论文阅读笔记 Improved Word Representation Learning with Sememes
论文阅读笔记 Improved Word Representation Learning with Sememes
一句话概括本文工作
使用词汇资源——知网——来提升词嵌入的表征能力,并提出了三种基于知网资源的词嵌入学习模型,在通用的中文词嵌入评测数据集上进行了评测,取得了较好的结果。
作者简介
该论文选自 ACL 2017,是清华大学孙茂松刘知远老师组的成果。论文的两名共同第一作者分别是牛艺霖和谢若冰。
牛艺霖,清华本科生。
谢若冰,清华研究生(2014-2017),清华本科生(2010-2014),发表过多篇机器学习领域高质量论文。[1]
论文立意
在表征学习领域,词嵌入(word embedding)问题是一个研究热点。其中,中文领域的词嵌入技术更是得到了很多深入地研究:从把词拆成字(CWE算法)[2],到把汉字拆偏旁部首 [3,4],再到根据人工总结的字件[5],再到基于汉字图片使用卷积神经网络自动提取特征的GWE [6],最后到2018年阿里巴巴提出的基于汉字笔画的词嵌入学习方法[7],中文词嵌入技术在形态学可谓已经被研究到了极致。
本文另辟蹊径,从词汇资源(Lexical Resource)——知网——入手,从词语背后的庞大信息量着手来提升词嵌入的表示能力。
词嵌入的研究方法综述
香港的 NLP 研究者刘李嫣然总结出了词嵌入的四大研究方向,分别是:Interpretable Relations、beyond words、lexical resource、beyond English [8]。
2018年,宋彦师兄创造性地提出了基于强化学习的词嵌入学习方法[9],至此,词嵌入的研究领域新增了一个新的研究方向——new model。也即引入其他学习方法的word embedding思路。
从2015年各大顶会论文的趋势来看,对于 word embedding 的研究已经进入基本完备,也就是进入了所谓的“后 word embedding 时代”[8]。关于word embedding的研究是这样的历史进程: 1954年,Harris 提出“语义相似的单词往往会出现在相似的上下文中 "[13]。2003年,Bengio 提出 神经网络语言模型[14]。2013年,google的Mikolov 提出 word2vec[15,16]。2015年,word embedding领域集大成之作的论文[17]横空出世,标志着后word embedding时代的到来。
本文贡献
首次利用知网中的义原来提高词向量的表征能力;采用注意力机制,从上下文中来寻找词义和学习表示。
本文工作
立意
词义由义原构成,本文改进了google 提出的 word2vec模型,加入注意力机制,从而可以很好的利用词义资源,以此来提高词向量的表征能力。
基线系统
google 提出的 word2vec 中的两种模型:Skip-Gram(SG) 和 CBOW。
斯坦福提出的 GloVe
训练数据集
Sougou-T,搜狗公司提出的互联网语料库,内含1.3亿张网页,相当于27亿个词汇,相当于 5TB 数据量。[10]
测试数据集
清华大学之前提出的词语相似度测试集 WordSim-240, WordSim-297, Analogy [11,12]
评测任务
词语相似度和词汇类推
模型方法
Simple Sememes Aggregation Model
仅利用了词对应的全部义原的平均值。
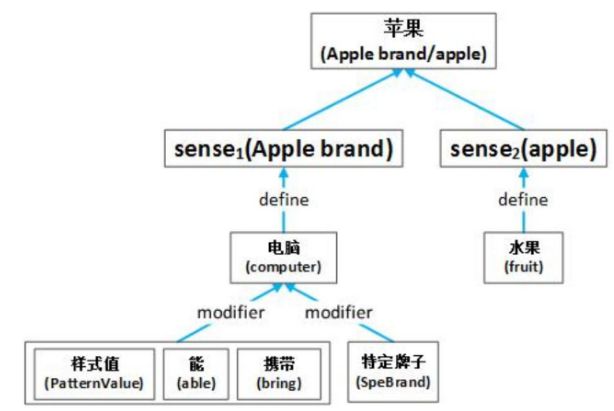
w 代表“词”;
S 代表词对应的词义集合;
X 代表词义对应的义原集合
m 代表全部义原的数量
Sememe Attention over Context Model
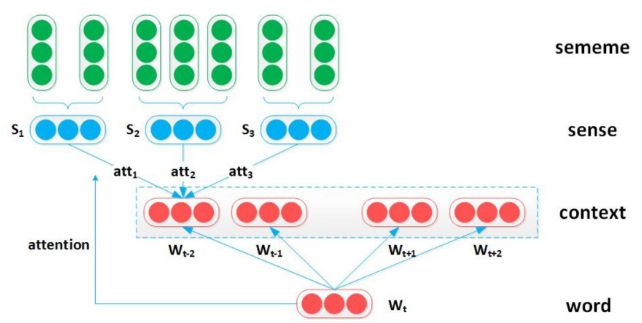
利用注意力机制,根据目标词选择上下文词的适当意义。
Sememes Attention over Target Model
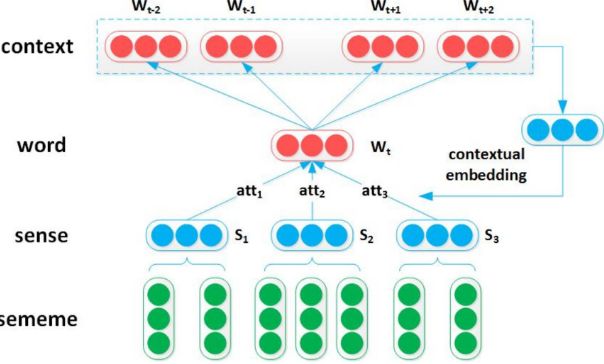
以上下文词为关注焦点,选择目标词的词义。
本文的不足
- 过于主观的评价方法,本文不同于其他的高水平词嵌入研究论文, 没有在较有说服力的机器翻译、文本分类上测试该词嵌入方法的性能。
