Spring原理Boot
Spring原理 SpringBoot
1 Boot
1.1 Boot 骨架项目
如果是 linux 环境,用以下命令即可获取 spring boot 的骨架 pom.xml
curl -G https://start.spring.io/pom.xml -d dependencies=web,mysql,mybatis -o pom.xml
也可以使用 Postman 等工具实现
若想获取更多用法,请参考
curl https://start.spring.io
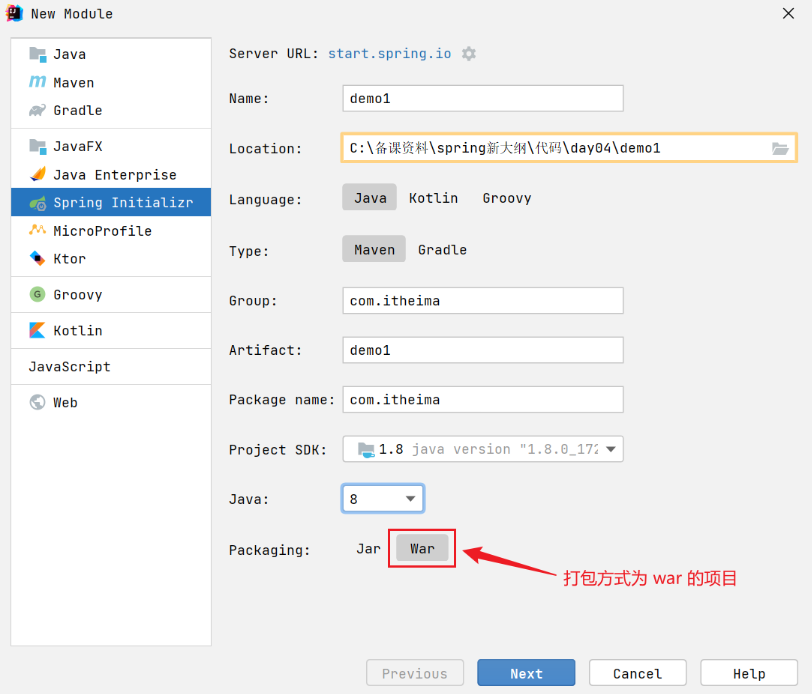
1.2 Boot War项目
步骤1:创建模块,区别在于打包方式选择 war
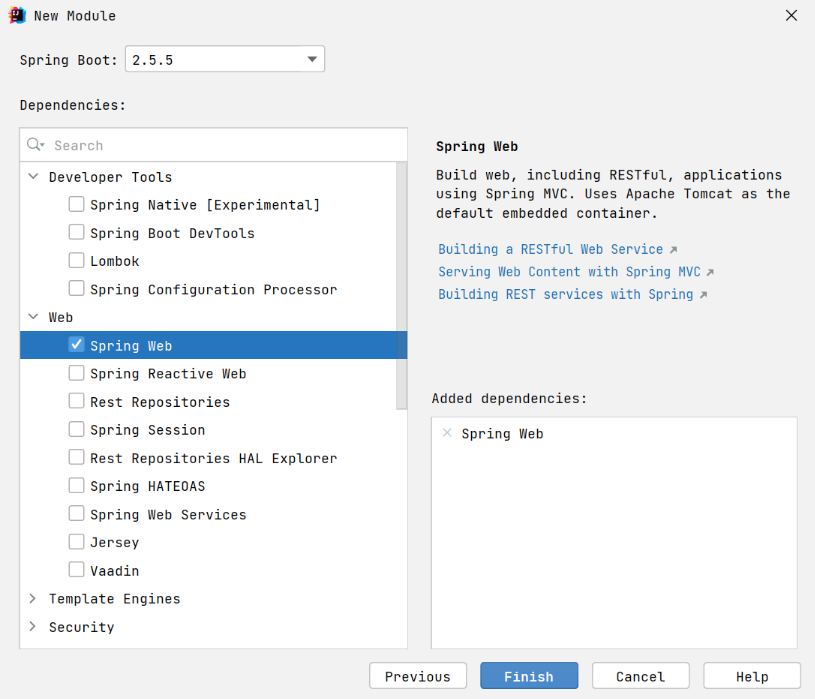
接下来勾选 Spring Web 支持
步骤2:编写控制器
@Controller
public class MyController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String abc() {
System.out.println("进入了控制器");
return "hello";
}
}
步骤3:编写 jsp 视图,新建 webapp 目录和一个 hello.jsp 文件,注意文件名与控制器方法返回的视图逻辑名一致
src
|- main
|- java
|- resources
|- webapp
|- hello.jsp
步骤4:配置视图路径,打开 application.properties 文件
spring.mvc.view.prefix=/
spring.mvc.view.suffix=.jsp
将来 prefix + 控制器方法返回值 + suffix 即为视图完整路径
测试
如果用 mvn 插件 mvn spring-boot:run 或 main 方法测试
- 必须添加如下依赖,因为此时用的还是内嵌 tomcat,而内嵌 tomcat 默认不带 jasper(用来解析 jsp)
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-jasper</artifactId>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
也可以使用 Idea 配置 tomcat 来测试,此时用的是外置 tomcat
- 骨架生成的代码中,多了一个 ServletInitializer,它的作用就是配置外置 Tomcat 使用的,在外置 Tomcat 启动后,去调用它创建和运行 SpringApplication
启示
对于 jar 项目,若要支持 jsp,也可以在加入 jasper 依赖的前提下,把 jsp 文件置入 META-INF/resources
1.3 Boot 启动过程
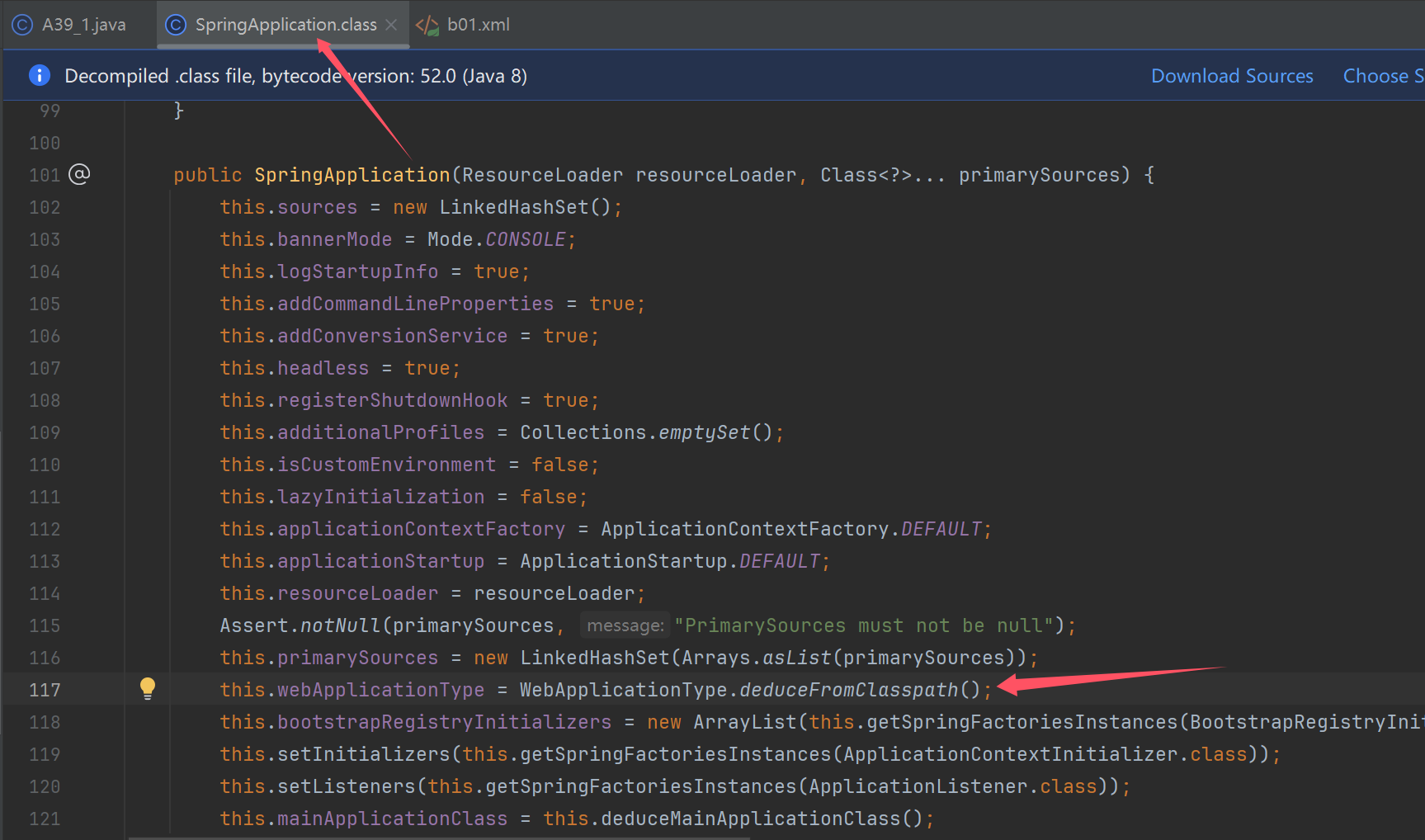
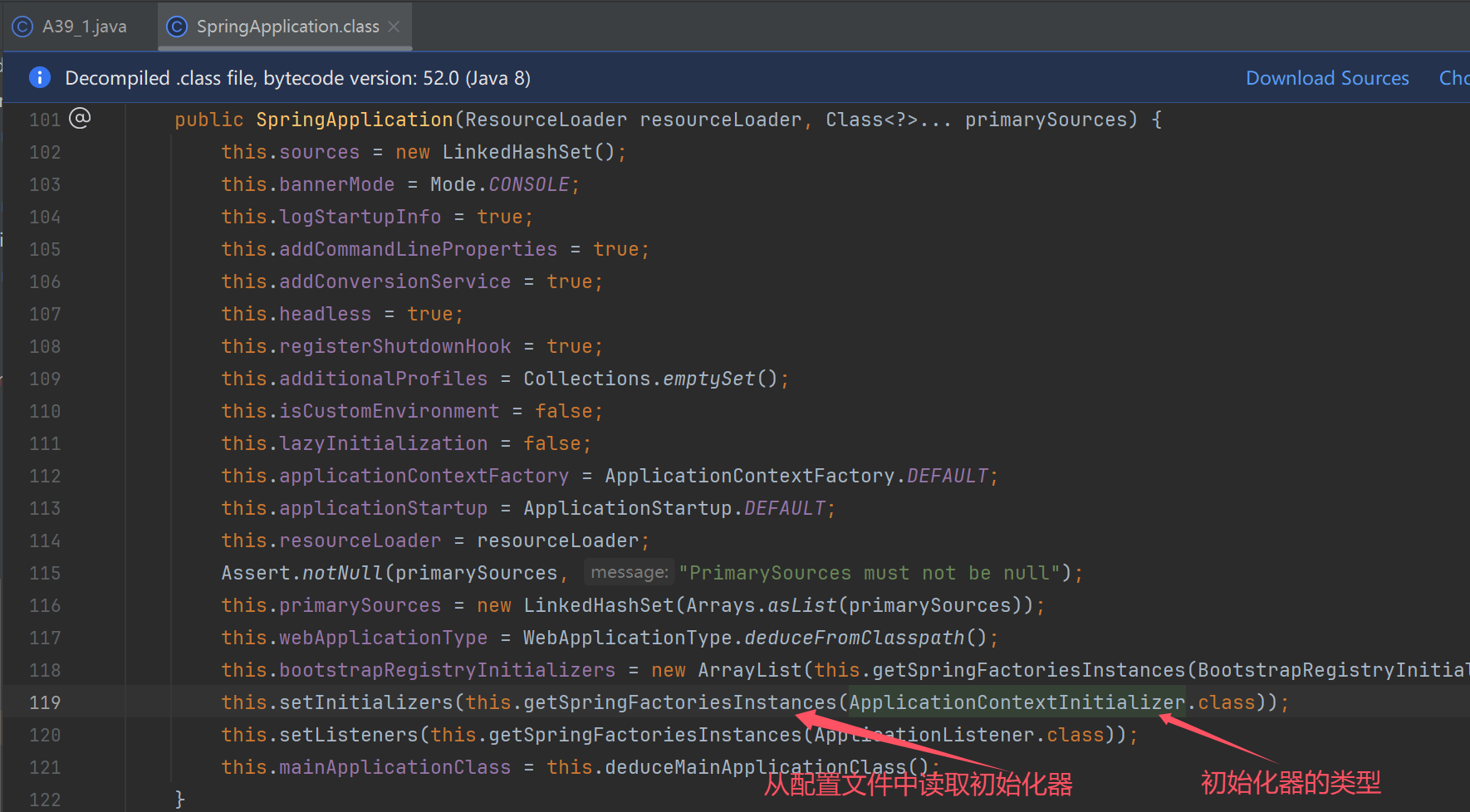
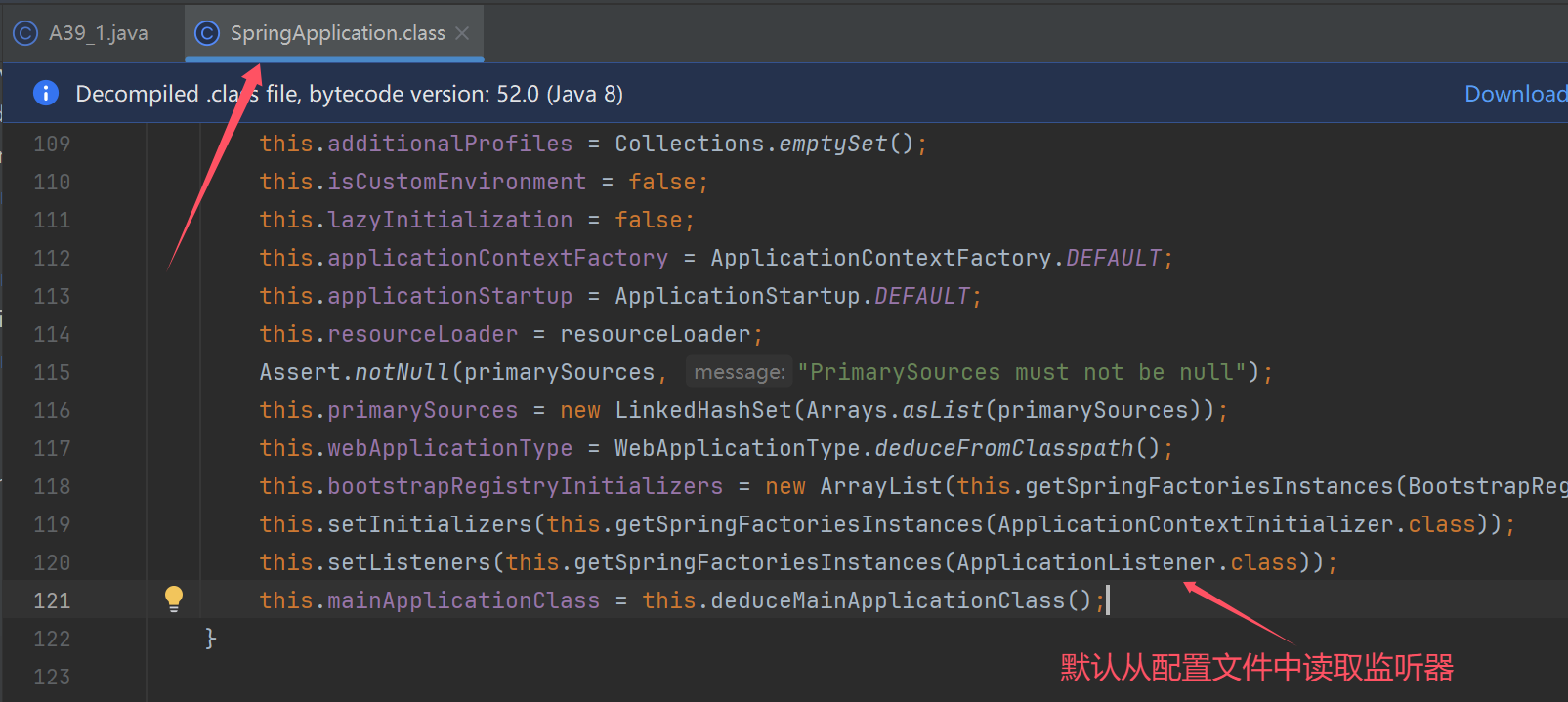
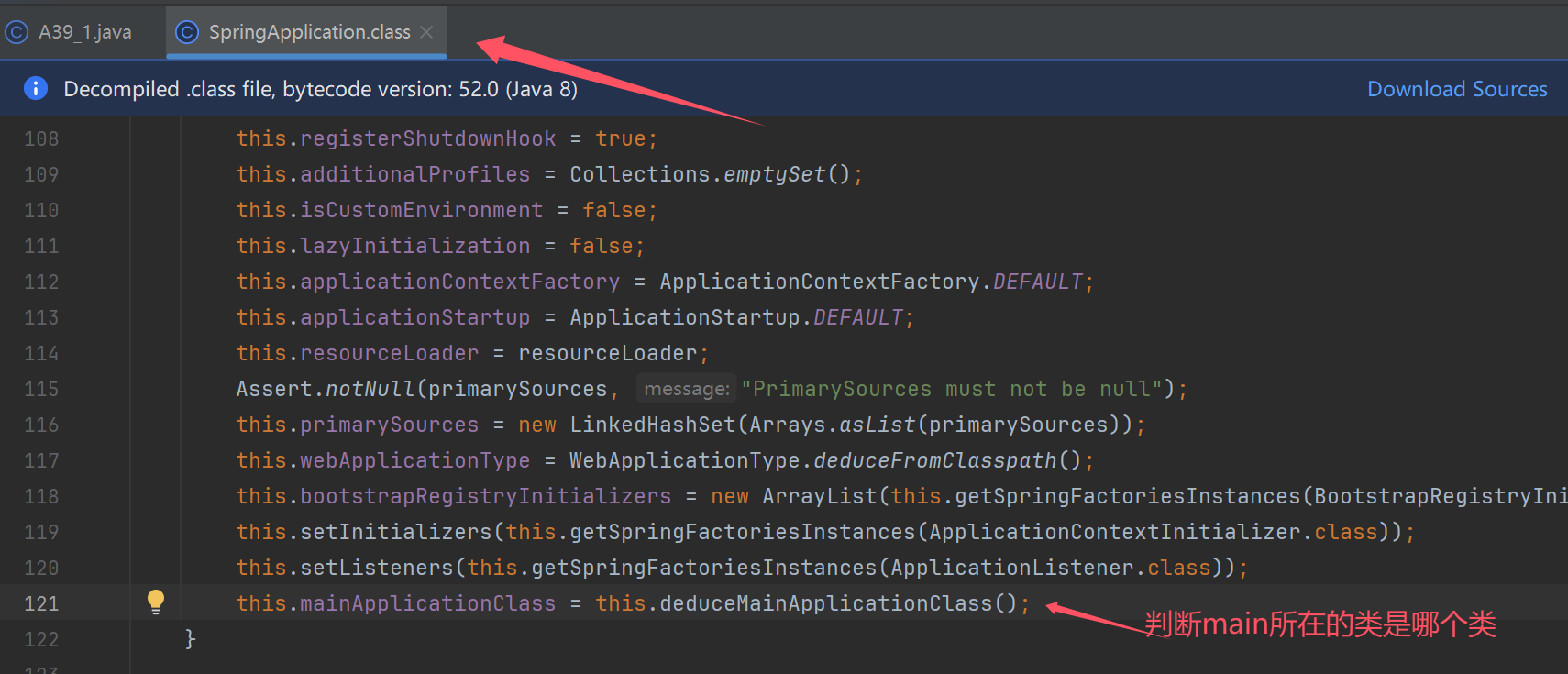
阶段一:SpringApplication 构造
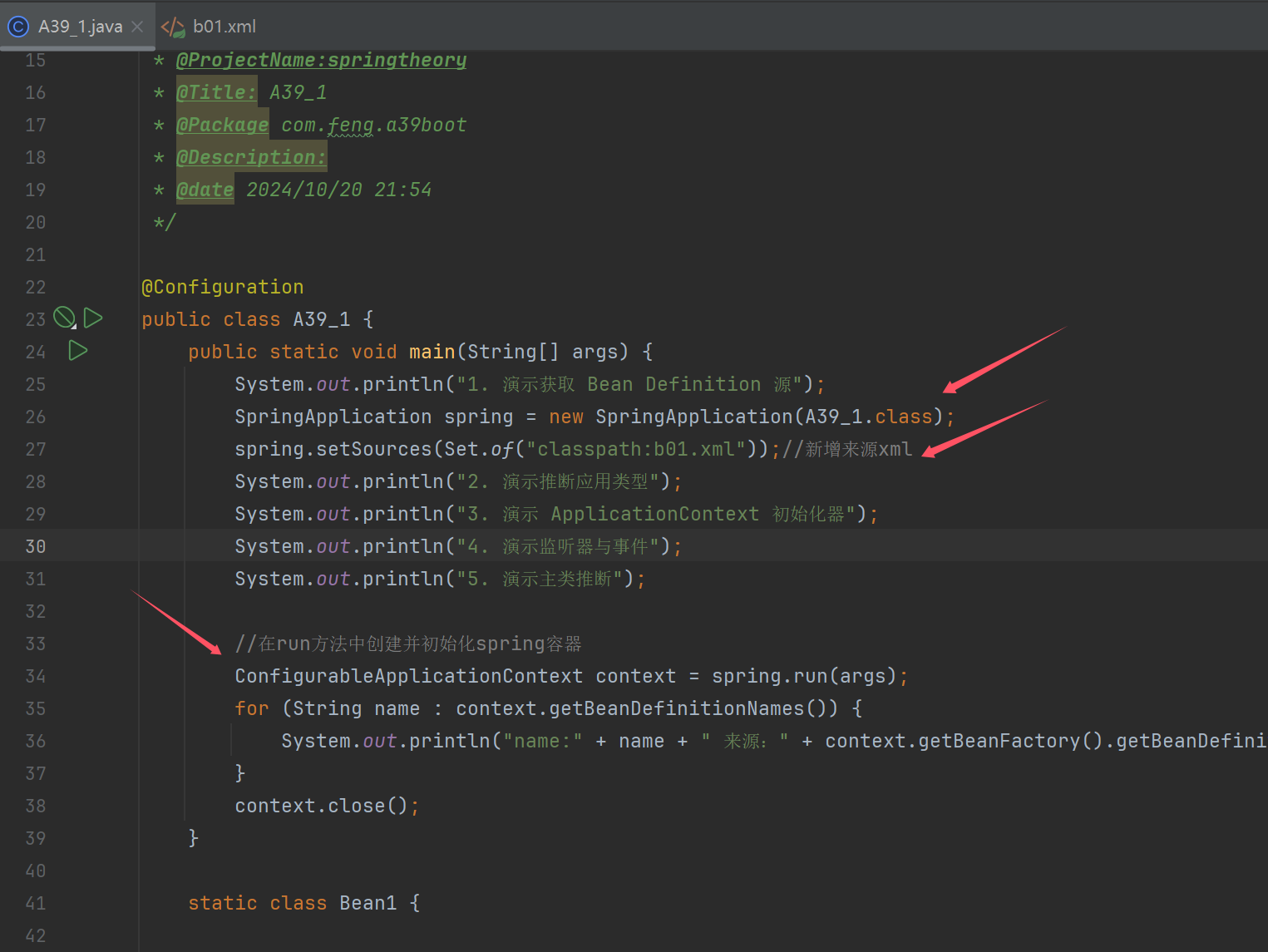
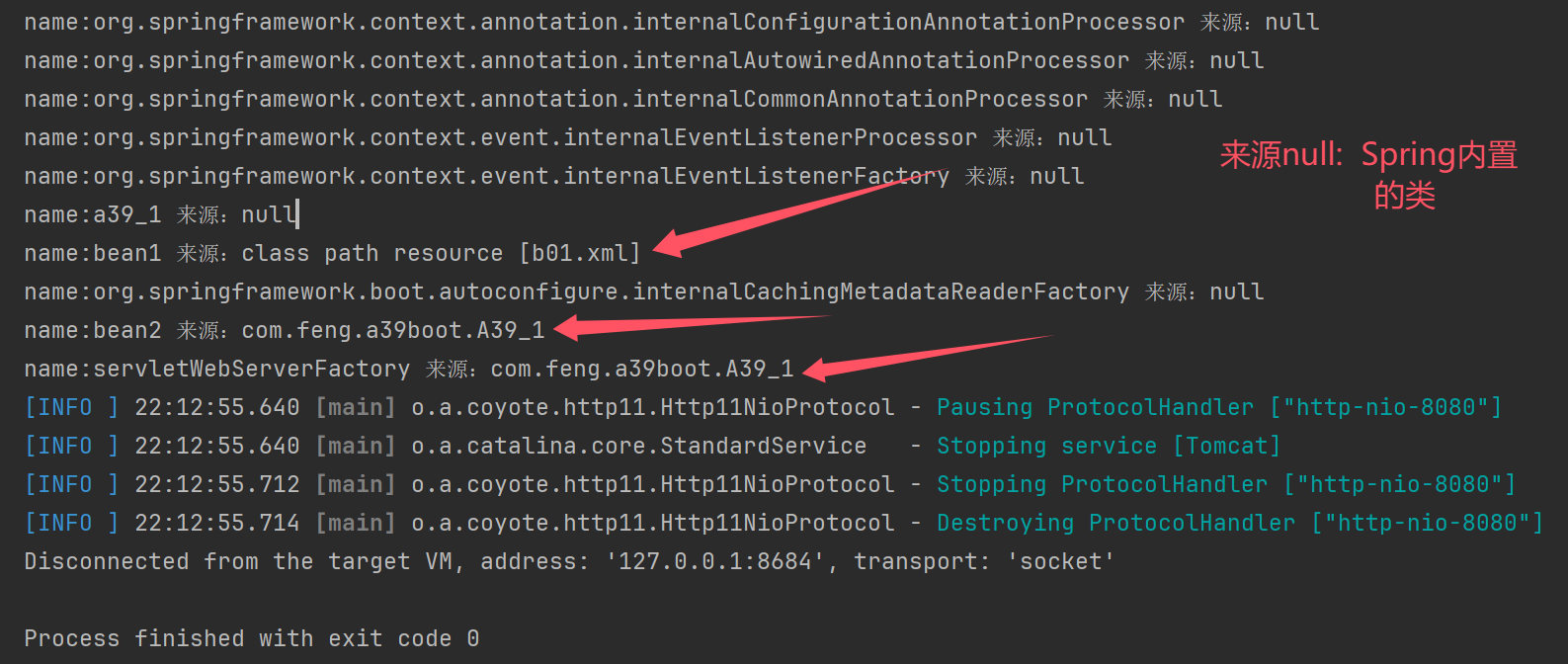
演示获取 Bean Definition 源
@Configuration
public class A39_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("1. 演示获取 Bean Definition 源");
SpringApplication spring = new SpringApplication(A39_1.class);
spring.setSources(Set.of("classpath:b01.xml"));//新增来源xml
System.out.println("2. 演示推断应用类型");
System.out.println("3. 演示 ApplicationContext 初始化器");
System.out.println("4. 演示监听器与事件");
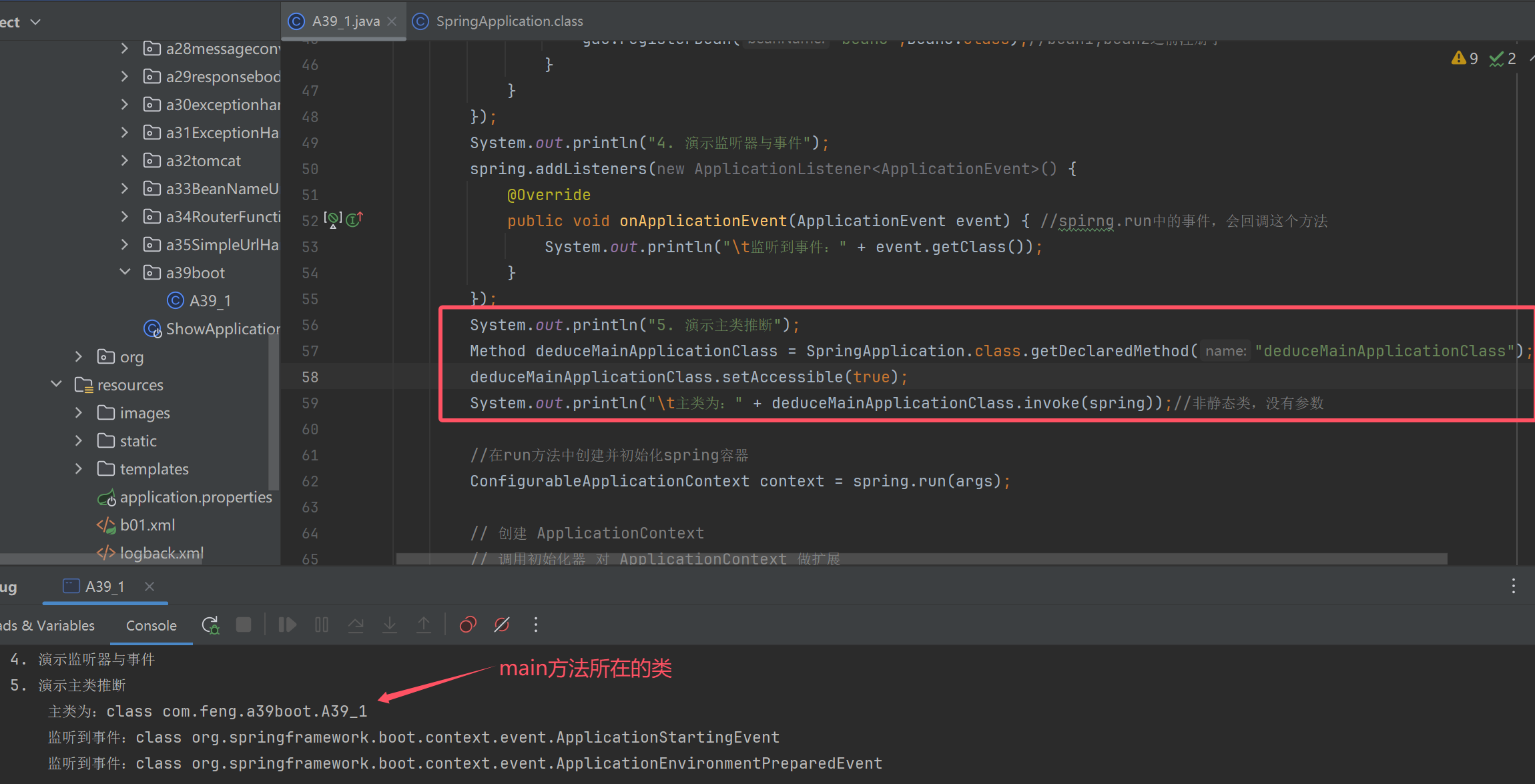
System.out.println("5. 演示主类推断");
//在run方法中创建并初始化spring容器
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = spring.run(args);
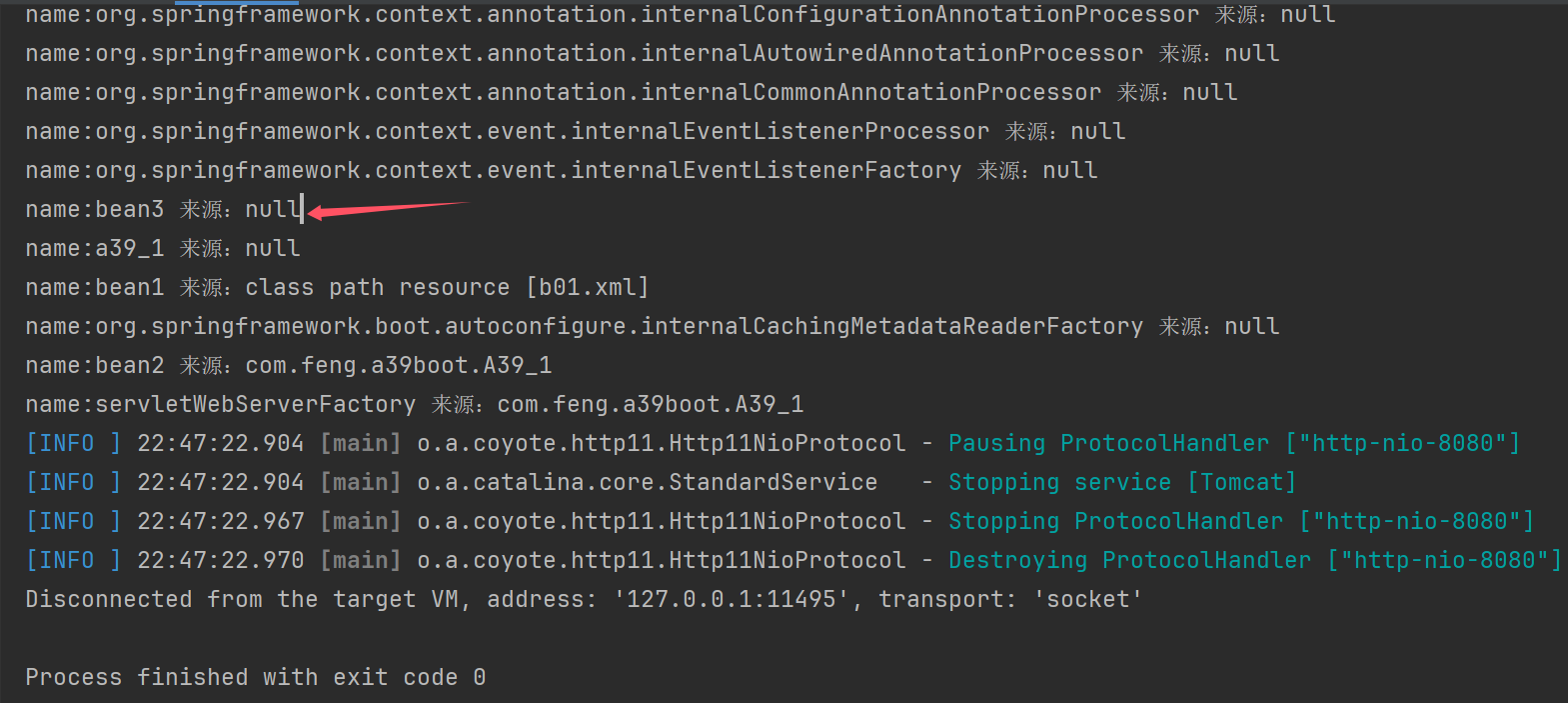
for (String name : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println("name:" + name + " 来源:" + context.getBeanFactory().getBeanDefinition(name).getResourceDescription());
}
context.close();
}
static class Bean1 {
}
static class Bean2 {
}
static class Bean3 {
}
@Bean
public Bean2 bean2() {
return new Bean2();
}
@Bean
public TomcatServletWebServerFactory servletWebServerFactory() {
return new TomcatServletWebServerFactory();
}
}
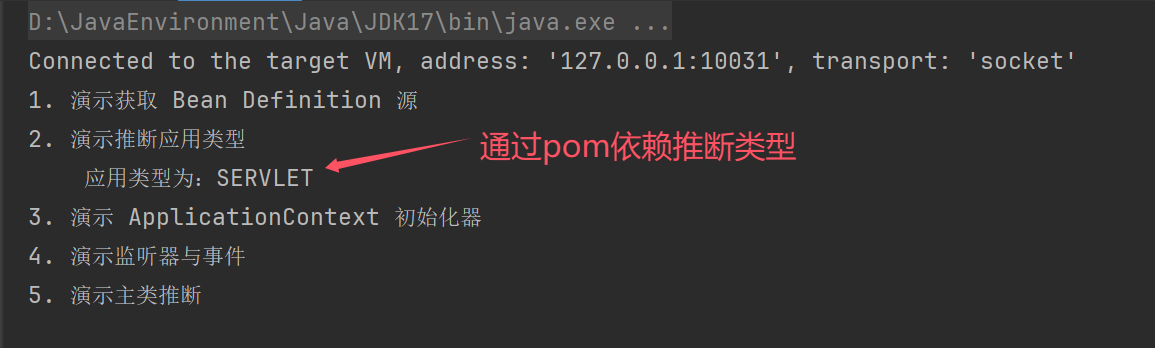
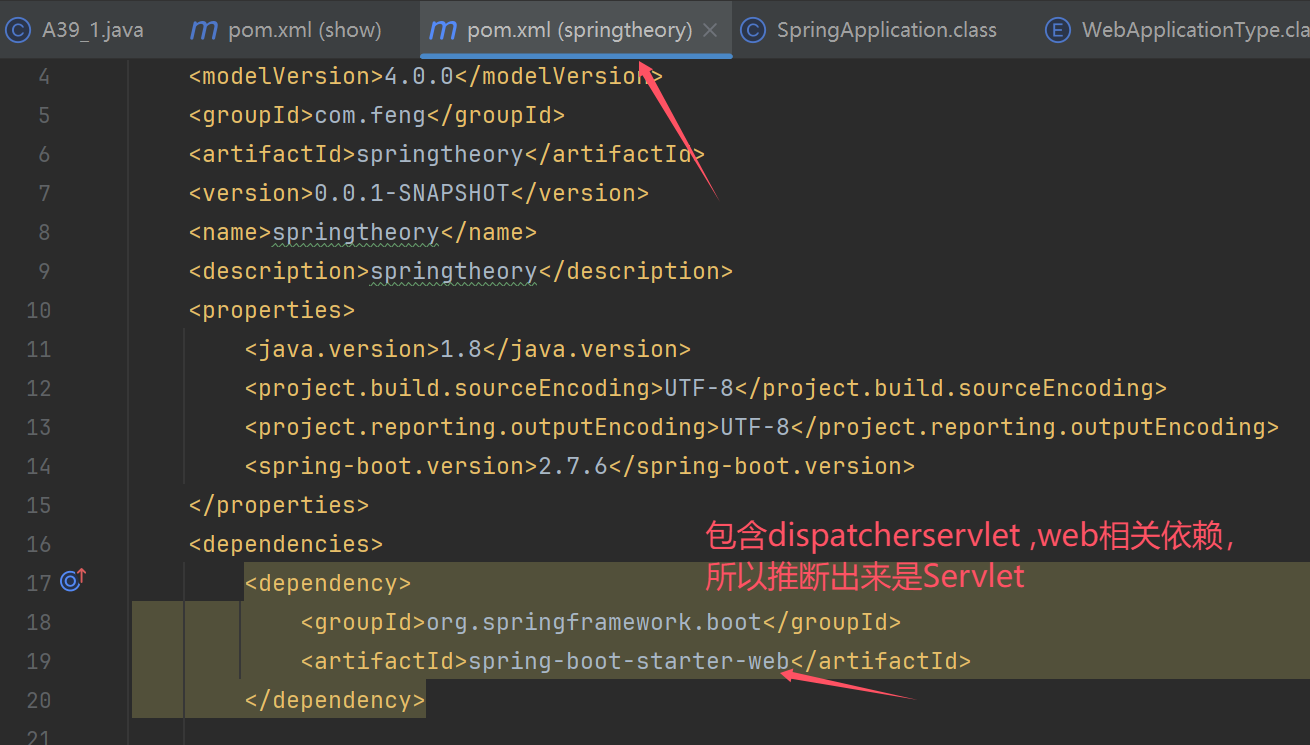
演示推断应用类型
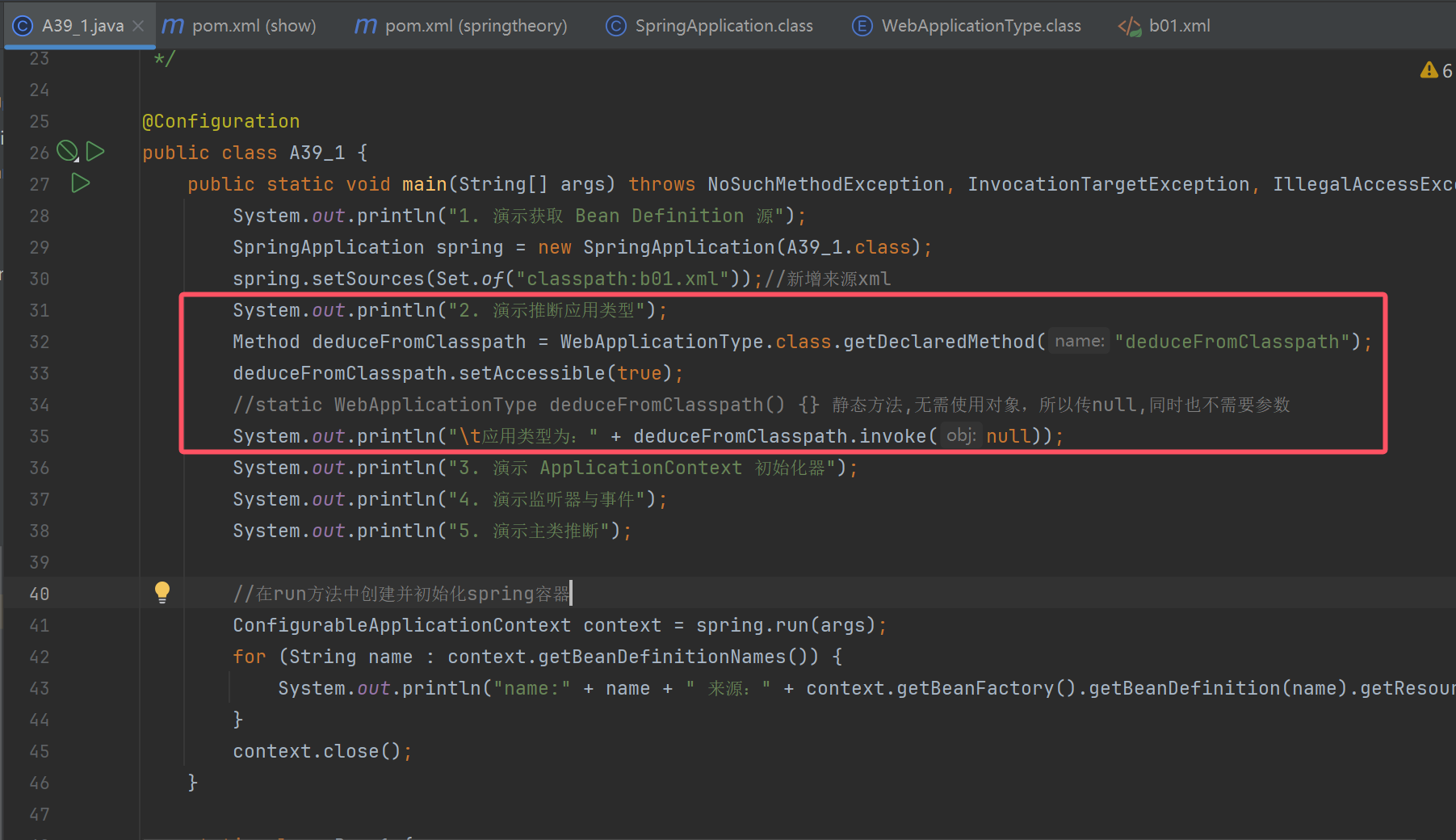
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
System.out.println("1. 演示获取 Bean Definition 源");
SpringApplication spring = new SpringApplication(A39_1.class);
spring.setSources(Set.of("classpath:b01.xml"));//新增来源xml
System.out.println("2. 演示推断应用类型");
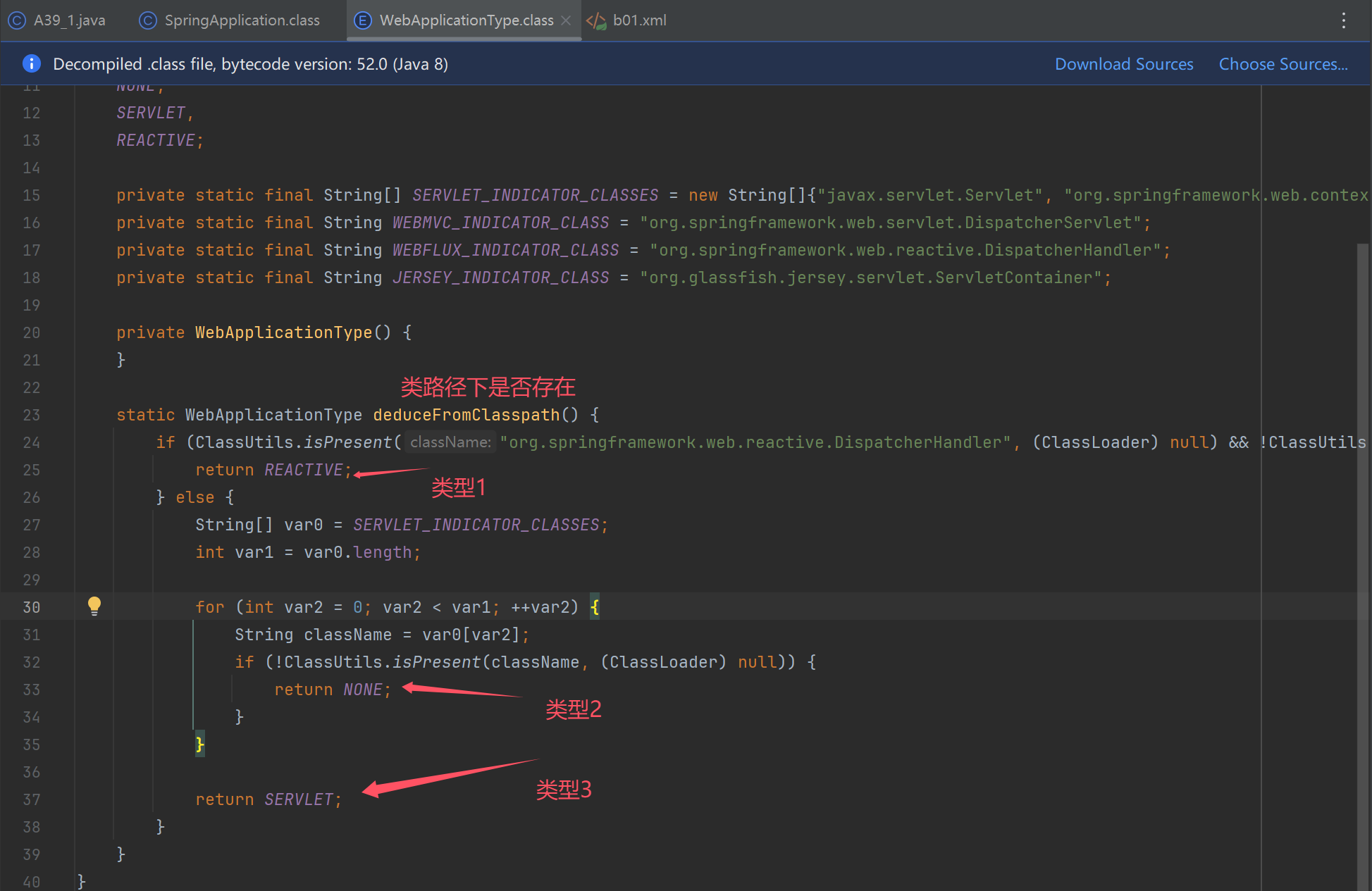
Method deduceFromClasspath = WebApplicationType.class.getDeclaredMethod("deduceFromClasspath");
deduceFromClasspath.setAccessible(true);
//static WebApplicationType deduceFromClasspath() {} 静态方法,无需使用对象,所以传null,同时也不需要参数
System.out.println("\t应用类型为:" + deduceFromClasspath.invoke(null));
System.out.println("3. 演示 ApplicationContext 初始化器");
System.out.println("4. 演示监听器与事件");
System.out.println("5. 演示主类推断");
//在run方法中创建并初始化spring容器
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = spring.run(args);
for (String name : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println("name:" + name + " 来源:" + context.getBeanFactory().getBeanDefinition(name).getResourceDescription());
}
context.close();
}
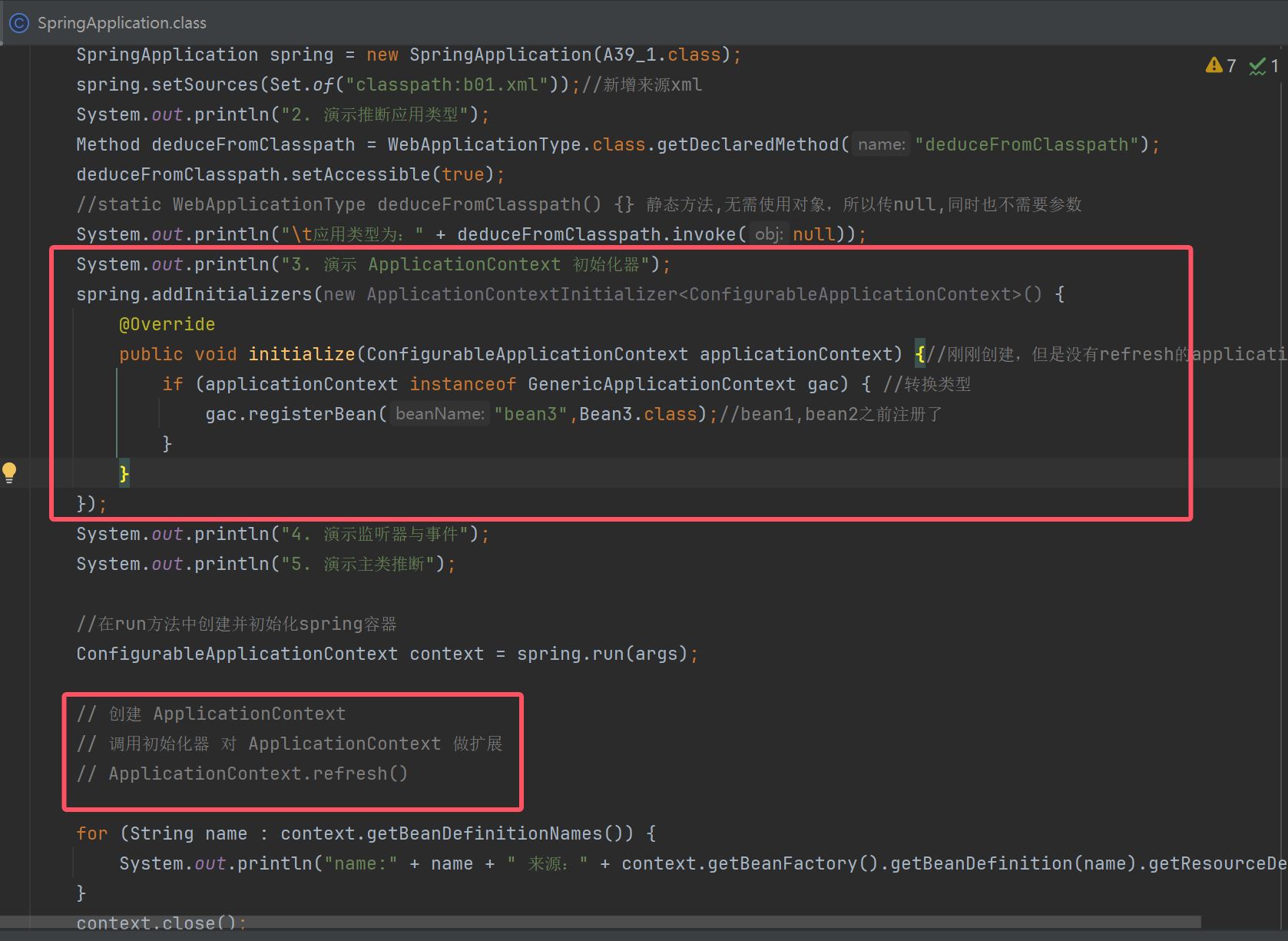
演示 ApplicationContext 初始化器
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
System.out.println("1. 演示获取 Bean Definition 源");
SpringApplication spring = new SpringApplication(A39_1.class);
spring.setSources(Set.of("classpath:b01.xml"));//新增来源xml
System.out.println("2. 演示推断应用类型");
Method deduceFromClasspath = WebApplicationType.class.getDeclaredMethod("deduceFromClasspath");
deduceFromClasspath.setAccessible(true);
//static WebApplicationType deduceFromClasspath() {} 静态方法,无需使用对象,所以传null,同时也不需要参数
System.out.println("\t应用类型为:" + deduceFromClasspath.invoke(null));
System.out.println("3. 演示 ApplicationContext 初始化器");
spring.addInitializers(new ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>() {
@Override
public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {//刚刚创建,但是没有refresh的applicationContext对象
if (applicationContext instanceof GenericApplicationContext gac) { //转换类型
gac.registerBean("bean3",Bean3.class);//bean1,bean2之前注册了
}
}
});
System.out.println("4. 演示监听器与事件");
System.out.println("5. 演示主类推断");
//在run方法中创建并初始化spring容器
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = spring.run(args);
// 创建 ApplicationContext
// 调用初始化器 对 ApplicationContext 做扩展
// ApplicationContext.refresh()
for (String name : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println("name:" + name + " 来源:" + context.getBeanFactory().getBeanDefinition(name).getResourceDescription());
}
context.close();
}
演示监听器与事件
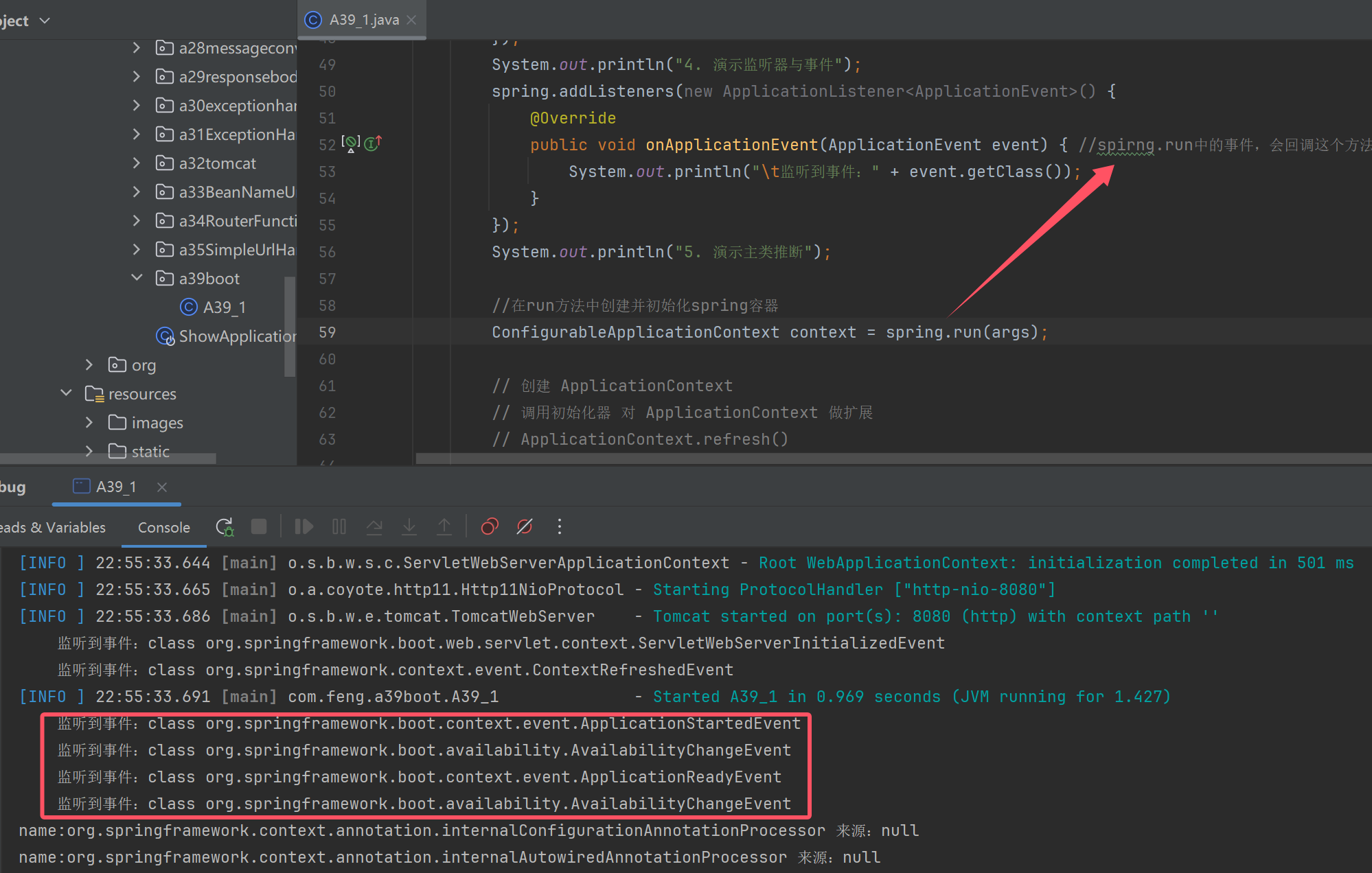
演示主类推断
阶段二:执行 run 方法
事件发布器 (run 1)
public class A39_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
//添加 app 监听器
SpringApplication app = new SpringApplication();
app.addListeners(e -> System.out.println(e.getClass()));
// 获取事件发送器实现类名
//参数1: 接口类型 , 参数2: ClassLoader 返回值:names:多个实现类的名字
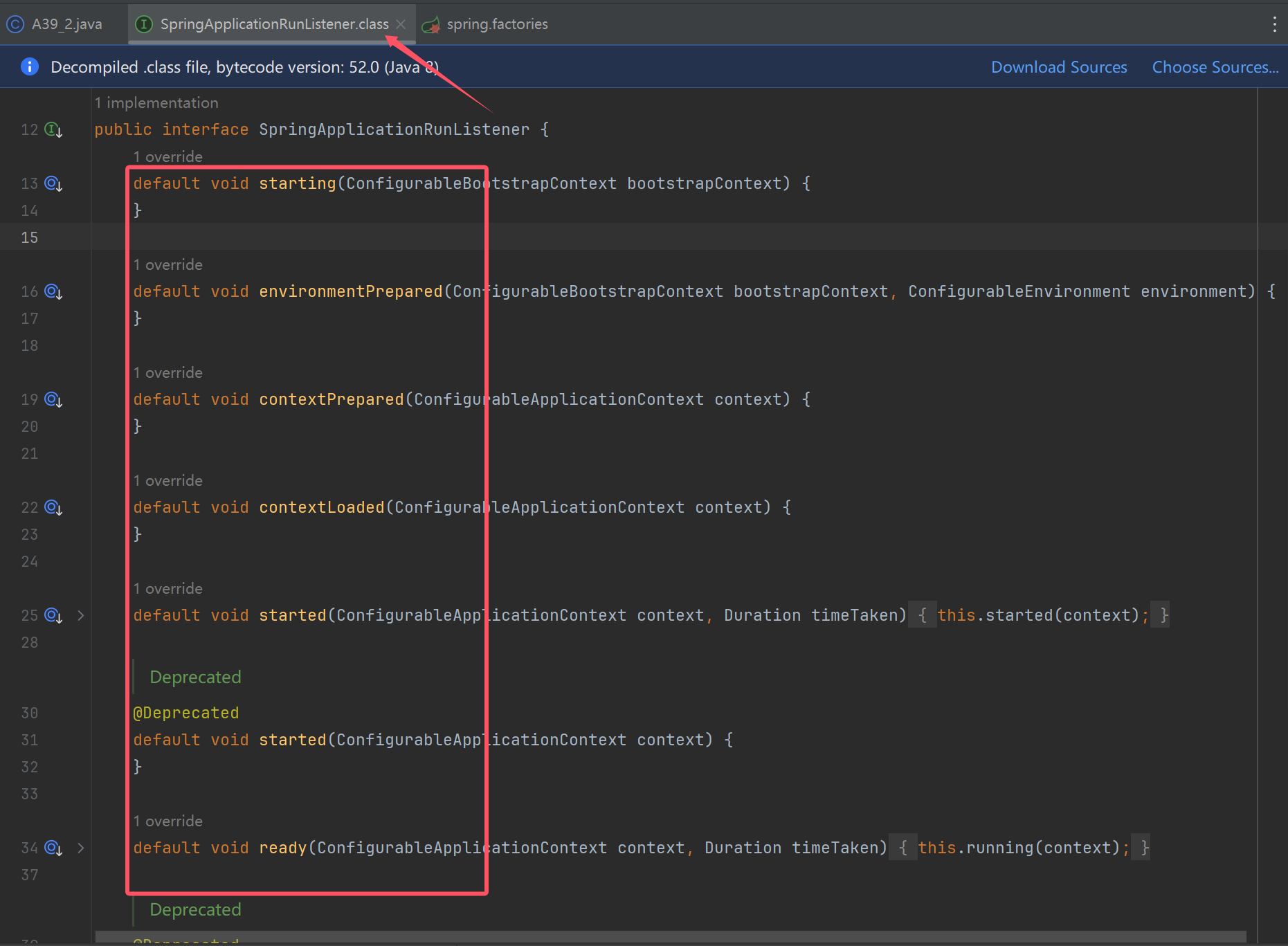
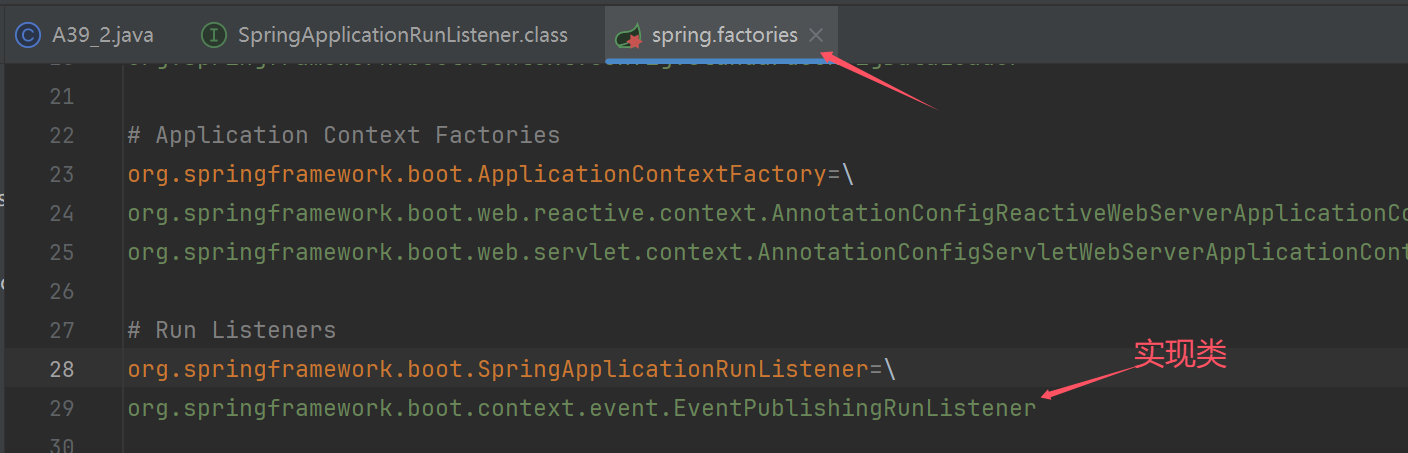
List<String> names = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(SpringApplicationRunListener.class, A39_2.class.getClassLoader());
for (String name : names) {
//org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener: 拿到了实现类的名字
System.out.println(name);
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(name);//拿到类对象
Constructor<?> constructor = clazz.getConstructor(SpringApplication.class, String[].class);//拿到类构造器
//事件发布器对象创建完成
EventPublishingRunListener publisher = (EventPublishingRunListener) constructor.newInstance(app, args);//创建对象
//发布事件
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = new DefaultBootstrapContext();
publisher.starting(bootstrapContext); //spring boot 开始启动
publisher.environmentPrepared(bootstrapContext,new StandardEnvironment()); //环境信息准备完毕
GenericApplicationContext context = new GenericApplicationContext();
publisher.contextPrepared(context); //在spring 容器创建,并调用初始化器之后,发送此事件
publisher.contextLoaded(context); // 所有 bean definition 加载完毕
context.refresh();
publisher.started(context); //spring 容器初始化完成(refresh 方法调用完毕)
publisher.running(context); //spring boot 启动完毕
publisher.failed(context,new Exception("出错")); //spring boot 启动出错
}
}
}
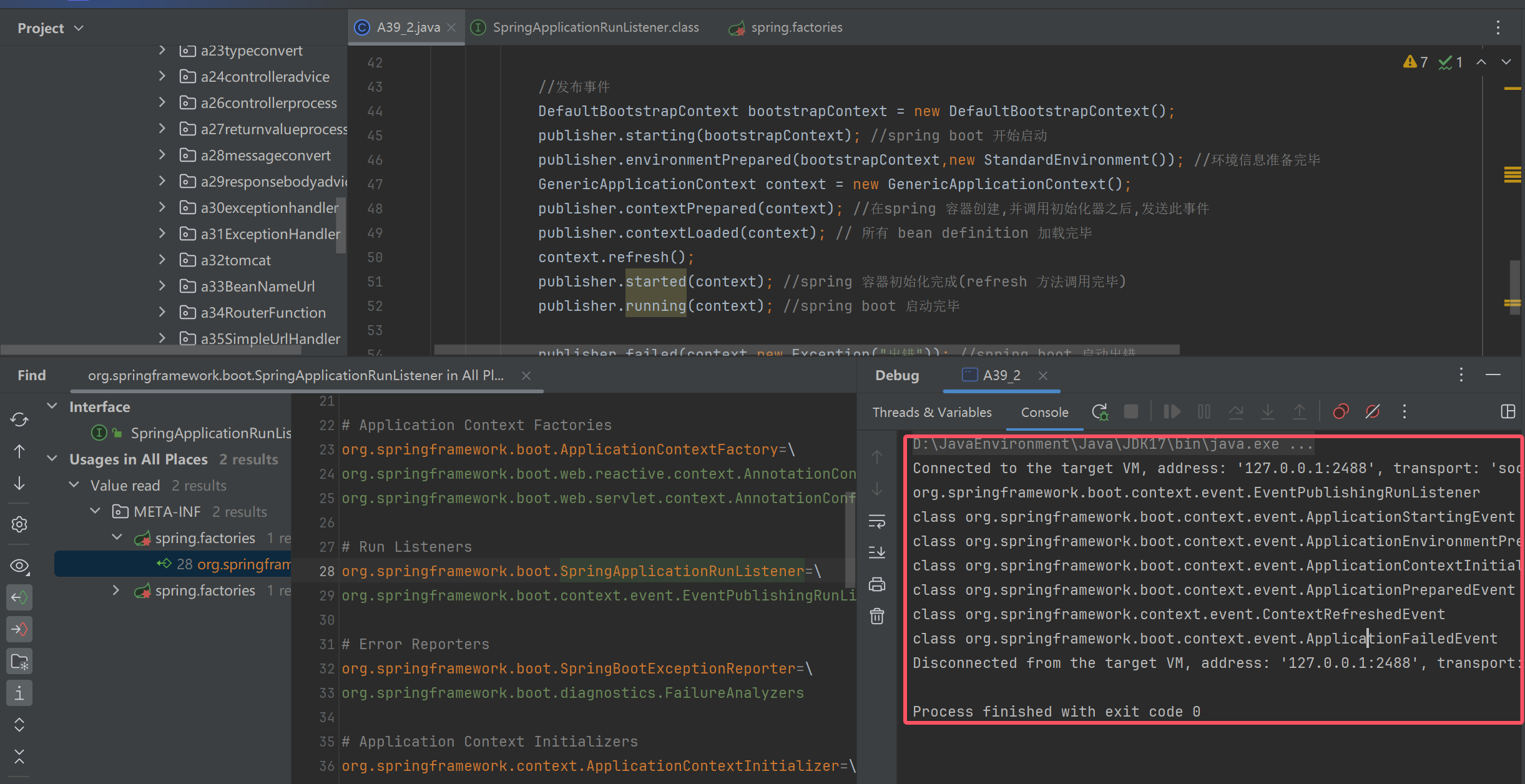
run 方法流程( 8 -11 )
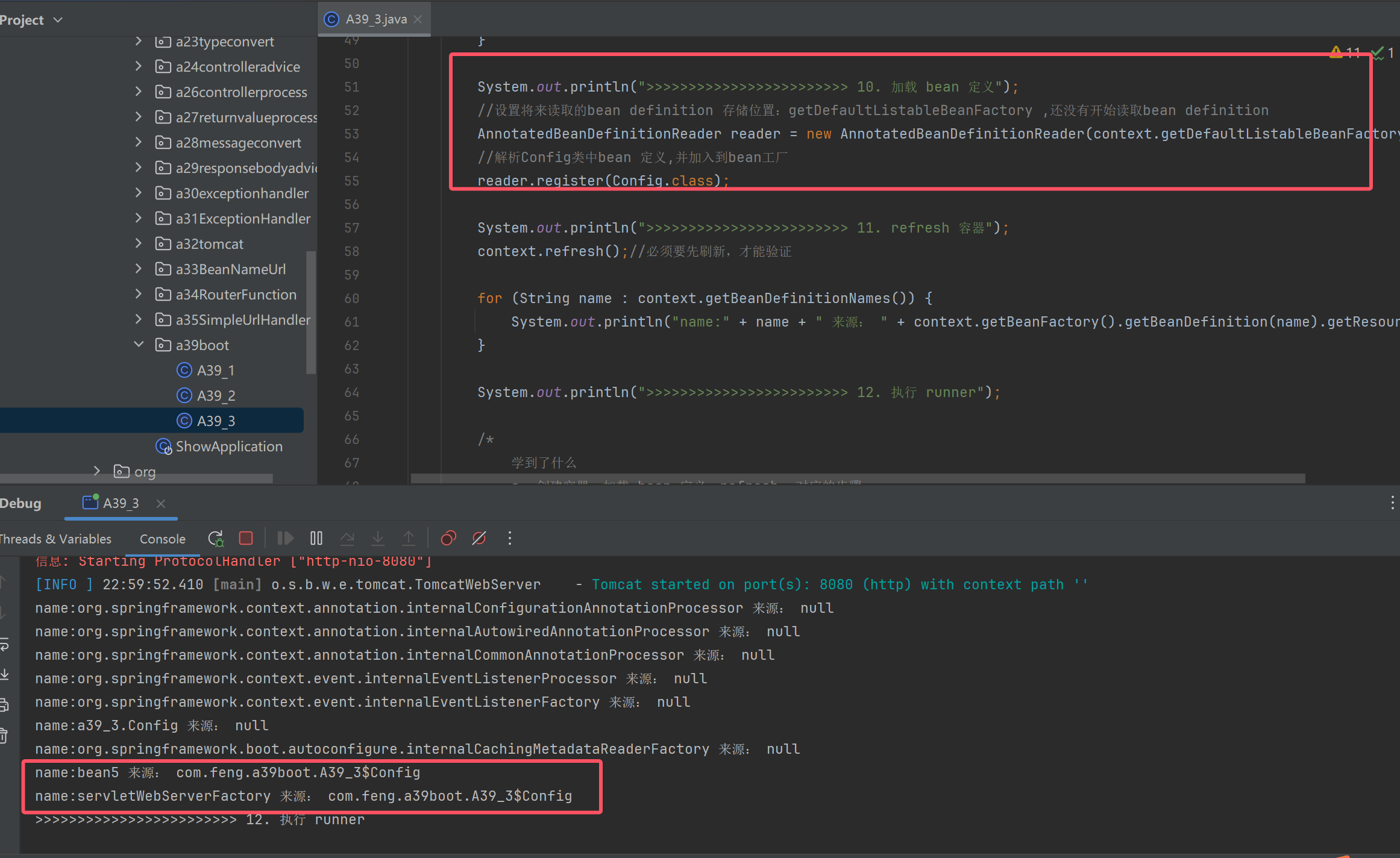
配置类获取bean 定义
public class A39_3 {
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SpringApplication app = new SpringApplication();
//新增一个初始化器
app.addInitializers(new ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>() {
@Override //需要提前准备容器,所以需要在第9.步骤回调这个初始化方法
public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {
}
});
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 2. 封装启动 args");
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 8. 创建容器");
