springboot(二十三)-自定义starter依赖
1.starter机制
SpringBoot中的starter是一种非常重要的机制,能够抛弃以前繁杂的配置,将其统一集成进starter,应用者只需要在maven中引入starter依赖,SpringBoot就能自动扫描到要加载的信息并启动相应的默认配置。starter让我们摆脱了各种依赖库的处理,需要配置各种信息的困扰。SpringBoot会自动通过classpath路径下的类发现需要的Bean,并注册进IOC容器。SpringBoot提供了针对日常企业应用研发各种场景的spring-boot-starter依赖模块。所有这些依赖模块都遵循着约定成俗的默认配置,并允许我们调整这些配置,即遵循“约定大于配置”的理念。
2.为什么要自定义starter
在我们的日常开发工作中,经常会有一些独立于业务之外的配置模块,比如对时间的处理,对字符串的处理。我们经常将其放到一个特定的包下,然后如果另一个工程需要复用这块功能的时候,需要将代码硬拷贝到另一个工程,重新集成一遍,麻烦至极。如果我们将这些可独立于业务代码之外的功配置模块封装成一个个starter,复用的时候只需要将其在pom中引用依赖即可,SpringBoot为我们完成自动装配,简直不要太爽。
3.自定义starter的案例
以下案例由笔者工作中遇到的部分场景
▲ 动态数据源。
▲ 登录模块。
▲ 基于AOP技术实现日志切面。
。。。。。。
4、自定义starter的命名规则
SpringBoot提供的starter以spring-boot-starter-xxx的方式命名的。官方建议自定义的starter使用xxx-spring-boot-starter命名规则。以区分SpringBoot生态提供的starter。
5.starter实现
1).先看目录结构
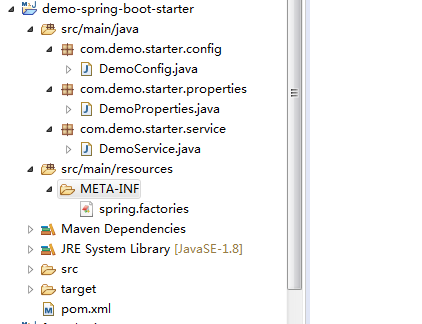
2).pom.xml文件
1 <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> 2 <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> 3 <groupId>com.demo</groupId> 4 <artifactId>demo-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> 5 <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> 6 <name>demo-spring-boot-starter</name> 7 <description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description> 8 9 <parent> 10 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 11 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> 12 <version>2.0.4.RELEASE</version> 13 </parent> 14 15 <properties> 16 <java.version>1.8</java.version> 17 </properties> 18 19 <dependencies> 20 <dependency> 21 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 22 <artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId> 23 <optional>true</optional> 24 </dependency> 25 26 <dependency> 27 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 28 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId> 29 </dependency> 30 </dependencies> 31 </project>
其中:spring默认使用yml中的配置,但有时候要用传统的xml或properties配置,就需要使用spring-boot-configuration-processor依赖了。
3).定义一个实体类映射配置信息
1 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "demo") 2 public class DemoProperties { 3 private String sayWhat; 4 private String toWho; 5 6 public String getSayWhat() { 7 return sayWhat; 8 } 9 10 public void setSayWhat(String sayWhat) { 11 this.sayWhat = sayWhat; 12 } 13 14 public String getToWho() { 15 return toWho; 16 } 17 18 public void setToWho(String toWho) { 19 this.toWho = toWho; 20 } 21 }
4).定义一个服务service
1 public class DemoService { 2 public String sayWhat; 3 public String toWho; 4 public DemoService(String sayWhat, String toWho){ 5 this.sayWhat = sayWhat; 6 this.toWho = toWho; 7 } 8 public String say(){ 9 return this.sayWhat + "! " + toWho; 10 } 11 12 public String getString(String a) { 13 return a+"1234"; 14 } 15 }