- 不好懂的句式、语法和词汇,不同于李航和周志华的英文论文,本文的阅读难度较大。
参考文献
[1] Ruobing Xie`s Profile. http://nlp.csai.tsinghua.edu.cn/~xrb/
[2] Chen X, Xu L, Liu Z, et al. Joint learning of character and word embeddings[C]// International Conference on Artificial Intelligence. AAAI Press, 2015:1236-1242.
[3] Sun Y, Lin L, Yang N, et al. Radical-Enhanced Chinese Character Embedding[J]. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2014, 8835:279-286.
[4] Li Y, Li W, Sun F, et al. Component-Enhanced Chinese Character Embeddings[J]. Computer Science, 2015.
[5] Yu J, Jian X, Xin H, et al. Joint Embeddings of Chinese Words, Characters, and Fine-grained Subcharacter Components[C]// Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. 2017:286-291.
[6] Su T R, Lee H Y. Learning Chinese Word Representations From Glyphs Of Characters[C]// Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. 2017:264-273.
[7] cw2vec: Learning Chinese Word Embeddings with Stroke n-gram Information. 2018 AAAI
[8] 刘李嫣然. 后 Word Embedding 的热点会在哪里?. 2015. http://yanran.li/peppypapers/2015/08/17/post-word-embedding.html
[9] Yan Song. Learning Word Embedding with Reinforcement Learning. IJCAI. 2018
[10] http://www.sogou.com/labs/resource/t.php
[11] https://github.com/Leonard-Xu/CWE/tree/master/data
[12] Zhiyuan Liu, Maosong Sun, et al. Joint Learning of Character and Word Embeddings. IJCAI 2015.
[13] Harris, Zellig S. Distributional structure. Word 1954
[14] Bengio, Yoshua, et al. A neural probabilistic language model. JMLR 2003
[15] Mikolov, Tomas, et al. Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space[J]. Computer Science. 2013
[16] Mikolov, Tomas, et al. Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. NIPS 2013
[17] Lai S, et al. How to Generate a Good Word Embedding[J]. IEEE Intelligent Systems, 2016, 31(6): 5-14.




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)