GenericApplicationContext context = createApplicationContext(WebApplicationType.SERVLET);
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 9. 准备容器");
for (ApplicationContextInitializer initializer : app.getInitializers()) {
//回调上面的初始化器方法
initializer.initialize(context);
}
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 10. 加载 bean 定义");
//设置将来读取的bean definition 存储位置:getDefaultListableBeanFactory ,还没有开始读取bean definition
AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(context.getDefaultListableBeanFactory());
//解析Config类中bean 定义,并加入到bean工厂
reader.register(Config.class);
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 11. refresh 容器");
context.refresh();//必须要先刷新,才能验证
for (String name : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println("name:" + name + " 来源: " + context.getBeanFactory().getBeanDefinition(name).getResourceDescription());
}
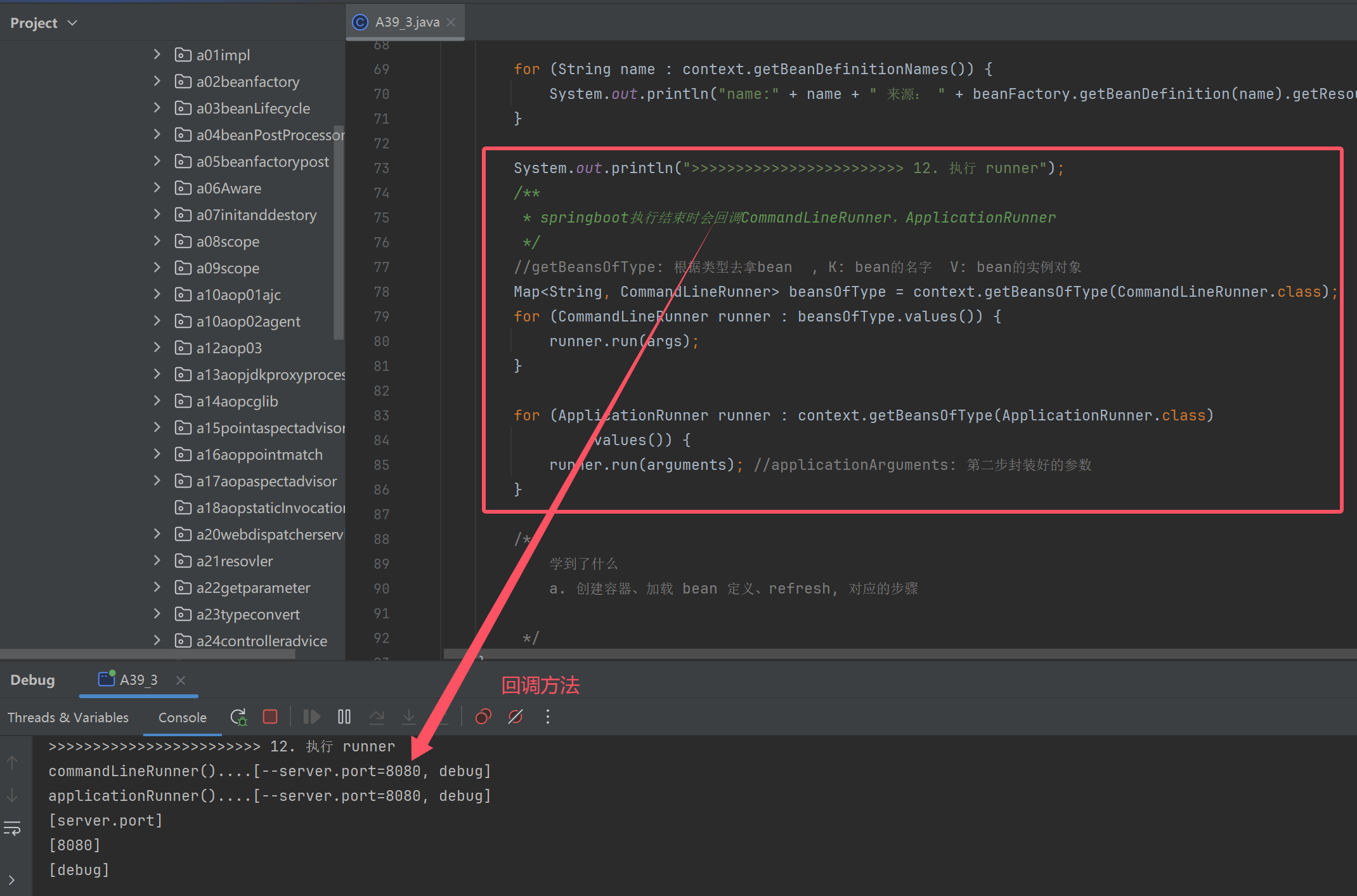
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 12. 执行 runner");
/*
学到了什么
a. 创建容器、加载 bean 定义、refresh, 对应的步骤
*/
}
private static GenericApplicationContext createApplicationContext(WebApplicationType type) {
GenericApplicationContext context = null;
switch (type) {
case SERVLET -> context = new AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext();
case REACTIVE -> context = new AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext();
case NONE -> context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
}
return context;
}
static class Bean4 {
}
static class Bean5 {
}
static class Bean6 {
}
@Configuration
static class Config {
@Bean
public Bean5 bean5() {
return new Bean5();
}
@Bean
public ServletWebServerFactory servletWebServerFactory() {
return new TomcatServletWebServerFactory();
}
}
}
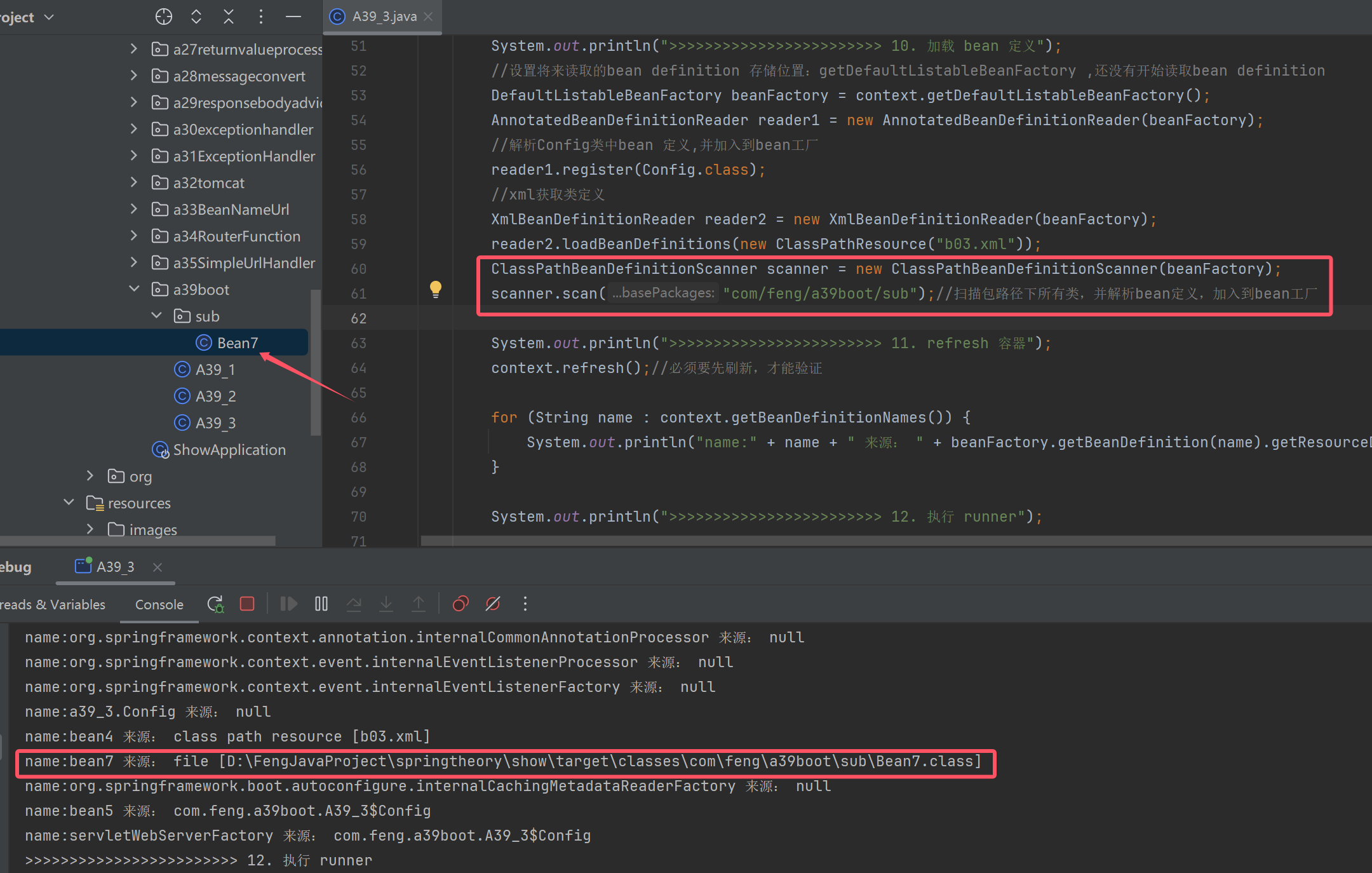
xml文件获取类定义
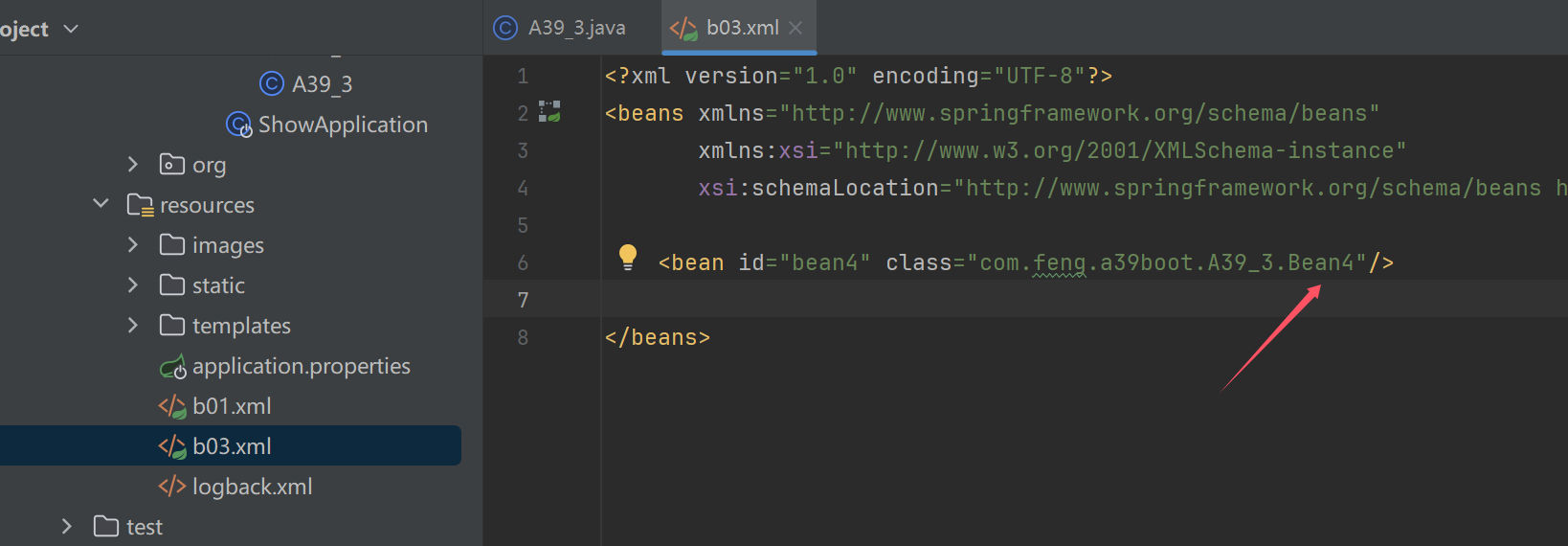
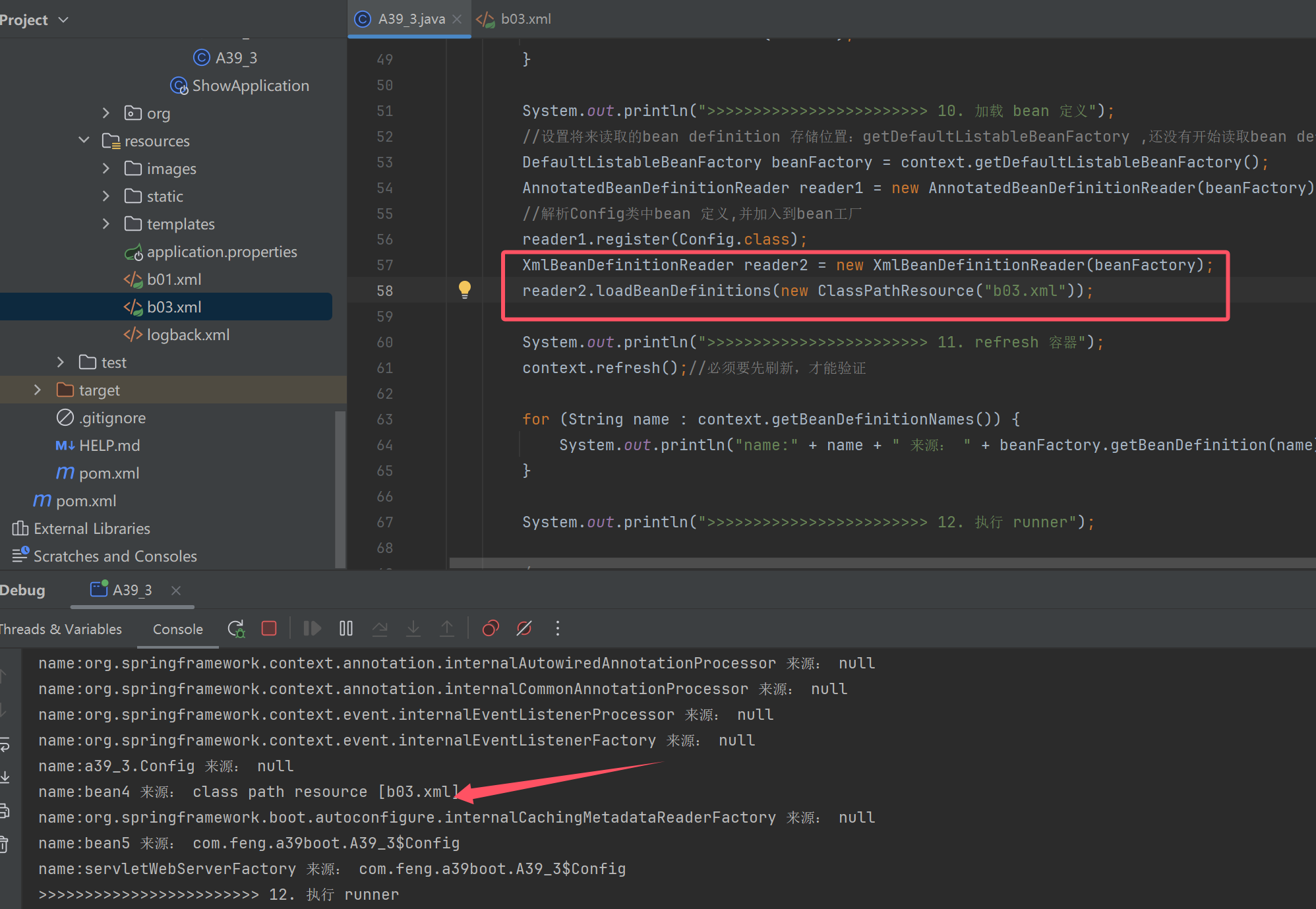
//xml获取类定义
XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader2 = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
reader2.loadBeanDefinitions(new ClassPathResource("b03.xml"));
包扫描获取类定义
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(beanFactory);
scanner.scan("com/feng/a39boot/sub");//扫描包路径下所有类,并解析bean定义,加入到bean工厂
run (2,12)
@Configuration
static class Config {
@Bean
public Bean5 bean5() {
return new Bean5();
}
@Bean
public ServletWebServerFactory servletWebServerFactory() {
return new TomcatServletWebServerFactory();
}
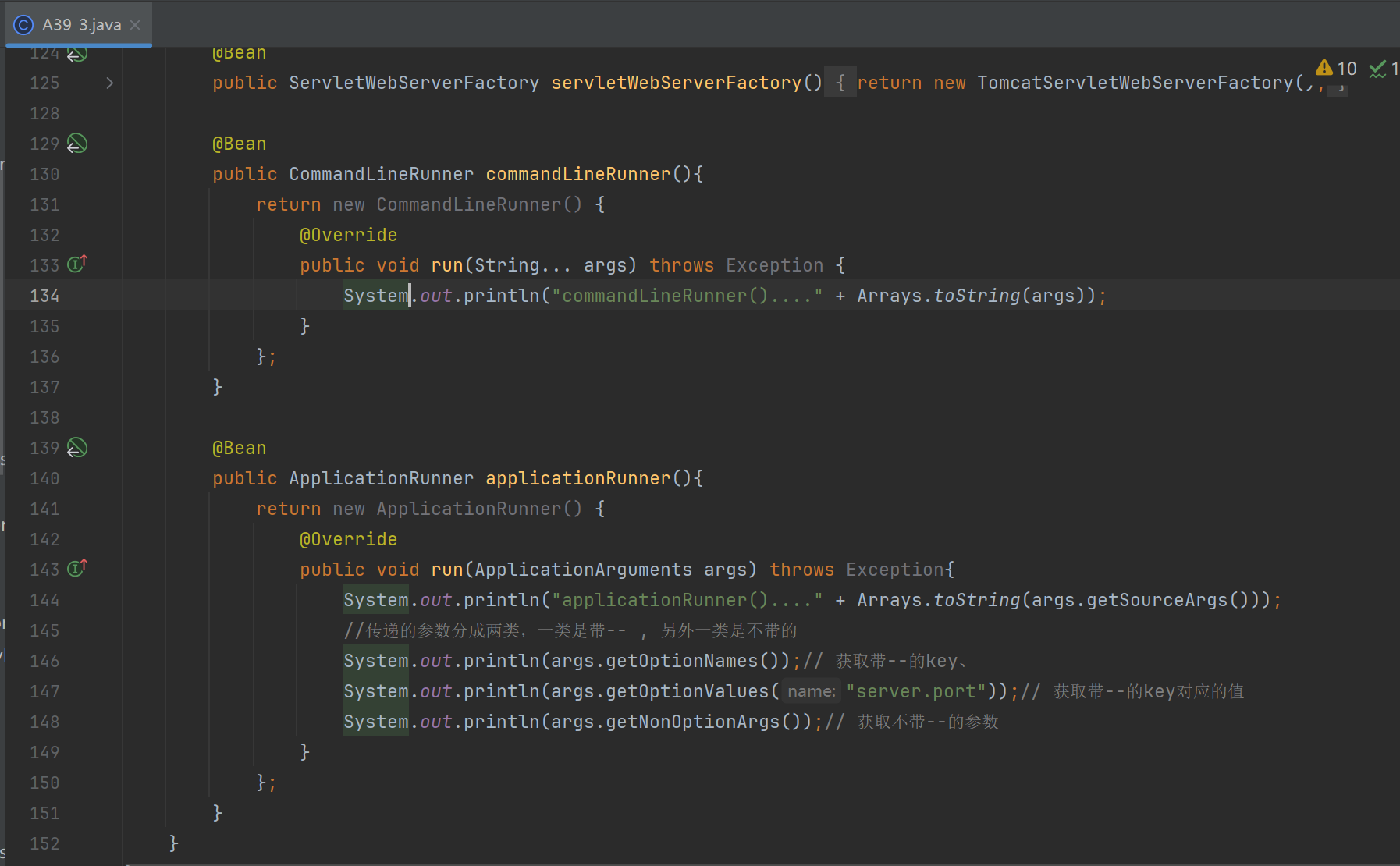
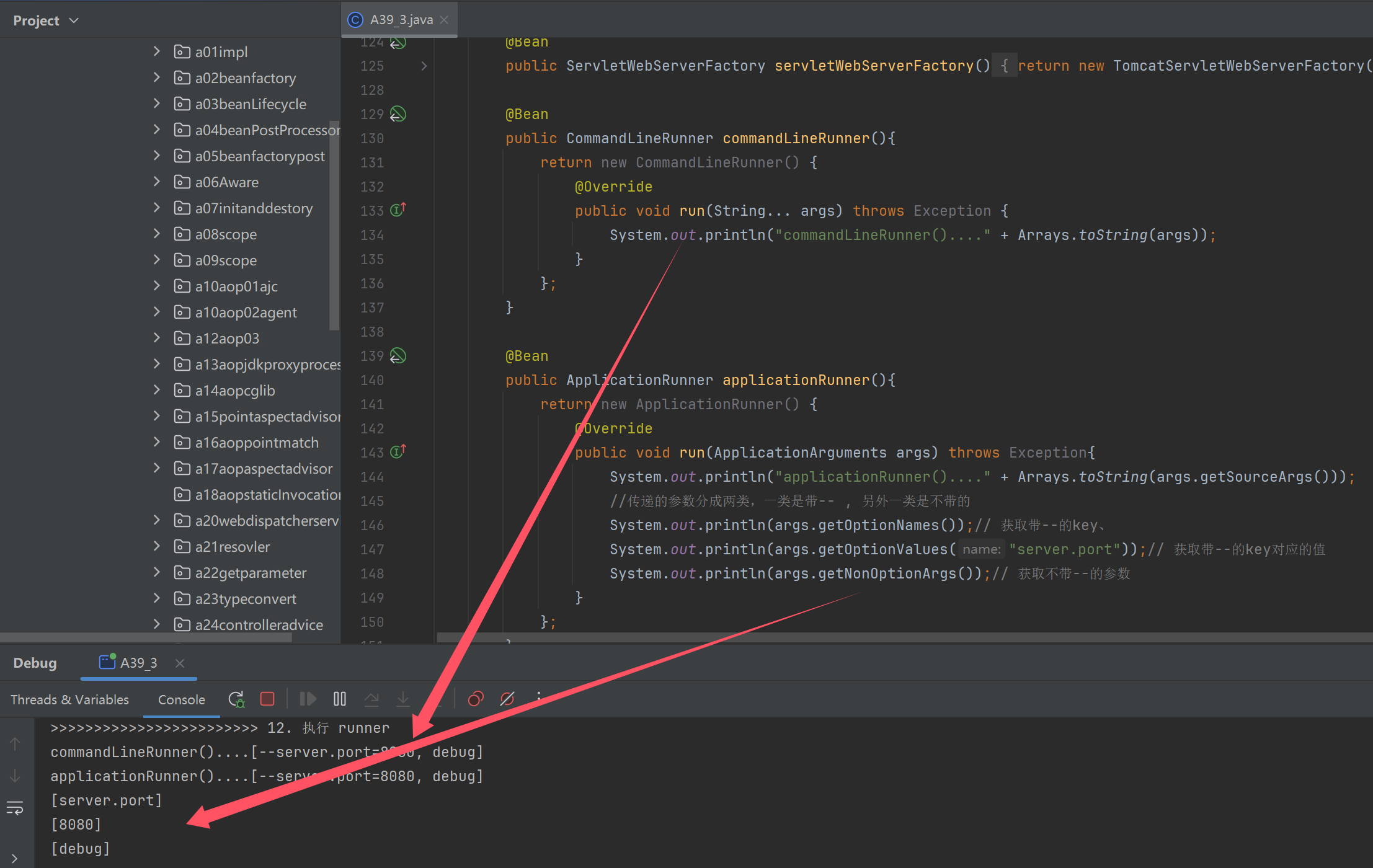
@Bean
public CommandLineRunner commandLineRunner(){
return new CommandLineRunner() {
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("commandLineRunner()...." + Arrays.toString(args));
}
};
}
@Bean
public ApplicationRunner applicationRunner(){
return new ApplicationRunner() {
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception{
System.out.println("applicationRunner()...." + Arrays.toString(args.getSourceArgs()));
//传递的参数分成两类,一类是带-- , 另外一类是不带的
System.out.println(args.getOptionNames());// 获取带--的key、
System.out.println(args.getOptionValues("server.port"));// 获取带--的key对应的值
System.out.println(args.getNonOptionArgs());// 获取不带--的参数
}
};
}
}
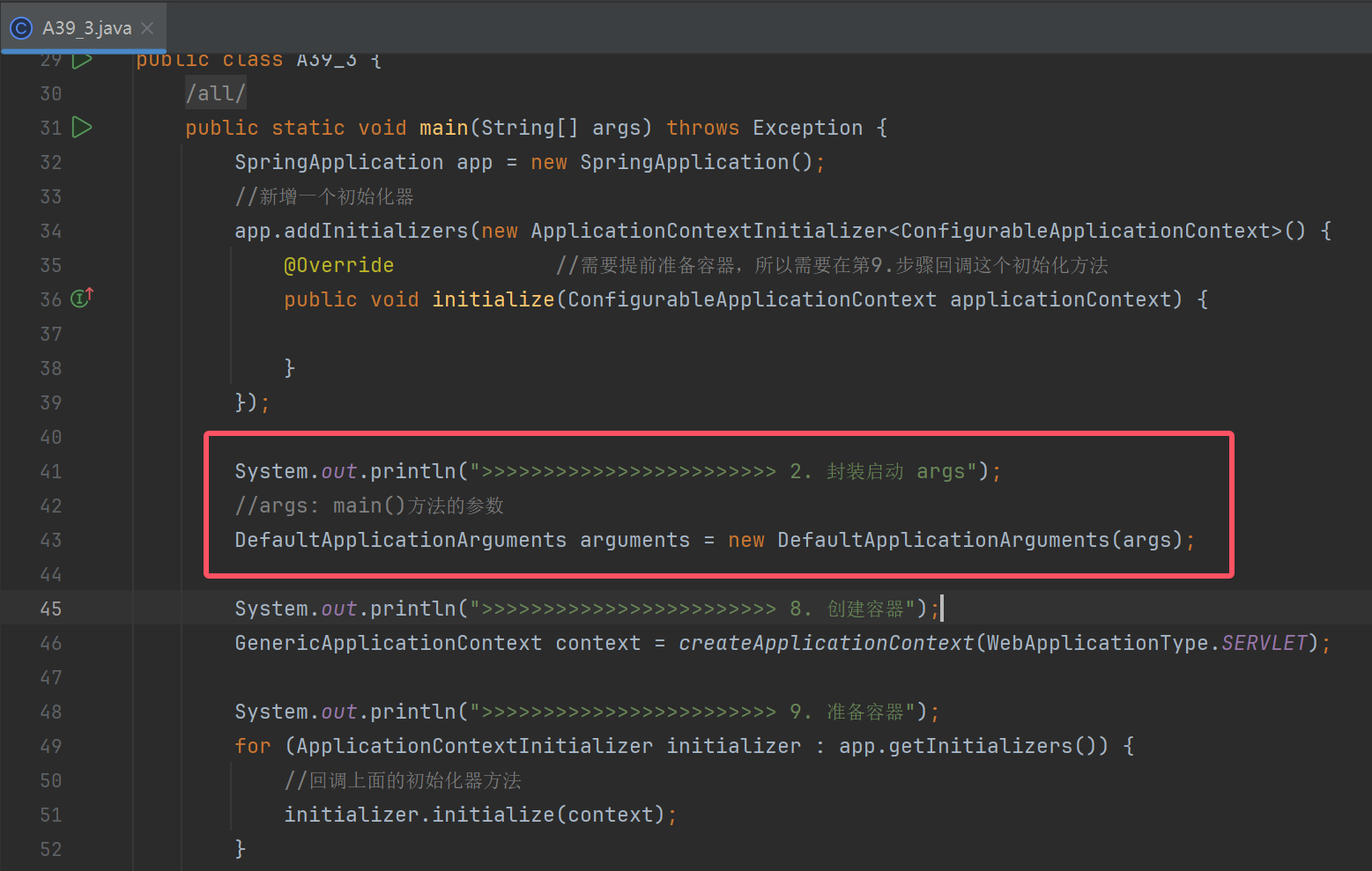
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 2. 封装启动 args");
//args: main()方法的参数
DefaultApplicationArguments arguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
完整代码
public class A39_3 {
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SpringApplication app = new SpringApplication();
//新增一个初始化器
app.addInitializers(new ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>() {
@Override //需要提前准备容器,所以需要在第9.步骤回调这个初始化方法
public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {
}
});
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 2. 封装启动 args");
//args: main()方法的参数
DefaultApplicationArguments arguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 8. 创建容器");
GenericApplicationContext context = createApplicationContext(WebApplicationType.SERVLET);
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 9. 准备容器");
for (ApplicationContextInitializer initializer : app.getInitializers()) {
//回调上面的初始化器方法
initializer.initialize(context);
}
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 10. 加载 bean 定义");
//设置将来读取的bean definition 存储位置:getDefaultListableBeanFactory ,还没有开始读取bean definition
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getDefaultListableBeanFactory();
AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader reader1 = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
//解析Config类中bean 定义,并加入到bean工厂
reader1.register(Config.class);
//xml获取类定义
XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader2 = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
reader2.loadBeanDefinitions(new ClassPathResource("b03.xml"));
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(beanFactory);
scanner.scan("com/feng/a39boot/sub");//扫描包路径下所有类,并解析bean定义,加入到bean工厂
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 11. refresh 容器");
context.refresh();//必须要先刷新,才能验证
for (String name : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println("name:" + name + " 来源: " + beanFactory.getBeanDefinition(name).getResourceDescription());
}
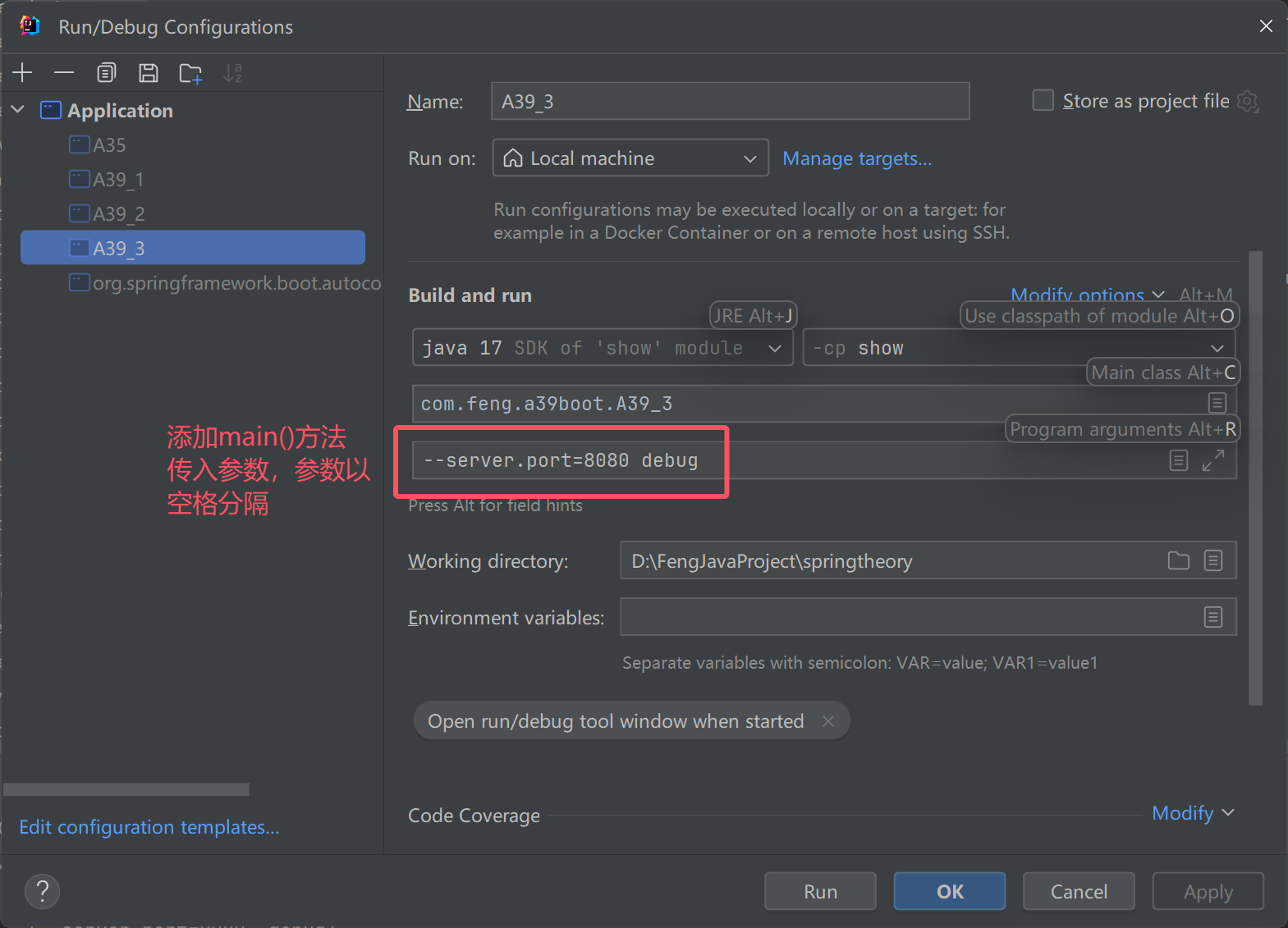
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 12. 执行 runner");
/**
* springboot执行结束时会回调CommandLineRunner,ApplicationRunner
*/
//getBeansOfType: 根据类型去拿bean , K: bean的名字 V: bean的实例对象
Map<String, CommandLineRunner> beansOfType = context.getBeansOfType(CommandLineRunner.class);
for (CommandLineRunner runner : beansOfType.values()) {
runner.run(args);
}
for (ApplicationRunner runner : context.getBeansOfType(ApplicationRunner.class)
.values()) {
runner.run(arguments); //applicationArguments: 第二步封装好的参数
}
/*
学到了什么
a. 创建容器、加载 bean 定义、refresh, 对应的步骤
*/
}
private static GenericApplicationContext createApplicationContext(WebApplicationType type) {
GenericApplicationContext context = null;
switch (type) {
case SERVLET -> context = new AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext();
case REACTIVE -> context = new AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext();
case NONE -> context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
}
return context;
}
static class Bean4 {
}
static class Bean5 {
}
static class Bean6 {
}
@Configuration
static class Config {
@Bean
public Bean5 bean5() {
return new Bean5();
}
@Bean
public ServletWebServerFactory servletWebServerFactory() {
return new TomcatServletWebServerFactory();
}
@Bean
public CommandLineRunner commandLineRunner(){
return new CommandLineRunner() {
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("commandLineRunner()...." + Arrays.toString(args));
}
};
}
@Bean
public ApplicationRunner applicationRunner(){
return new ApplicationRunner() {
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception{
System.out.println("applicationRunner()...." + Arrays.toString(args.getSourceArgs()));
//传递的参数分成两类,一类是带-- , 另外一类是不带的
System.out.println(args.getOptionNames());// 获取带--的key、
System.out.println(args.getOptionValues("server.port"));// 获取带--的key对应的值
System.out.println(args.getNonOptionArgs());// 获取不带--的参数
}
};
}
}
}
run 3
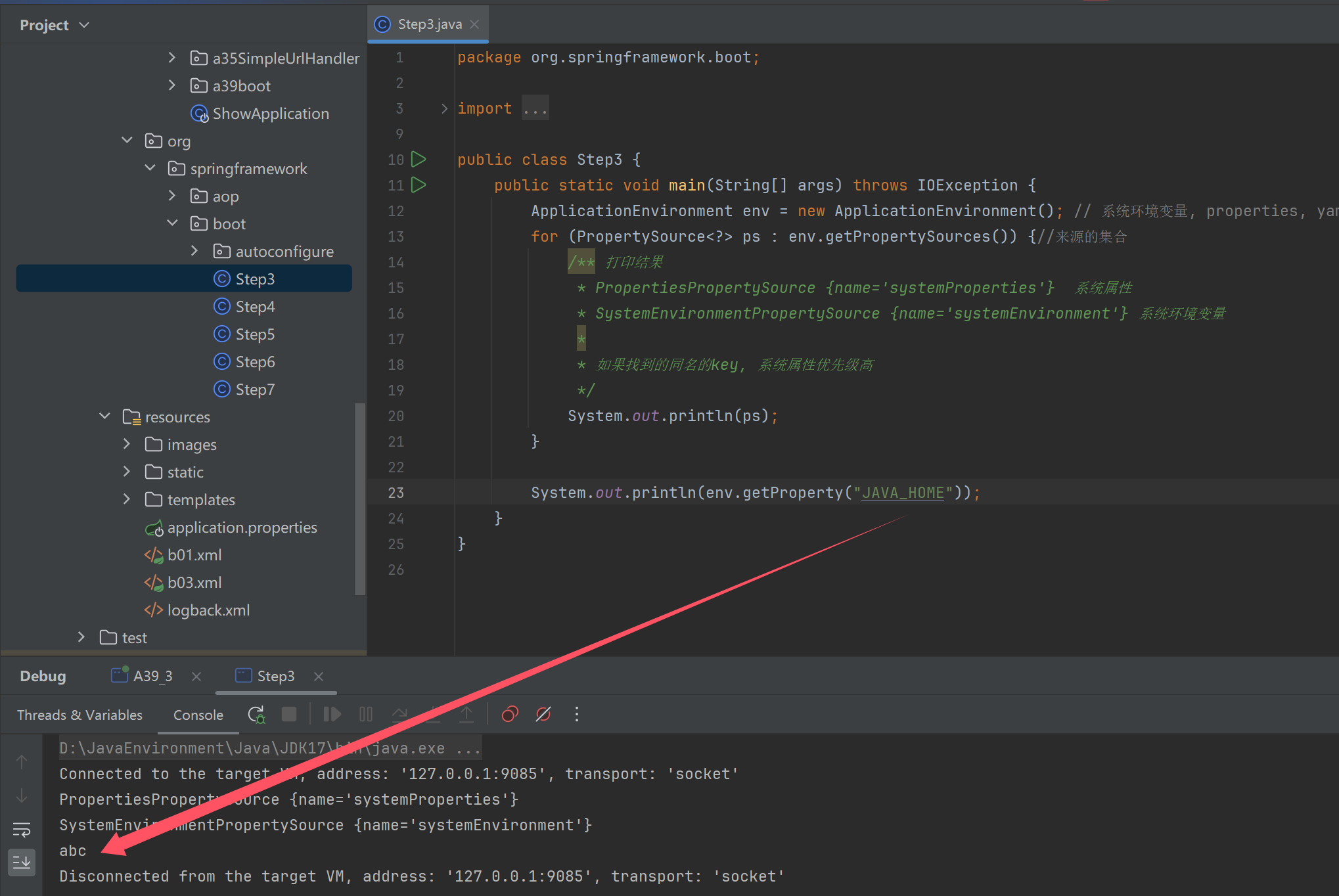
public class Step3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ApplicationEnvironment env = new ApplicationEnvironment(); // 系统环境变量, properties, yaml
