二叉查找树(Binary Search Tree)
简介(Introduction)
二叉搜索树作为一种经典的数据结构,它既有链表的快速插入与删除操作的特点,又有数组快速查找的优势;所以应用十分广泛,例如在文件系统和数据库系统一般会采用这种数据结构进行高效率的排序与检索操作。
描述(Description)
- 性质:
- 若它的左子树不为空,则左子树上所有节点的值都小于根节点的值
- 若它的右子树不为空,则右子树上所有节点的值都大于根节点的值
- 它的左右子树也分别为二叉搜索树
Tip: 二叉搜索树 中序遍历 的结果是有序的
- 操作:时间复杂度:\(O(\log n)\)
- 插入
- 删除:
- 若当前节点的值大于 \(x\),递归删除左子树
- 若当前节点的值小于 \(x\),递归删除右子树
- 若当前节点的值等于 \(x\),
- 若当前节点为 叶子节点,则直接删除
- 若当前节点 没有左子树,则将当前节点的右子树上移到该点
- 若当前节点 没有右子树,则将当前节点的左子树上移到该点
- 若当前节点 均有左右子树,则需找到当前节点的 左节点的最右节点 的值代替当前节点,并将找到的节点删除
- 查找
示例(Example)
-
查找
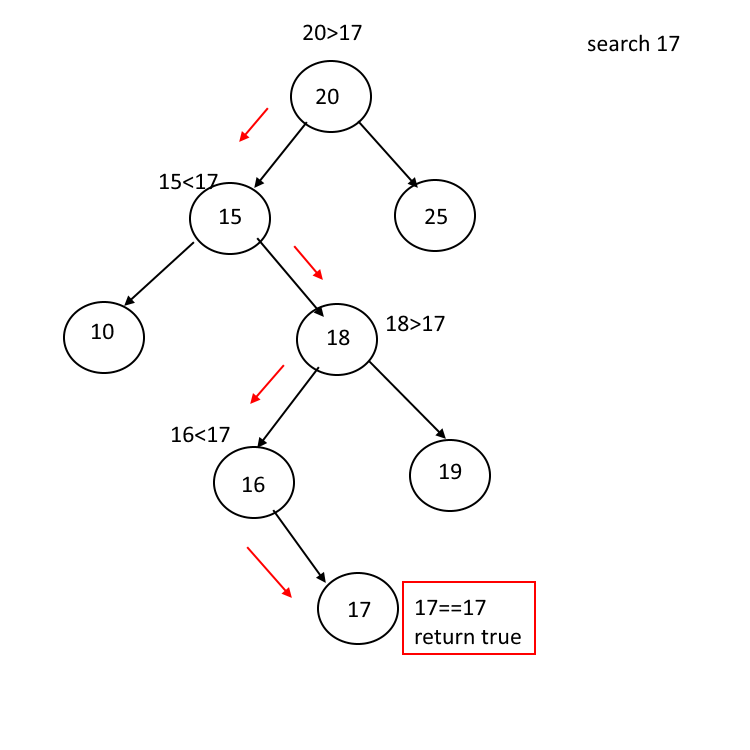
-
插入:
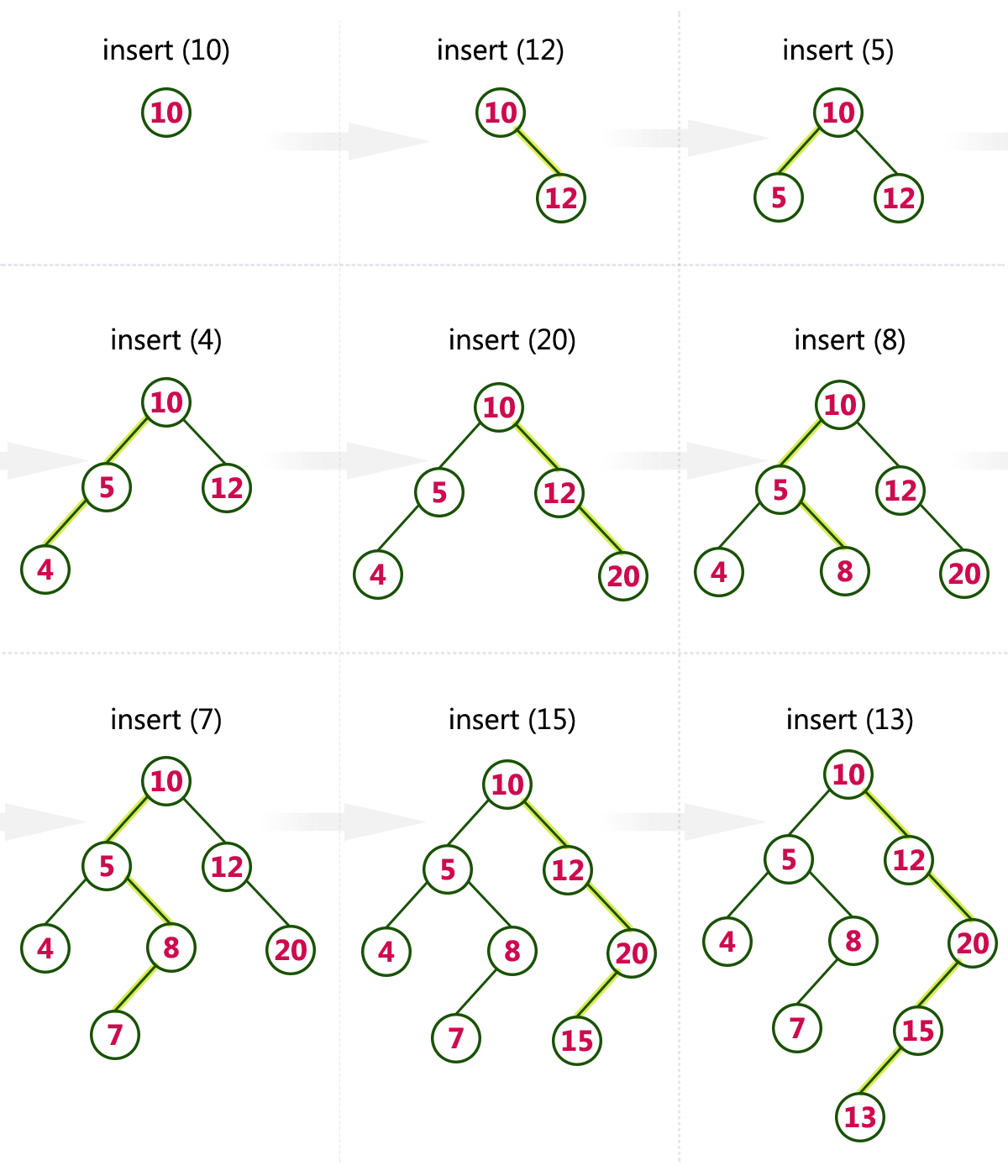
-
删除:
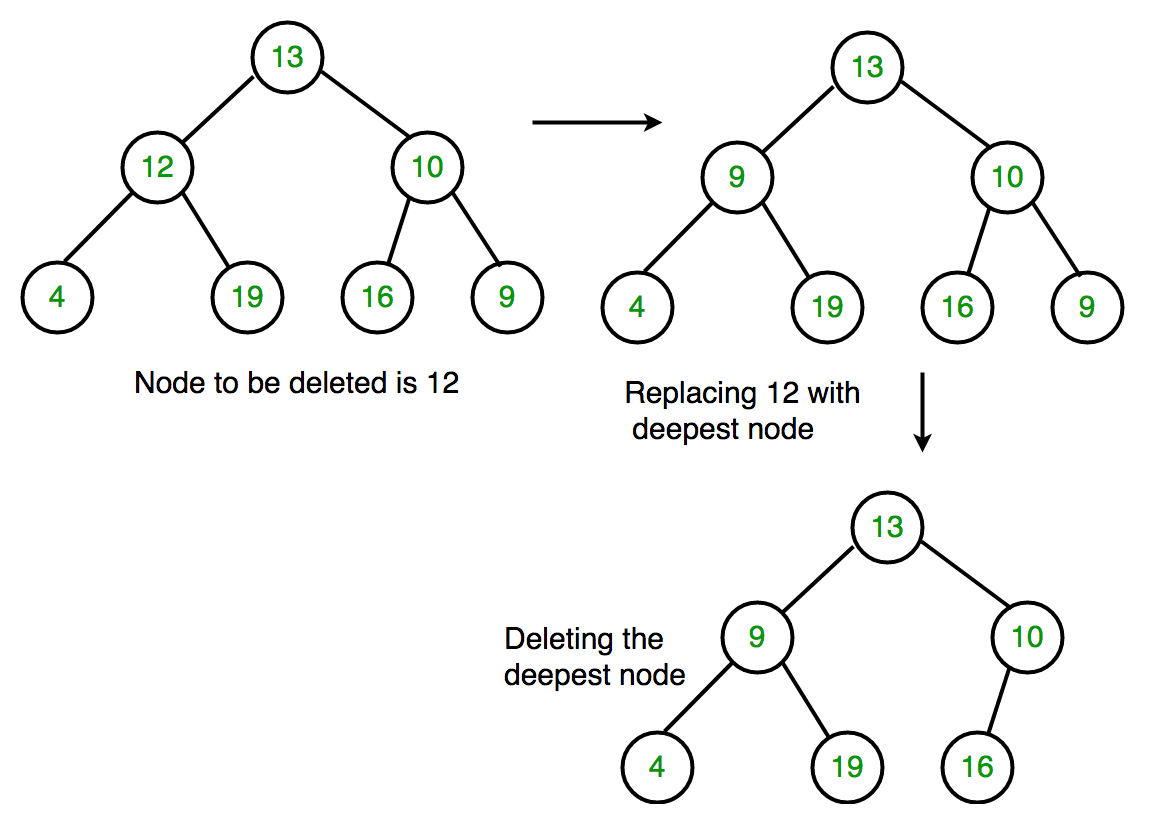
代码(Code)
-
节点定义:
struct TreeNode { int val; TreeNode *left, *right; TreeNode(int _val) : val(_val), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} } *root; -
查找:
const int INF = 1e9; int get_pre(TreeNode* root, int x) { // 找到小于 x 的最大的数(前驱) if (!root) return -INF; // 没有则返回 -INF if (root->val >= x) return get_pre(root->left, x); // 当前节点值大于等于 x 说明结果在左子树中 return max(root->val, get_pre(root->right, x)); // 当前节点也可能是目标值,取右子树的结果与当前值的较大值即可 } -
插入:
void insert(TreeNode* &root, int x) { if (!root) root = new TreeNode(x); // 直接插入 if (root->val == x) return; // 已存在该点则返回 if (root->val > x) insert(root->left, x); else insert(root->right, x); } -
删除:
void remove(TreeNode* &root, int x) { if (!root) return; if (root->val > x) remove(root->left, x); else if (root->val < x) remove(root->right, x); else { if (!root->left && !root->right) root = NULL; else if (!root->left) root = root->right; else if (!root->right) root = root->left; else { auto t = root->left; while (t->right) t = t->right; root->val = t->val; remove(root->left, t->val); } } }
应用(Application)
二叉排序树
你需要写一种数据结构,来维护一些数,其中需要提供以下操作:
- 插入数值 \(x\)。
- 删除数值 \(x\)。
- 输出数值 \(x\) 的前驱(前驱定义为现有所有数中小于 \(x\) 的最大的数)。
- 输出数值 \(x\) 的后继(后继定义为现有所有数中大于 \(x\) 的最小的数)。
题目保证:
- 操作 \(1\) 插入的数值各不相同。
- 操作 \(2\) 删除的数值一定存在。
- 操作 \(3\) 和 \(4\) 的结果一定存在。
输入格式
第一行包含整数 \(n\),表示共有 \(n\) 个操作命令。
接下来 \(n\) 行,每行包含两个整数 \(opt\) 和 \(x\),表示操作序号和操作数值。
输出格式
对于操作 \(3,4\),每行输出一个操作结果。
数据范围
\(1 \le n \le 2000\),
\(-10000 \le x \le 10000\)
输入样例:
6
1 1
1 3
1 5
3 4
2 3
4 2
输出样例:
3
5
- 题解:
#include <cstdio> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> using namespace std; const int INF = 1e9; struct TreeNode { int val; TreeNode *left, *right; TreeNode(int _val) : val(_val), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} } *root; void insert(TreeNode* &root, int x) { if (!root) root = new TreeNode(x); if (root->val == x) return; if (root->val > x) insert(root->left, x); else insert(root->right, x); } void remove(TreeNode* &root, int x) { if (!root) return; if (root->val > x) remove(root->left, x); else if (root->val < x) remove(root->right, x); else { if (!root->left && !root->right) root = NULL; else if (!root->left) root = root->right; else if (!root->right) root = root->left; else { auto t = root->left; while (t->right) t = t->right; root->val = t->val; remove(root->left, t->val); } } } int get_pre(TreeNode* root, int x) { if (!root) return -INF; if (root->val >= x) return get_pre(root->left, x); return max(root->val, get_pre(root->right, x)); } int get_lat(TreeNode* root, int x) { if (!root) return INF; if (root->val <= x) return get_lat(root->right, x); return min(root->val, get_lat(root->left, x)); } int main() { int n; cin >> n; while (n -- ) { int t, x; cin >> t >> x; if (t == 1) insert(root, x); else if (t == 2) remove(root, x); else if (t == 3) cout << get_pre(root, x) << endl; else cout << get_lat(root, x) << endl; } return 0; }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号