5).定义一个配置类
1 @Configuration 2 @EnableConfigurationProperties(DemoProperties.class) 3 @ConditionalOnProperty( 4 prefix = "demo", 5 name = "isopen", 6 havingValue = "true" 7 ) 8 public class DemoConfig { 9 @Autowired 10 private DemoProperties demoProperties; 11 12 @Bean(name = "demo") 13 public DemoService demoService(){ 14 return new DemoService(demoProperties.getSayWhat(), demoProperties.getToWho()); 15 } 16 }
这里,我们将DemoService类定义为一个Bean,交给Ioc容器。
@Configuration表示这是一个配置类
@EnableConfigurationProperties 确保SpringBoot支持@ConfigurationProperties注解的Bean对象。让springboot在初始化容器的时候,能够也将@ConfigurationProperties注解的Bean对象初始化到容器中。
当然了,也可以在上面 DemoProperties 类上面加上@Configuration注解或者@Component注解。
@ConditionalOnProperty 注解控制 @Configuration 是否生效。简单来说也就是我们可以通过在yml配置文件中控制 @Configuration 注解的配置类是否生效
6).spring.factories文件
1 #-------starter自动装配--------- 2 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=com.demo.starter.config.DemoConfig
在该文件中加入这个配置,该配置指定上步骤中定义的配置类为自动装配的配置。让springboot注解关键三个之一的@EnableAutoConfiguration注解去工作。
测试
1.选中项目-右击- run as - maven install

本地仓库中就有了我们自定义的starter依赖。
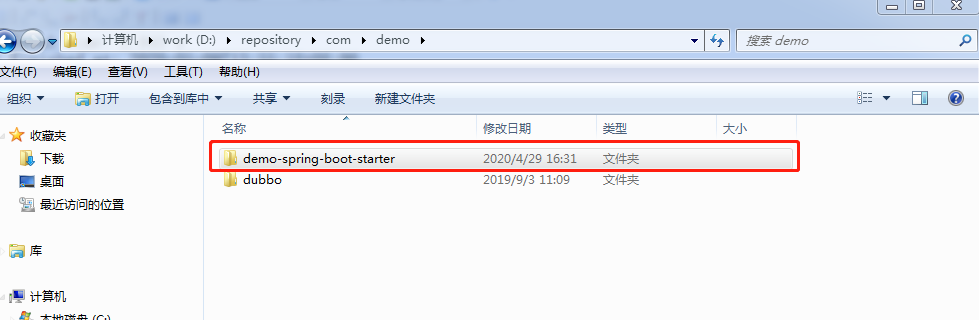
2.然后在测试项目中添加上依赖
<dependency> <groupId>com.demo</groupId> <artifactId>demo-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> </dependency>
配置文件
demo.isopen=true
demo.sayWhat=hello
demo.toWho= fengyuduke
写个测试类
1 @RestController 2 public class HelloController { 3 @GetMapping("/hello") 4 public String hello() { 5 return "hello"; 6 } 7 8 @Autowired 9 private DemoService demoService; 10 11 @GetMapping("/say") 12 public String sayWhat(){ 13 return demoService.say(); 14 } 15 @GetMapping("/getString") 16 public String getString() { 17 return demoService.getString("风雨渡客"); 18 } 19 }
访问测试
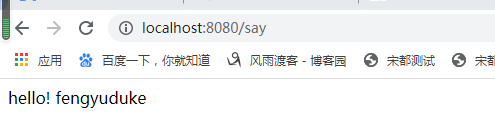
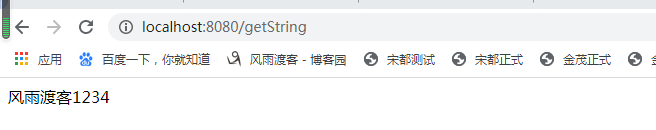
这时候,你如果把xml文件中的demo.isopen设置为false 或者注掉。
#demo.isopen=false demo.sayWhat=hello demo.toWho=fengyuduke
服务是起不来的,控制台报错信息也很明显。
Description: Field demoService in org.javaboy.formlogin.HelloController required a bean of type 'com.demo.starter.service.DemoService' that could not be found. The injection point has the following annotations: - @org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired(required=true) The following candidates were found but could not be injected: - Bean method 'demoService' in 'DemoConfig' not loaded because @ConditionalOnProperty (demo.isopen=true) found different value in property 'isopen' Action: Consider revisiting the entries above or defining a bean of type 'com.demo.starter.service.DemoService' in your configuration.
(非原创)参考链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/hello-shf/p/10864977.html