for (PropertySource<?> ps : env.getPropertySources()) {//来源的集合
/** 打印结果
* PropertiesPropertySource {name='systemProperties'} 系统属性
* SystemEnvironmentPropertySource {name='systemEnvironment'} 系统环境变量
*
* 如果找到的同名的key, 系统属性优先级高
*/
System.out.println(ps);
}
System.out.println(env.getProperty("JAVA_HOME"));
}
}
添加配置文件来源
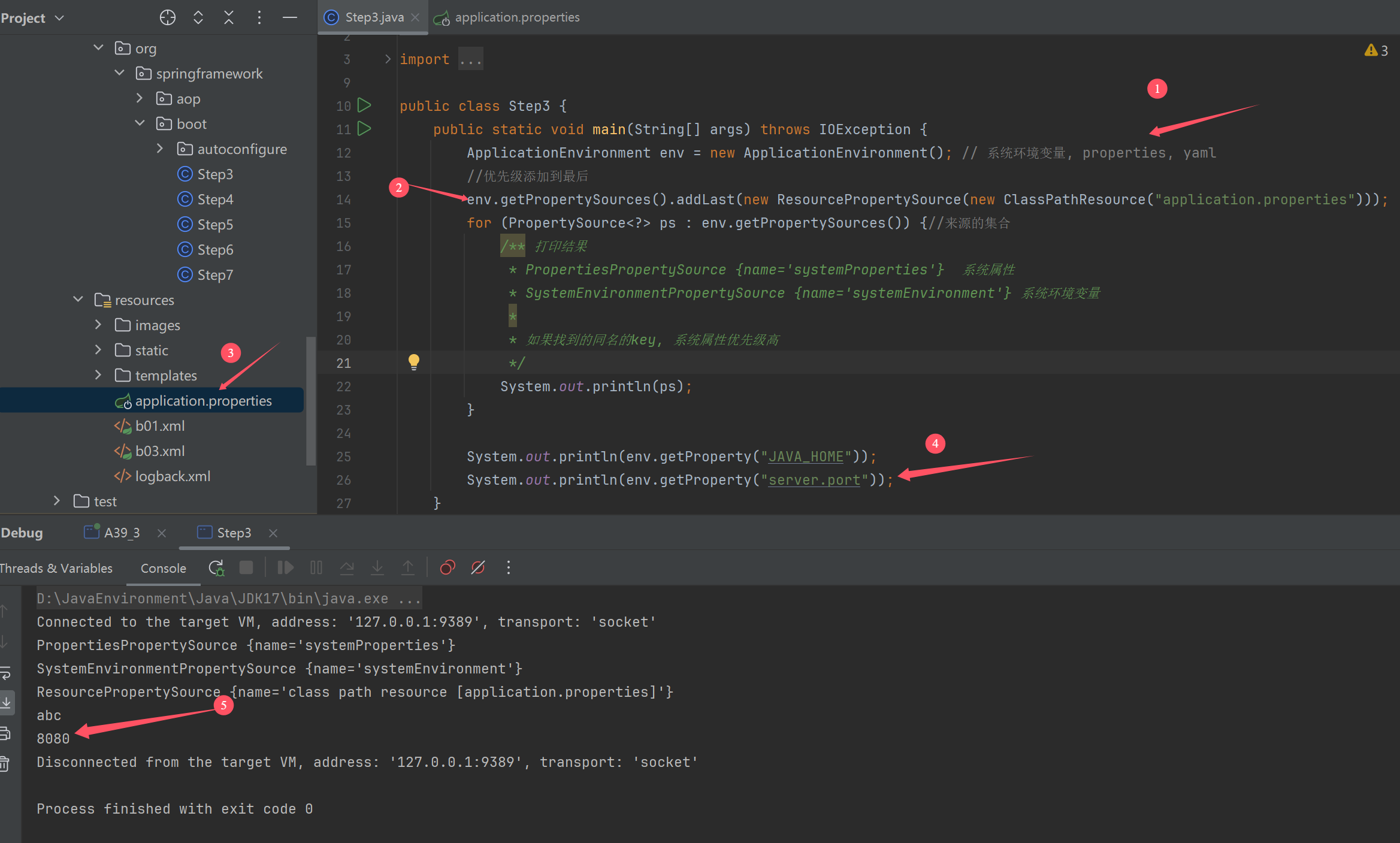
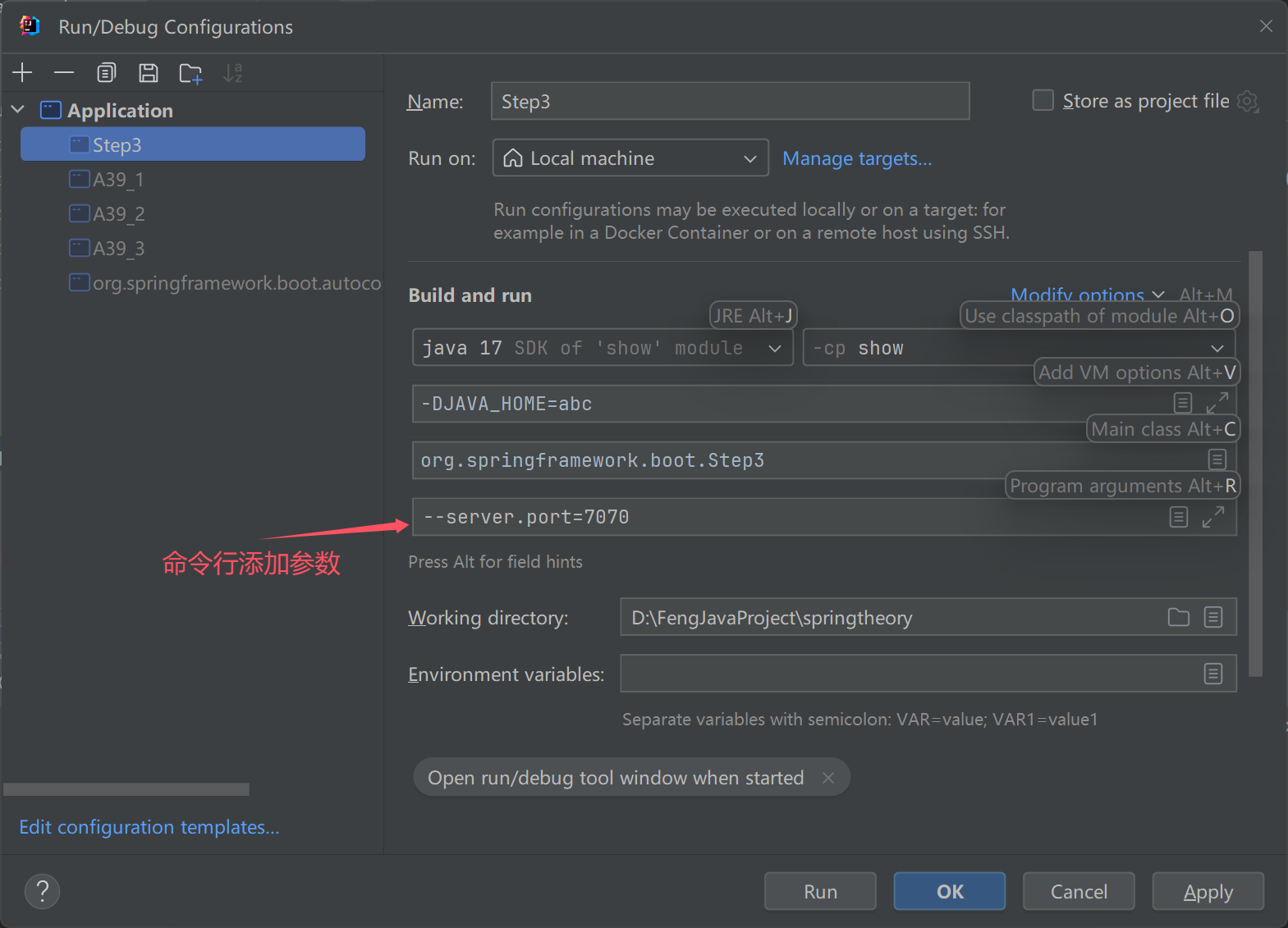
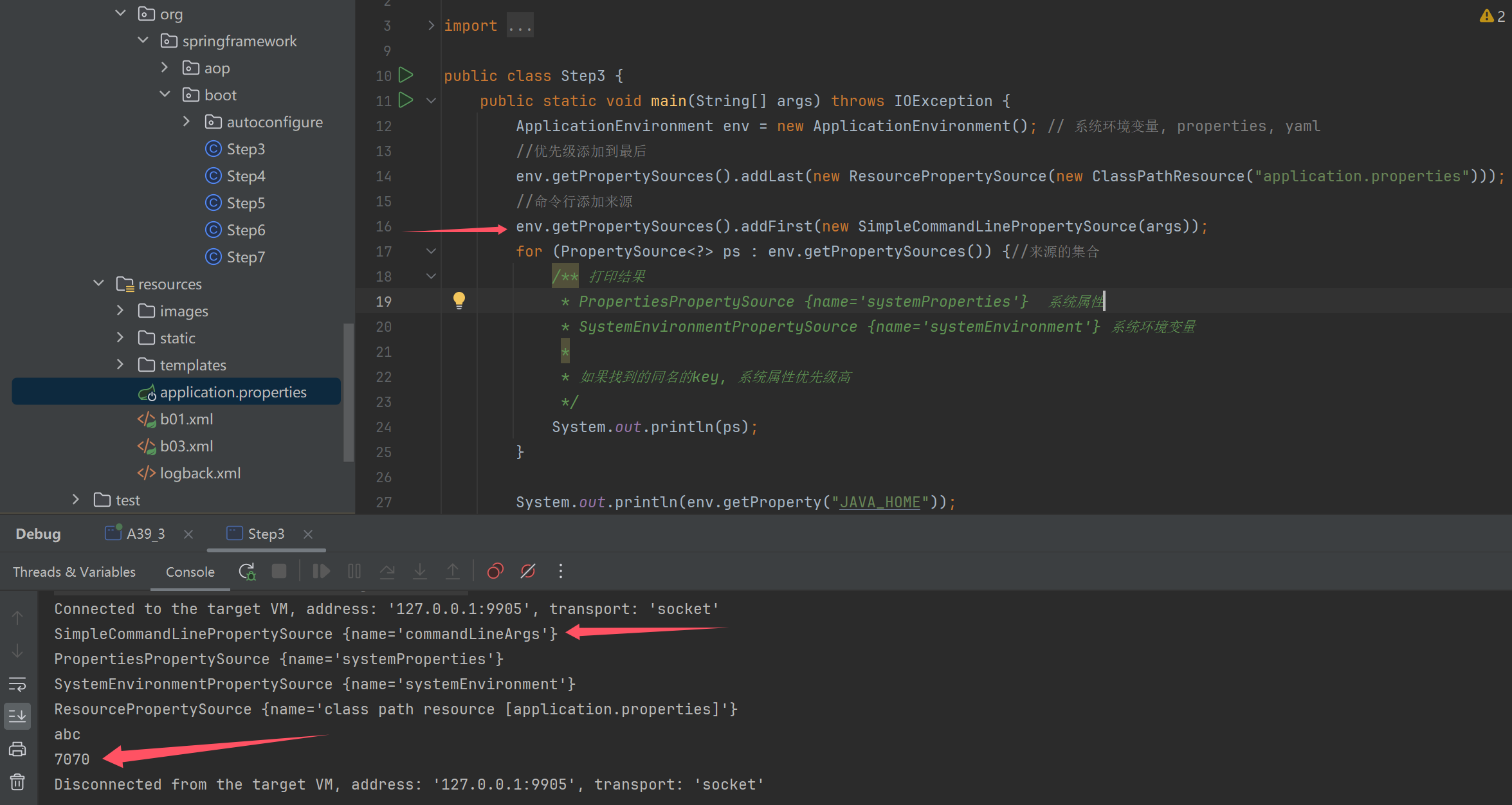
添加命令行来源
public class Step3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ApplicationEnvironment env = new ApplicationEnvironment(); // 系统环境变量, properties, yaml
//优先级添加到最后
env.getPropertySources().addLast(new ResourcePropertySource(new ClassPathResource("application.properties")));
//命令行添加来源
env.getPropertySources().addFirst(new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource(args));
for (PropertySource<?> ps : env.getPropertySources()) {//来源的集合
/** 打印结果
* PropertiesPropertySource {name='systemProperties'} 系统属性
* SystemEnvironmentPropertySource {name='systemEnvironment'} 系统环境变量
*
* 如果找到的同名的key, 系统属性优先级高
*/
System.out.println(ps);
}
System.out.println(env.getProperty("JAVA_HOME"));
System.out.println(env.getProperty("server.port"));
}
}
run 4
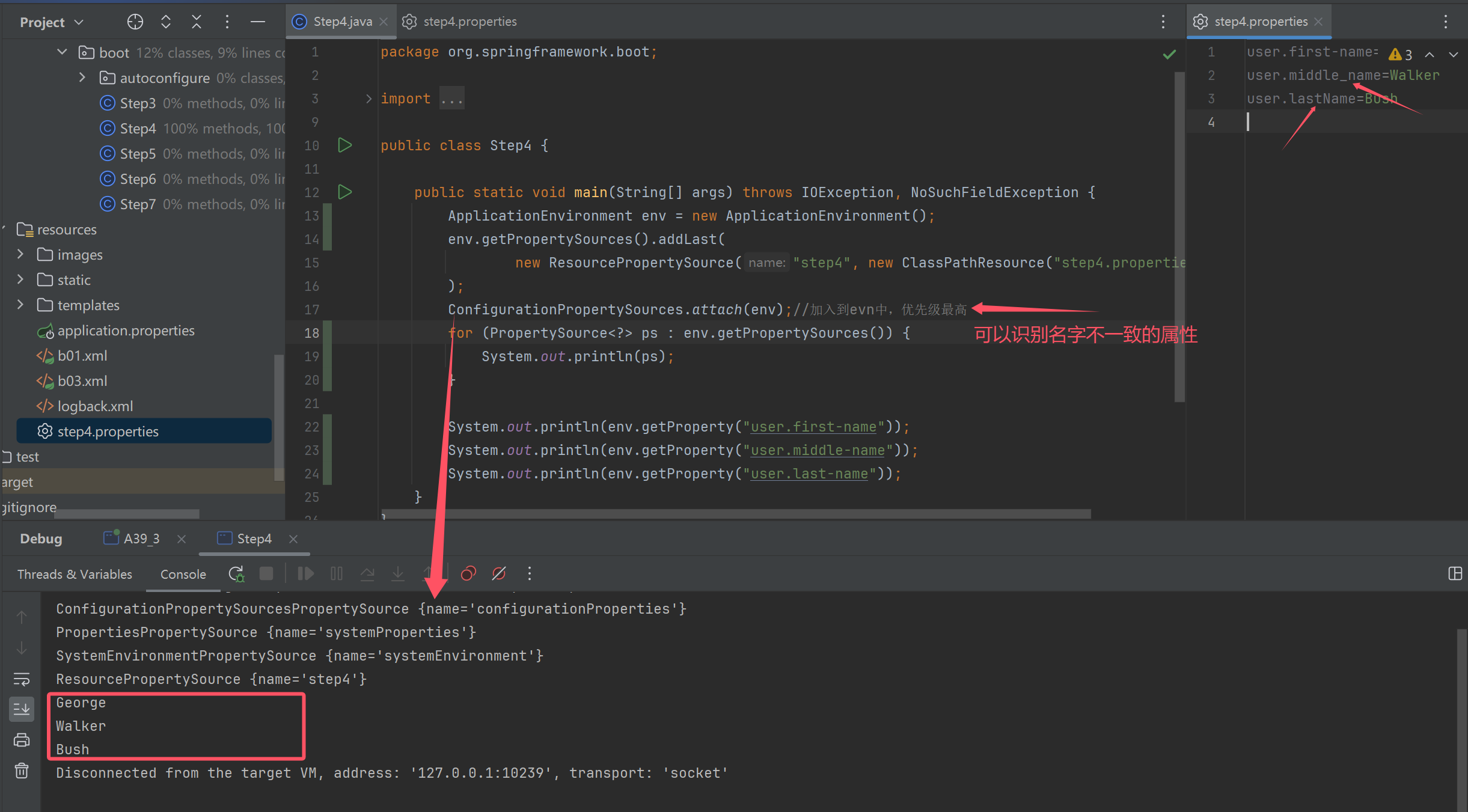
public class Step4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, NoSuchFieldException {
ApplicationEnvironment env = new ApplicationEnvironment();
env.getPropertySources().addLast(
new ResourcePropertySource("step4", new ClassPathResource("step4.properties"))
);
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(env);//加入到evn中,优先级最高
for (PropertySource<?> ps : env.getPropertySources()) {
System.out.println(ps);
}
System.out.println(env.getProperty("user.first-name"));
System.out.println(env.getProperty("user.middle-name"));
System.out.println(env.getProperty("user.last-name"));
}
}
run 5
后置处理器增强添加源
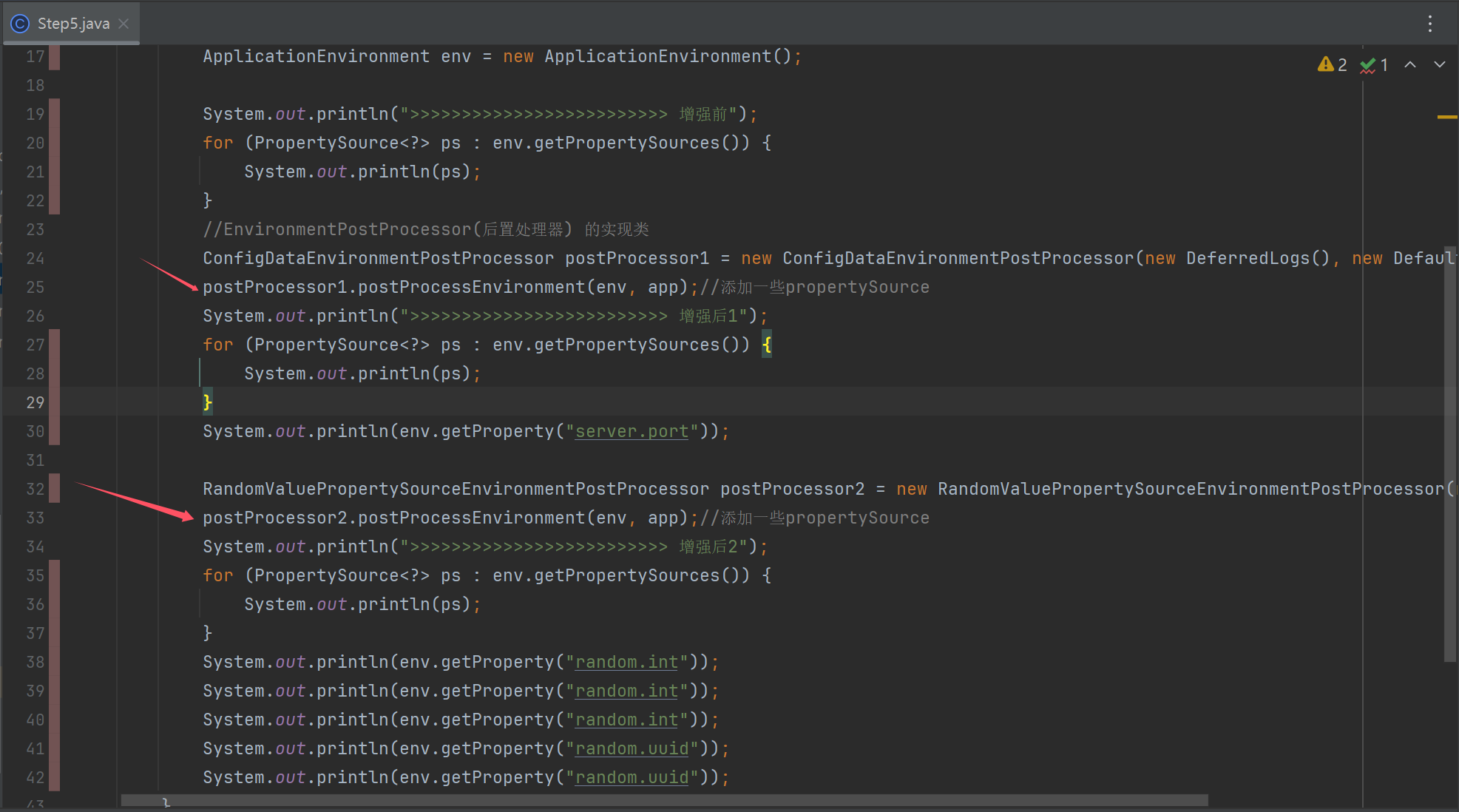
public class Step5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication app = new SpringApplication();
ApplicationEnvironment env = new ApplicationEnvironment();
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 增强前");
for (PropertySource<?> ps : env.getPropertySources()) {
System.out.println(ps);
}
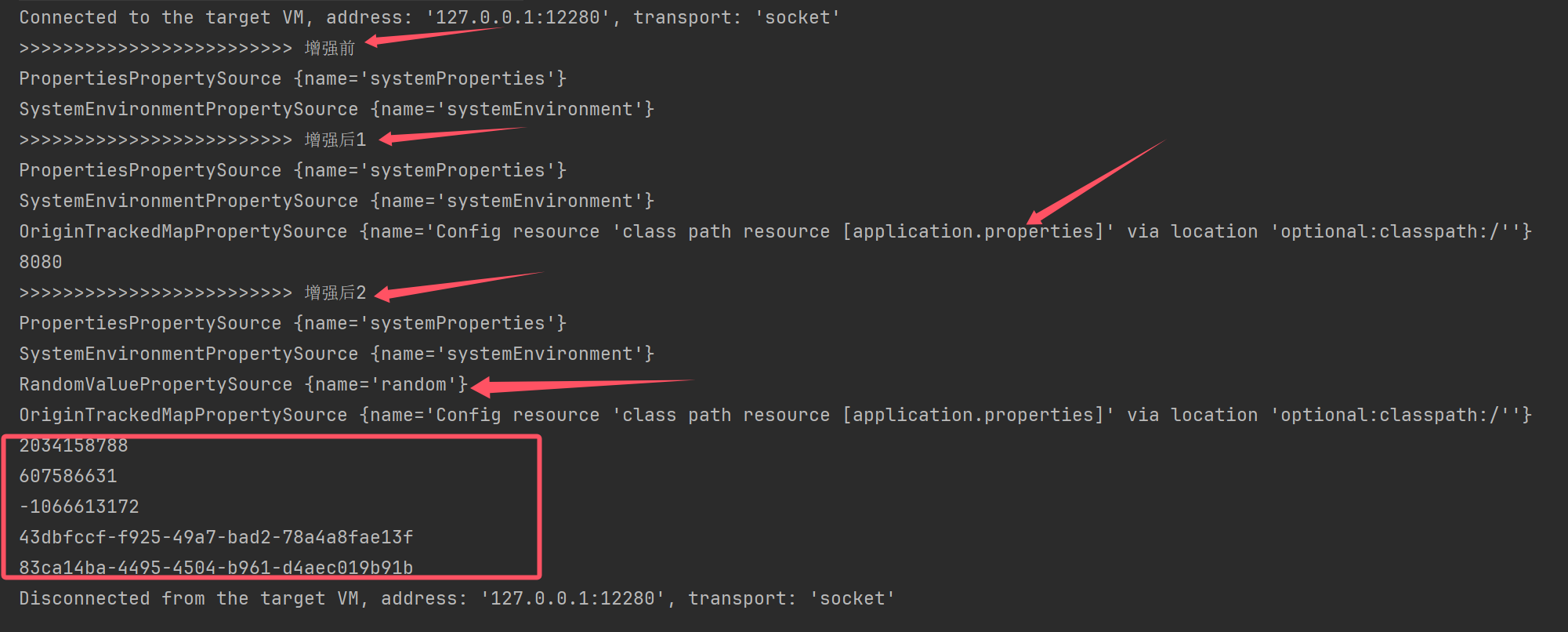
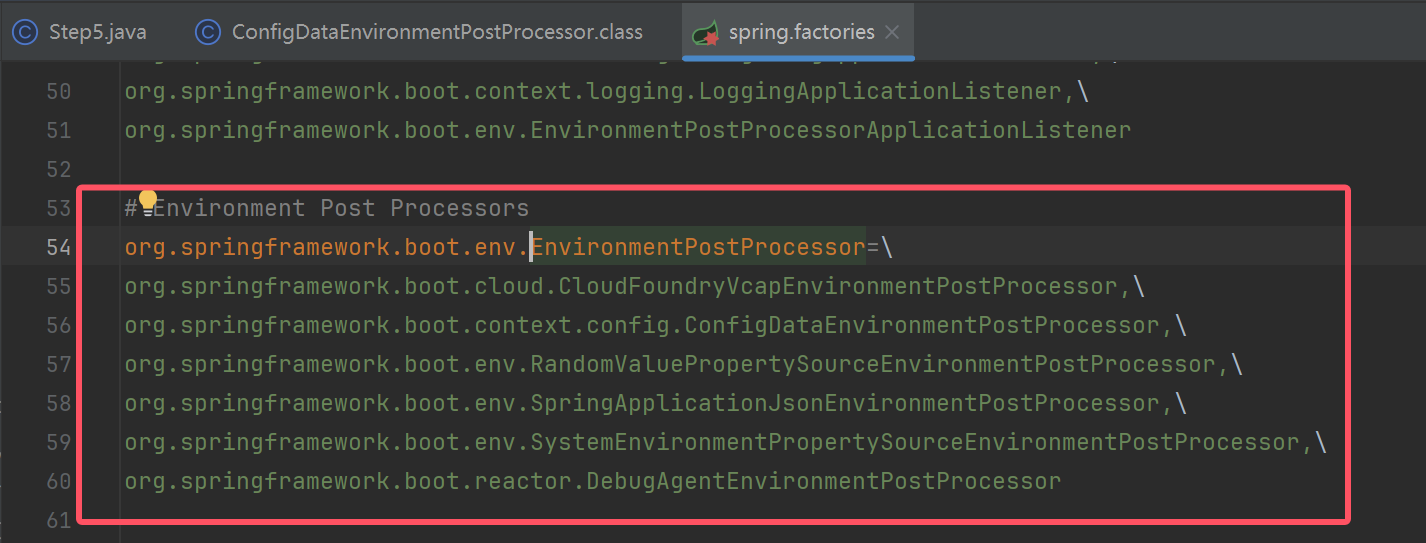
//EnvironmentPostProcessor(后置处理器) 的实现类
ConfigDataEnvironmentPostProcessor postProcessor1 = new ConfigDataEnvironmentPostProcessor(new DeferredLogs(), new DefaultBootstrapContext());
postProcessor1.postProcessEnvironment(env, app);//添加一些propertySource
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 增强后1");
for (PropertySource<?> ps : env.getPropertySources()) {
System.out.println(ps);
}
System.out.println(env.getProperty("server.port"));
RandomValuePropertySourceEnvironmentPostProcessor postProcessor2 = new RandomValuePropertySourceEnvironmentPostProcessor(new DeferredLog());
postProcessor2.postProcessEnvironment(env, app);//添加一些propertySource
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 增强后2");
for (PropertySource<?> ps : env.getPropertySources()) {
System.out.println(ps);
}
System.out.println(env.getProperty("random.int"));
System.out.println(env.getProperty("random.int"));
System.out.println(env.getProperty("random.int"));
System.out.println(env.getProperty("random.uuid"));
System.out.println(env.getProperty("random.uuid"));
}
}
之前都是使用硬编码方法,springboot都是使用配置文件
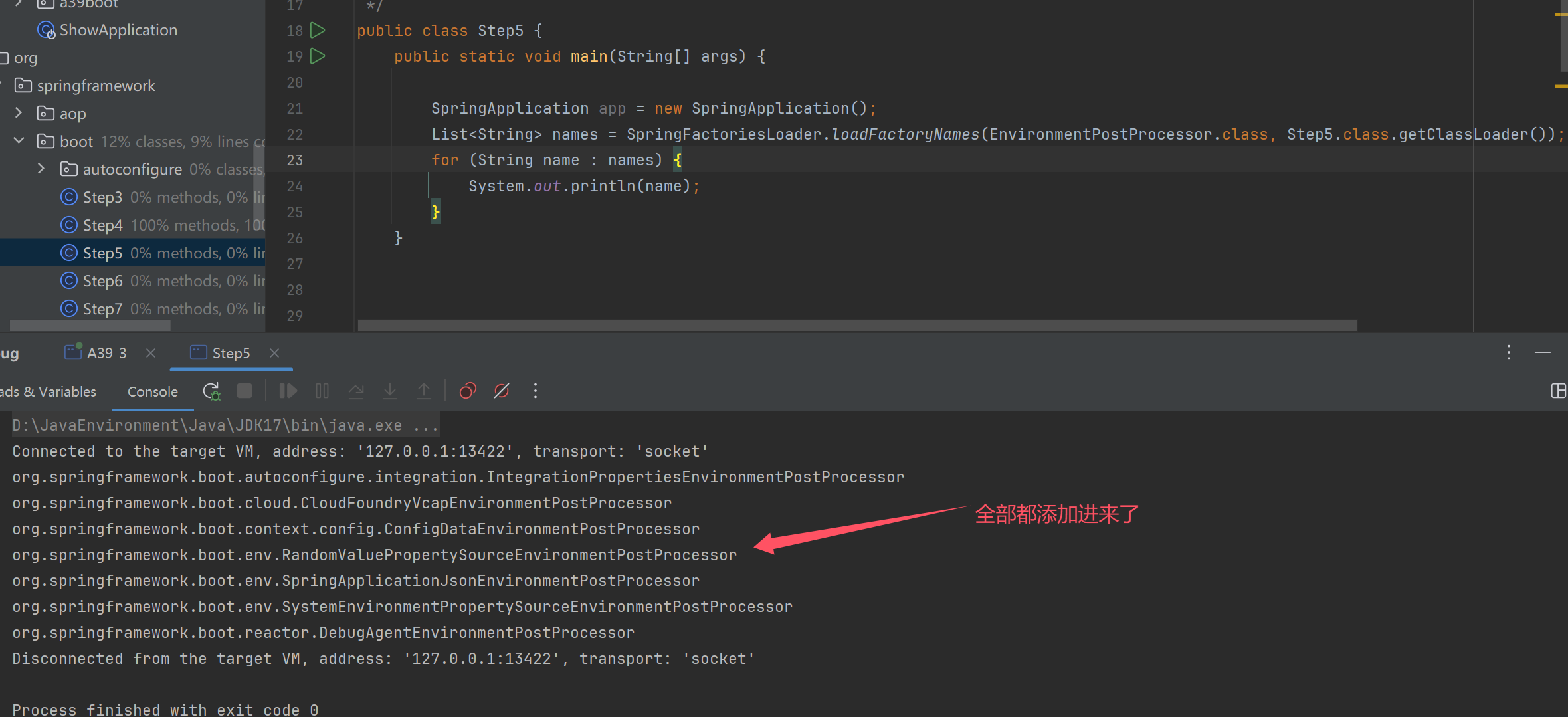
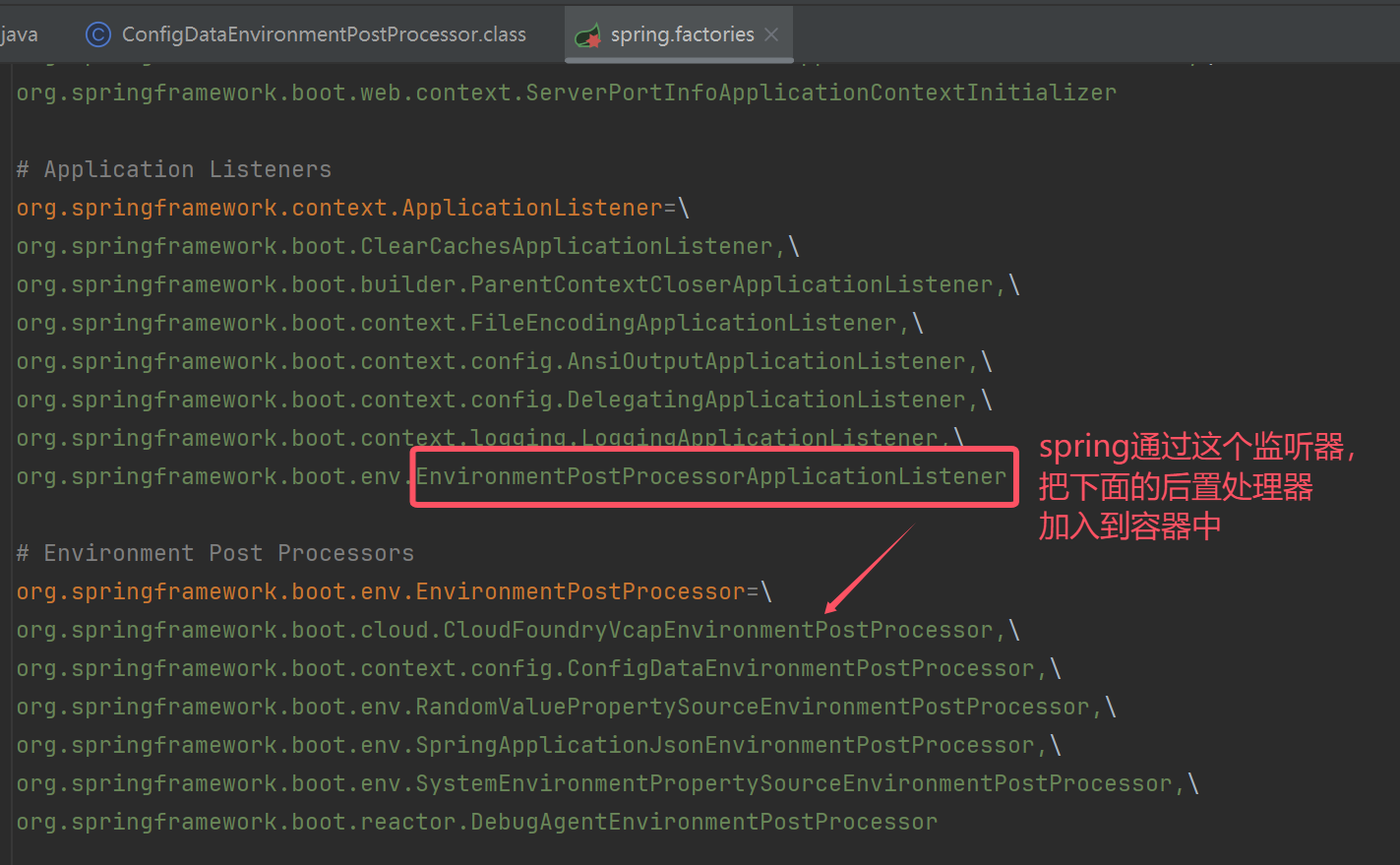
spring通过监听器实现上面步骤
public class Step5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication app = new SpringApplication();
app.addListeners(new EnvironmentPostProcessorApplicationListener());
/*List<String> names = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(EnvironmentPostProcessor.class, Step5.class.getClassLoader());
for (String name : names) {
System.out.println(name);
}*/
//run 的第3,4步,创建envirment对象,初始化一些属性,第5步才可以添加监听器,所以第5步,添加一个事件发布器触发监听事件
EventPublishingRunListener publisher = new EventPublishingRunListener(app, args);
ApplicationEnvironment env = new ApplicationEnvironment();
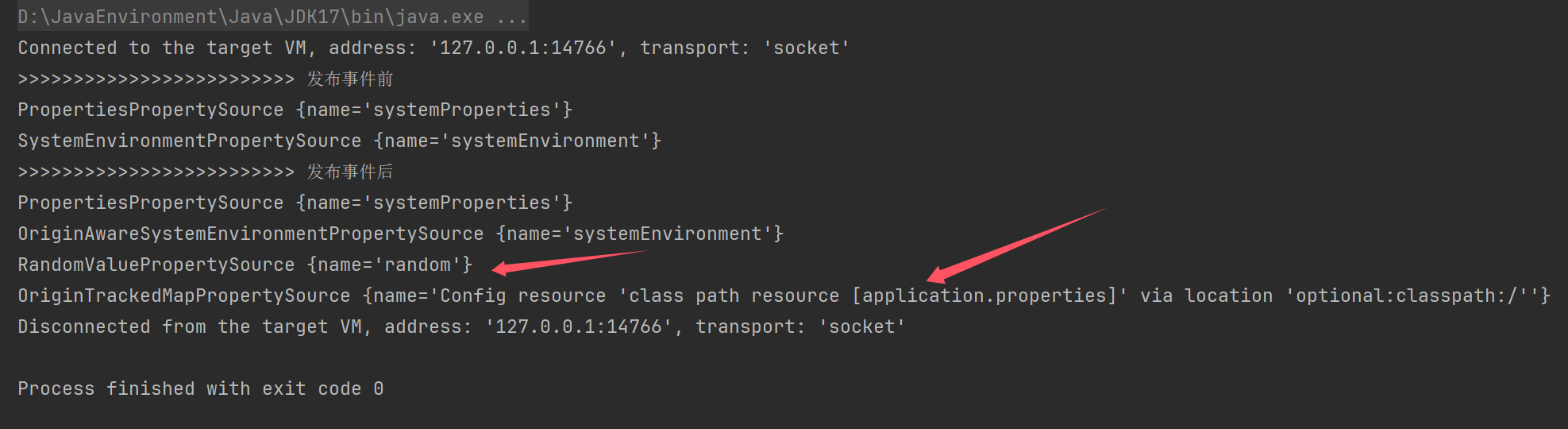
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 发布事件前");
for (PropertySource<?> ps : env.getPropertySources()) {
System.out.println(ps);
}
publisher.environmentPrepared(new DefaultBootstrapContext(),env); //发布事件,触发上面的监听器,通过配置文件,添加后置处理器增强
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 发布事件后");
for (PropertySource<?> ps : env.getPropertySources()) {
System.out.println(ps);
}
}
run 6
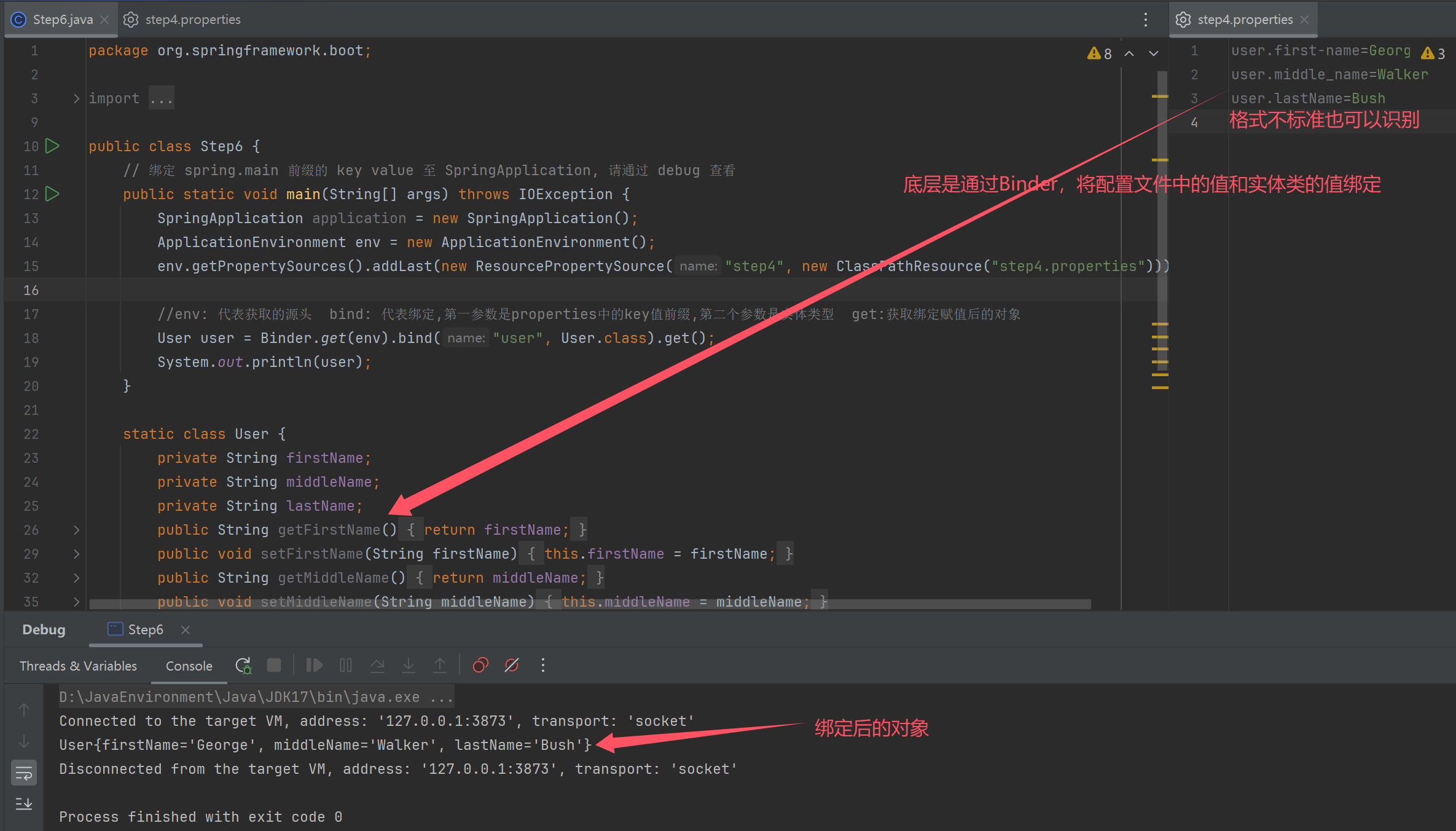
public class Step6 {
// 绑定 spring.main 前缀的 key value 至 SpringApplication, 请通过 debug 查看
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
SpringApplication application = new SpringApplication();
ApplicationEnvironment env = new ApplicationEnvironment();
env.getPropertySources().addLast(new ResourcePropertySource("step4", new ClassPathResource("step4.properties")));
//env: 代表获取的源头 bind: 代表绑定,第一参数是properties中的key值前缀,第二个参数是实体类型 get:获取绑定赋值后的对象
User user = Binder.get(env).bind("user", User.class).get();
System.out.println(user);
}
static class User {
private String firstName;
private String middleName;
private String lastName;
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public String getMiddleName() {
return middleName;
}
public void setMiddleName(String middleName) {
this.middleName = middleName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"firstName='" + firstName + '\'' +
", middleName='" + middleName + '\'' +
", lastName='" + lastName + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
}
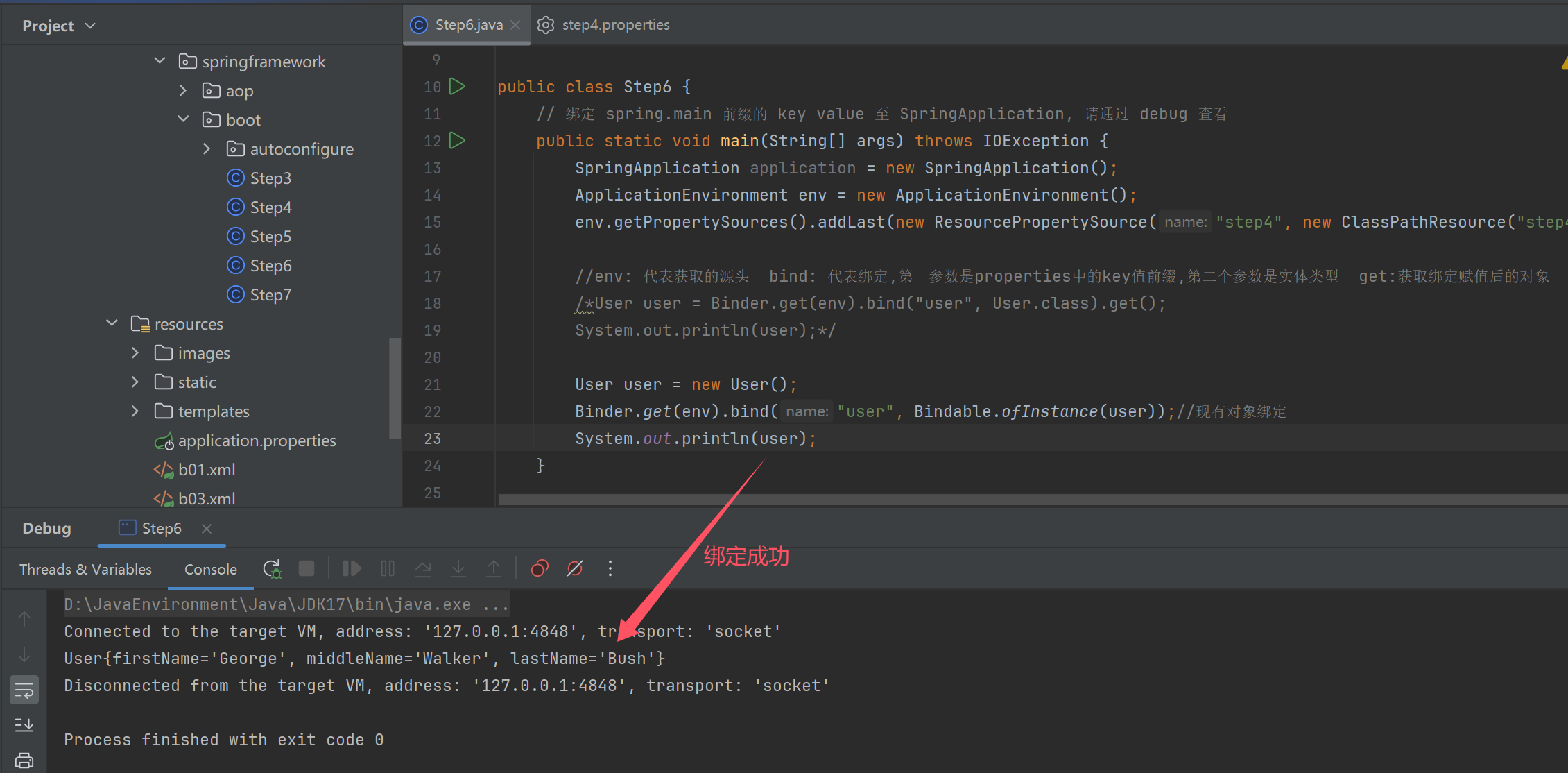
User user = new User();
Binder.get(env).bind("user", Bindable.ofInstance(user));//现有对象绑定
System.out.println(user);
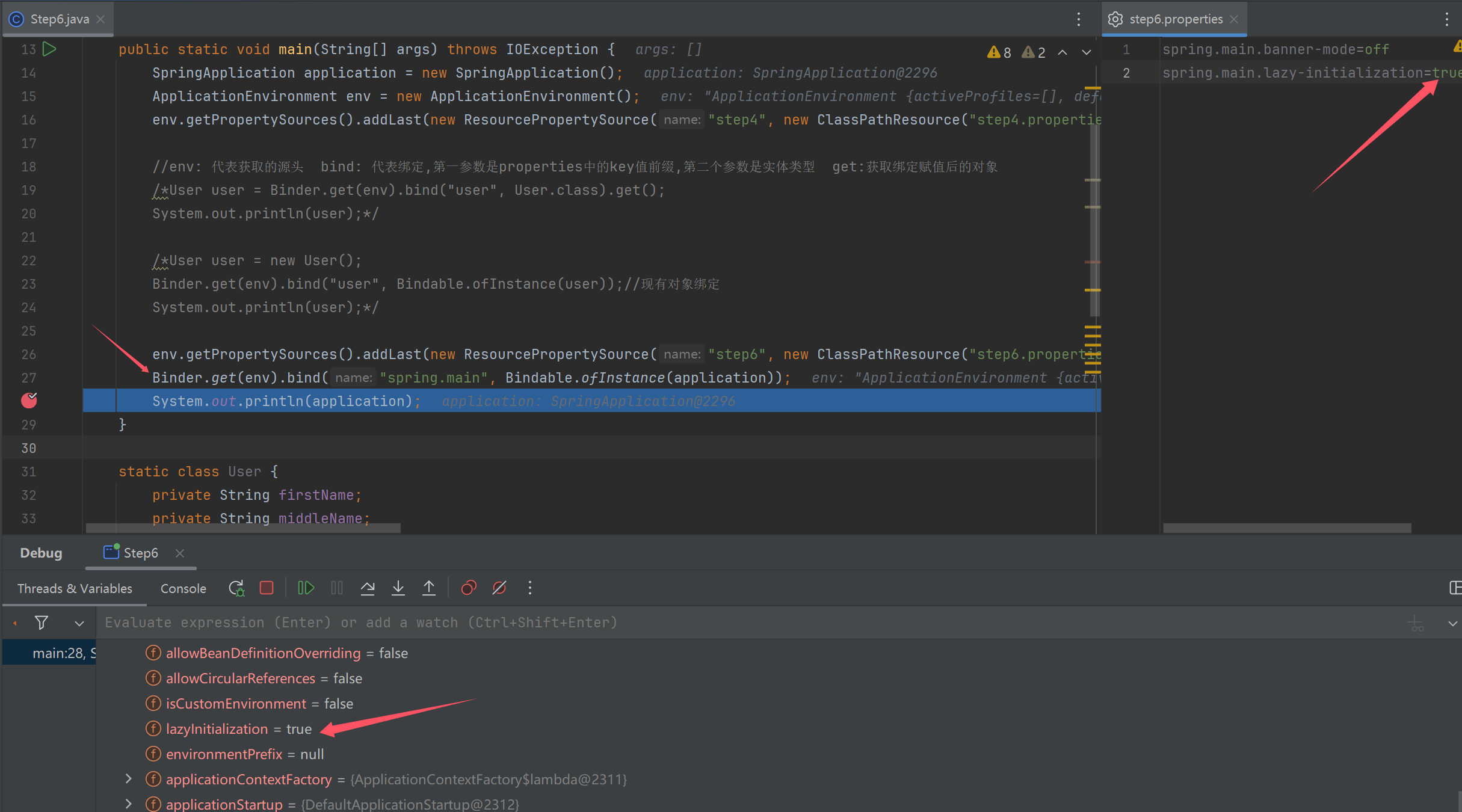
// 绑定 spring.main 前缀的 key value 至 SpringApplication, 请通过 debug 查看
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
SpringApplication application = new SpringApplication();
ApplicationEnvironment env = new ApplicationEnvironment();
env.getPropertySources().addLast(new ResourcePropertySource("step4", new ClassPathResource("step4.properties")));
//env: 代表获取的源头 bind: 代表绑定,第一参数是properties中的key值前缀,第二个参数是实体类型 get:获取绑定赋值后的对象
/*User user = Binder.get(env).bind("user", User.class).get();
System.out.println(user);*/
/*User user = new User();
Binder.get(env).bind("user", Bindable.ofInstance(user));//现有对象绑定
System.out.println(user);*/
env.getPropertySources().addLast(new ResourcePropertySource("step6", new ClassPathResource("step6.properties")));
Binder.get(env).bind("spring.main", Bindable.ofInstance(application));
System.out.println(application);
}
step6主要是把spring.main中的属性和配置文件中的值绑定
run 7
输出图片
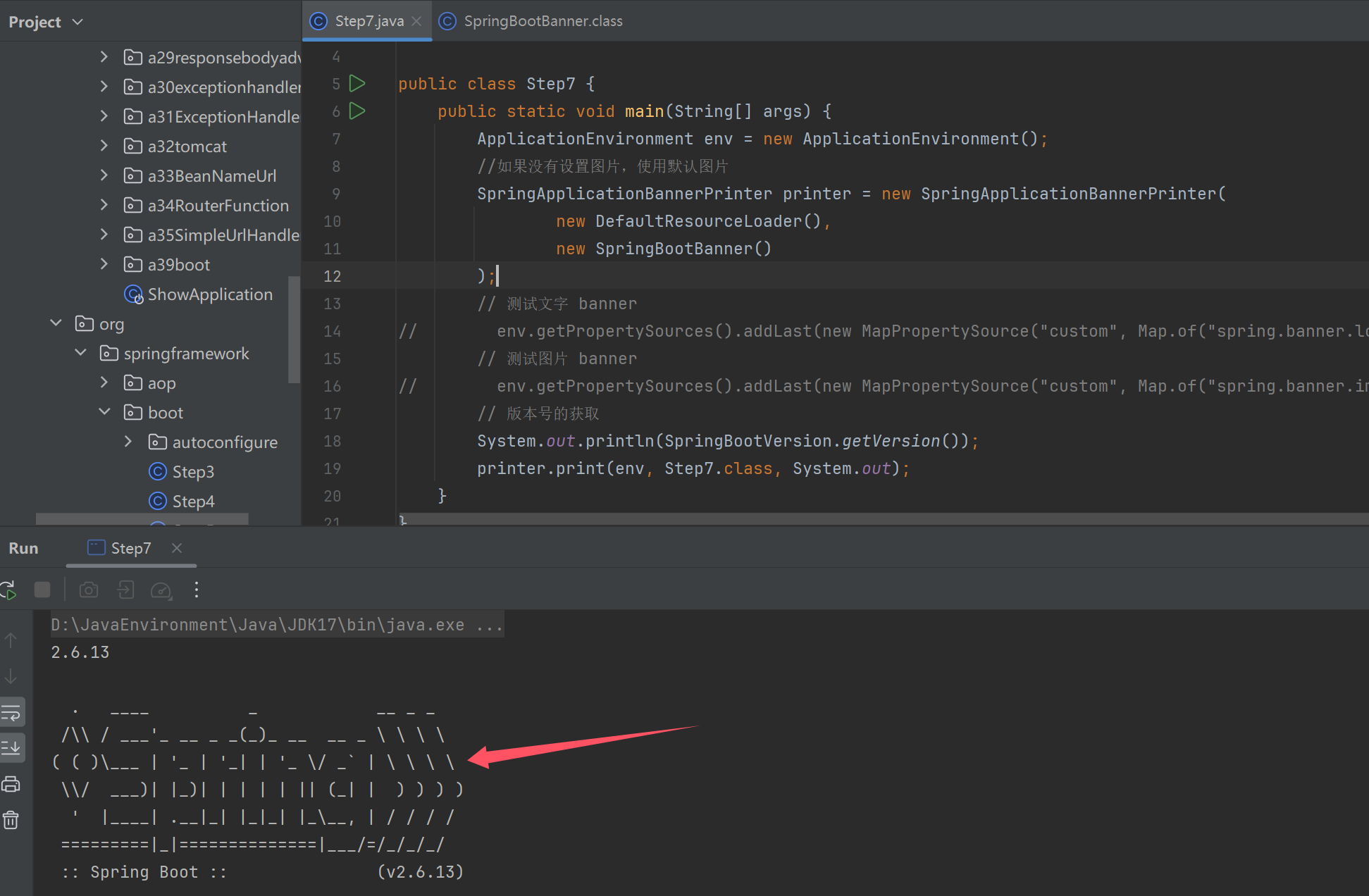
public class Step7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationEnvironment env = new ApplicationEnvironment();
//如果没有设置图片,使用默认图片
SpringApplicationBannerPrinter printer = new SpringApplicationBannerPrinter(
new DefaultResourceLoader(),
new SpringBootBanner()
);
// 测试文字 banner
// env.getPropertySources().addLast(new MapPropertySource("custom", Map.of("spring.banner.location","banner1.txt")));
// 测试图片 banner
// env.getPropertySources().addLast(new MapPropertySource("custom", Map.of("spring.banner.image.location","banner2.png")));
// 版本号的获取
System.out.println(SpringBootVersion.getVersion());
