Asp.net缓存技术(HttpRuntime.Cache)
一.缓存:
- 5个等级的缓存
- 1级是网络级缓存,缓存在浏览器,CDN以及代理服务器中 (举个例子:每个帮助页面都进行了缓存,访问一个页面的代码非常简单)
- 2级是由.net框架 HttpRuntime.Cache完成,在每台服务器的内存中。
- 3级Redis,分布式内存键值存储,在多个支撑同一个站点的服务器上共享缓存项。
- 4级SQL Server Cache,整个数据库,所有数据都被放到内存中。
- 5级SSD。通常只在SQL Server预热后才生效。
二.下面主要介绍HttpRuntime.Cache缓存:
意义:
把数据放到Cache中,在指定的时间内,可以直接从Cache中获取,避免对数据库等的压力。
设置和读取:
设置:
// // 摘要: // 向 System.Web.Caching.Cache 中插入具有依赖项和到期策略的对象。 // // 参数: // key: // 用于引用该对象的缓存键。 // // value: // 要插入缓存中的对象。 // // dependencies: // 所插入对象的文件依赖项或缓存键依赖项。 当任何依赖项更改时,该对象即无效,并从缓存中移除。 如果没有依赖项,则此参数包含 null。 // // absoluteExpiration: // 所插入对象将到期并被从缓存中移除的时间。 要避免可能的本地时间问题(例如从标准时间改为夏时制),请使用 System.DateTime.UtcNow // 而不是 System.DateTime.Now 作为此参数值。 如果使用绝对到期,则 slidingExpiration 参数必须为 System.Web.Caching.Cache.NoSlidingExpiration。 // // slidingExpiration: // 最后一次访问所插入对象时与该对象到期时之间的时间间隔。 如果该值等效于 20 分钟,则对象在最后一次被访问 20 分钟之后将到期并被从缓存中移除。 // 如果使用可调到期,则 absoluteExpiration 参数必须为 System.Web.Caching.Cache.NoAbsoluteExpiration。 // // 异常: // System.ArgumentNullException: // key 或 value 参数为 null。 // // System.ArgumentOutOfRangeException: // 将 slidingExpiration 参数设置为小于 TimeSpan.Zero 或大于一年的等效值。 // // System.ArgumentException: // 为要添加到 Cache 中的项设置 absoluteExpiration 和 slidingExpiration 参数。 public void Insert(string key, object value, CacheDependency dependencies, DateTime absoluteExpiration, TimeSpan slidingExpiration);
读取:
HttpRuntime.Cache[“name”]
三.案例分析:
代码:
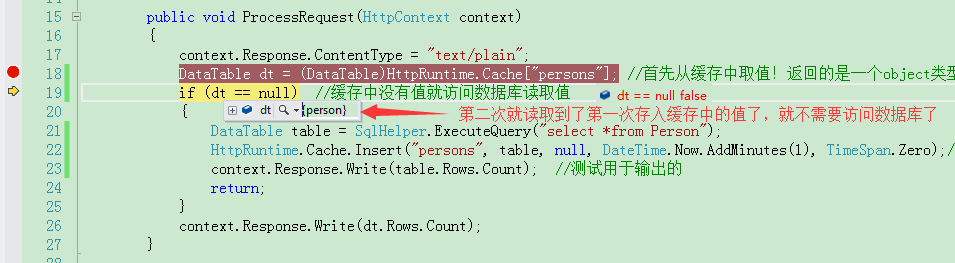
////Cache是全局共享的 public void ProcessRequest(HttpContext context) { context.Response.ContentType = "text/plain"; DataTable dt = (DataTable)HttpRuntime.Cache["persons"]; //首先从缓存中取值!返回的是一个object类型的值 if (dt == null) //缓存中没有值就访问数据库读取值 { DataTable table = SqlHelper.ExecuteQuery("select *from Person"); HttpRuntime.Cache.Insert("persons", table, null, DateTime.Now.AddMinutes(1), TimeSpan.Zero);//将查询到的值在存入缓存中 context.Response.Write(table.Rows.Count); //测试用于输出的 return; } context.Response.Write(dt.Rows.Count); }
执行过程:
第一次访问:

第二次访问: