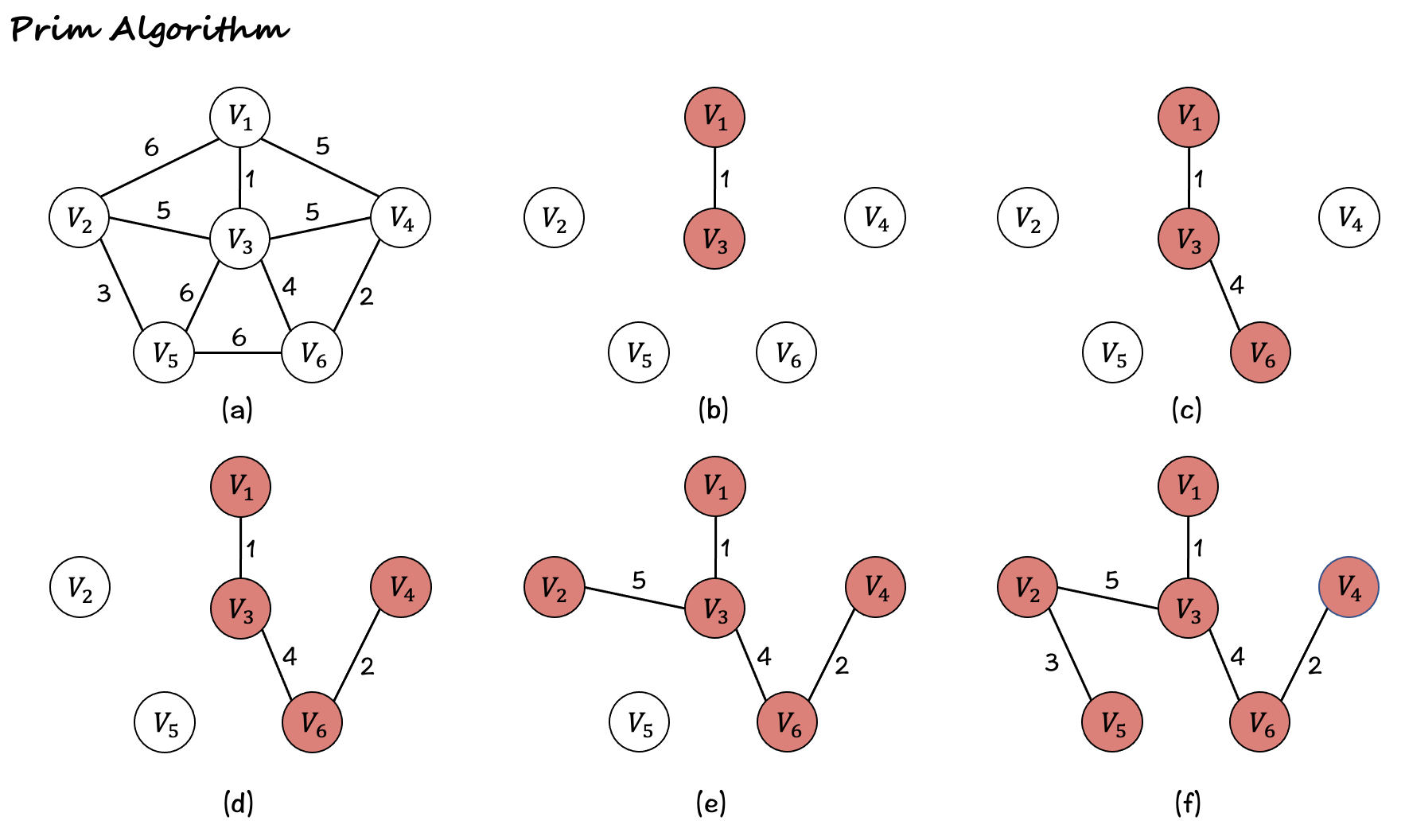
- 运行结果:

代码(Code)
// C++ Version
const int N = 1010;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int n, m, res; // res 为最小生成树大小
int g[N][N];
int d[N], la[N];
bool vis[N];
int prim() {
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist); // 初始化正无穷
d[1] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
int t = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ ) { // 遍历所有点
if (!vis[j] && (!t || d[t] > d[j])) // 找到距离集合最近的一个点
t = j;
}
if (d[t] == inf) return inf; // 最近的点到集合的距离都是正无穷,图不连通。
vis[t] = 1; // 加入集合,标记已经使用
res += d[t]; // 找到最小的点,加上对应的路径
if (i) {
cout << "加入 <" << la[t] << ","<< t << "> 权值为:" << d[t] << endl;
cout << "当前的 d 数组为;";
for (int i = 1; i < n; i ++ ) cout << d[i] << ' ';
cout << endl;
}
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ )
if (!vis[j] && d[j] > g[t][j]) { // 注意这里和 Dijkstra 的区别
d[j] = g[t][j]; // 用 t 这个点更新到其他的点的距离。
la[j] = t; // 记录上一次的路径
}
}
return res;
}
// 注意: 最小生成树中不应存在自环,因此 res 更新应该在 t 遍历更新距离之前。这样就不会把自环更新进来。
应用(Application)
最小生成树
给出一个无向图,求出最小生成树,如果该图不连通,则输出
orz。
输入格式第一行包含两个整数 \(N,M\),表示该图共有 \(N\) 个结点和 \(M\) 条无向边。
接下来 \(M\) 行每行包含三个整数 \(X_i,Y_i,Z_i\),表示有一条长度为 \(Z_i\) 的无向边连接结点 \(X_i,Y_i\)。
输出格式
如果该图连通,则输出一个整数表示最小生成树的各边的长度之和。如果该图不连通则输出
orz。数据范围
对于 \(20\%\) 的数据,\(N\le 5\),\(M\le 20\)。
对于 \(40\%\) 的数据,\(N\le 50\),\(M\le 2500\)。
对于 \(70\%\) 的数据,\(N\le 500\),\(M\le 10^4\)。
对于 \(100\%\) 的数据:\(1\le N\le 5000\),\(1\le M\le 2\times 10^5\),\(1\le Z_i \le 10^4\)。
输入样例:
4 5
1 2 2
1 3 2
1 4 3
2 3 4
3 4 3
输出样例:
7
- 题解:
#include <cstdio> #include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <ctime> #include <cmath> #include <map> #include <set> #include <unordered_set> #include <unordered_map> #include <sstream> #include <algorithm> #include <bitset> #include <vector> #include <deque> #define pb push_back #define opb pop_back #define yes puts("YES") #define no puts("NO") #define all(a) a.begin(), a.end() #define show(x) cout << x << endl #define rep2(i, a, b) for (int i = a; i <= b; i ++ ) #define rep1(i, a, b) for (int i = a; i < b; i ++ ) #define per2(i, a, b) for (int i = a; i >= b; i -- ) #define per1(i, a, b) for (int i = a; i > b; i -- ) #define fio ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cout.tie(0), cin.tie(0) #define ff first #define ss second using namespace std; typedef unsigned long long ull; typedef pair<int, int> pii; typedef pair<string, int> psi; typedef pair<double, double> pdd; typedef long long ll; const int N = 100010, M = 5010; const int mod = 1000000007; const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f; int n, m; int g[M][M]; int dist[N]; bool st[N]; void prim() { memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist); dist[1] = 0; // 初始化起点 for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) { int t = -1; for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ ) if (!st[j] && (t == -1 || dist[t] > dist[j])) t = j; st[t] = true; for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ ) if (!st[j]) dist[j] = min(dist[j], g[t][j]); } } int main() { fio; cin >> n >> m; memset(g, 0x3f, sizeof g); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) g[i][i] = 0; while (m -- ) { int a, b, c; cin >> a >> b >> c; g[a][b] = g[b][a] = min(g[a][b], c); } prim(); int res = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) { if (dist[i] == inf) { cout << "orz"; return 0; } res += dist[i]; } cout << res << endl; return 0; }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号