printer.print(env, Step7.class, System.out);
}
}
run 方法小结
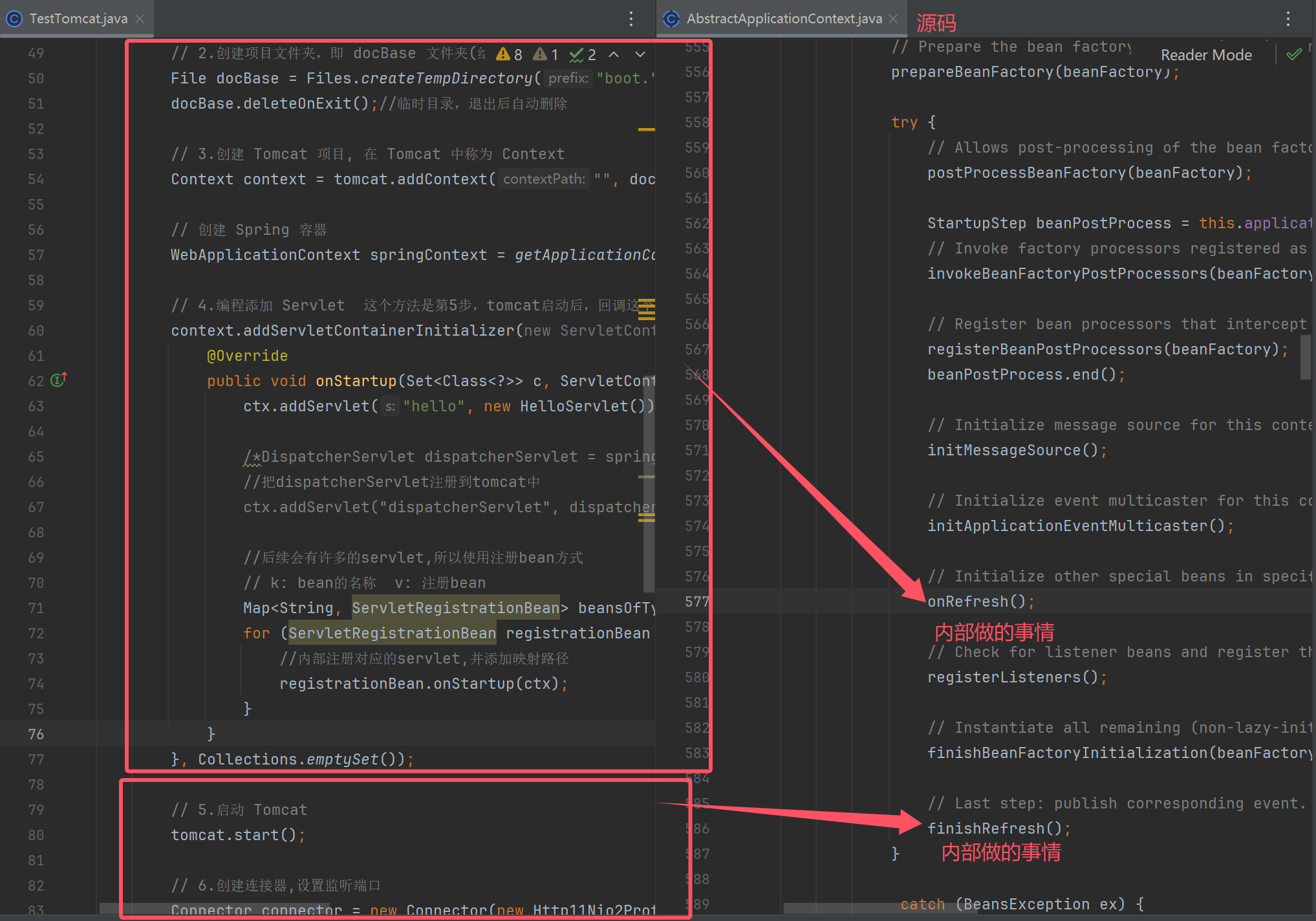
源码
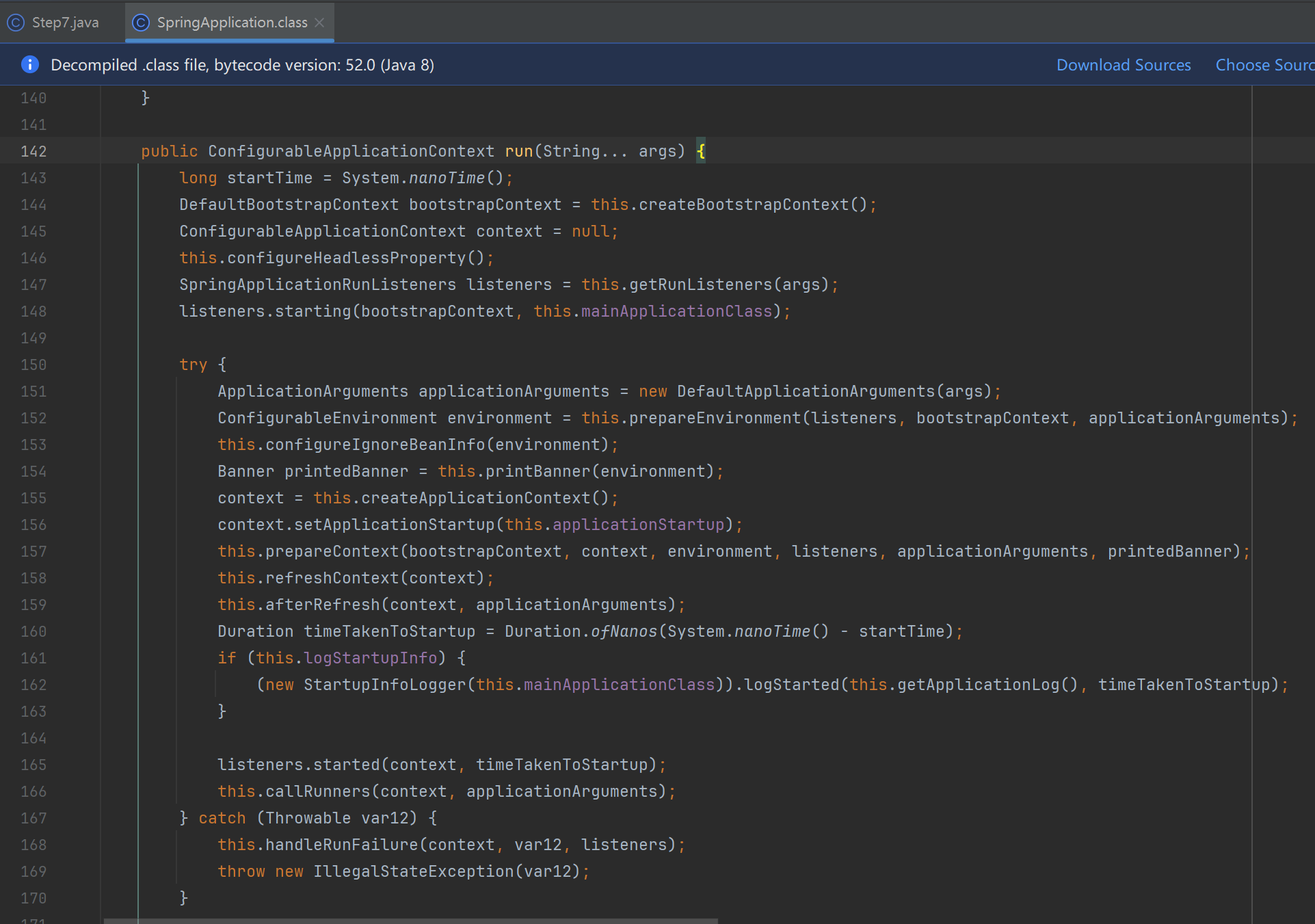
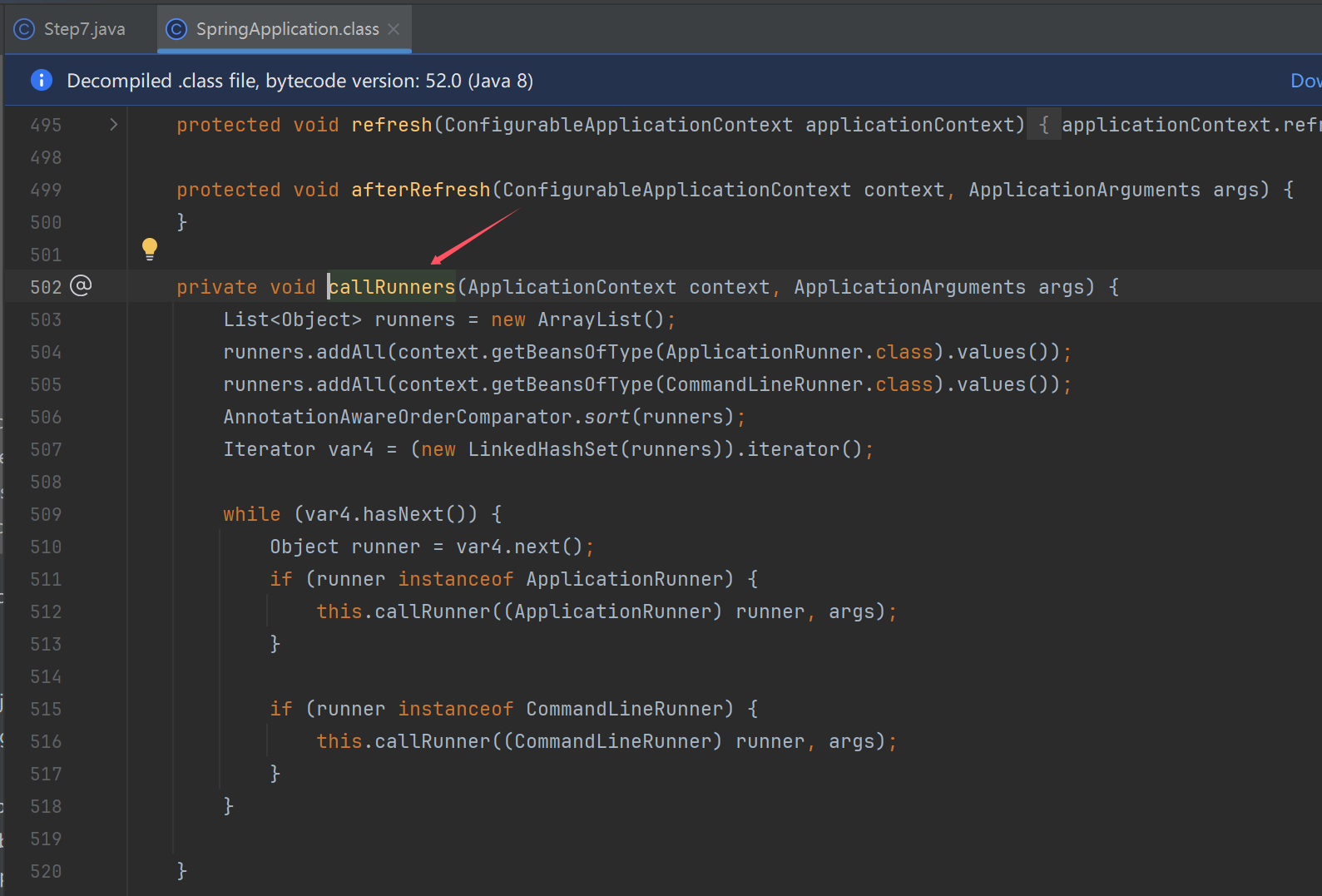
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = this.createBootstrapContext();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
this.configureHeadlessProperty();
//1步骤:根据spring.factory读取里面的事件发布器
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = this.getRunListeners(args);
//springboot开始启动了
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
try {
//2步骤:分装main参数,分成一个 --符号的选项参数 和一个非选项参数
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
//查看下方源码方法
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = this.prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);
this.configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
//7步骤:打印banner信息
Banner printedBanner = this.printBanner(environment);
//8步骤:创建spring容器,根据在构造方法中推断出来的容器类型,在三种类型中,选择一种容器实现
context = this.createApplicationContext();
context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup);
//查看下方源码
this.prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
//调用容器refresh方法,调用各种bean工厂后处理器,准备各种bean的后处理器。然后初始化每个单例
this.refreshContext(context);
this.afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
Duration timeTakenToStartup = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
(new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)).logStarted(this.getApplicationLog(), timeTakenToStartup);
}
//发布一个started事件
listeners.started(context, timeTakenToStartup);
//查看下方源码
this.callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
} catch (Throwable var12) {
this.handleRunFailure(context, var12, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(var12);
}
try {
Duration timeTakenToReady = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime);
//发布一个ready事件,表明springboot项目启动完成
listeners.ready(context, timeTakenToReady);
return context;
} catch (Throwable var11) {
//如果出现异常,发布一个失败事件
this.handleRunFailure(context, var11, (SpringApplicationRunListeners)null);
throw new IllegalStateException(var11);
}
}
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
//3步骤:创建environment环境 如果非web环境,创建applicationContext对象
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = this.getOrCreateEnvironment();
//把参数信息封装成properties源数据对象,添加到environment中(environment从参数中获取一些键值(只能是选项参数--符号)信息)
this.configureEnvironment((ConfigurableEnvironment)environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
//4步骤:把参数中key中以_分隔或者驼峰分隔的,转成-分隔
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach((Environment)environment);
//5步骤:事件的发布与响应,为environmen对象添加源
listeners.environmentPrepared(bootstrapContext, (ConfigurableEnvironment)environment);
DefaultPropertiesPropertySource.moveToEnd((ConfigurableEnvironment)environment);
Assert.state(!((ConfigurableEnvironment)environment).containsProperty("spring.main.environment-prefix"), "Environment prefix cannot be set via properties.");
//6步骤:把environment中spring.main前缀和springapplication对象绑定
this.bindToSpringApplication((ConfigurableEnvironment)environment);
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
environment = this.convertEnvironment((ConfigurableEnvironment)environment);
}
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach((Environment)environment);
return (ConfigurableEnvironment)environment;
}
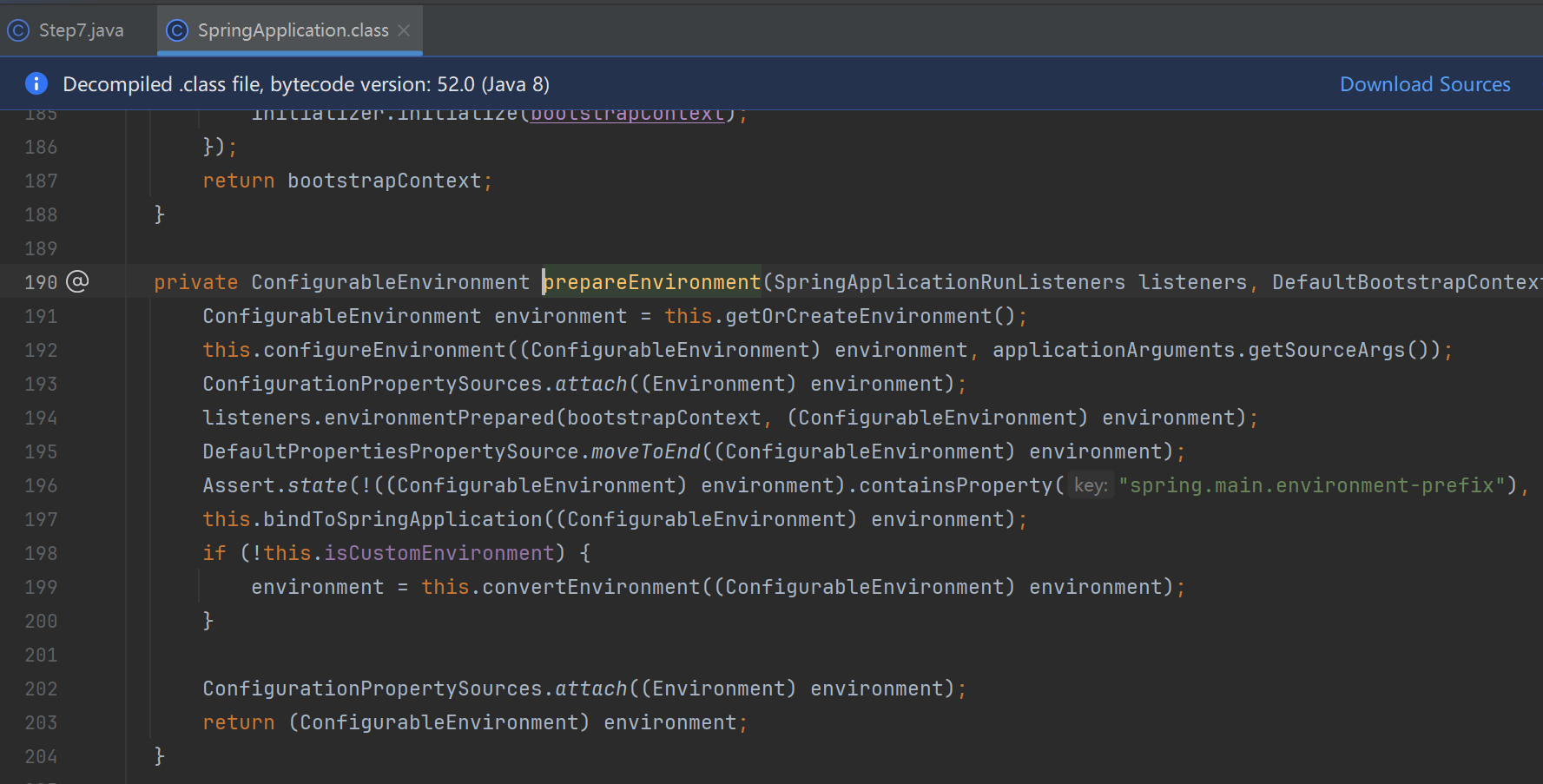
private void prepareContext(DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
context.setEnvironment(environment);
this.postProcessApplicationContext(context);
//9步骤:应用初始化器,对applicationContext做功能增强
this.applyInitializers(context);
//发布contextPrepared事件,容器创建好,并初始化容器后,发布这个事件
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
bootstrapContext.close(context);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
this.logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
this.logStartupProfileInfo(context);
}
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
}
if (beanFactory instanceof AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory) {
((AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory)beanFactory).setAllowCircularReferences(this.allowCircularReferences);
if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {
((DefaultListableBeanFactory)beanFactory).setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
}
}
if (this.lazyInitialization) {
context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new LazyInitializationBeanFactoryPostProcessor());
}
context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new PropertySourceOrderingBeanFactoryPostProcessor(context));
//第10步骤,获取所有beanDefination源
Set<Object> sources = this.getAllSources();
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
//把获取的源加载到容器,加载各种beanDefination
this.load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));
//发布contextLoaded事件
listeners.contextLoaded(context);
}
private void callRunners(ApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {
List<Object> runners = new ArrayList();
//12步骤,调用所有实现了ApplicationRunner.class或者是CommandLineRunner.class的bean
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(ApplicationRunner.class).values());
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(CommandLineRunner.class).values());
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(runners);
Iterator var4 = (new LinkedHashSet(runners)).iterator();
while(var4.hasNext()) {
Object runner = var4.next();
if (runner instanceof ApplicationRunner) {
this.callRunner((ApplicationRunner)runner, args);
}
if (runner instanceof CommandLineRunner) {
this.callRunner((CommandLineRunner)runner, args);
}
}
}
boot启动过程总结
阶段一:SpringApplication 构造
- 记录 BeanDefinition 源
- 推断应用类型
- 记录 ApplicationContext 初始化器
- 记录监听器
- 推断主启动类
阶段二:执行 run 方法
-
得到 SpringApplicationRunListeners,名字取得不好,实际是事件发布器
- 发布 application starting 事件1️⃣
-
封装启动 args
-
准备 Environment 添加命令行参数(*)
-
ConfigurationPropertySources 处理(*)
- 发布 application environment 已准备事件2️⃣
-
通过 EnvironmentPostProcessorApplicationListener 进行 env 后处理(*)
- application.properties,由 StandardConfigDataLocationResolver 解析
- spring.application.json
-
绑定 spring.main 到 SpringApplication 对象(*)
-
打印 banner(*)
-
创建容器
-
准备容器
- 发布 application context 已初始化事件3️⃣
-
加载 bean 定义
- 发布 application prepared 事件4️⃣
-
refresh 容器
- 发布 application started 事件5️⃣
-
执行 runner
-
发布 application ready 事件6️⃣
-
这其中有异常,发布 application failed 事件7️⃣
-
带 * 的有独立的示例
演示 - 启动过程
a39.A39_1 对应 SpringApplication 构造
a39.A39_2 对应第1步,并演示 7 个事件
a39.A39_3 对应第2、8到12步
org.springframework.boot.Step3
org.springframework.boot.Step4
org.springframework.boot.Step5
org.springframework.boot.Step6
org.springframework.boot.Step7
收获💡
- SpringApplication 构造方法中所做的操作
- 可以有多种源用来加载 bean 定义
- 应用类型推断
- 添加容器初始化器
- 添加监听器
- 演示主类推断
- 如何读取 spring.factories 中的配置
- 从配置中获取重要的事件发布器:SpringApplicationRunListeners
- 容器的创建、初始化器增强、加载 bean 定义等
- CommandLineRunner、ApplicationRunner 的作用
- 环境对象
- 命令行 PropertySource
- ConfigurationPropertySources 规范环境键名称
- EnvironmentPostProcessor 后处理增强
- 由 EventPublishingRunListener 通过监听事件2️⃣来调用
- 绑定 spring.main 前缀的 key value 至 SpringApplication
- Banner
1.4 Tomcat 内嵌容器
Tomcat 基本结构
Server
└───Service
├───Connector (协议, 端口)
└───Engine
└───Host(虚拟主机 localhost)
├───Context1 (应用1, 可以设置虚拟路径, / 即 url 起始路径; 项目磁盘路径, 即 docBase )
│ │ index.html
│ └───WEB-INF
│ │ web.xml (servlet, filter, listener) 3.0
│ ├───classes (servlet, controller, service ...)
│ ├───jsp
│ └───lib (第三方 jar 包)
└───Context2 (应用2)
│ index.html
└───WEB-INF
web.xml
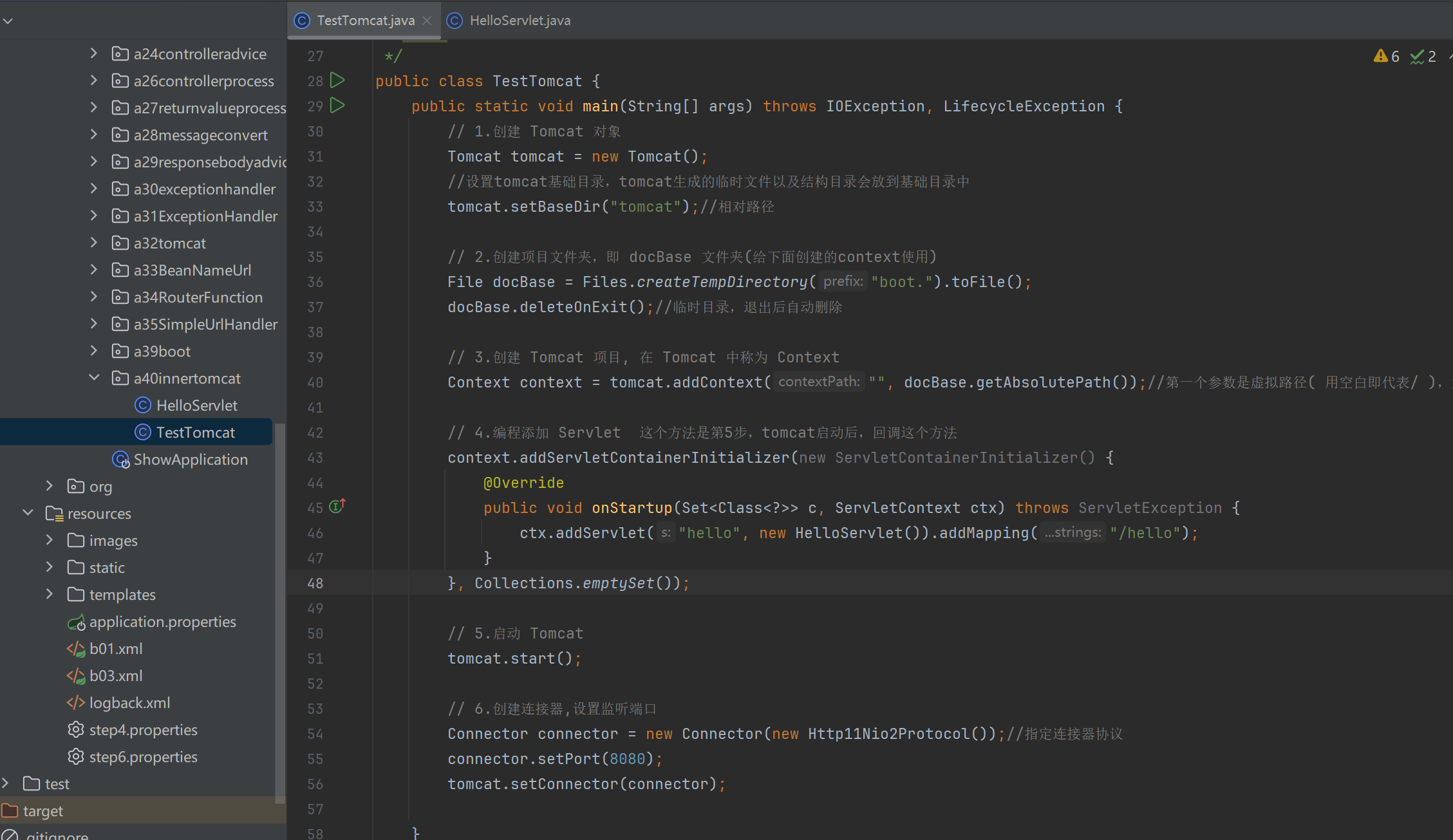
演示1 - Tomcat 内嵌容器
HelloServlet
public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
resp.getWriter().write("""
<h1>hello servlet</h1>
""");
}
}
TestTomcat
public class TestTomcat {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, LifecycleException {
// 1.创建 Tomcat 对象
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
//设置tomcat基础目录,tomcat生成的临时文件以及结构目录会放到基础目录中
tomcat.setBaseDir("tomcat");//相对路径
// 2.创建项目文件夹,即 docBase 文件夹(给下面创建的context使用)
File docBase = Files.createTempDirectory("boot.").toFile();
docBase.deleteOnExit();//临时目录,退出后自动删除
// 3.创建 Tomcat 项目, 在 Tomcat 中称为 Context
Context context = tomcat.addContext("", docBase.getAbsolutePath());//第一个参数是虚拟路径( 用空白即代表/ ),第二个参数是docBase
// 4.编程添加 Servlet 这个方法是第5步,tomcat启动后,回调这个方法
context.addServletContainerInitializer(new ServletContainerInitializer() {
@Override
public void onStartup(Set<Class<?>> c, ServletContext ctx) throws ServletException {
ctx.addServlet("hello", new HelloServlet()).addMapping("/hello");
}
}, Collections.emptySet());
// 5.启动 Tomcat
tomcat.start();
// 6.创建连接器,设置监听端口
Connector connector = new Connector(new Http11Nio2Protocol());//指定连接器协议
connector.setPort(8080);
tomcat.setConnector(connector);
}
}
演示2 - 集成 Spring 容器
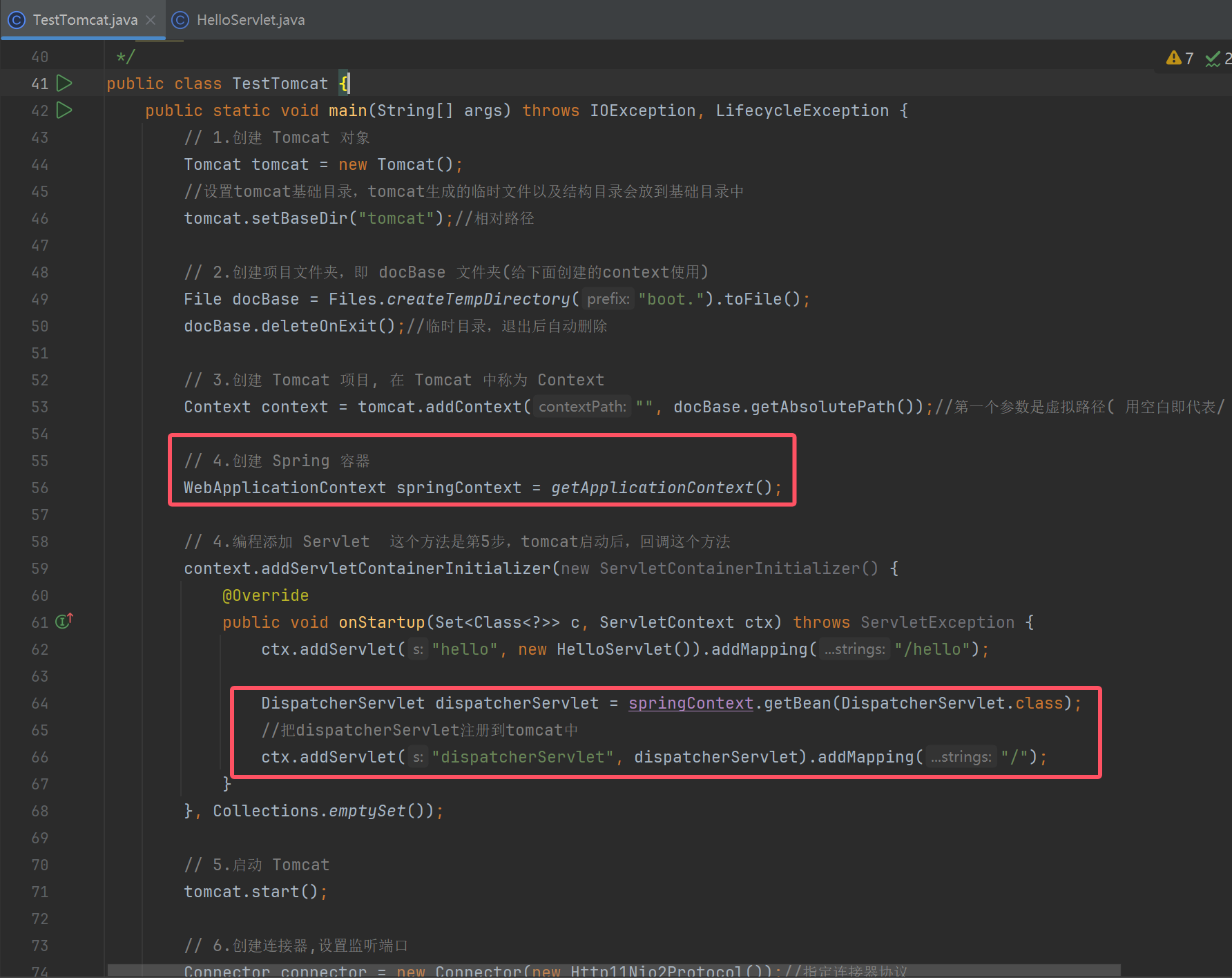
public static WebApplicationContext getApplicationContext(){
//AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext: 内嵌tomcat
//AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext: 不包含tomcat
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
context.register(Config.class);
context.refresh();
return context;
}
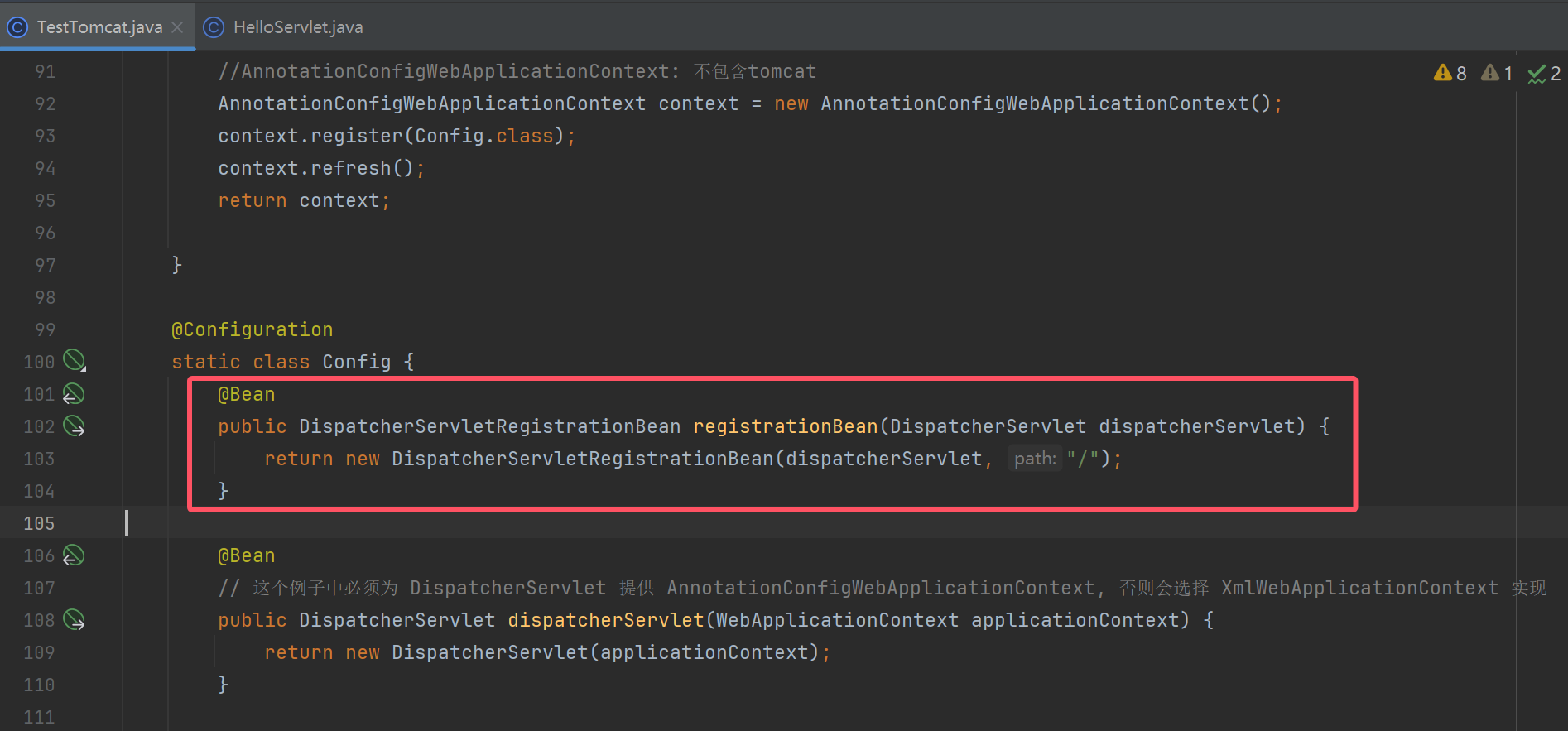
@Configuration
static class Config {
@Bean
public DispatcherServletRegistrationBean registrationBean(DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet) {
return new DispatcherServletRegistrationBean(dispatcherServlet, "/");
}
@Bean
// 这个例子中必须为 DispatcherServlet 提供 AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext, 否则会选择 XmlWebApplicationContext 实现
public DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet(WebApplicationContext applicationContext) {
return new DispatcherServlet(applicationContext);
}
@Bean
public RequestMappingHandlerAdapter requestMappingHandlerAdapter() {
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter handlerAdapter = new RequestMappingHandlerAdapter();
//默认的HandlerAdapter没有json的消息转换器MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter
handlerAdapter.setMessageConverters(List.of(new MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter()));
return handlerAdapter;
}
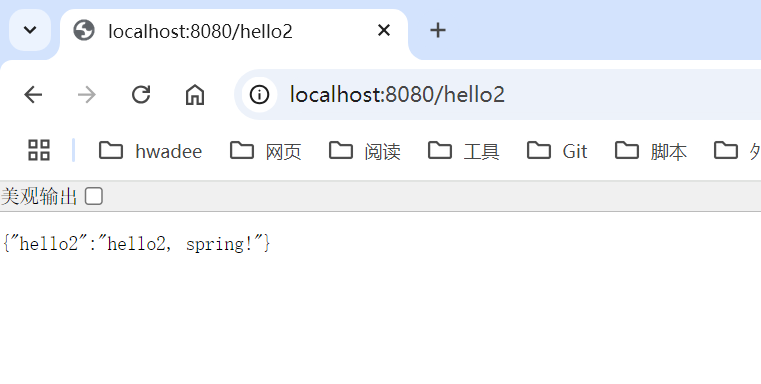
@RestController
static class MyController {
@GetMapping("hello2")
public Map<String,Object> hello() {
return Map.of("hello2", "hello2, spring!");
}
}
}
使用注册bean方式
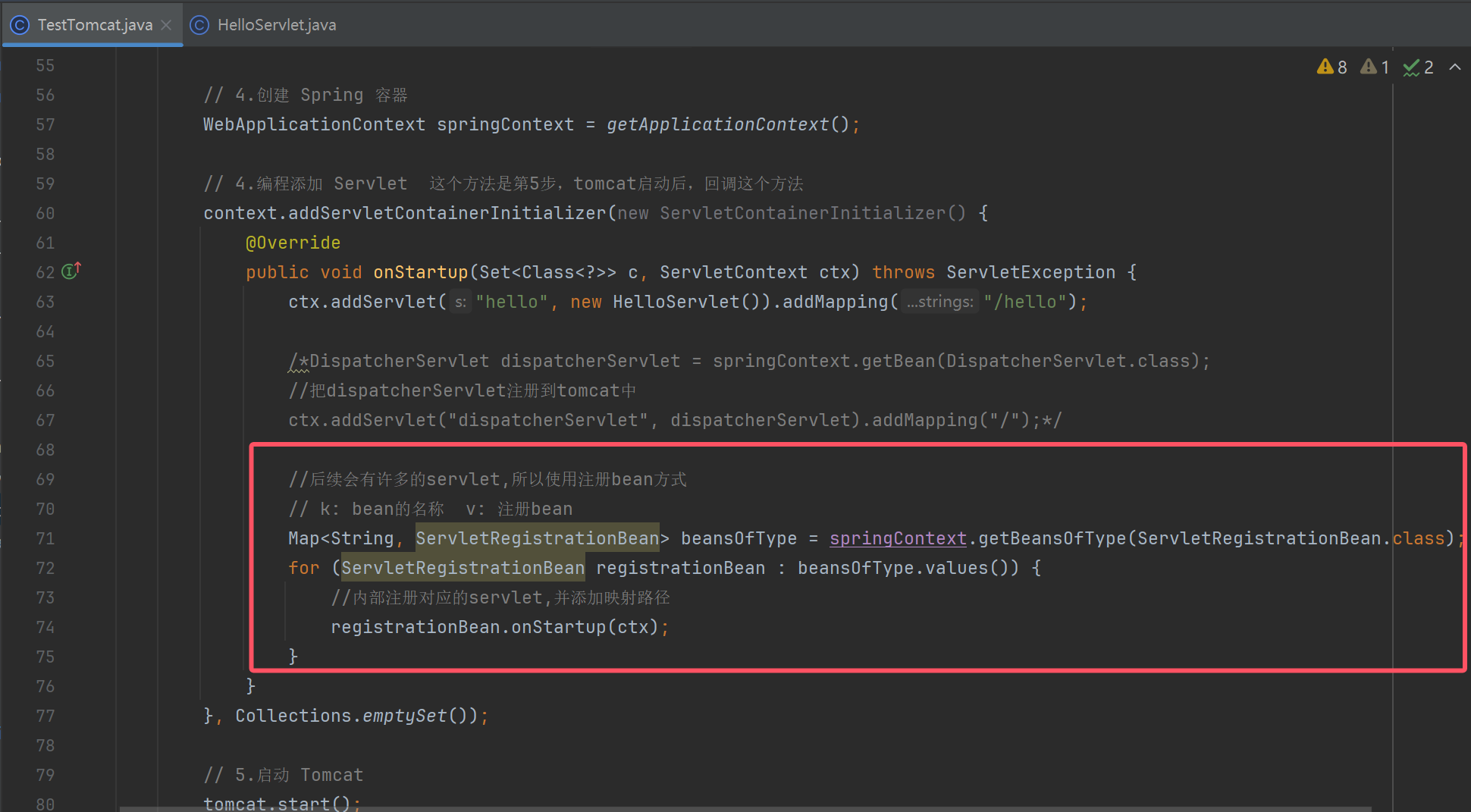
// 4.编程添加 Servlet 这个方法是第5步,tomcat启动后,回调这个方法
context.addServletContainerInitializer(new ServletContainerInitializer() {
@Override
public void onStartup(Set<Class<?>> c, ServletContext ctx) throws ServletException {
ctx.addServlet("hello", new HelloServlet()).addMapping("/hello");
/*DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet = springContext.getBean(DispatcherServlet.class);
//把dispatcherServlet注册到tomcat中
ctx.addServlet("dispatcherServlet", dispatcherServlet).addMapping("/");*/
//后续会有许多的servlet,所以使用注册bean方式
// k: bean的名称 v: 注册bean
Map<String, ServletRegistrationBean> beansOfType = springContext.getBeansOfType(ServletRegistrationBean.class);
for (ServletRegistrationBean registrationBean : beansOfType.values()) {
//内部注册对应的servlet,并添加映射路径
registrationBean.onStartup(ctx);
}
}
}, Collections.emptySet());
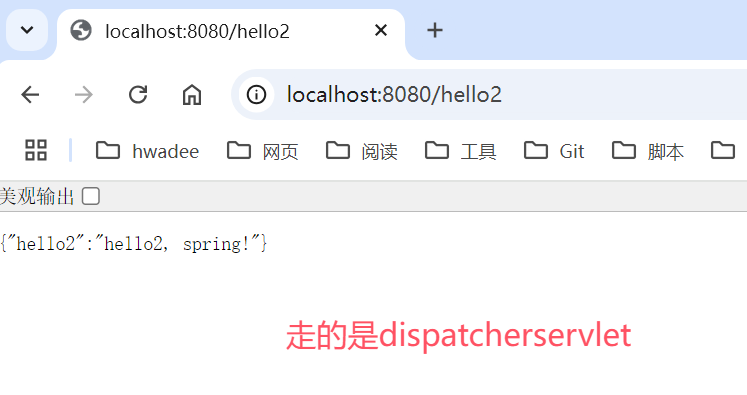
1.5 Boot 自动配置
自动配置原理
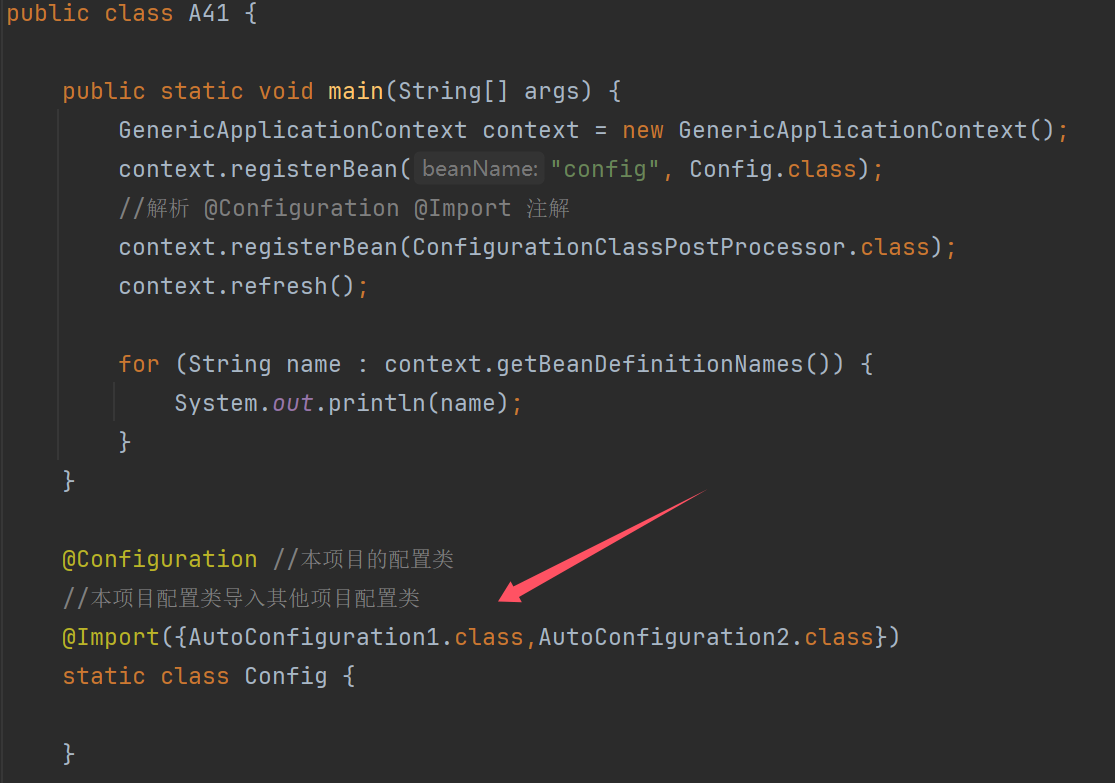
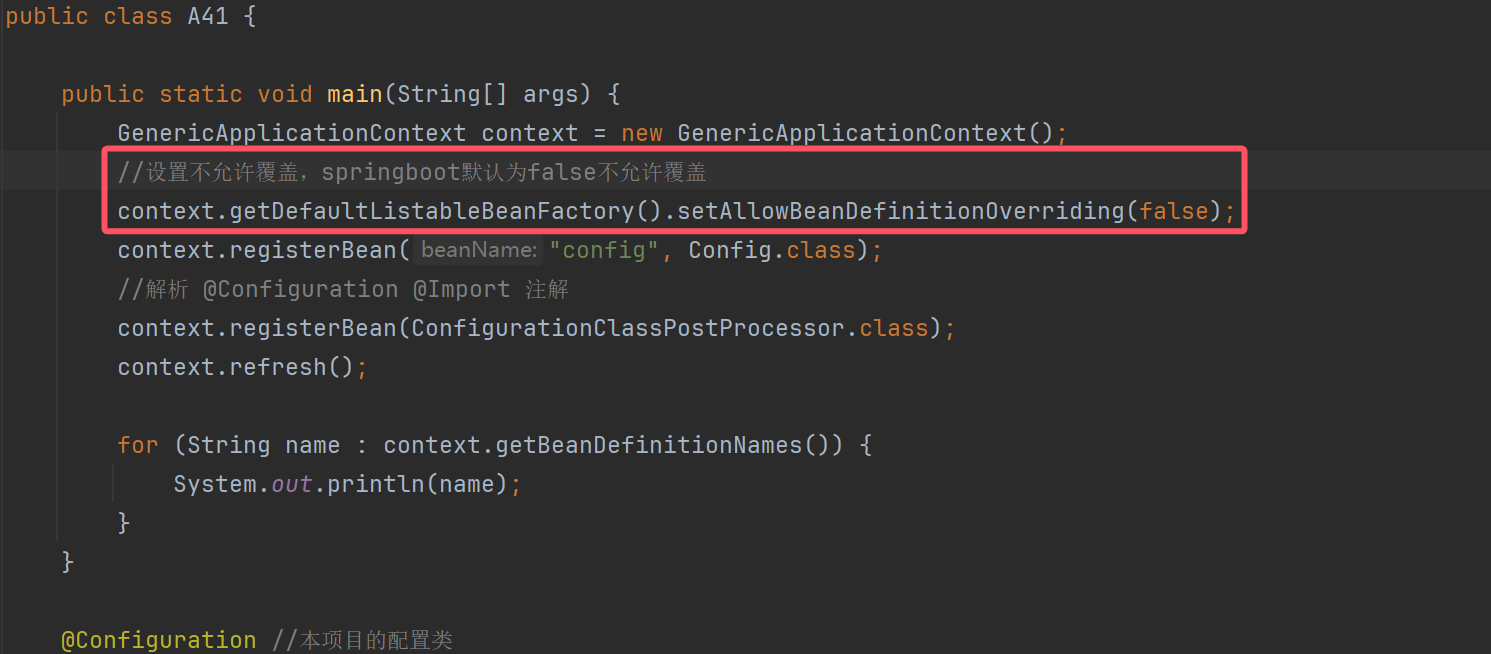
public class A41 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GenericApplicationContext context = new GenericApplicationContext();
context.registerBean("config", Config.class);
//解析 @Configuration @Import 注解
context.registerBean(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class);
context.refresh();
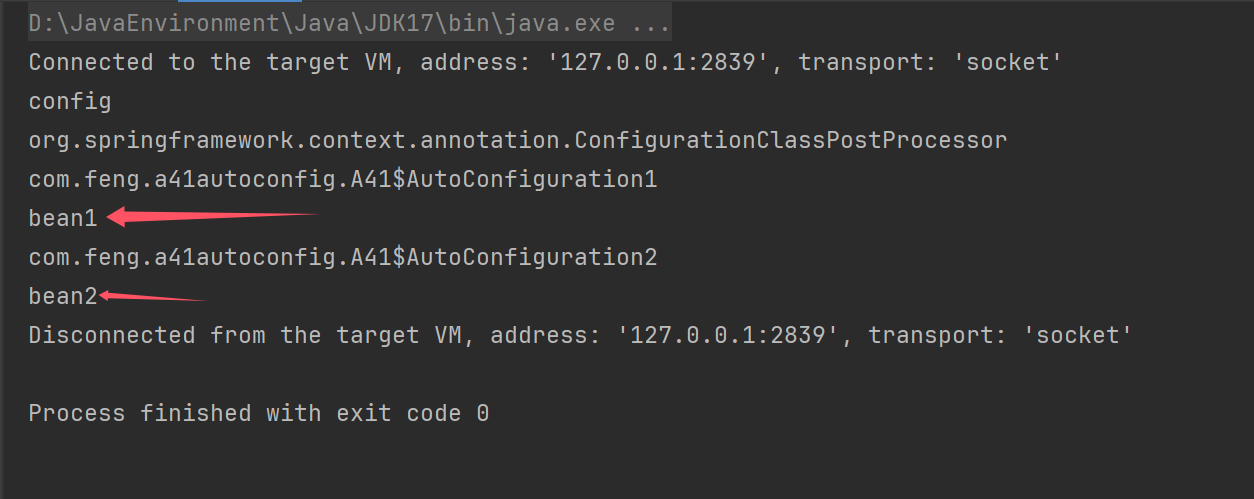
for (String name : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
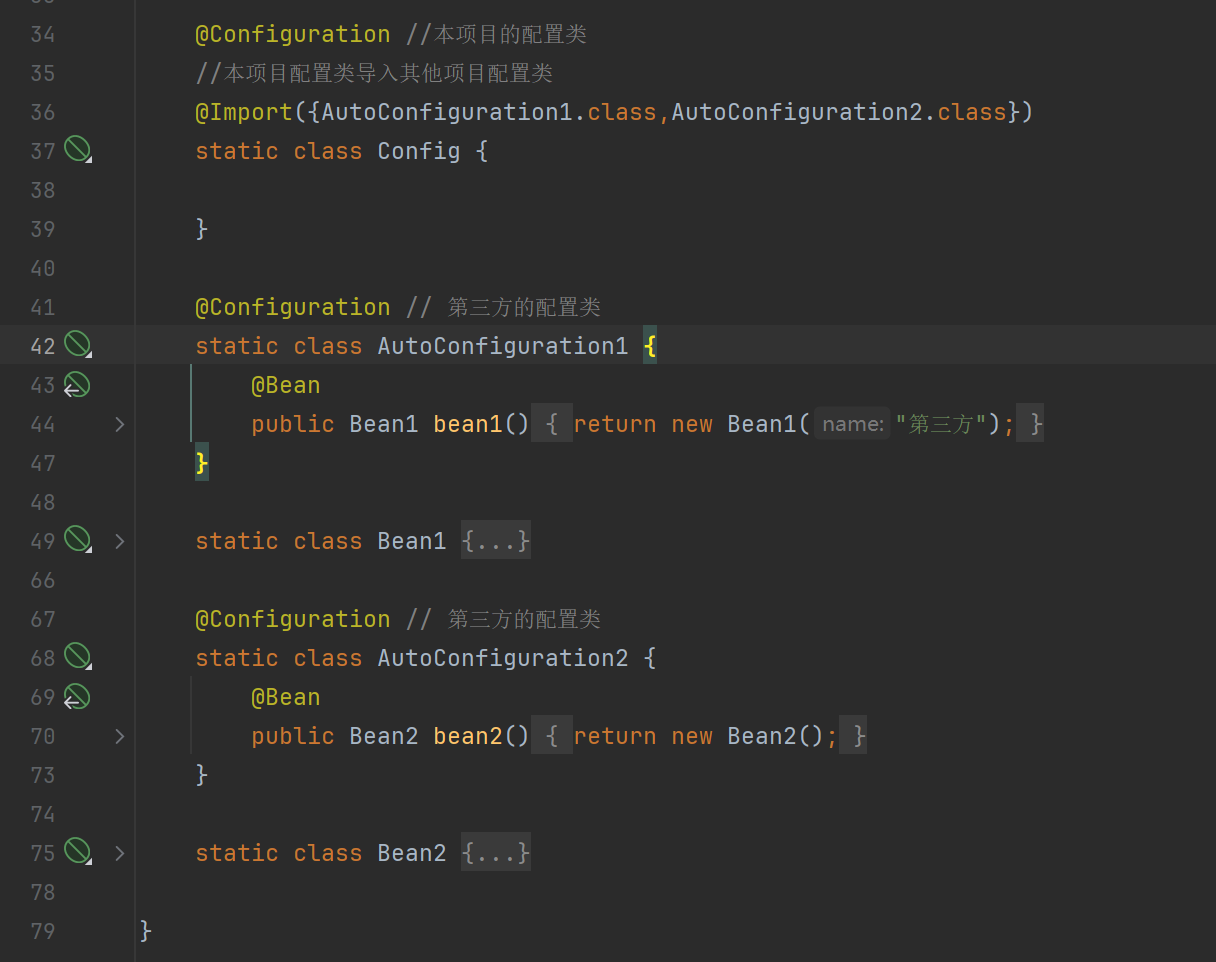
@Configuration //本项目的配置类
//本项目配置类导入其他项目配置类
@Import({AutoConfiguration1.class,AutoConfiguration2.class})
static class Config {
}
@Configuration // 第三方的配置类
static class AutoConfiguration1 {
@Bean
public Bean1 bean1() {
return new Bean1("第三方");
}
}
static class Bean1 {
private String name;
public Bean1() {
}
public Bean1(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Bean1{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
@Configuration // 第三方的配置类
static class AutoConfiguration2 {
@Bean
public Bean2 bean2() {
return new Bean2();
}
}
static class Bean2 {
}
}
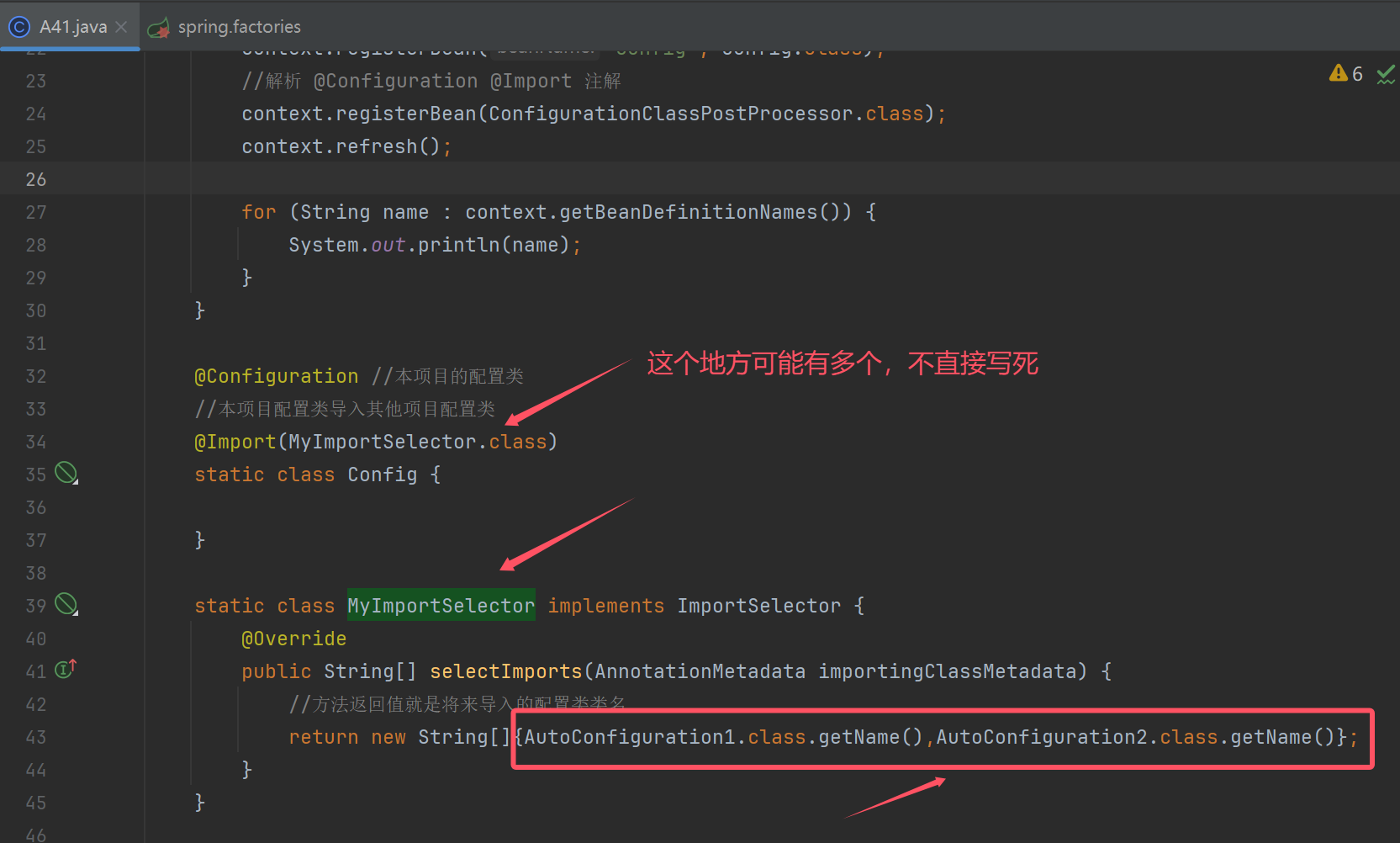
结果
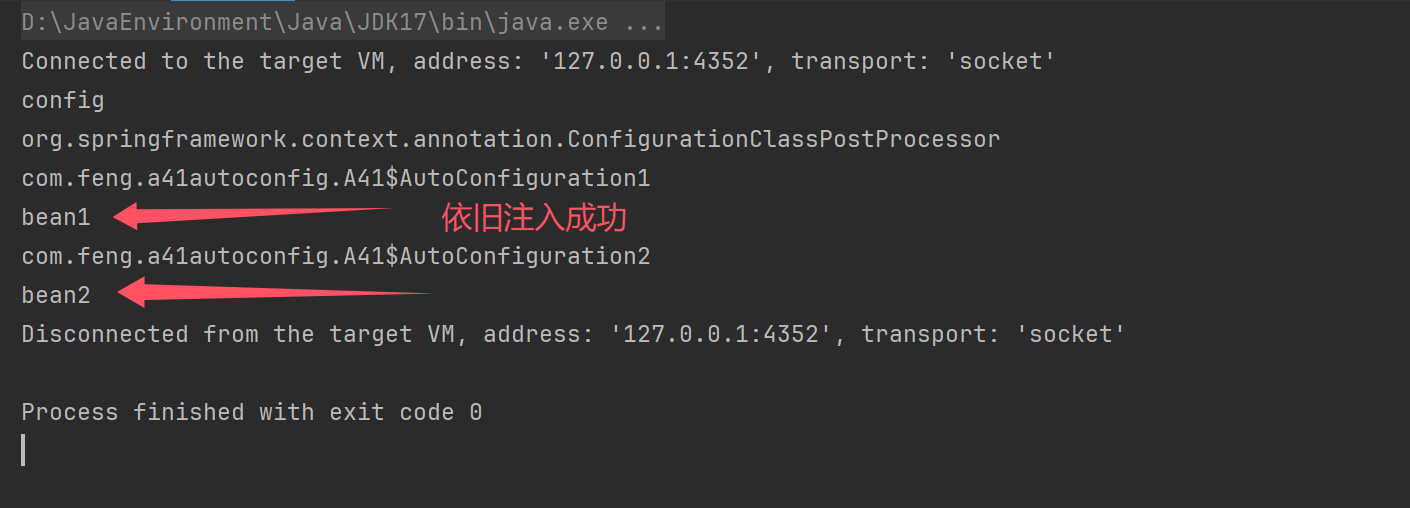
\ 代表换行,方便查看
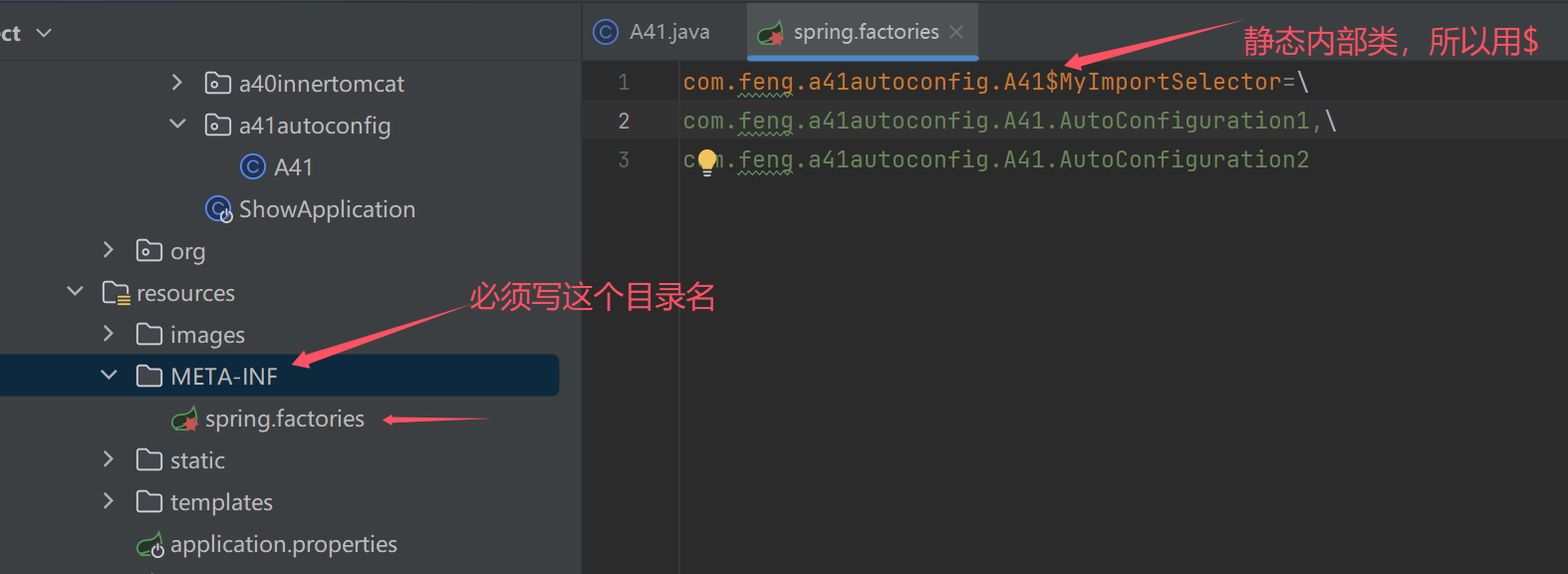
除了会读当前的项目中的spring.factories,也会读取其他依赖的spring.factories
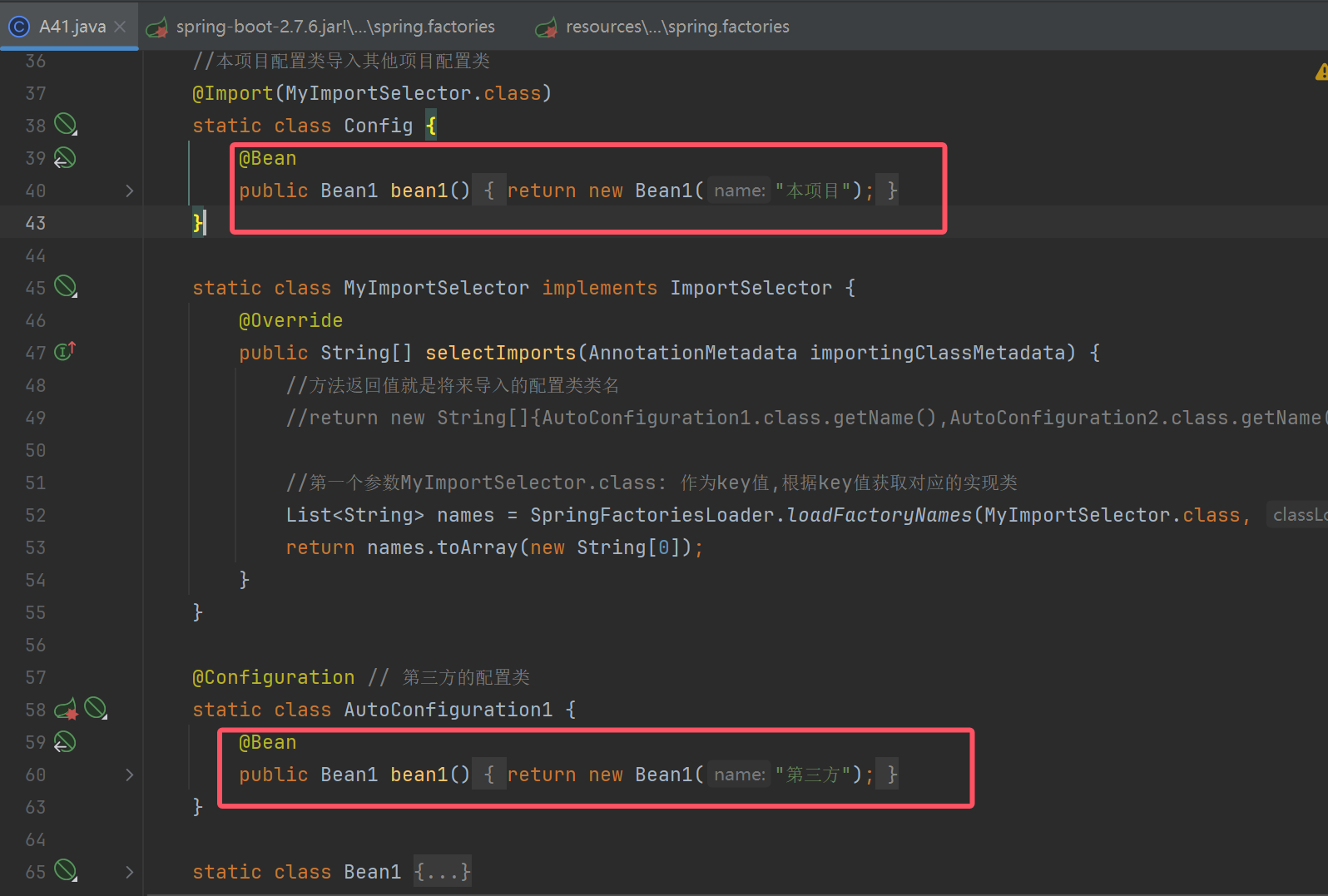
@Configuration //本项目的配置类
//本项目配置类导入其他项目配置类
@Import(MyImportSelector.class)
static class Config {
}
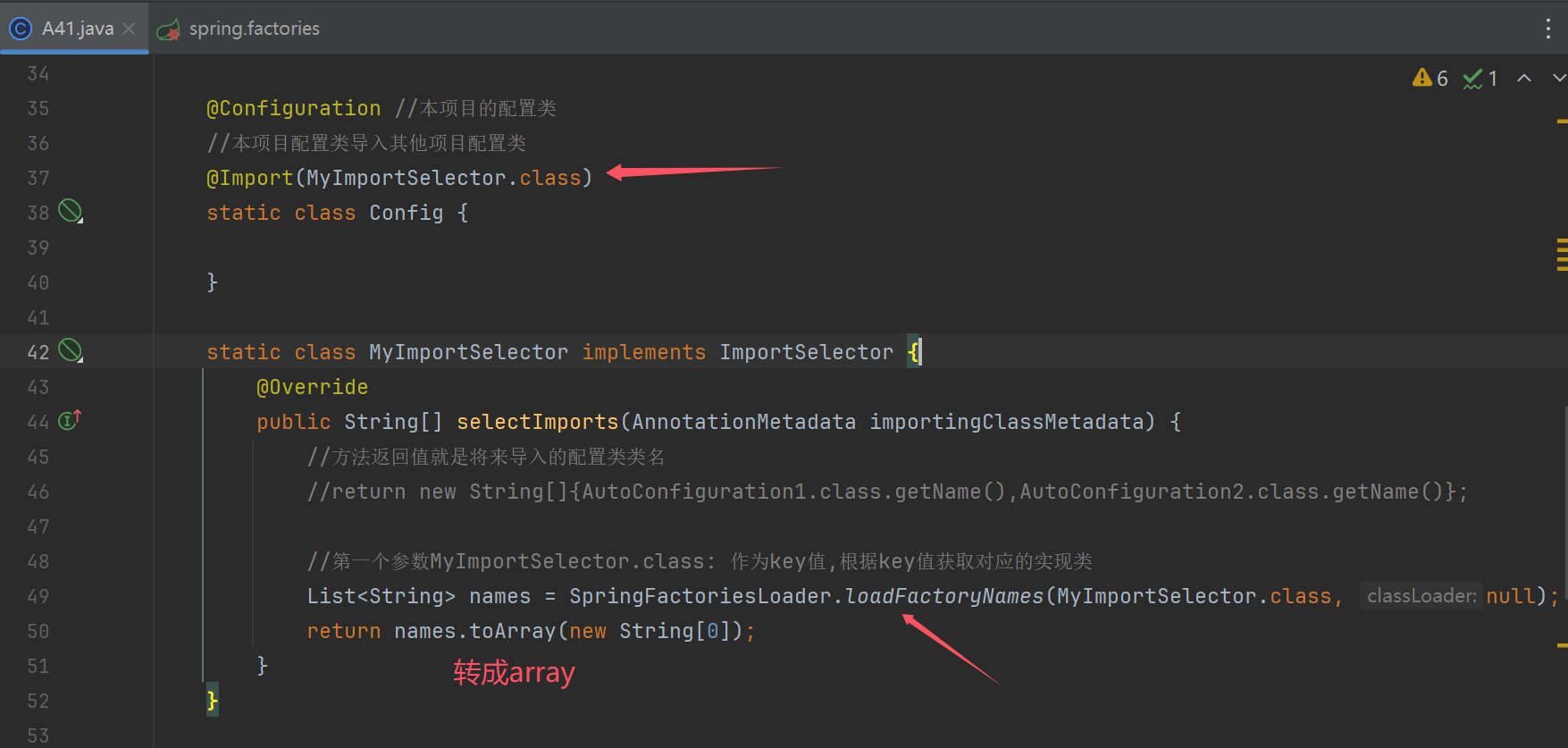
static class MyImportSelector implements ImportSelector {
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) {
//方法返回值就是将来导入的配置类类名
//return new String[]{AutoConfiguration1.class.getName(),AutoConfiguration2.class.getName()};
//第一个参数MyImportSelector.class: 作为key值,根据key值获取对应的实现类
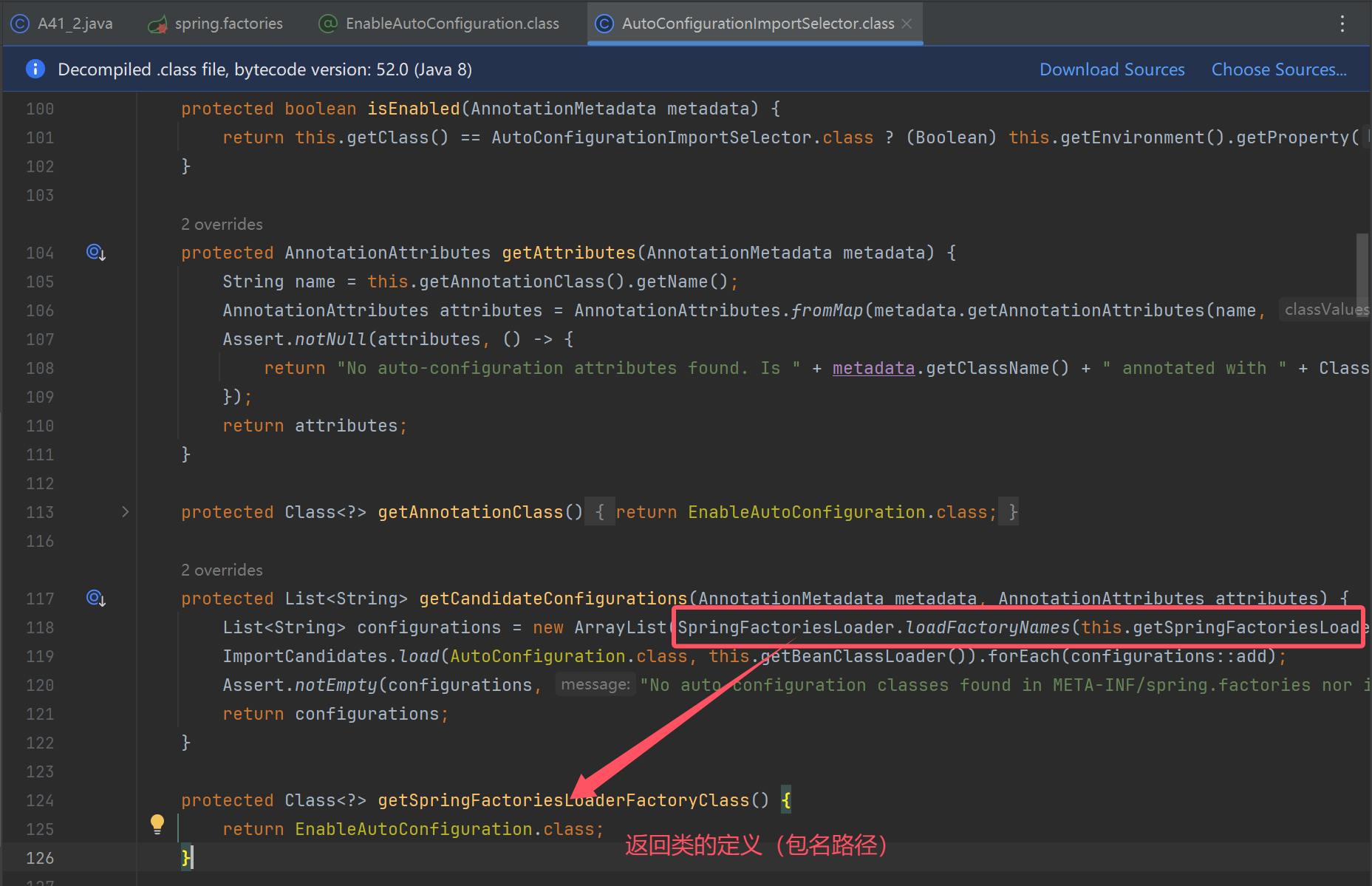
List<String> names = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(MyImportSelector.class, null);
return names.toArray(new String[0]);
}
}
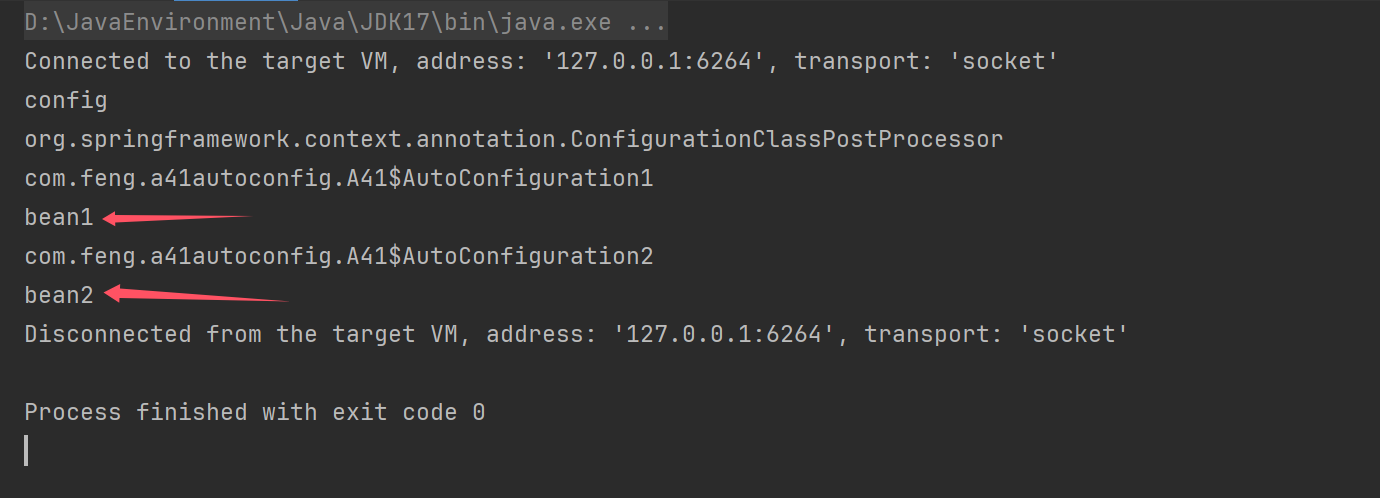
如果本项目中的bean定义和第三方中的bean定义冲突,本项目的bean生效(但是第三方的优先级高,先加载)
原因
1、解析时机不同
先通过@Import解析第三方的配置类,然后在解析Config中的配置类
2、覆盖
bean工厂默认后注册的bean会覆盖之前的bean
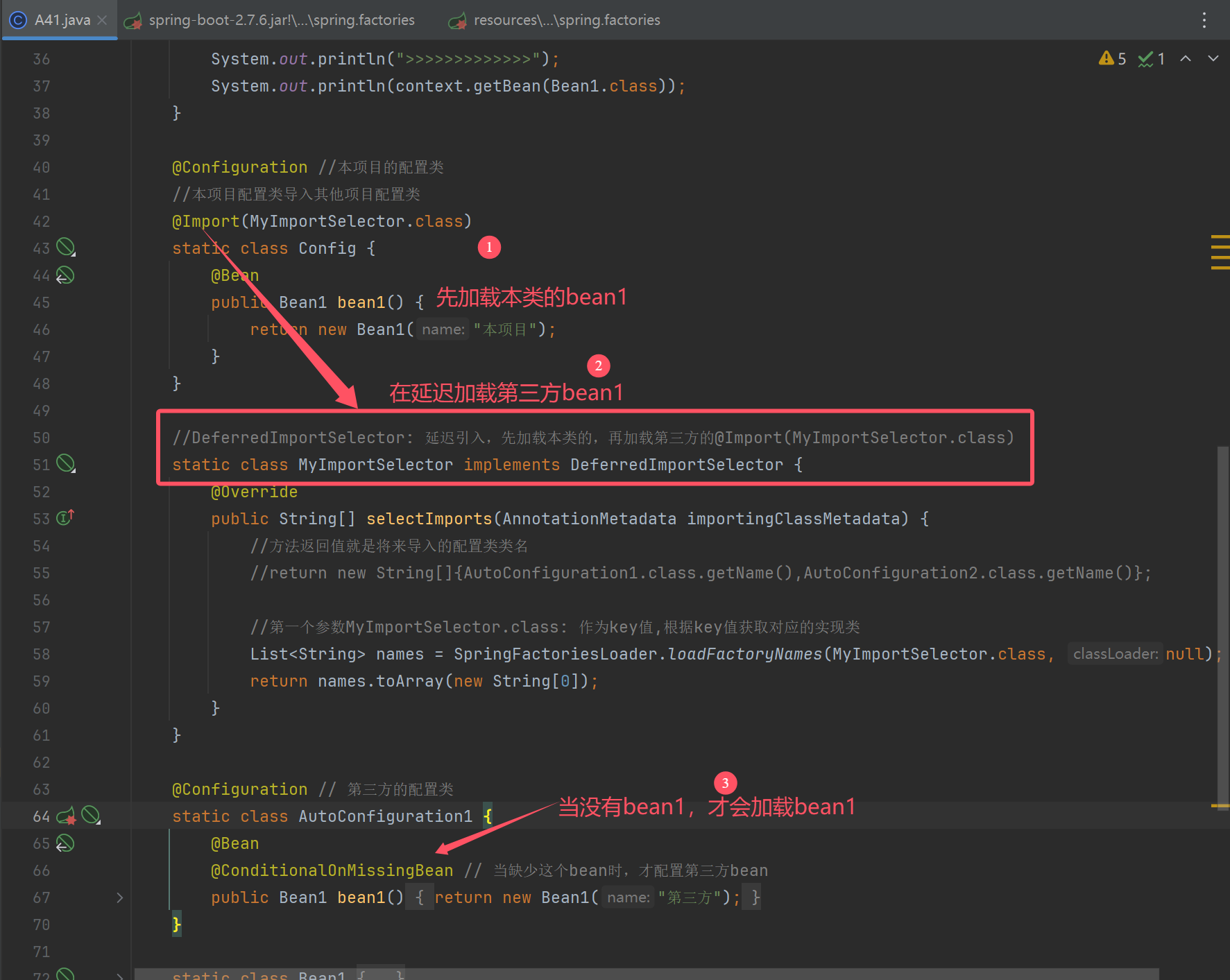
修改加载时机,优先加载本类
AopAutoConfiguration
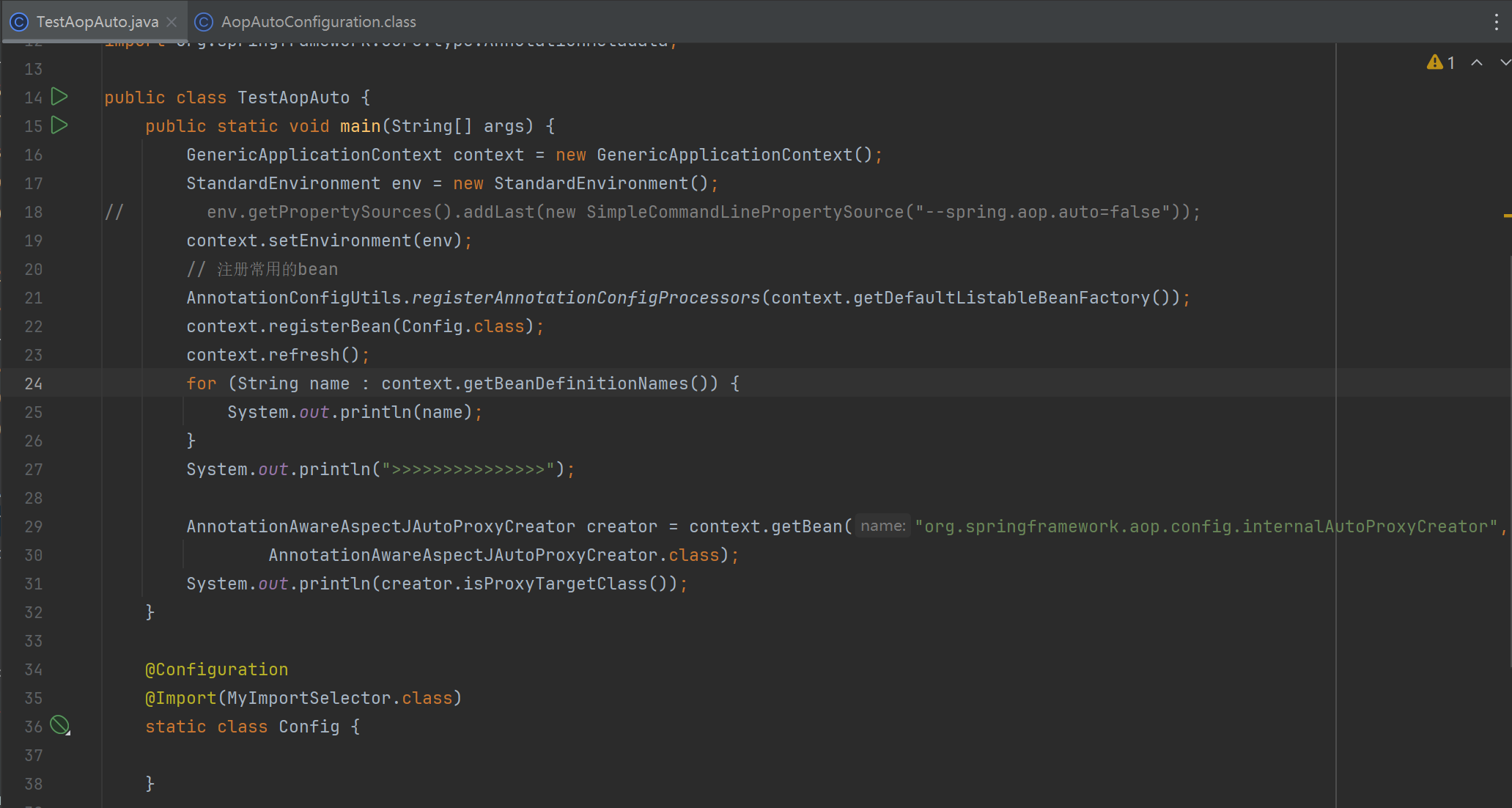
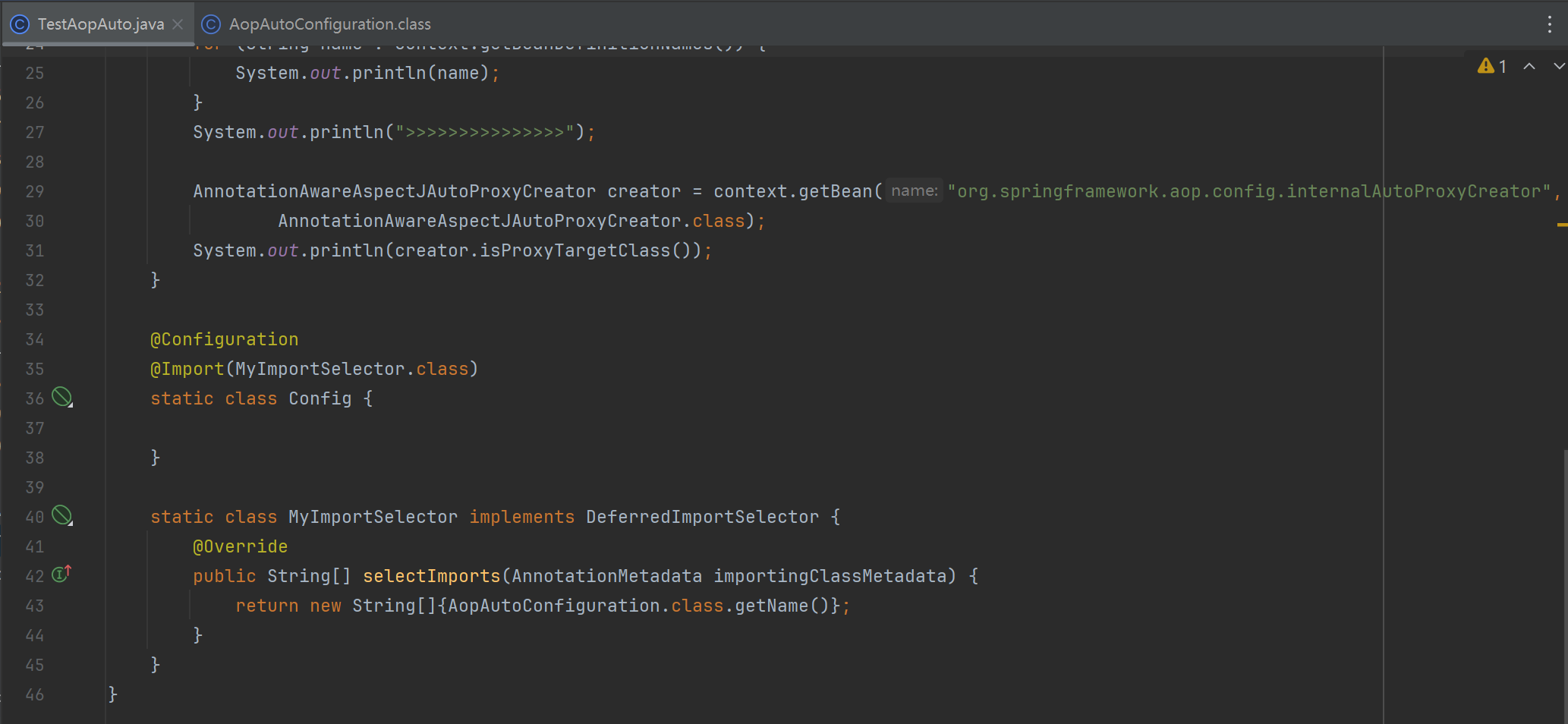
TestAopAuto
public class TestAopAuto {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GenericApplicationContext context = new GenericApplicationContext();
StandardEnvironment env = new StandardEnvironment();
// env.getPropertySources().addLast(new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource("--spring.aop.auto=false"));
context.setEnvironment(env);
// 注册常用的bean
AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(context.getDefaultListableBeanFactory());
context.registerBean(Config.class);
context.refresh();
for (String name : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println(name);
}
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>");
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator creator = context.getBean("org.springframework.aop.config.internalAutoProxyCreator",
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.class);
System.out.println(creator.isProxyTargetClass());
}
@Configuration
@Import(MyImportSelector.class)
static class Config {
}
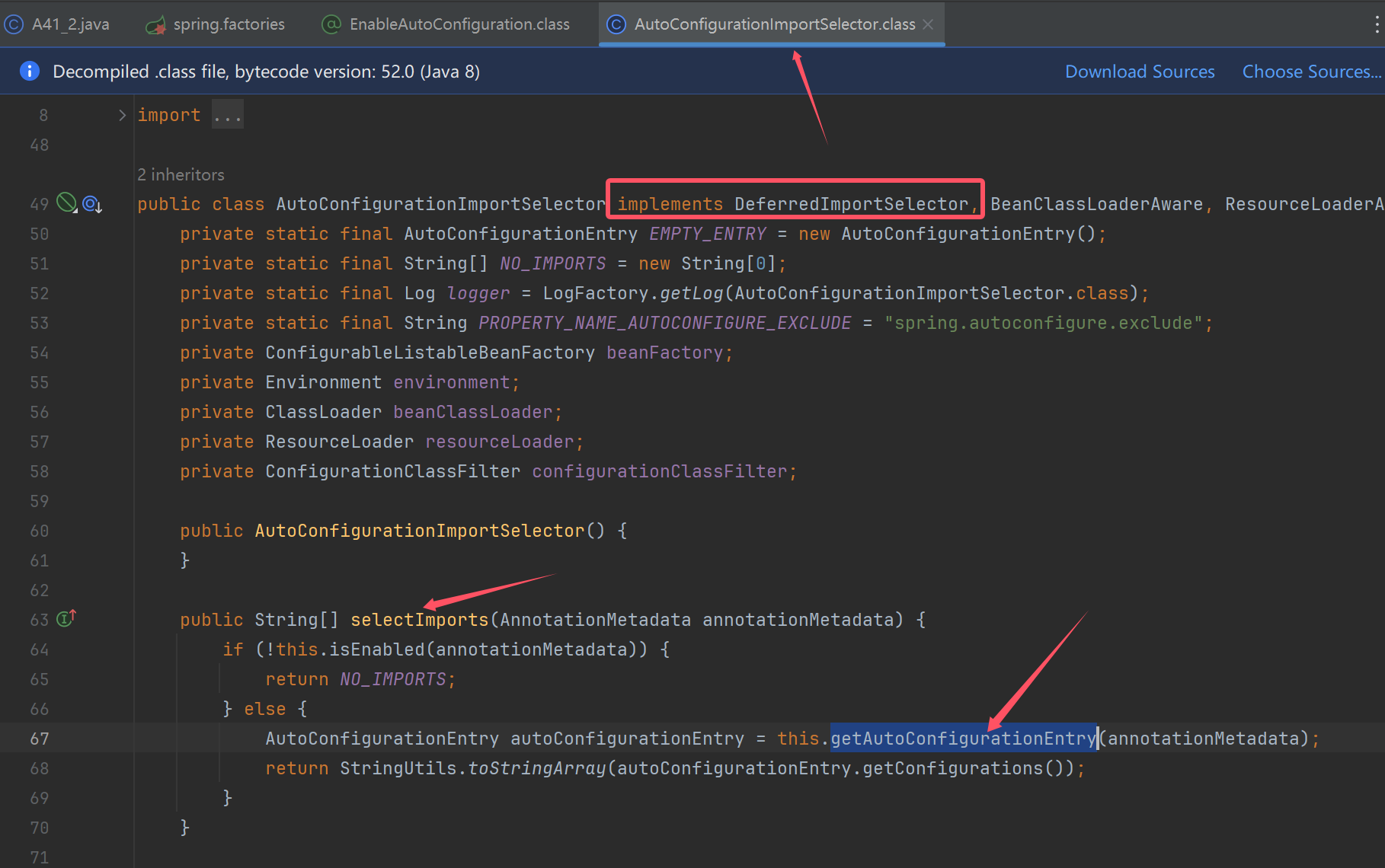
static class MyImportSelector implements DeferredImportSelector {
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) {
return new String[]{AopAutoConfiguration.class.getName()};
}
}
}
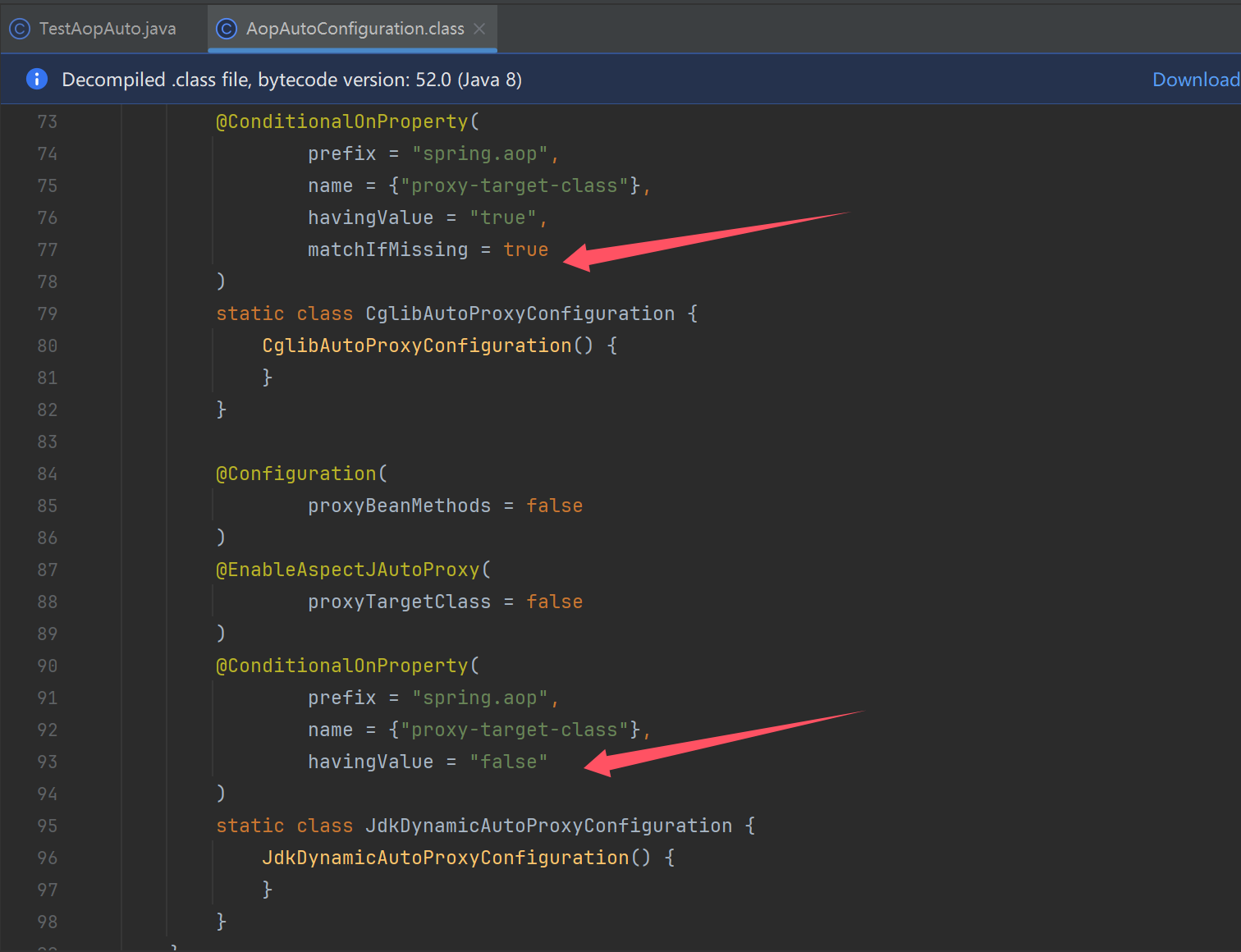
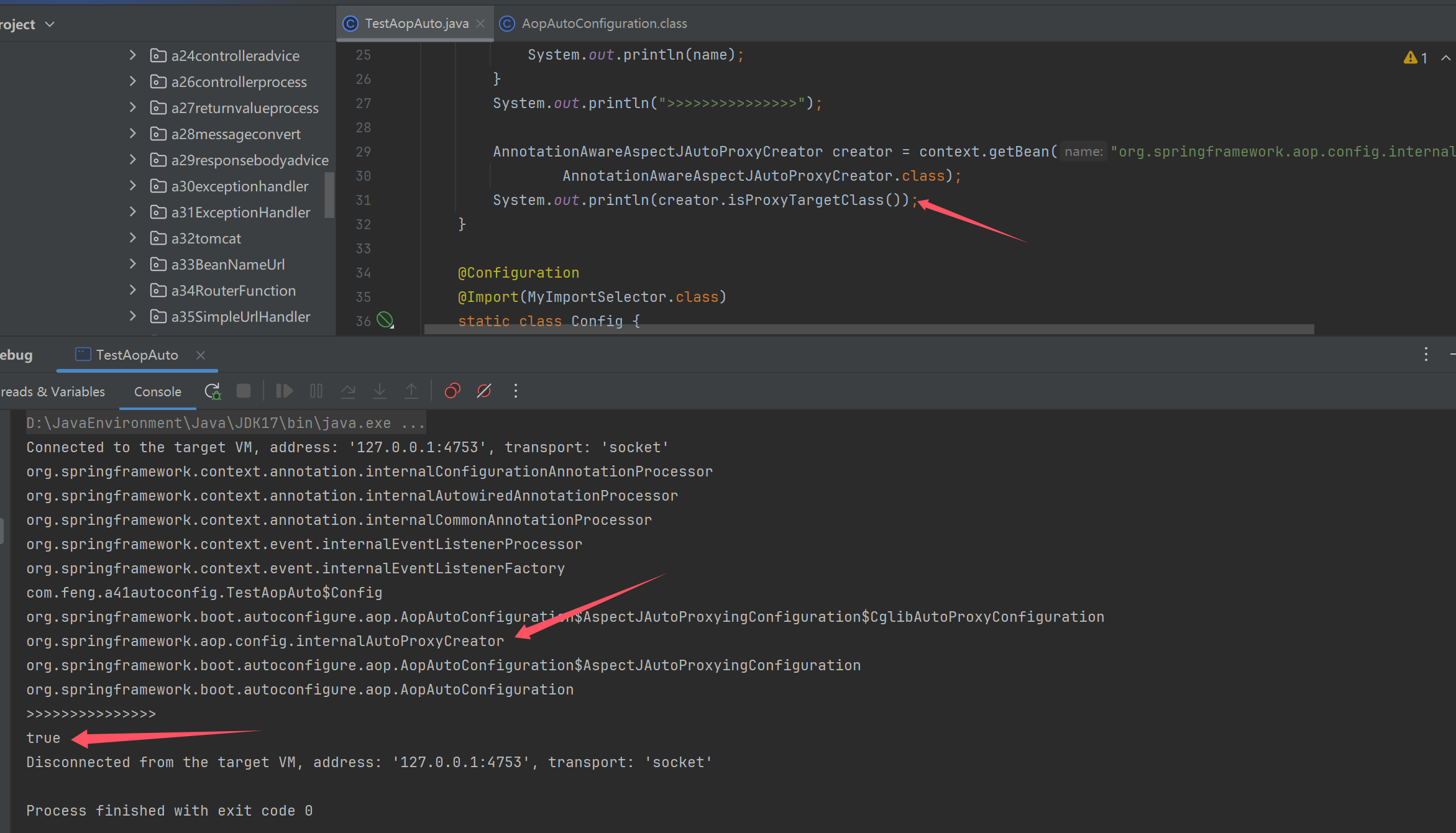
收获
Spring Boot 是利用了自动配置类来简化了 aop 相关配置
- AOP 自动配置类为
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration - 可以通过
spring.aop.auto=false禁用 aop 自动配置 - AOP 自动配置的本质是通过
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy来开启了自动代理,如果在引导类上自己添加了@EnableAspectJAutoProxy那么以自己添加的为准 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy的本质是向容器中添加了AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator这个 bean 后处理器,它能够找到容器中所有切面,并为匹配切点的目标类创建代理,创建代理的工作一般是在 bean 的初始化阶段完成的
DataSourceAutoConfiguration
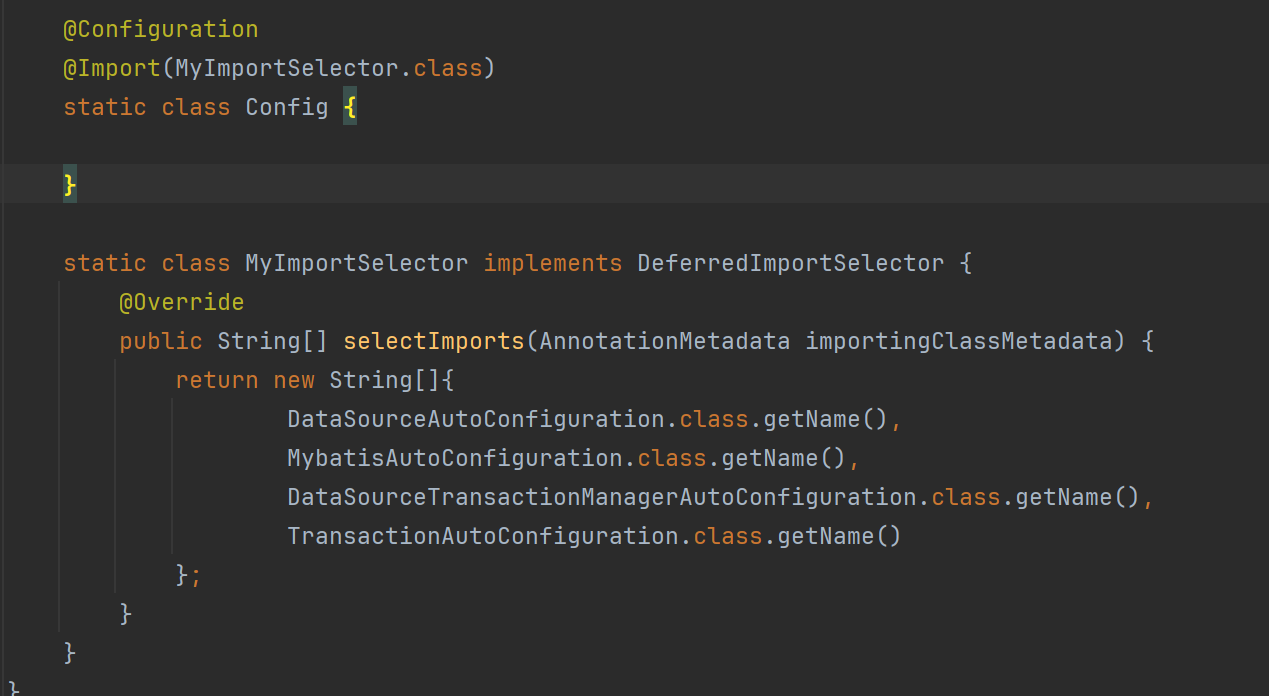
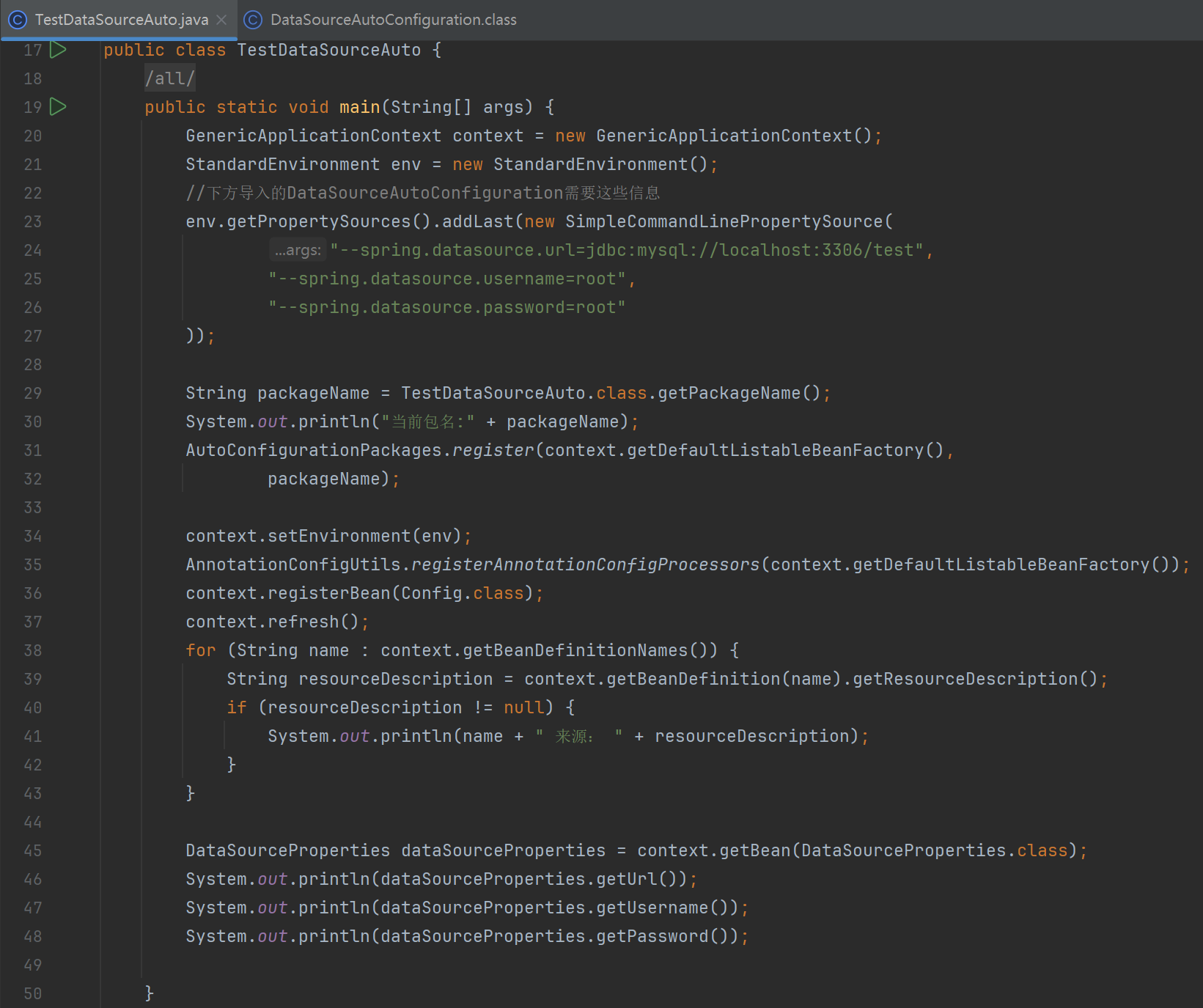
public class TestDataSourceAuto {
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public static void main(String[] args) {
GenericApplicationContext context = new GenericApplicationContext();
StandardEnvironment env = new StandardEnvironment();
//下方导入的DataSourceAutoConfiguration需要这些信息
env.getPropertySources().addLast(new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource(
"--spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test",
"--spring.datasource.username=root",
"--spring.datasource.password=root"
));
String packageName = TestDataSourceAuto.class.getPackageName();
System.out.println("当前包名:" + packageName);
AutoConfigurationPackages.register(context.getDefaultListableBeanFactory(),
packageName);
context.setEnvironment(env);
AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(context.getDefaultListableBeanFactory());
context.registerBean(Config.class);
context.refresh();
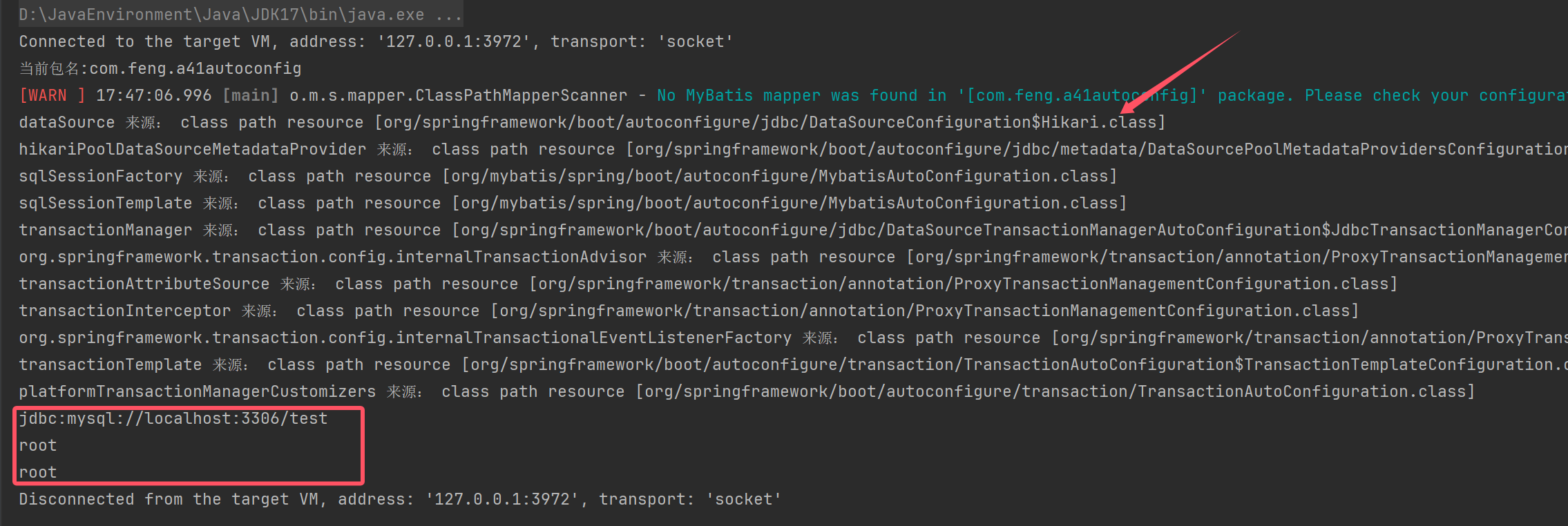
for (String name : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
String resourceDescription = context.getBeanDefinition(name).getResourceDescription();
if (resourceDescription != null) {
System.out.println(name + " 来源: " + resourceDescription);
}
}
DataSourceProperties dataSourceProperties = context.getBean(DataSourceProperties.class);
System.out.println(dataSourceProperties.getUrl());
System.out.println(dataSourceProperties.getUsername());
System.out.println(dataSourceProperties.getPassword());
}
@Configuration
@Import(MyImportSelector.class)
static class Config {
}
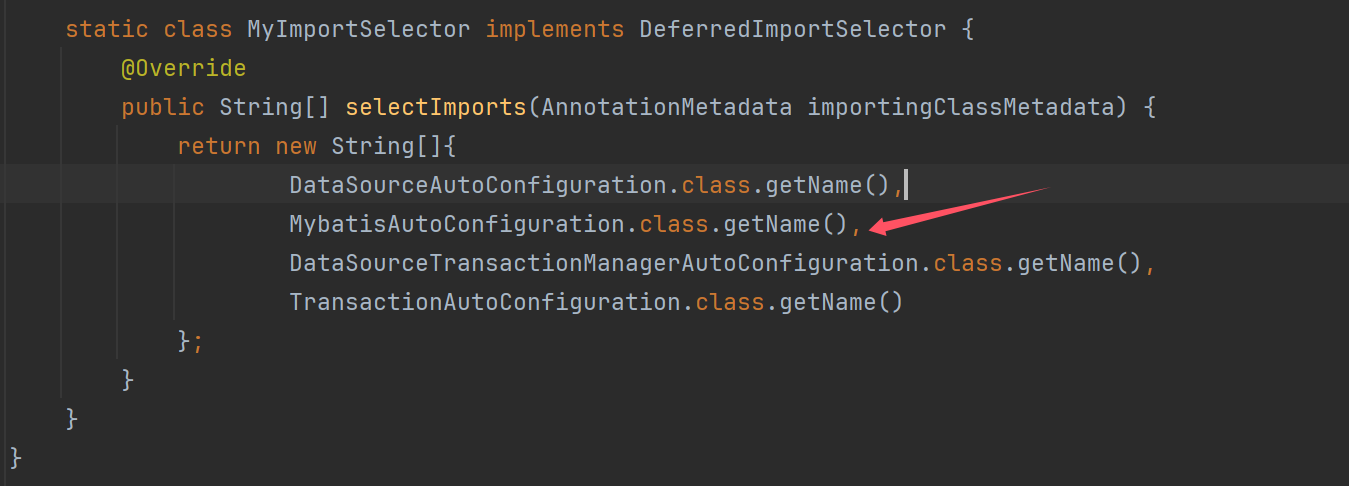
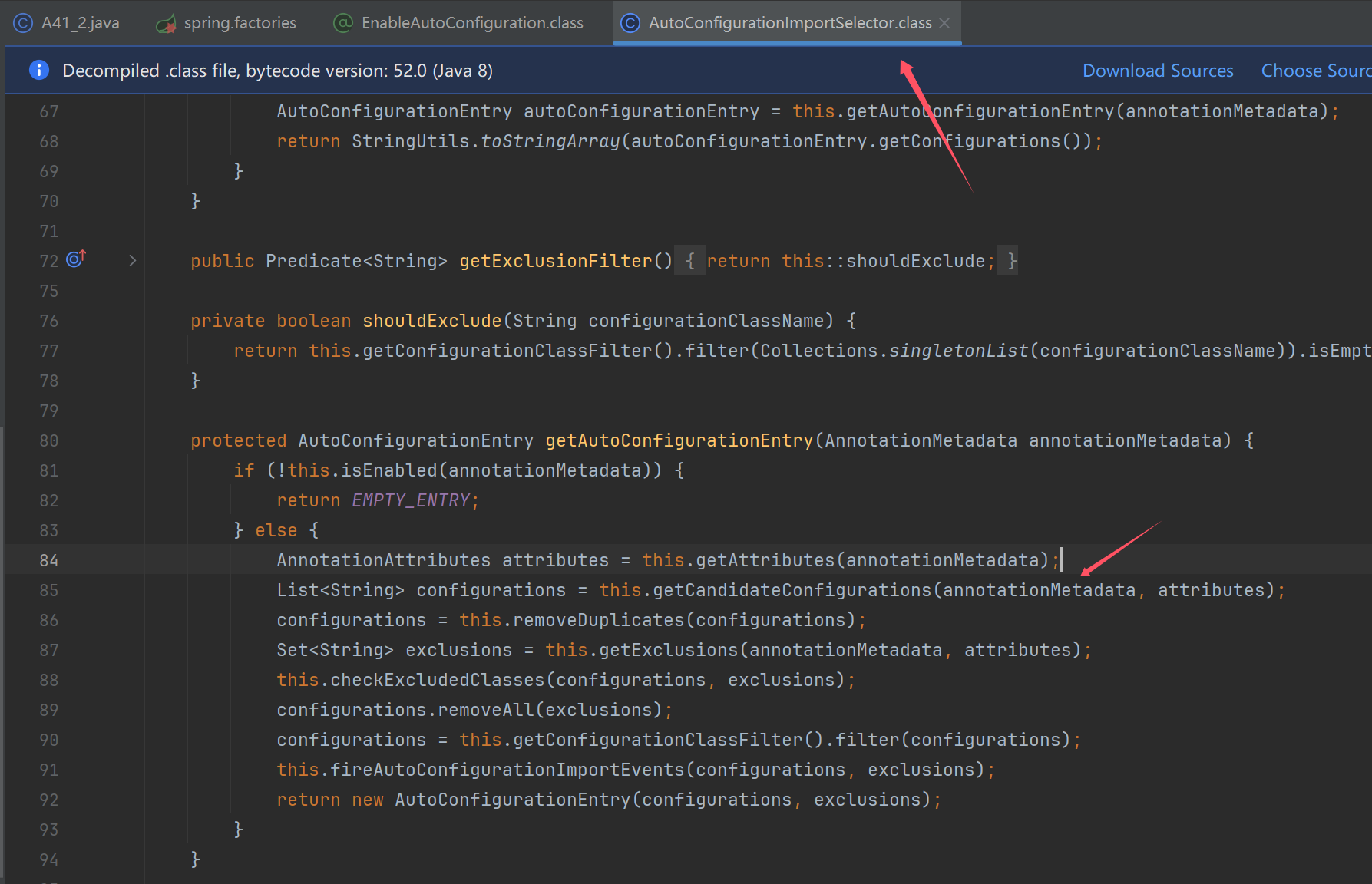
static class MyImportSelector implements DeferredImportSelector {
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) {
return new String[]{
DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class.getName(),
MybatisAutoConfiguration.class.getName(),
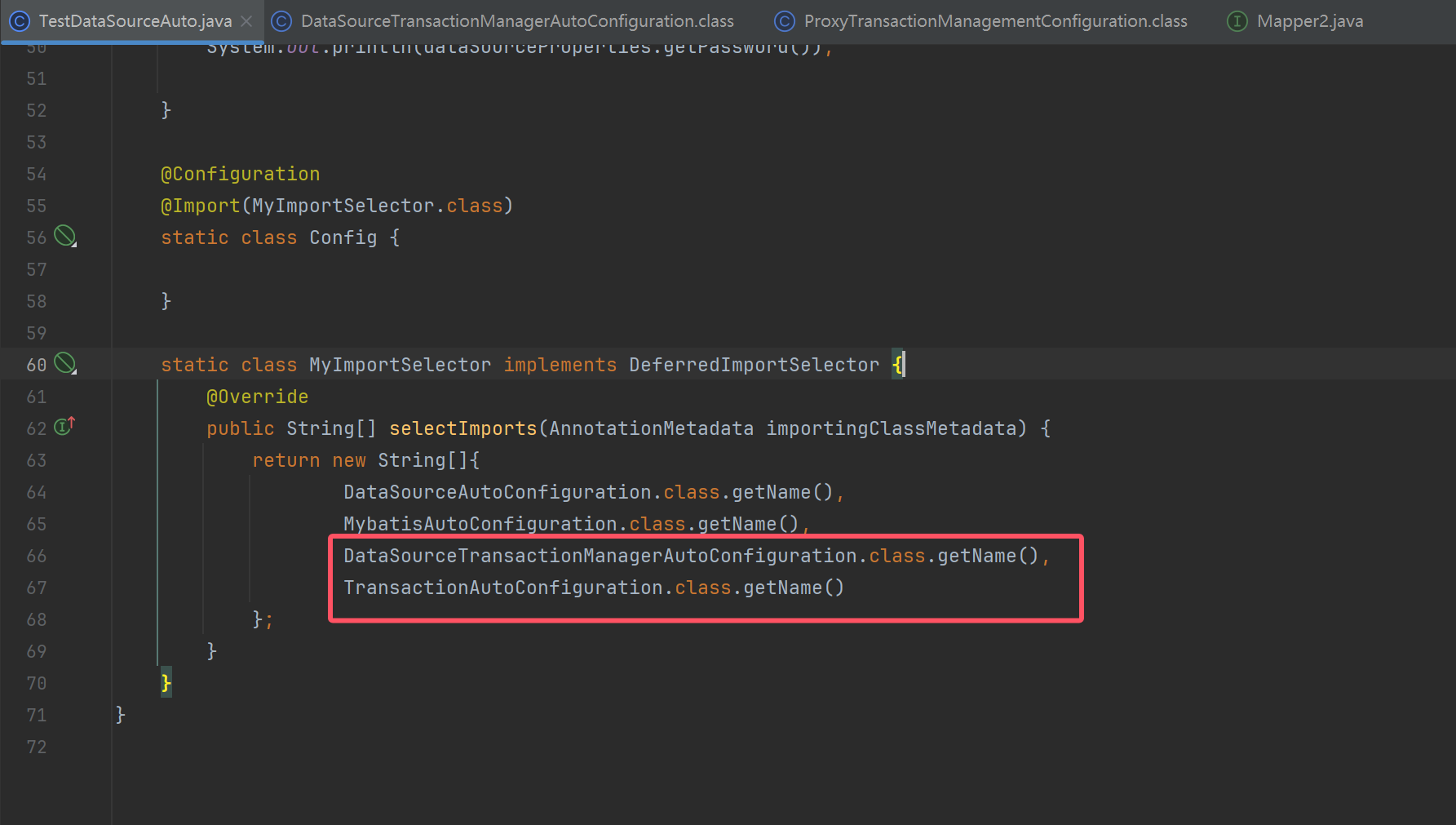
DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration.class.getName(),
TransactionAutoConfiguration.class.getName()
};
}
}
}
收获
- 对应的自动配置类为:org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration
- 它内部采用了条件装配,通过检查容器的 bean,以及类路径下的 class,来决定该 @Bean 是否生效
简单说明一下,Spring Boot 支持两大类数据源:
- EmbeddedDatabase - 内嵌数据库连接池
- PooledDataSource - 非内嵌数据库连接池
PooledDataSource 又支持如下数据源
- hikari 提供的 HikariDataSource
- tomcat-jdbc 提供的 DataSource
- dbcp2 提供的 BasicDataSource
- oracle 提供的 PoolDataSourceImpl
如果知道数据源的实现类类型,即指定了 spring.datasource.type,理论上可以支持所有数据源,但这样做的一个最大问题是无法订制每种数据源的详细配置(如最大、最小连接数等)
MybatisAutoConfiguration
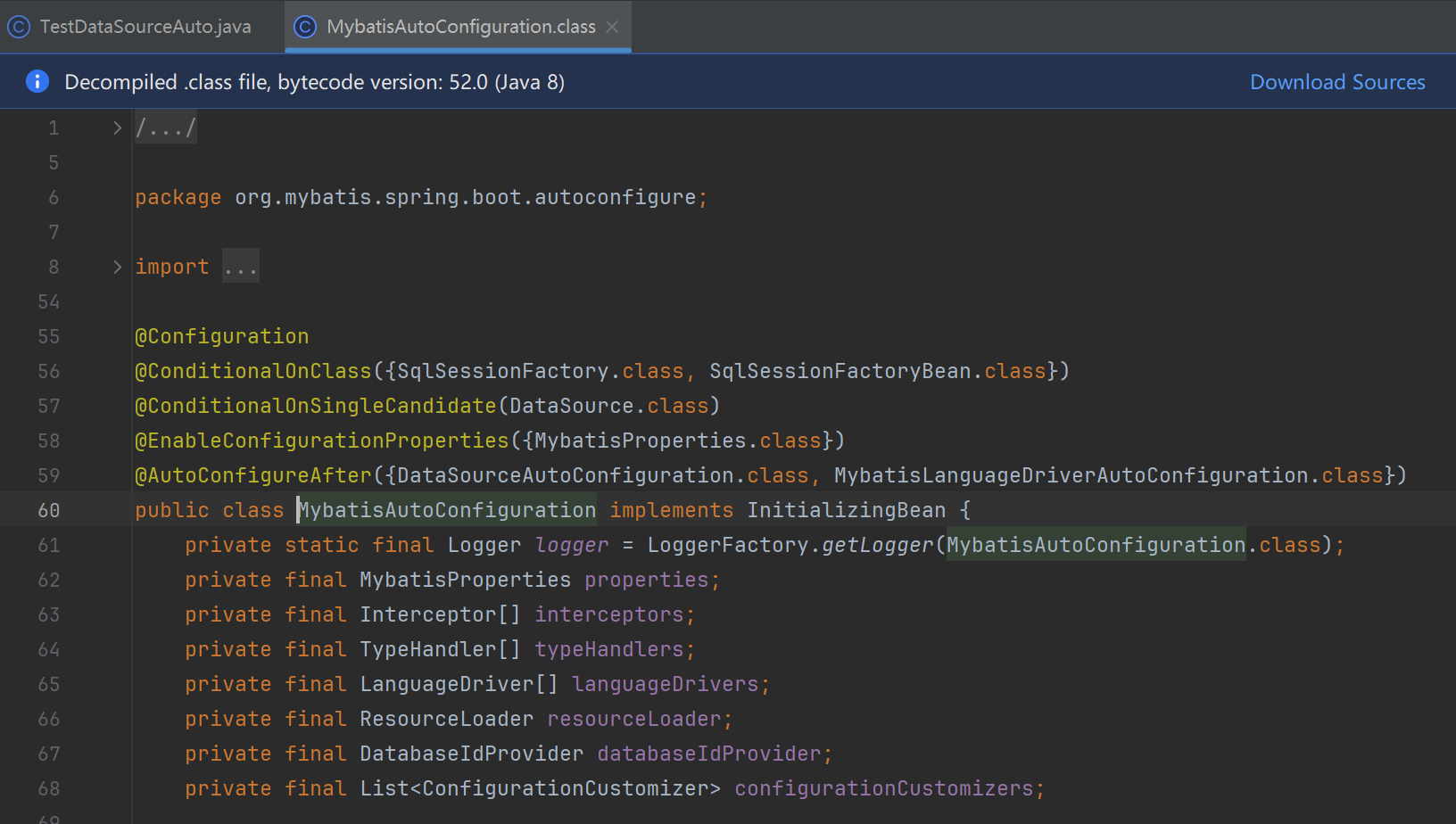
@Configuration
//后面的这些类型,必须在类路径下能够找到(和mybatis整合了,mybatis的jar下有)
@ConditionalOnClass({SqlSessionFactory.class, SqlSessionFactoryBean.class})
//容器中有且仅有一个DataSource时,条件成立(单一候选者)
@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate(DataSource.class)
//将来创建一个MybatisProperties属性对象,用于环境中的键值对象绑定(见下图)
@EnableConfigurationProperties({MybatisProperties.class})
//控制多个配置类的解析顺序的
@AutoConfigureAfter({DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class, MybatisLanguageDriverAutoConfiguration.class})
public class MybatisAutoConfiguration implements InitializingBean {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MybatisAutoConfiguration.class);
private final MybatisProperties properties;
private final Interceptor[] interceptors;
private final TypeHandler[] typeHandlers;
private final LanguageDriver[] languageDrivers;
private final ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
private final DatabaseIdProvider databaseIdProvider;
private final List<ConfigurationCustomizer> configurationCustomizers;
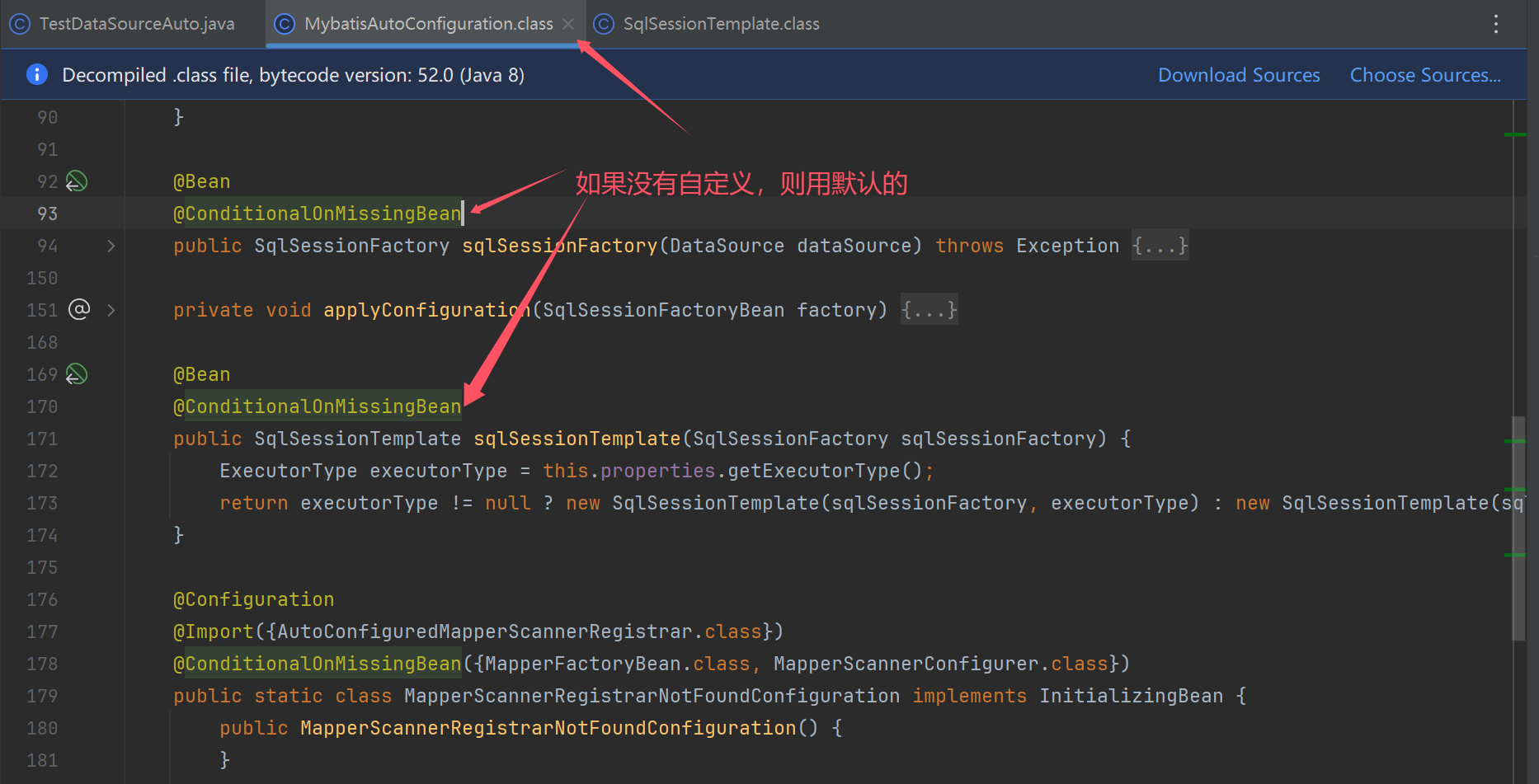
sqlSessionTemplate使用位置(spring和mybatis整合时,需要用到它)
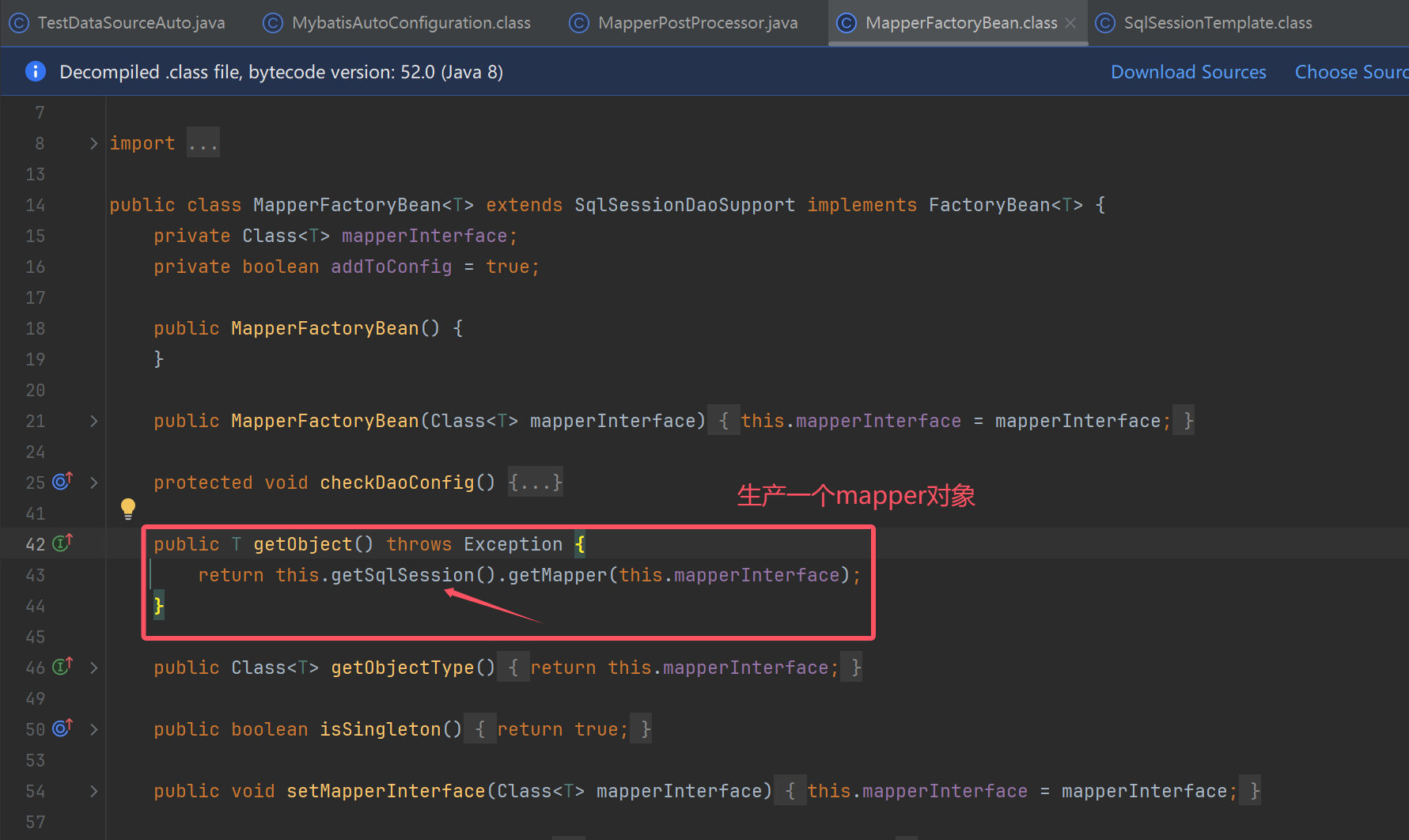
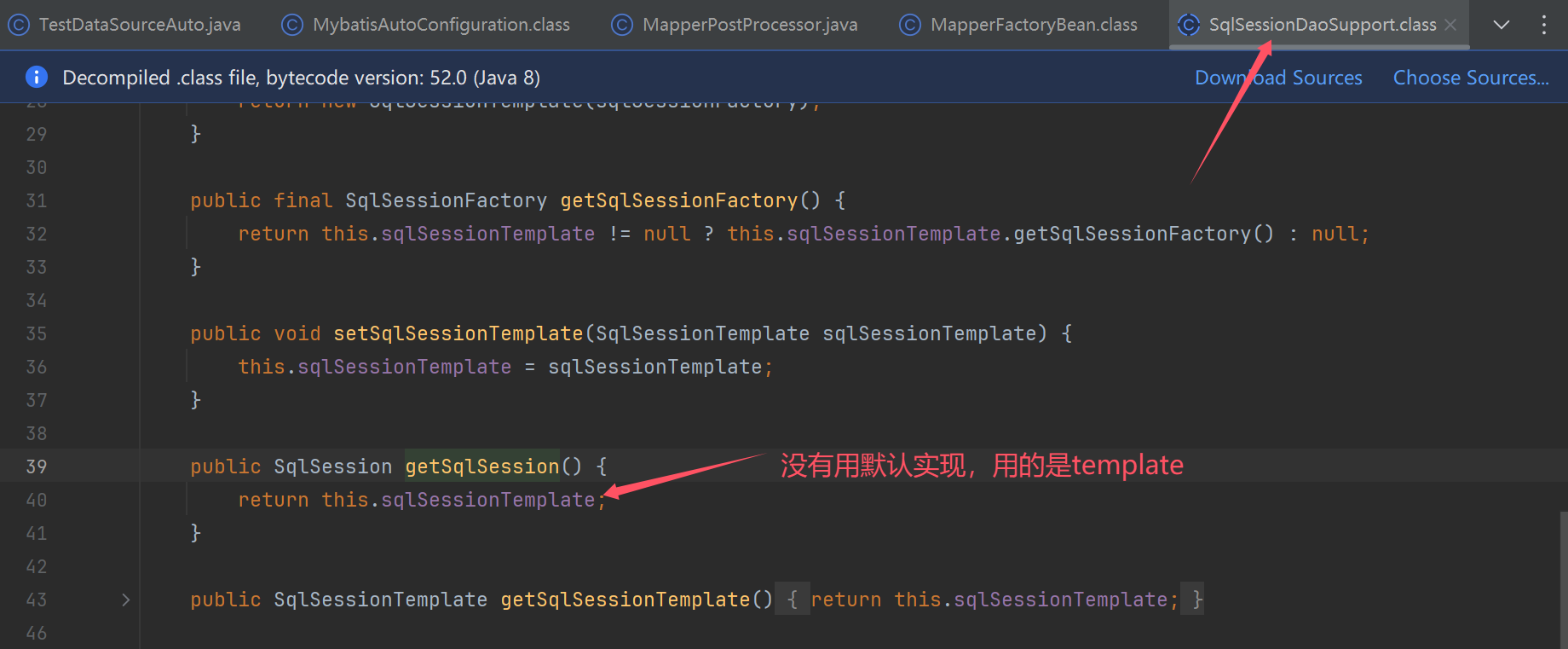
mapper扫描
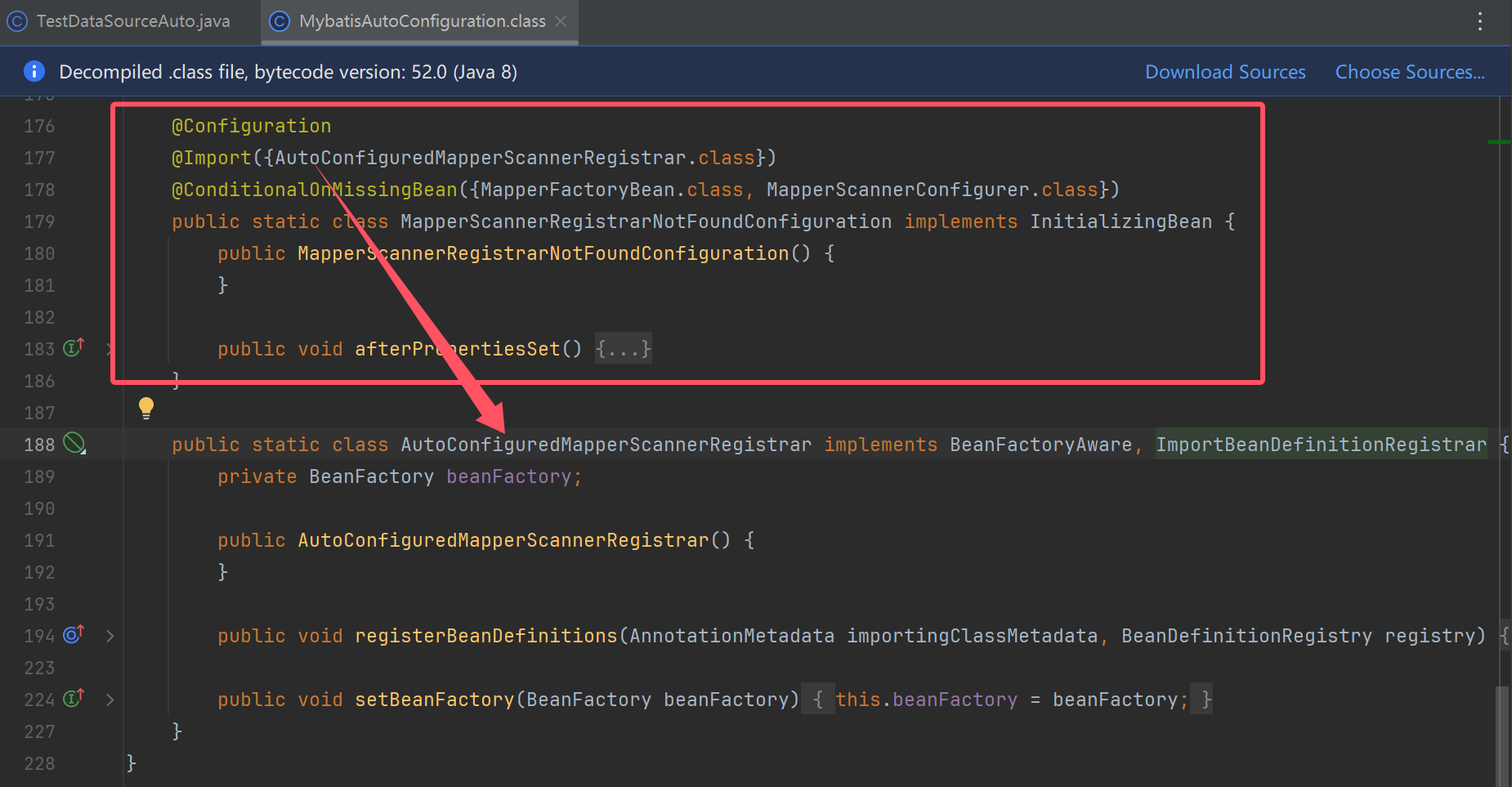
@Configuration
//注入下方的AutoConfiguredMapperScannerRegistrar
@Import({AutoConfiguredMapperScannerRegistrar.class})
//必须缺失bean成立
@ConditionalOnMissingBean({MapperFactoryBean.class, MapperScannerConfigurer.class})
public static class MapperScannerRegistrarNotFoundConfiguration implements InitializingBean {
public MapperScannerRegistrarNotFoundConfiguration() {
}
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
MybatisAutoConfiguration.logger.debug("Not found configuration for registering mapper bean using @MapperScan, MapperFactoryBean and MapperScannerConfigurer.");
}
}
//作用:实现了ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar:用编程的方式补充bean的definenation,这里补充的是mapper的definenation
//根据mapper接口类型,把每个mapper封装成MapperFactoryBean,作为bean definenation加到bean工厂
public static class AutoConfiguredMapperScannerRegistrar implements BeanFactoryAware, ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar {
private BeanFactory beanFactory;
public AutoConfiguredMapperScannerRegistrar() {
}
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
}
}
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
}

String packageName = TestDataSourceAuto.class.getPackageName();
System.out.println("当前包名:" + packageName);
//AutoConfigurationPackages:把springboot引导类的包名记录下来,
// 后面执行到MybatisAutoConfiguration中的AutoConfiguredMapperScannerRegistrar方法时,就可以确定mapper的扫描范围
AutoConfigurationPackages.register(context.getDefaultListableBeanFactory(),
packageName);
收获
- MyBatis 自动配置类为
org.mybatis.spring.boot.autoconfigure.MybatisAutoConfiguration - 它主要配置了两个 bean
- SqlSessionFactory - MyBatis 核心对象,用来创建 SqlSession
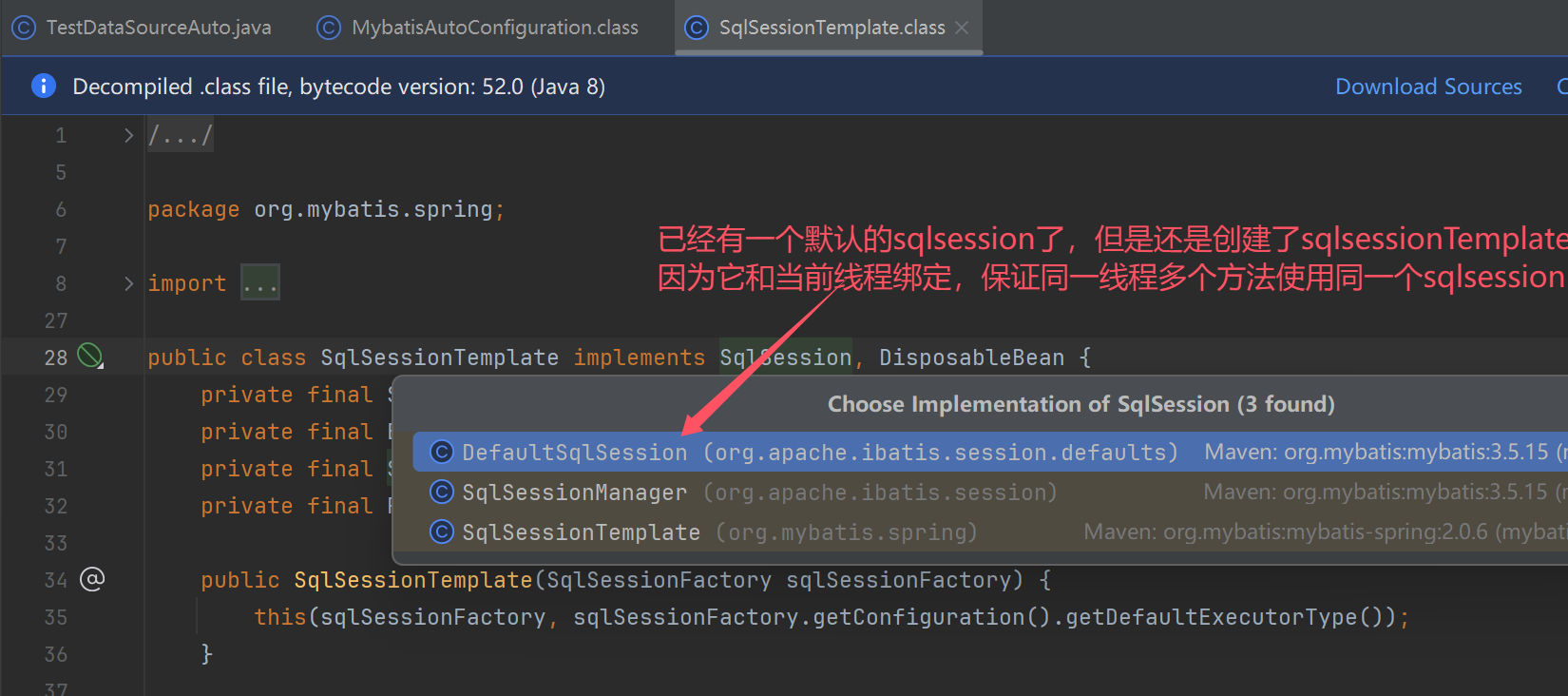
- SqlSessionTemplate - SqlSession 的实现,此实现会与当前线程绑定
- 用 ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar 的方式扫描所有标注了 @Mapper 注解的接口
- 用 AutoConfigurationPackages 来确定扫描的包
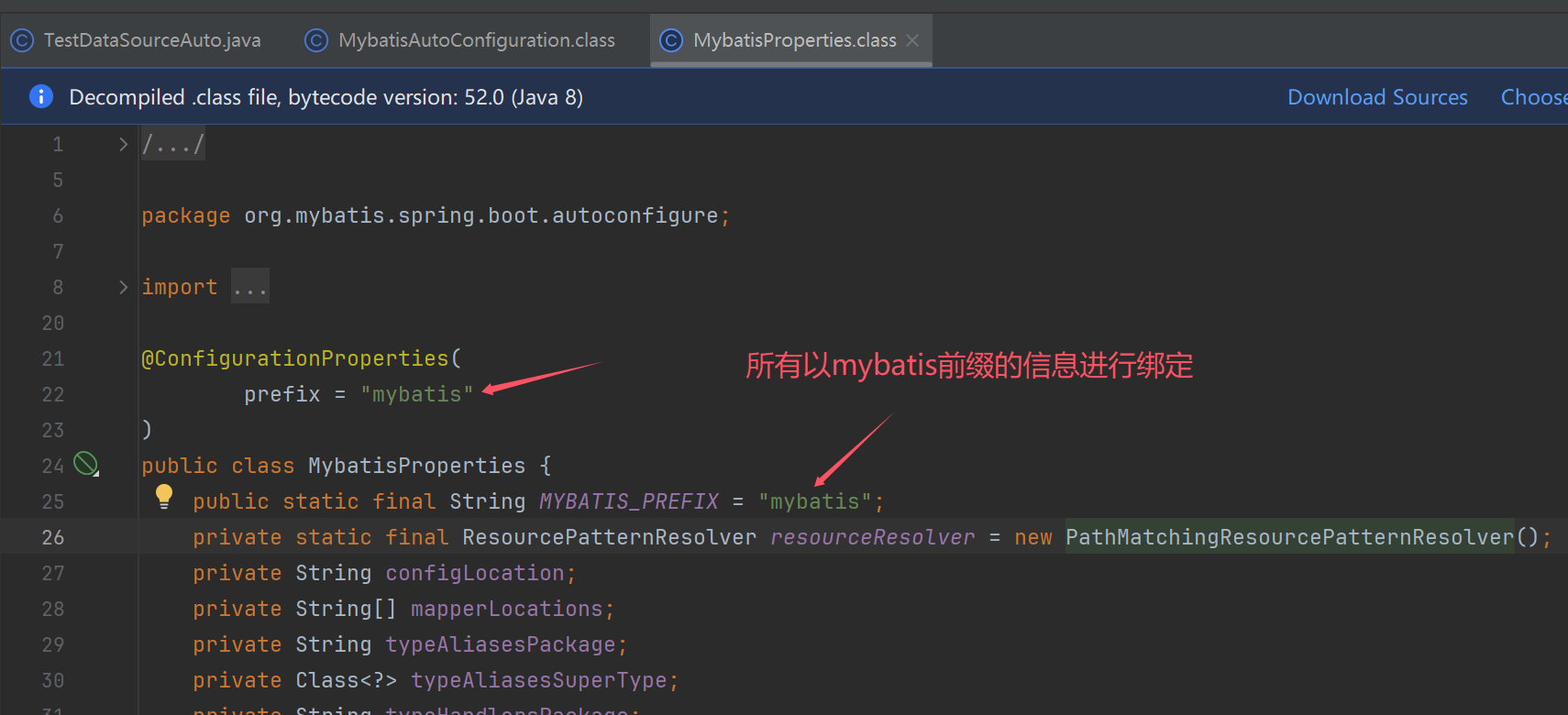
- 还有一个相关的 bean:MybatisProperties,它会读取配置文件中带
mybatis.前缀的配置项进行定制配置
@MapperScan 注解的作用与 MybatisAutoConfiguration 类似,会注册 MapperScannerConfigurer 有如下区别
- @MapperScan 扫描具体包(当然也可以配置关注哪个注解)
- @MapperScan 如果不指定扫描具体包,则会把引导类范围内,所有接口当做 Mapper 接口
- MybatisAutoConfiguration 关注的是所有标注 @Mapper 注解的接口,会忽略掉非 @Mapper 标注的接口
这里有同学有疑问,之前介绍的都是将具体类交给 Spring 管理,怎么到了 MyBatis 这儿,接口就可以被管理呢?
- 其实并非将接口交给 Spring 管理,而是每个接口会对应一个 MapperFactoryBean,是后者被 Spring 所管理,接口只是作为 MapperFactoryBean 的一个属性来配置
TransactionAutoConfiguration
收获
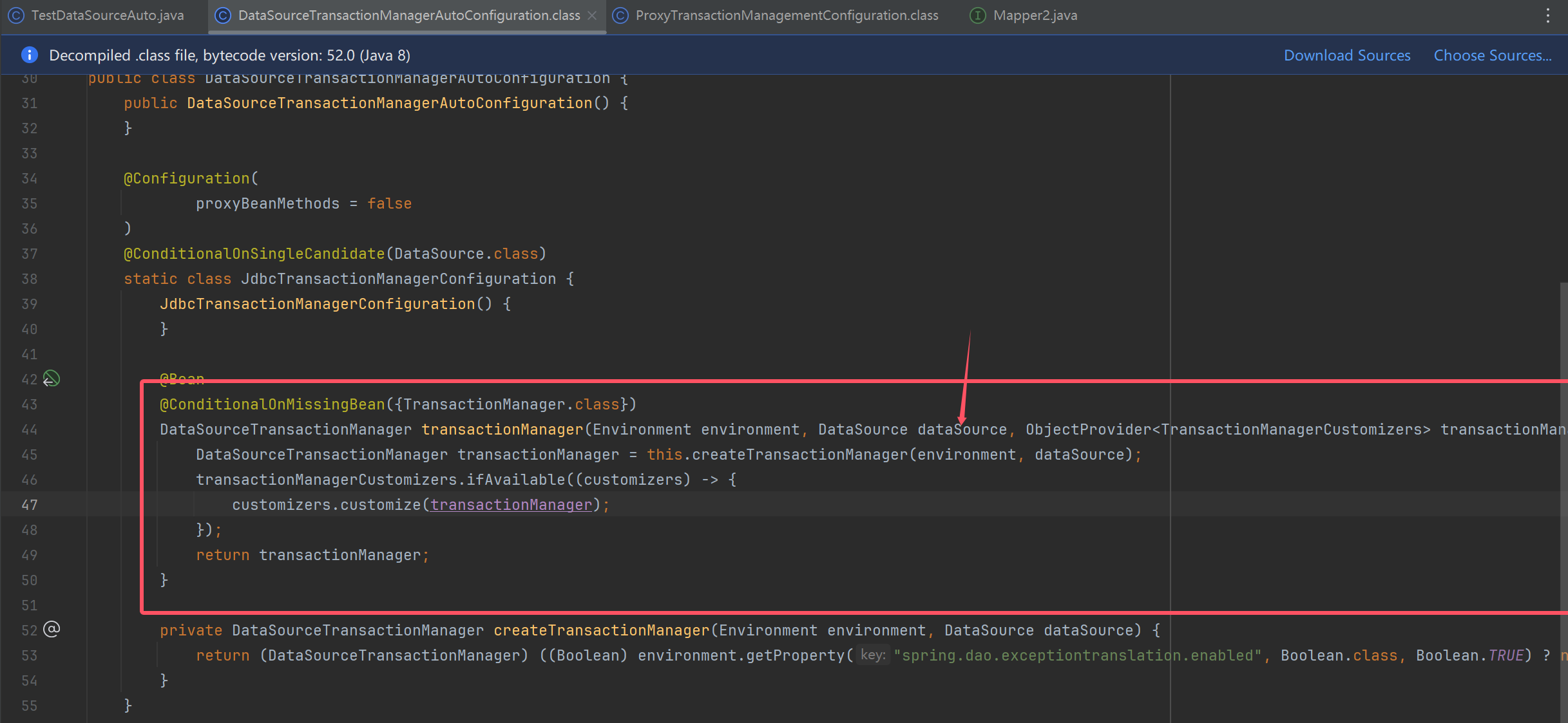
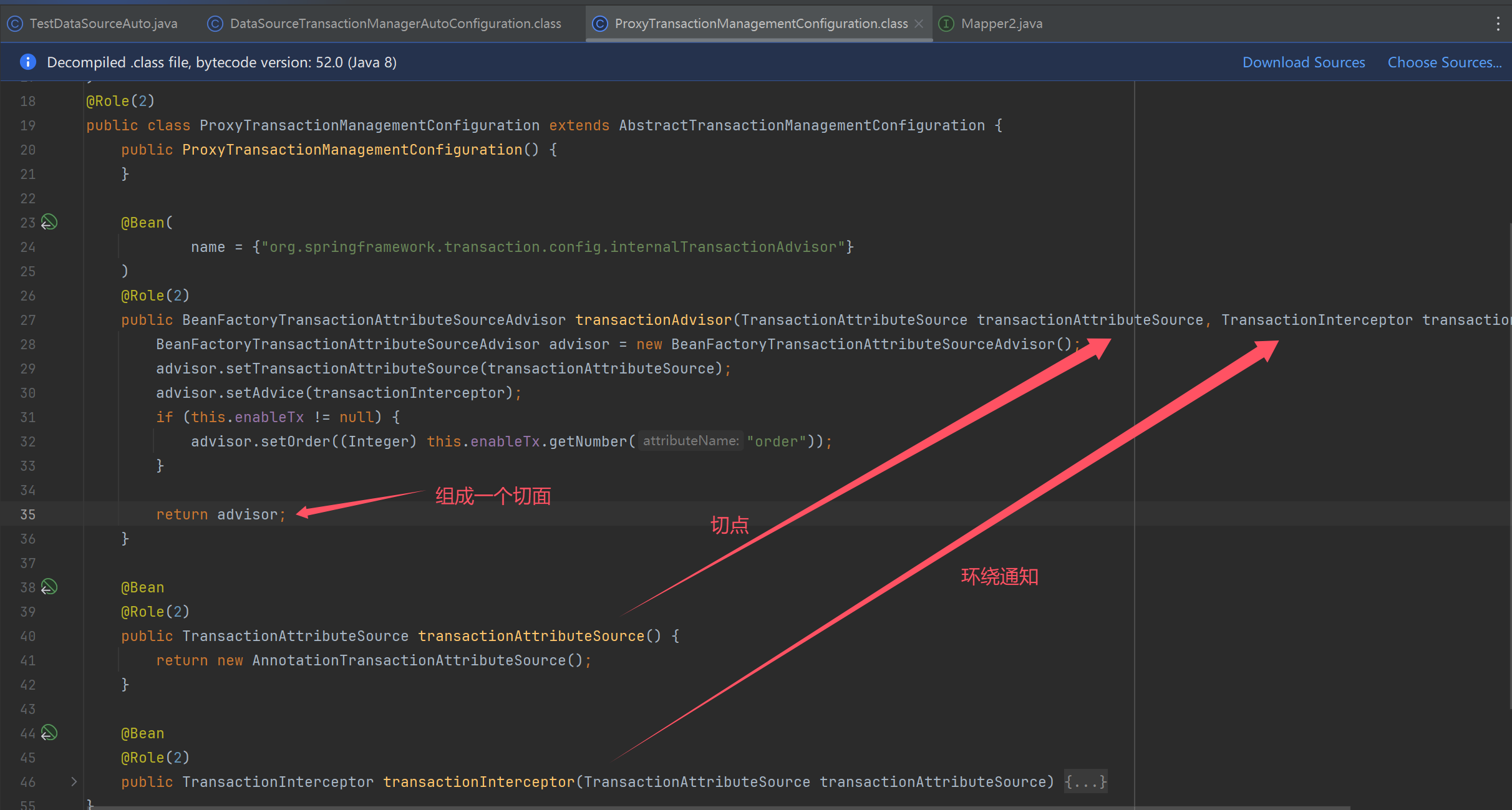
- 事务自动配置类有两个:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfigurationorg.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.TransactionAutoConfiguration
- 前者配置了 DataSourceTransactionManager 用来执行事务的提交、回滚操作
- 后者功能上对标 @EnableTransactionManagement,包含以下三个 bean
- BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor 事务切面类,包含通知和切点
- TransactionInterceptor 事务通知类,由它在目标方法调用前后加入事务操作
- AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource 会解析 @Transactional 及事务属性,也包含了切点功能
- 如果自己配置了 DataSourceTransactionManager 或是在引导类加了 @EnableTransactionManagement,则以自己配置的为准
mvc配置
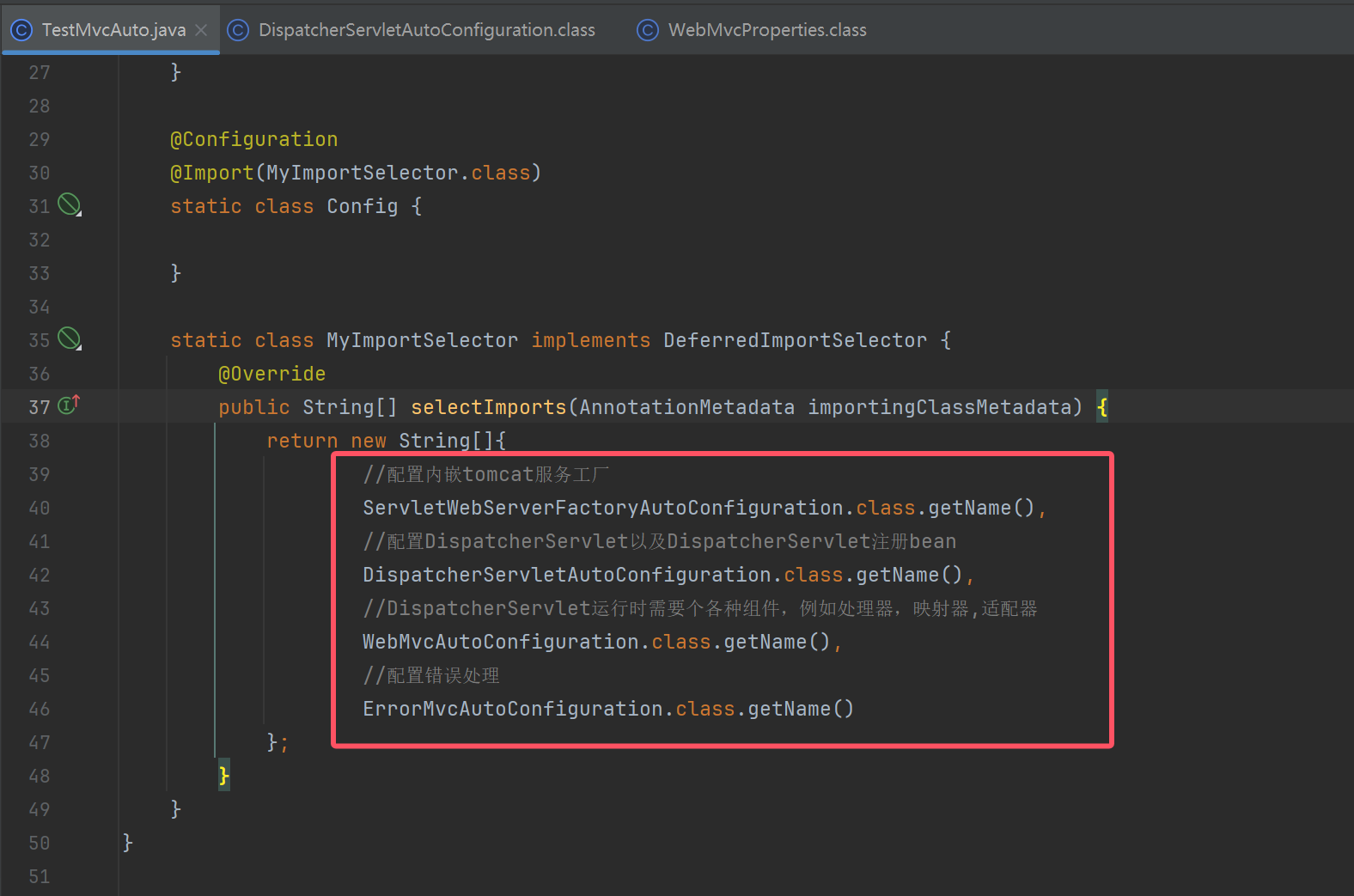
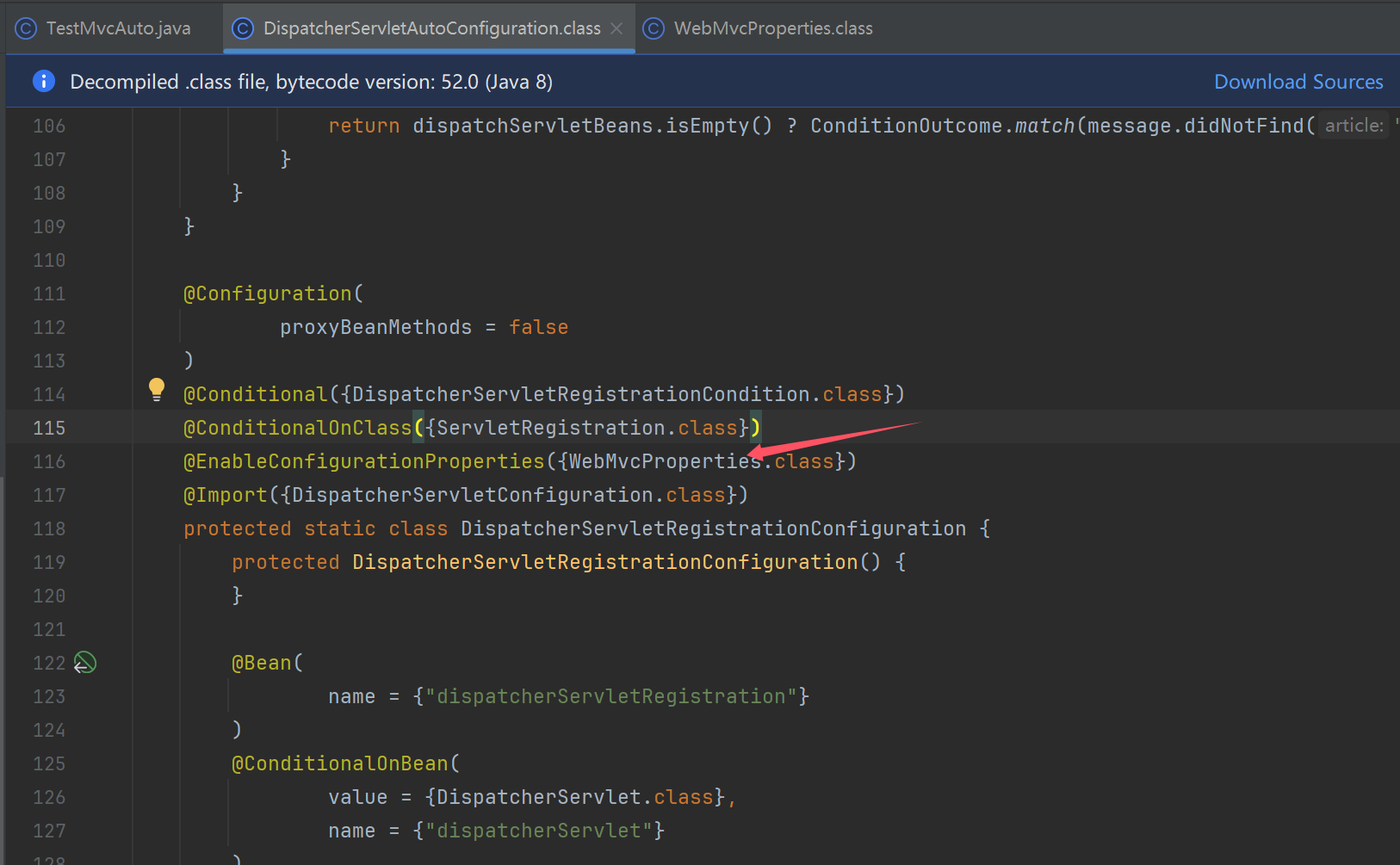
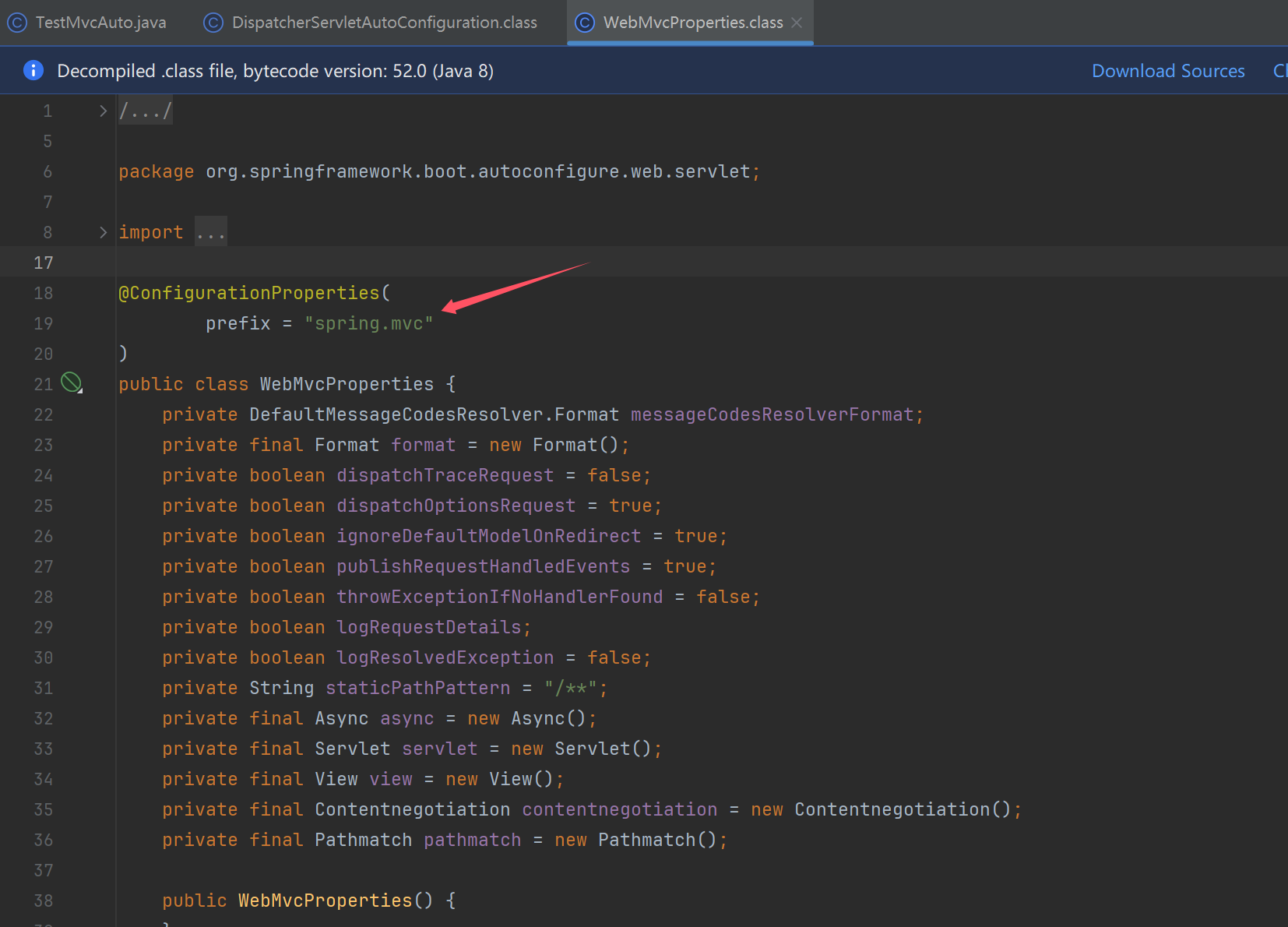
TestMvcAuto
public class TestMvcAuto {
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext();
context.registerBean(Config.class);
context.refresh();
for (String name : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
String source = context.getBeanDefinition(name).getResourceDescription();
if (source != null) {
System.out.println(name + " 来源:" + source);
}
}
context.close();
}
@Configuration
@Import(MyImportSelector.class)
static class Config {
}
static class MyImportSelector implements DeferredImportSelector {
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) {
return new String[]{
//配置内嵌tomcat服务工厂
ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration.class.getName(),
//配置DispatcherServlet以及DispatcherServlet注册bean
DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.class.getName(),
//DispatcherServlet运行时需要个各种组件,例如处理器,映射器,适配器
WebMvcAutoConfiguration.class.getName(),
//配置错误处理
ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration.class.getName()
};
}
}
}
ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration
- 提供 ServletWebServerFactory
DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration
- 提供 DispatcherServlet
- 提供 DispatcherServletRegistrationBean
WebMvcAutoConfiguration
- 配置 DispatcherServlet 的各项组件,提供的 bean 见过的有
- 多项 HandlerMapping
- 多项 HandlerAdapter
- HandlerExceptionResolver
ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration
- 提供的 bean 有 BasicErrorController
MultipartAutoConfiguration
- 它提供了 org.springframework.web.multipart.support.StandardServletMultipartResolver
- 该 bean 用来解析 multipart/form-data 格式的数据
HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration
- POST 请求参数如果有中文,无需特殊设置,这是因为 Spring Boot 已经配置了 org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.filter.OrderedCharacterEncodingFilter
- 对应配置 server.servlet.encoding.charset=UTF-8,默认就是 UTF-8
- 当然,它只影响非 json 格式的数据
自定义自动配置类
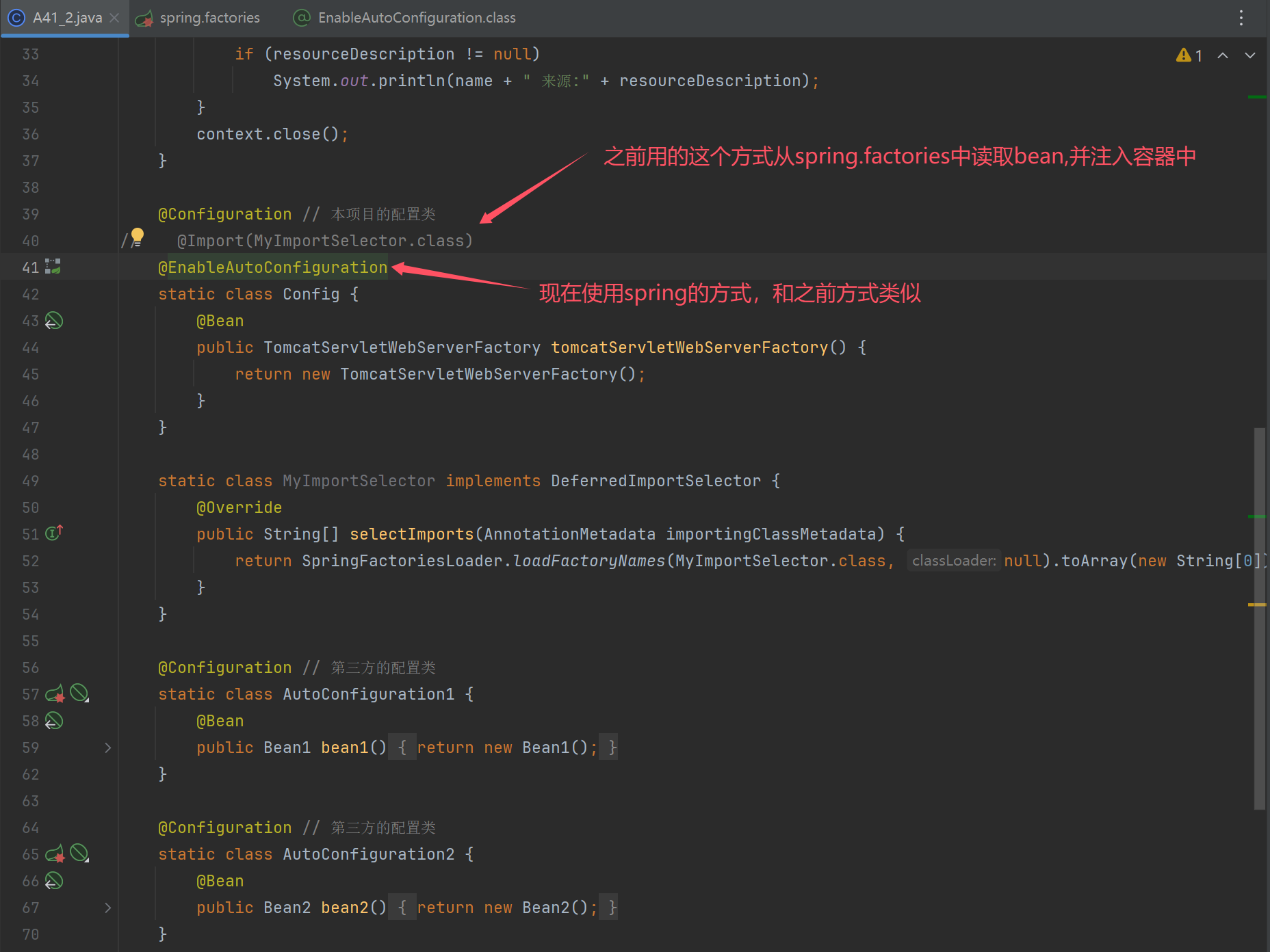
public class A41_2 {
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext();
StandardEnvironment env = new StandardEnvironment();
env.getPropertySources().addLast(new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource(
"--spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test",
"--spring.datasource.username=root",
"--spring.datasource.password=root"
));
context.setEnvironment(env);
context.registerBean("config", Config.class);
context.refresh();
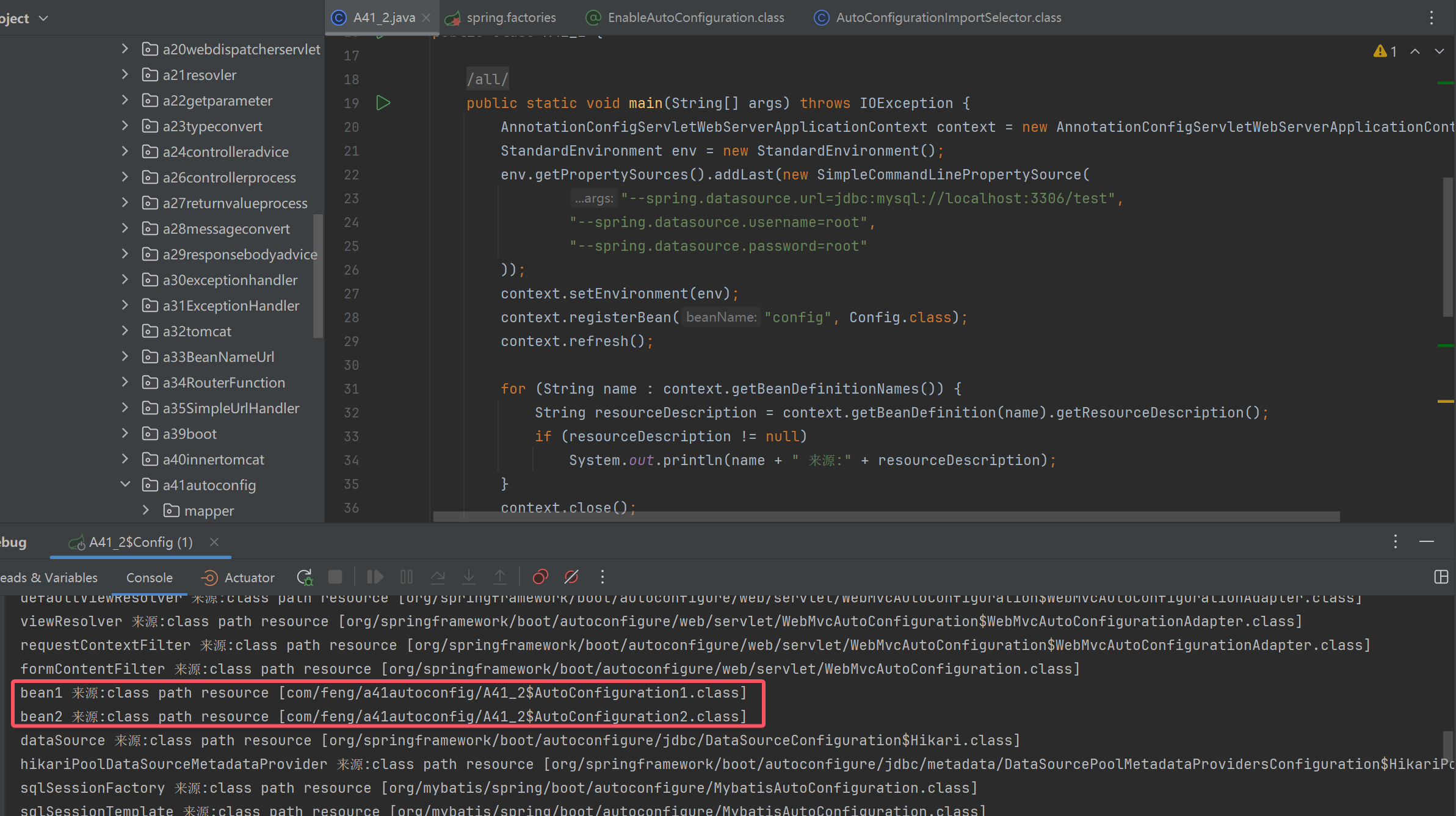
for (String name : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
String resourceDescription = context.getBeanDefinition(name).getResourceDescription();
if (resourceDescription != null)
System.out.println(name + " 来源:" + resourceDescription);
}
context.close();
}
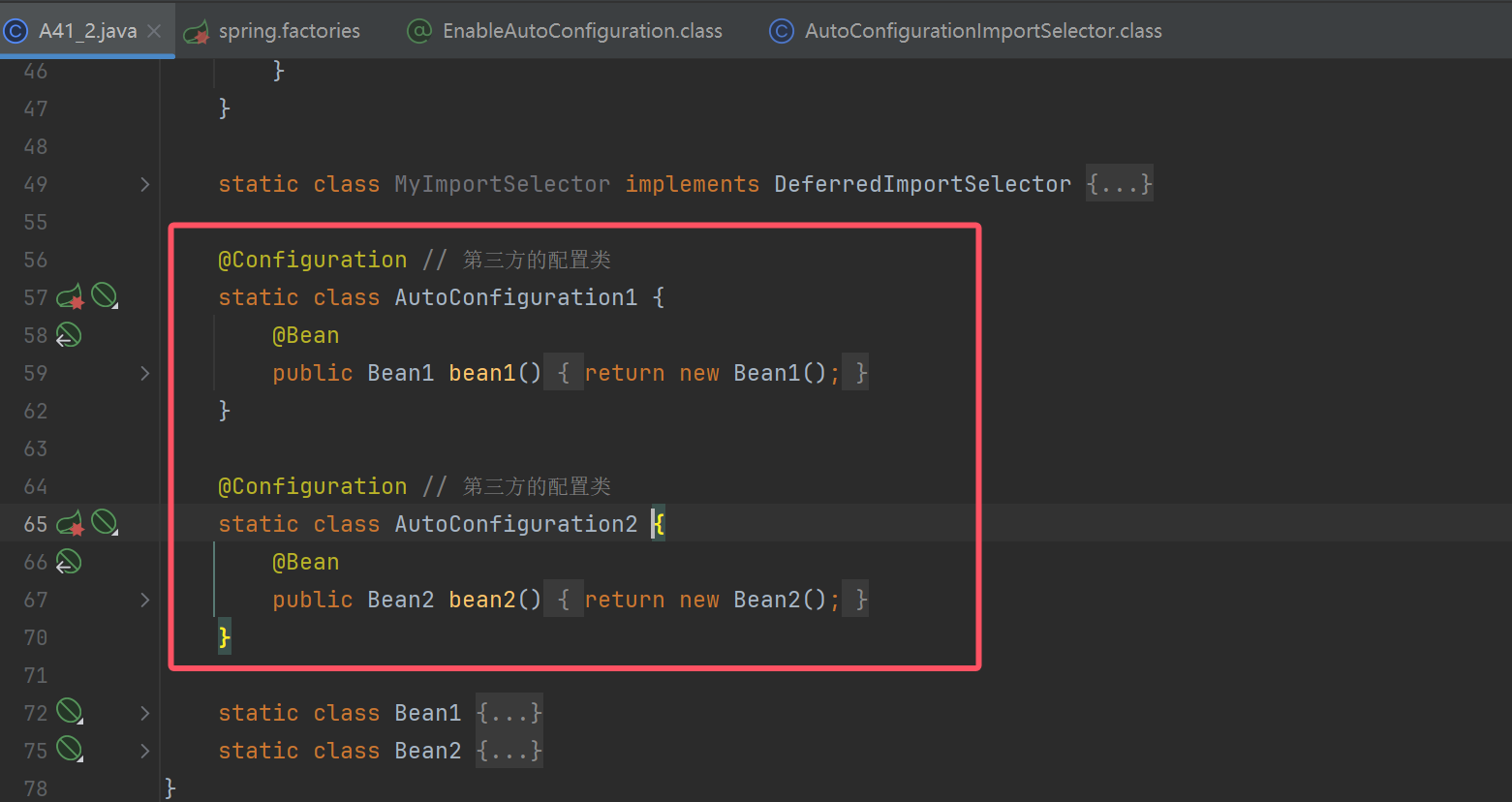
@Configuration // 本项目的配置类
// @Import(MyImportSelector.class)
@EnableAutoConfiguration
static class Config {
@Bean
public TomcatServletWebServerFactory tomcatServletWebServerFactory() {
return new TomcatServletWebServerFactory();
}
}
static class MyImportSelector implements DeferredImportSelector {
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) {
return SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(MyImportSelector.class, null).toArray(new String[0]);
}
}
@Configuration // 第三方的配置类
static class AutoConfiguration1 {
@Bean
public Bean1 bean1() {
return new Bean1();
}
}
@Configuration // 第三方的配置类
static class AutoConfiguration2 {
@Bean
public Bean2 bean2() {
return new Bean2();
}
}
static class Bean1 {
}
static class Bean2 {
}
}
关键代码
假设已有第三方的两个自动配置类
@Configuration // ⬅️第三方的配置类
static class AutoConfiguration1 {
@Bean
public Bean1 bean1() {
return new Bean1();
}
}
@Configuration // ⬅️第三方的配置类
static class AutoConfiguration2 {
@Bean
public Bean2 bean2() {
return new Bean2();
}
}
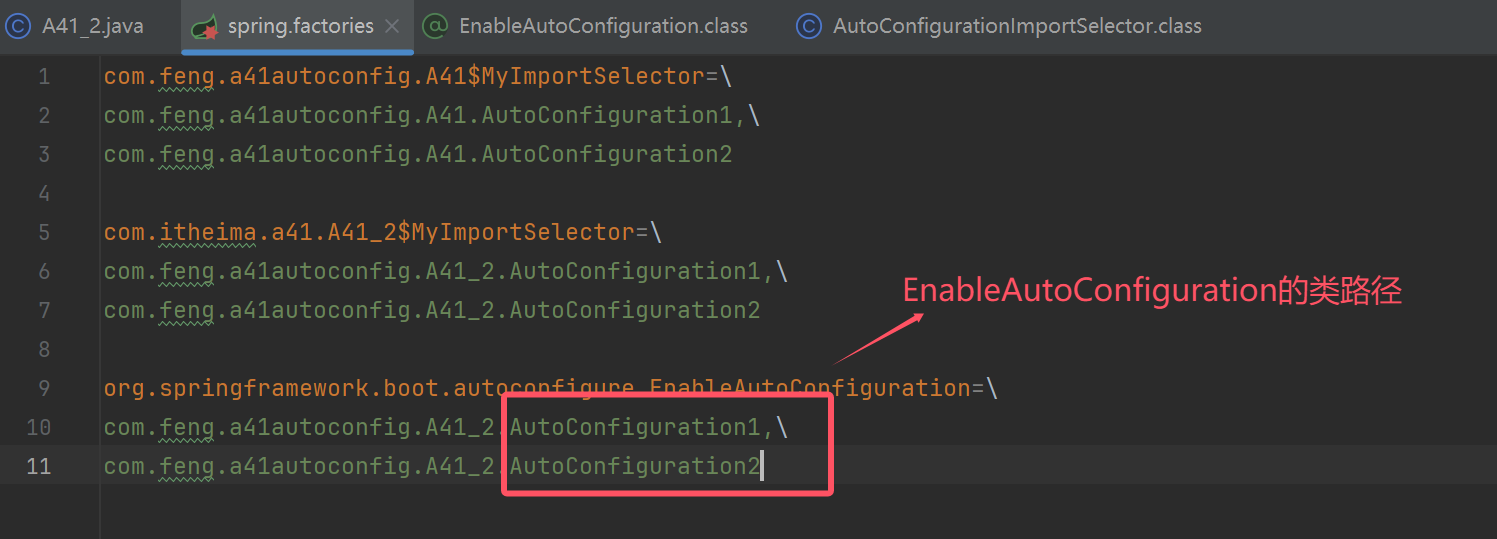
提供一个配置文件 META-INF/spring.factories,key 为导入器类名,值为多个自动配置类名,用逗号分隔
MyImportSelector=\
AutoConfiguration1,\
AutoConfiguration2
注意
- 上述配置文件中 MyImportSelector 与 AutoConfiguration1,AutoConfiguration2 为简洁均省略了包名,自己测试时请将包名根据情况补全
引入自动配置
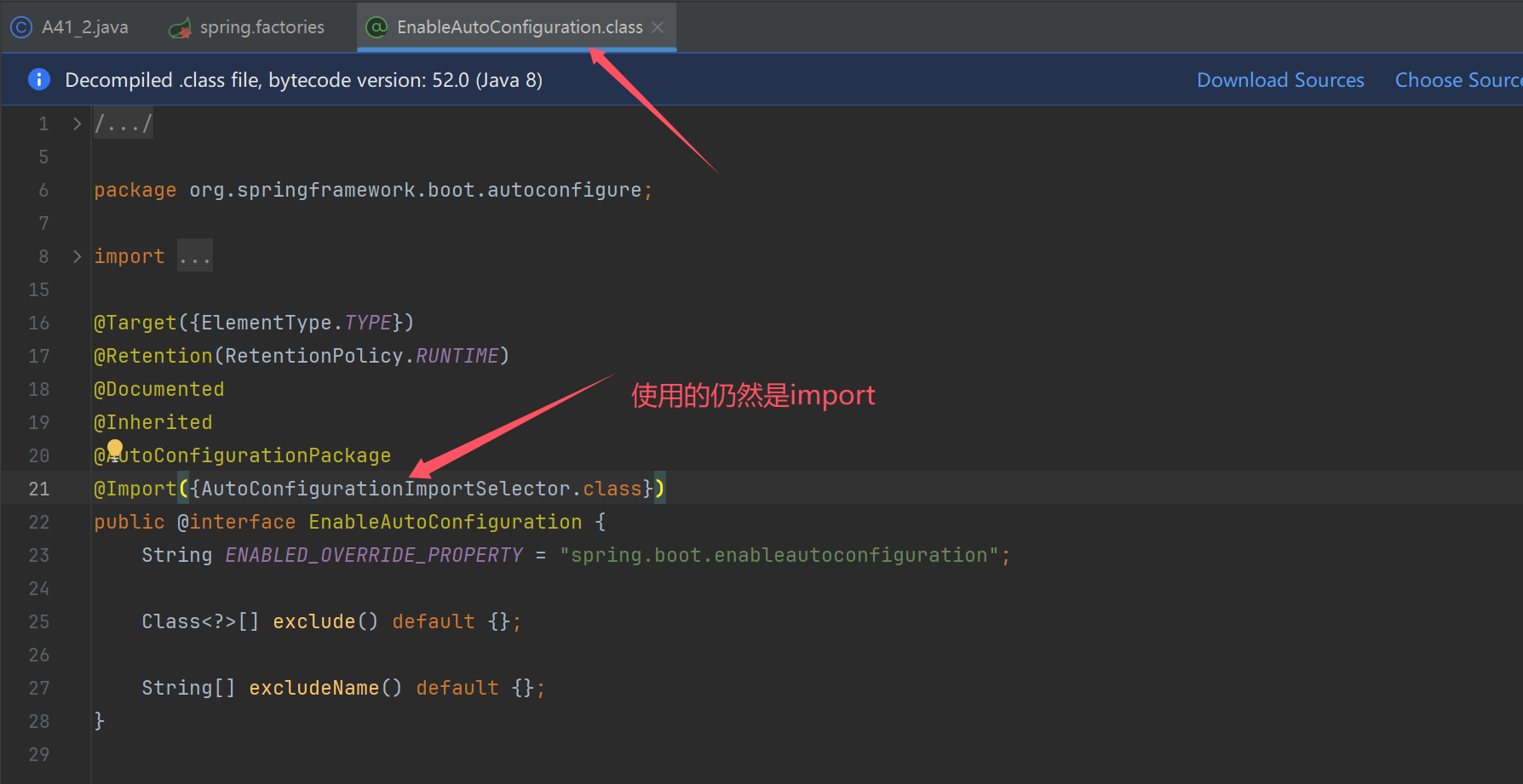
@Configuration // ⬅️本项目的配置类
@Import(MyImportSelector.class)
static class Config { }
static class MyImportSelector implements DeferredImportSelector {
// ⬇️该方法从 META-INF/spring.factories 读取自动配置类名,返回的 String[] 即为要导入的配置类
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) {
return SpringFactoriesLoader
.loadFactoryNames(MyImportSelector.class, null).toArray(new String[0]);
}
}
收获💡
- 自动配置类本质上就是一个配置类而已,只是用 META-INF/spring.factories 管理,与应用配置类解耦
- @Enable 打头的注解本质是利用了 @Import
- @Import 配合 DeferredImportSelector 即可实现导入,selectImports 方法的返回值即为要导入的配置类名
- DeferredImportSelector 的导入会在最后执行,为的是让其它配置优先解析
1.6 条件装配底层
public class A42_1 {
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
GenericApplicationContext context = new GenericApplicationContext();
context.registerBean("config", Config.class);
context.registerBean(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class);
context.refresh();
for (String name : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
@Configuration // 本项目的配置类
@Import(MyImportSelector.class)
static class Config {
}
static class MyImportSelector implements DeferredImportSelector {
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) {
return new String[]{AutoConfiguration1.class.getName(), AutoConfiguration2.class.getName()};
}
}
static class MyCondition1 implements Condition { //存在druid依赖
@Override
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
//存在druid依赖
return ClassUtils.isPresent("com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource", null);
}
}
static class MyCondition2 implements Condition { //不存在druid依赖
@Override
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
//是否存在druid依赖
return !ClassUtils.isPresent("com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource", null);
}
}
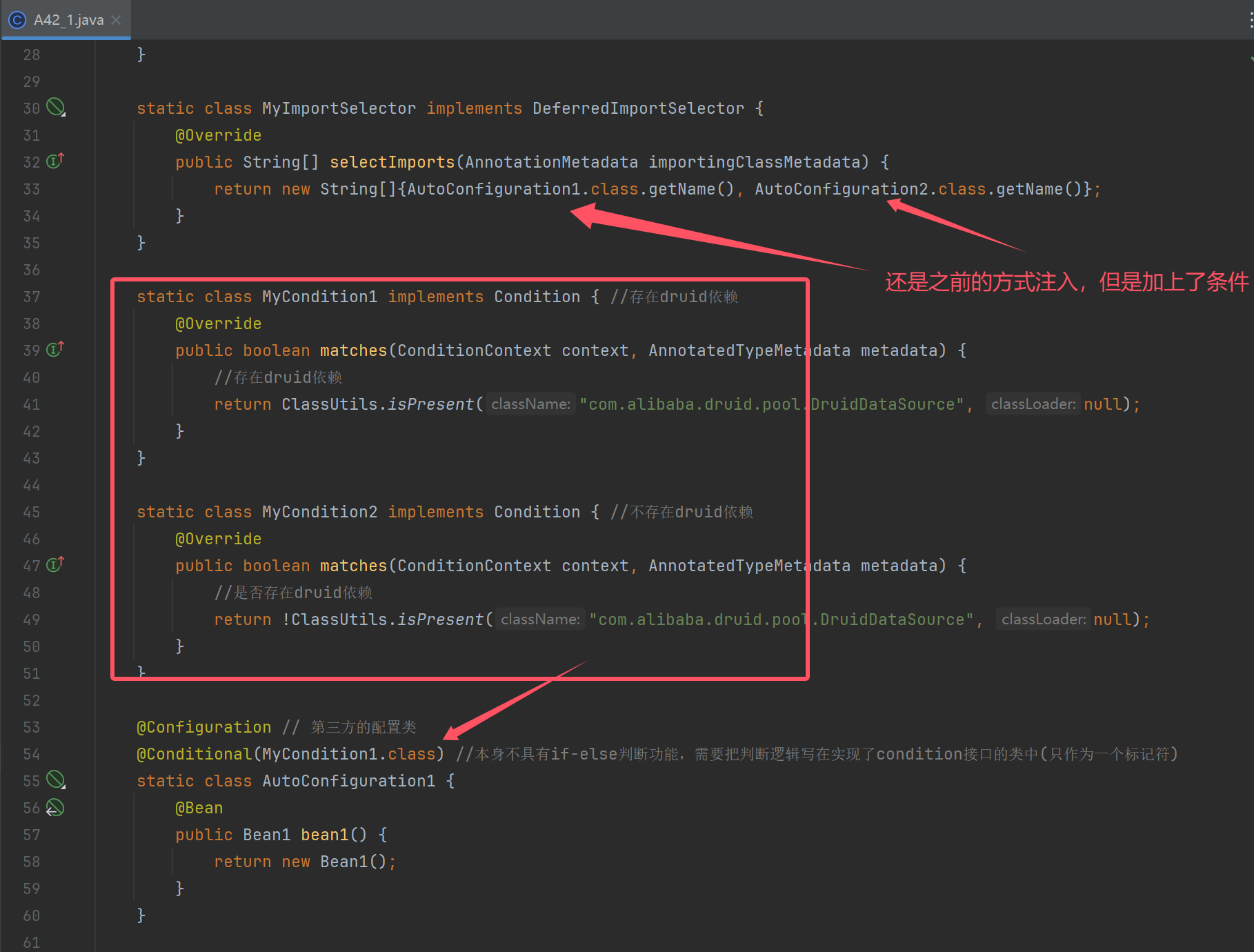
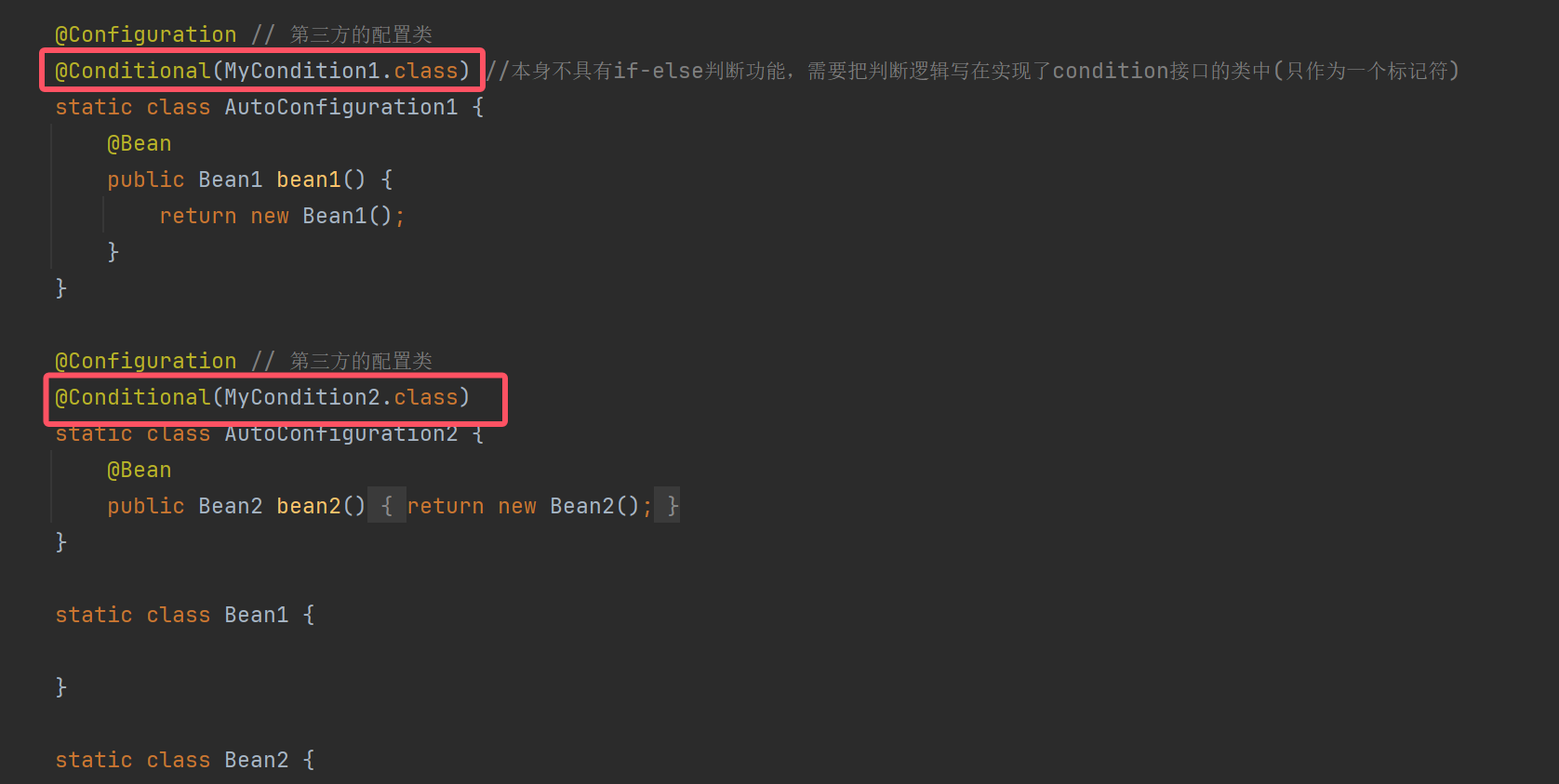
@Configuration // 第三方的配置类
@Conditional(MyCondition1.class) //本身不具有if-else判断功能,需要把判断逻辑写在实现了condition接口的类中(只作为一个标记符)
static class AutoConfiguration1 {
@Bean
public Bean1 bean1() {
return new Bean1();
}
}
@Configuration // 第三方的配置类
@Conditional(MyCondition2.class)
static class AutoConfiguration2 {
@Bean
public Bean2 bean2() {
return new Bean2();
}
}
static class Bean1 {
}
static class Bean2 {
}
}
自定义条件注解
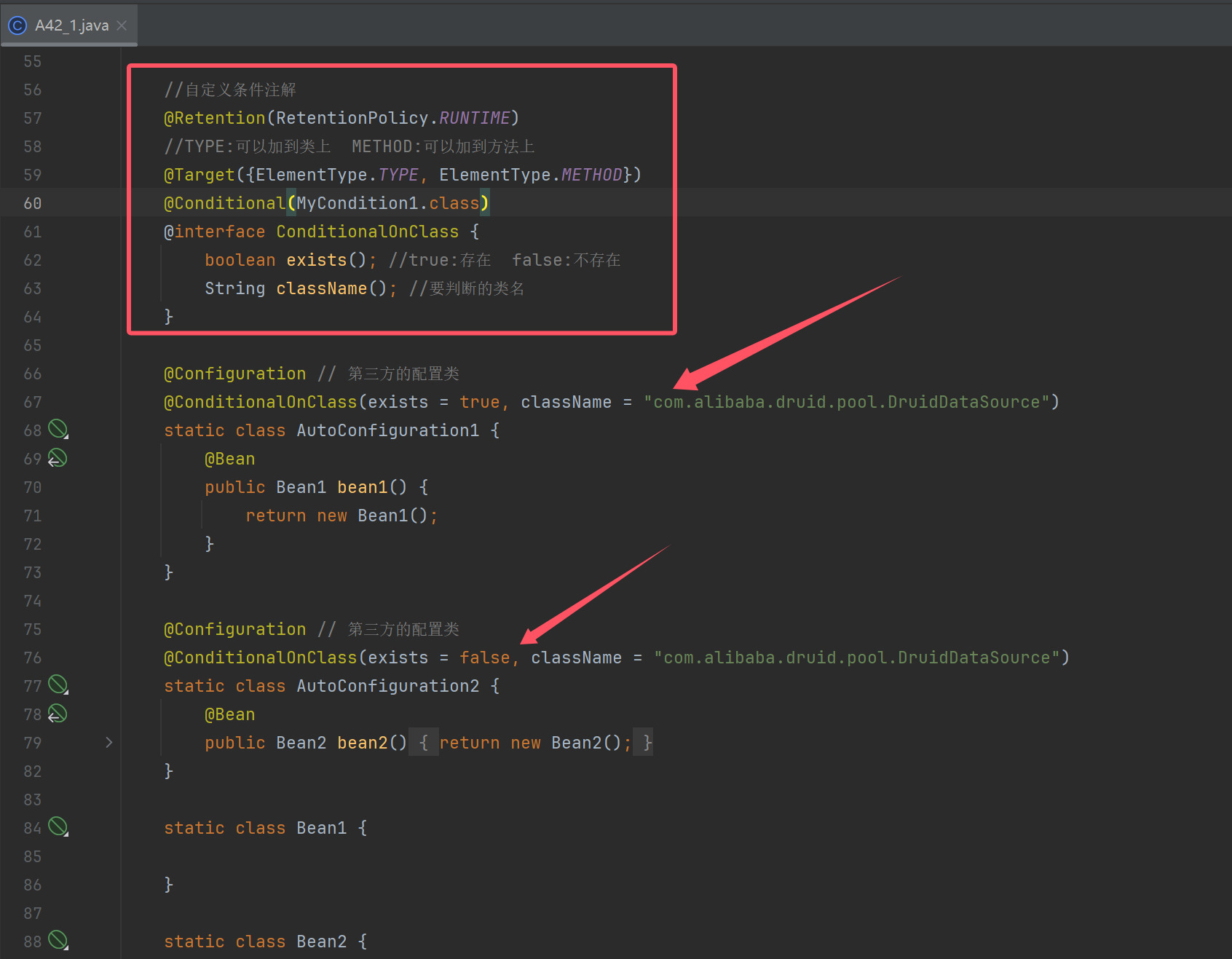
public class A42_1 {
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
GenericApplicationContext context = new GenericApplicationContext();
context.registerBean("config", Config.class);
context.registerBean(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class);
context.refresh();
for (String name : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
@Configuration // 本项目的配置类
@Import(MyImportSelector.class)
static class Config {
}
static class MyImportSelector implements DeferredImportSelector {
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) {
return new String[]{AutoConfiguration1.class.getName(), AutoConfiguration2.class.getName()};
}
}
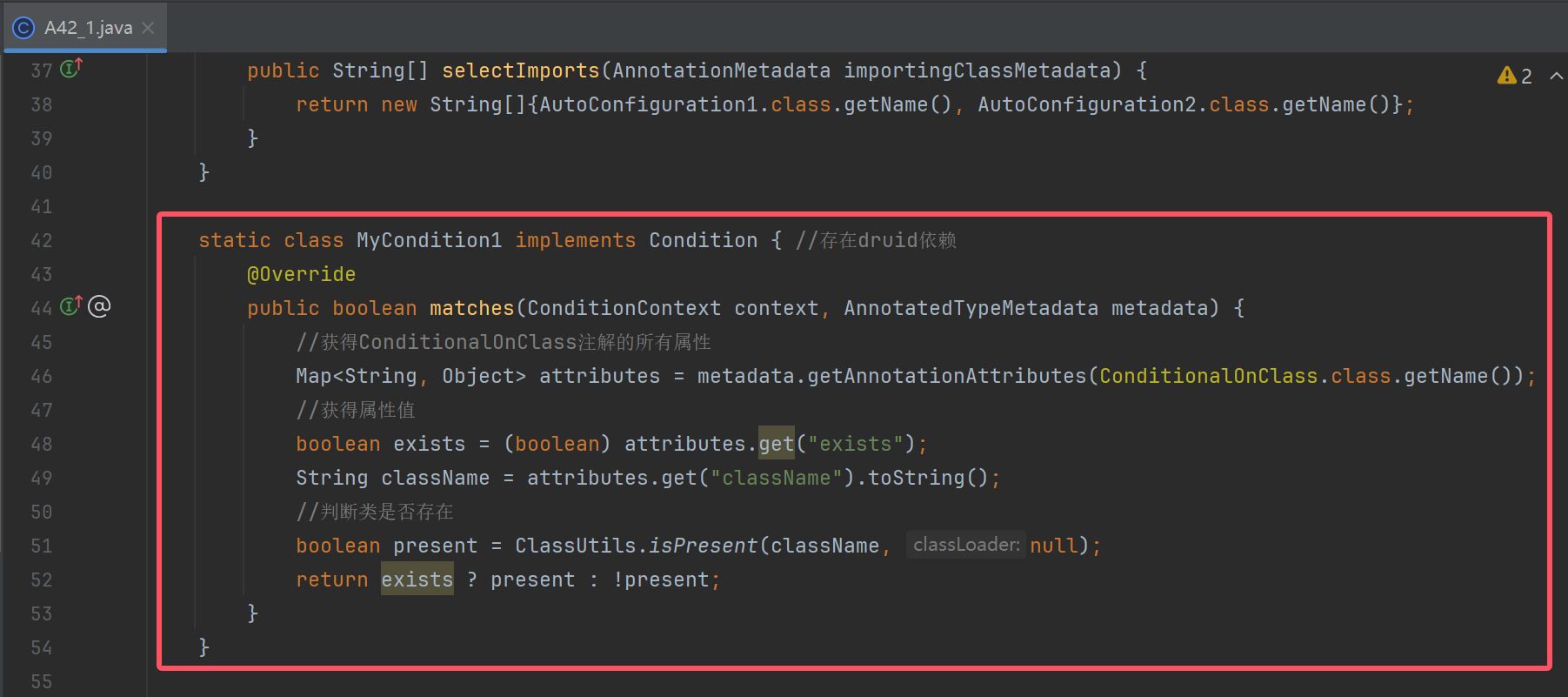
static class MyCondition1 implements Condition { //存在druid依赖
@Override
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
//获得ConditionalOnClass注解的所有属性
Map<String, Object> attributes = metadata.getAnnotationAttributes(ConditionalOnClass.class.getName());
//获得属性值
boolean exists = (boolean) attributes.get("exists");
String className = attributes.get("className").toString();
//判断类是否存在
boolean present = ClassUtils.isPresent(className, null);
return exists ? present : !present;
}
}
//自定义条件注解
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
//TYPE:可以加到类上 METHOD:可以加到方法上
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Conditional(MyCondition1.class)
@interface ConditionalOnClass {
boolean exists(); //true:存在 false:不存在
String className(); //要判断的类名
}
@Configuration // 第三方的配置类
@ConditionalOnClass(exists = true, className = "com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource")
static class AutoConfiguration1 {
@Bean
public Bean1 bean1() {
return new Bean1();
}
}
@Configuration // 第三方的配置类
@ConditionalOnClass(exists = false, className = "com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource")
static class AutoConfiguration2 {
@Bean
public Bean2 bean2() {
return new Bean2();
}
}
static class Bean1 {
}
static class Bean2 {
}
}
条件装配的底层是本质上是 @Conditional 与 Condition,这两个注解。引入自动配置类时,期望满足一定条件才能被 Spring 管理,不满足则不管理,怎么做呢?
比如条件是【类路径下必须有 dataSource】这个 bean ,怎么做呢?
首先编写条件判断类,它实现 Condition 接口,编写条件判断逻辑
static class MyCondition1 implements Condition {
// ⬇️如果存在 Druid 依赖,条件成立
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
return ClassUtils.isPresent("com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource", null);
}
}
其次,在要导入的自动配置类上添加 @Conditional(MyCondition1.class),将来此类被导入时就会做条件检查
@Configuration // 第三方的配置类
@Conditional(MyCondition1.class) // ⬅️加入条件
static class AutoConfiguration1 {
@Bean
public Bean1 bean1() {
return new Bean1();
}
}
分别测试加入和去除 druid 依赖,观察 bean1 是否存在于容器
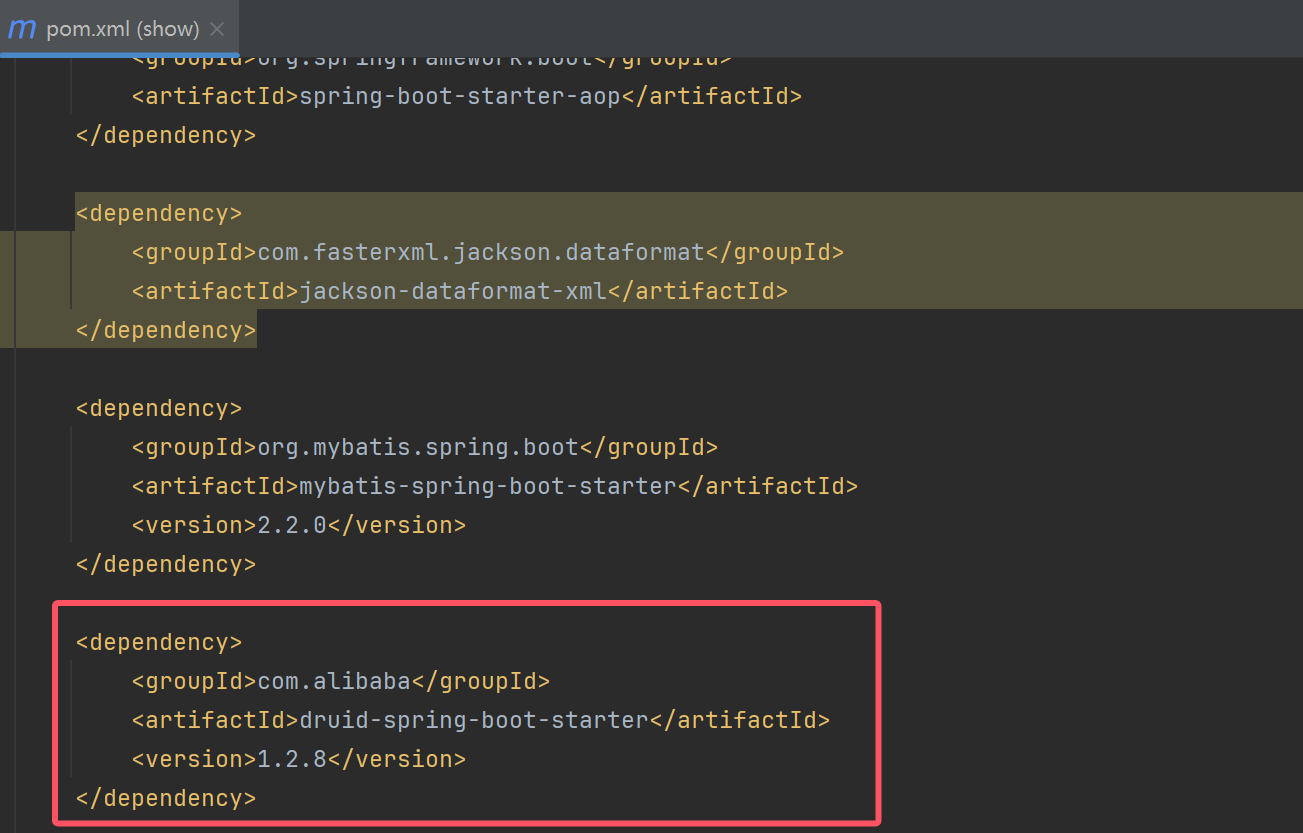
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.17</version>
</dependency>
收获💡
- 学习一种特殊的 if - else
2 其它
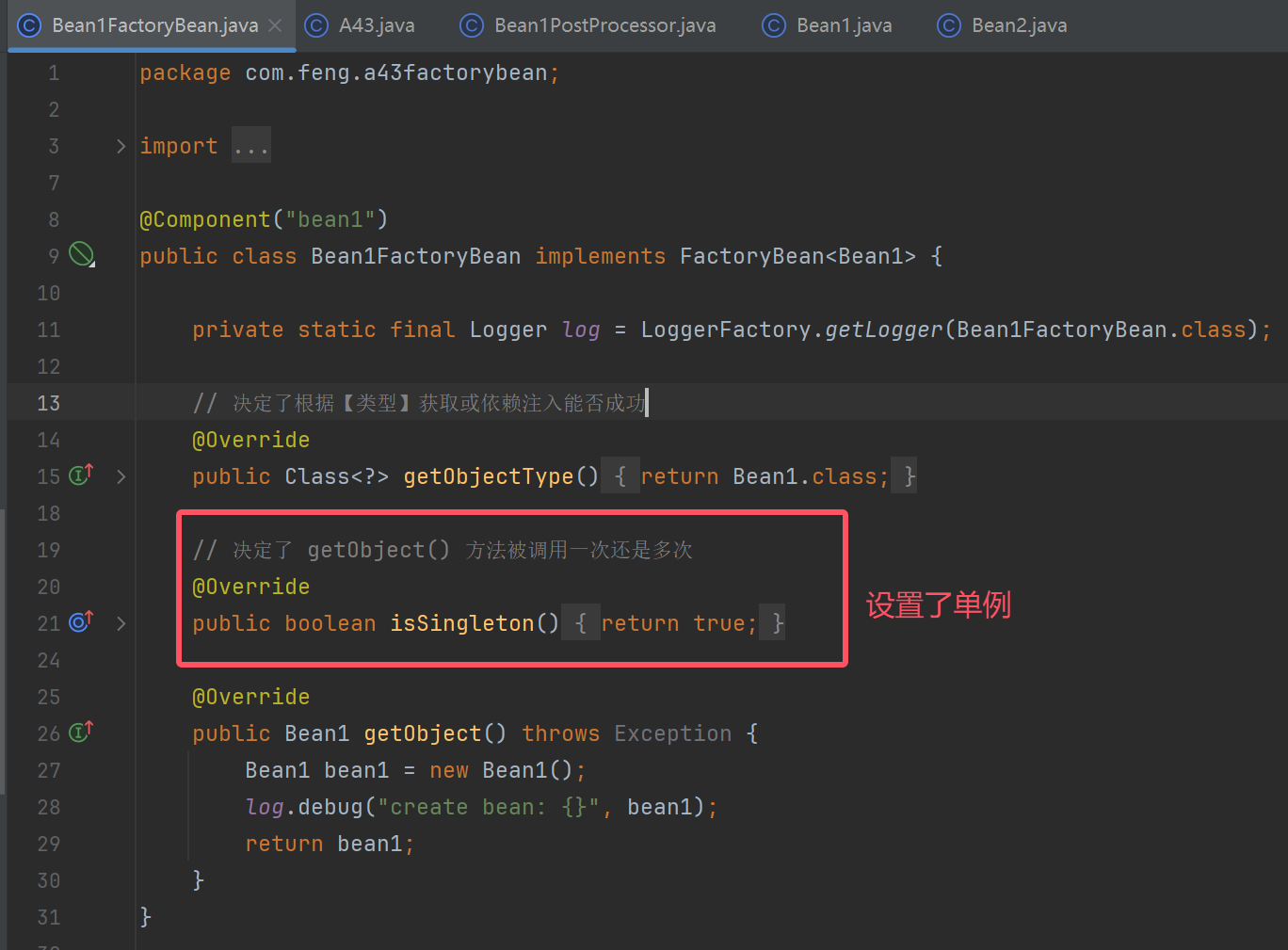
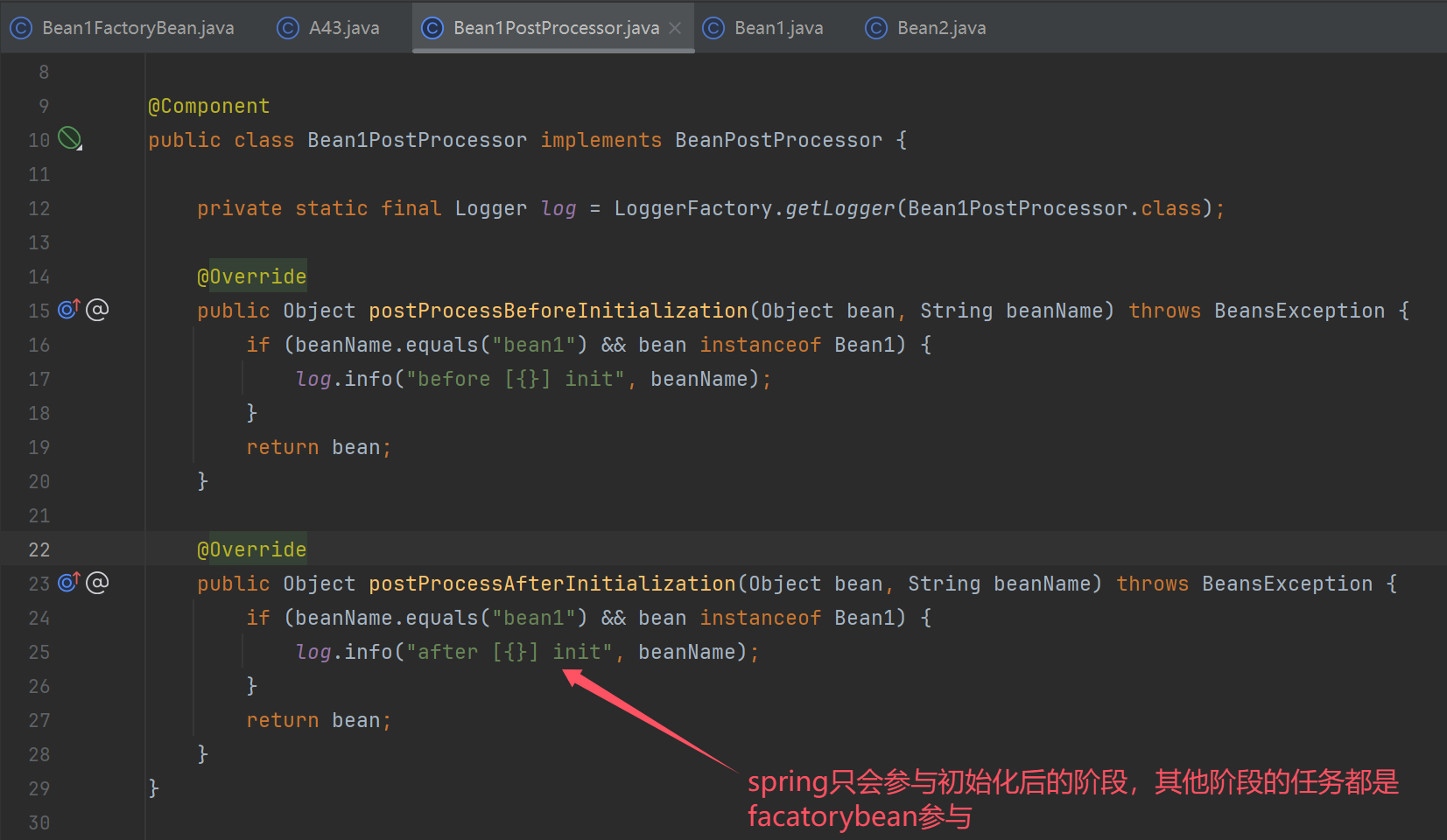
2.1 FactoryBean
@ComponentScan
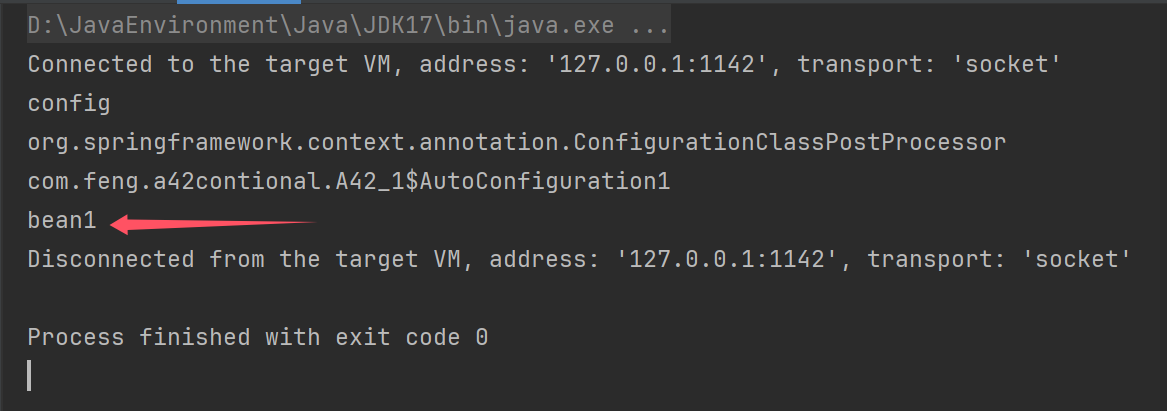
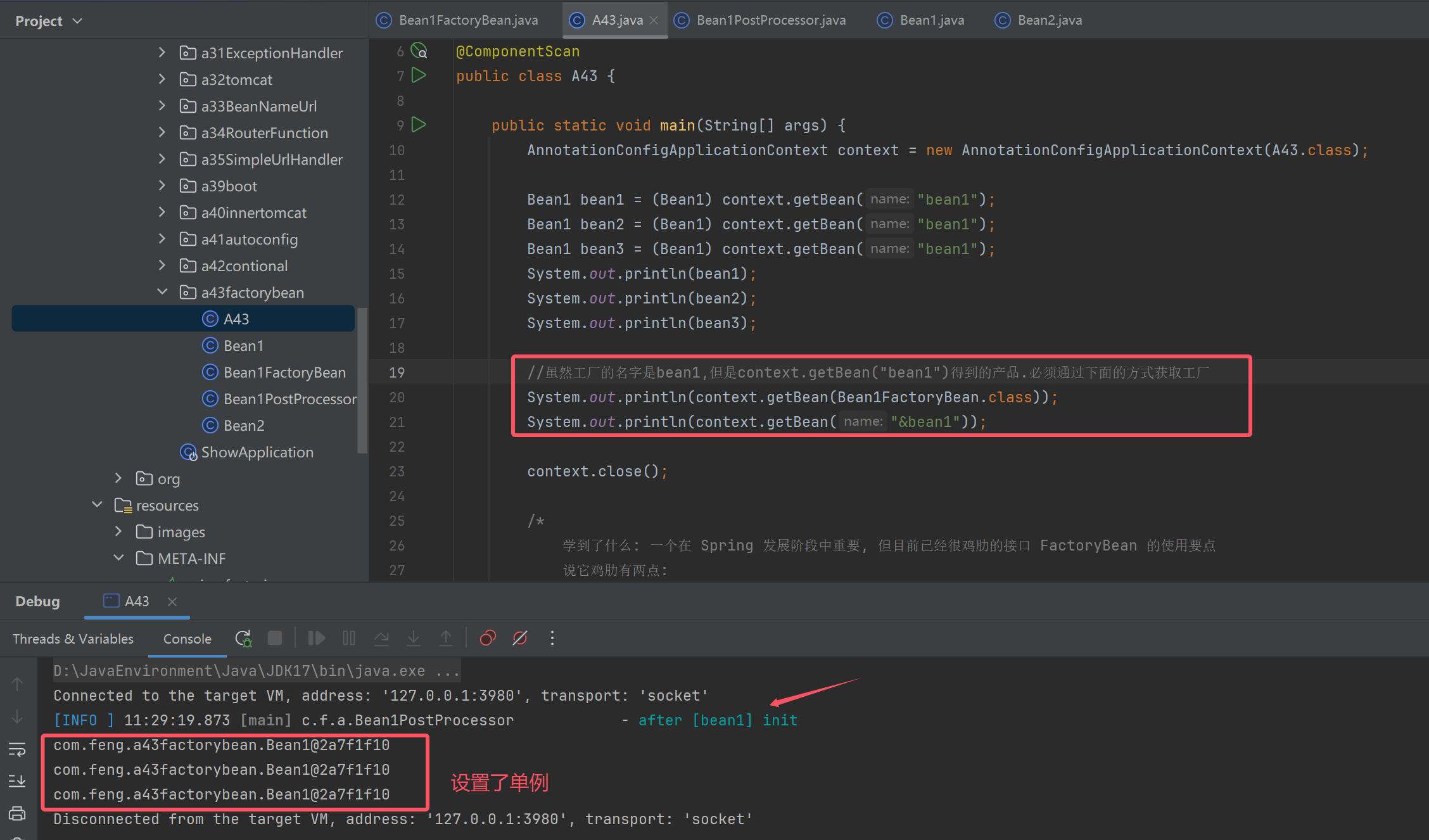
public class A43 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(A43.class);
Bean1 bean1 = (Bean1) context.getBean("bean1");
Bean1 bean2 = (Bean1) context.getBean("bean1");
Bean1 bean3 = (Bean1) context.getBean("bean1");
System.out.println(bean1);
System.out.println(bean2);
System.out.println(bean3);
//虽然工厂的名字是bean1,但是context.getBean("bean1")得到的产品.必须通过下面的方式获取工厂
System.out.println(context.getBean(Bean1FactoryBean.class));
System.out.println(context.getBean("&bean1"));
context.close();
/*
学到了什么: 一个在 Spring 发展阶段中重要, 但目前已经很鸡肋的接口 FactoryBean 的使用要点
说它鸡肋有两点:
1. 它的作用是用制造创建过程较为复杂的产品, 如 SqlSessionFactory, 但 @Bean 已具备等价功能
2. 使用上较为古怪, 一不留神就会用错
a. 被 FactoryBean 创建的产品
- 会认为创建、依赖注入、Aware 接口回调、前初始化这些都是 FactoryBean 的职责, 这些流程都不会走
- 唯有后初始化的流程会走, 也就是产品可以被代理增强
- 单例的产品不会存储于 BeanFactory 的 singletonObjects 成员中, 而是另一个 factoryBeanObjectCache 成员中
b. 按名字去获取时, 拿到的是产品对象, 名字前面加 & 获取的是工厂对象
就说恶心不?
但目前此接口的实现仍被大量使用, 想被全面废弃很难
*/
}
}
收获💡
- 它的作用是用制造创建过程较为复杂的产品, 如 SqlSessionFactory, 但 @Bean 已具备等价功能
- 使用上较为古怪, 一不留神就会用错
- 被 FactoryBean 创建的产品
- 会认为创建、依赖注入、Aware 接口回调、前初始化这些都是 FactoryBean 的职责, 这些流程都不会走
- 唯有后初始化的流程会走, 也就是产品可以被代理增强
- 单例的产品不会存储于 BeanFactory 的 singletonObjects 成员中, 而是另一个 factoryBeanObjectCache 成员中
- 按名字去获取时, 拿到的是产品对象, 名字前面加 & 获取的是工厂对象
- 被 FactoryBean 创建的产品
2.2 @Indexed 原理
@Component
public class Bean1 {
}
@Component
public class Bean2 {
}
@Component
public class Bean3 {
}
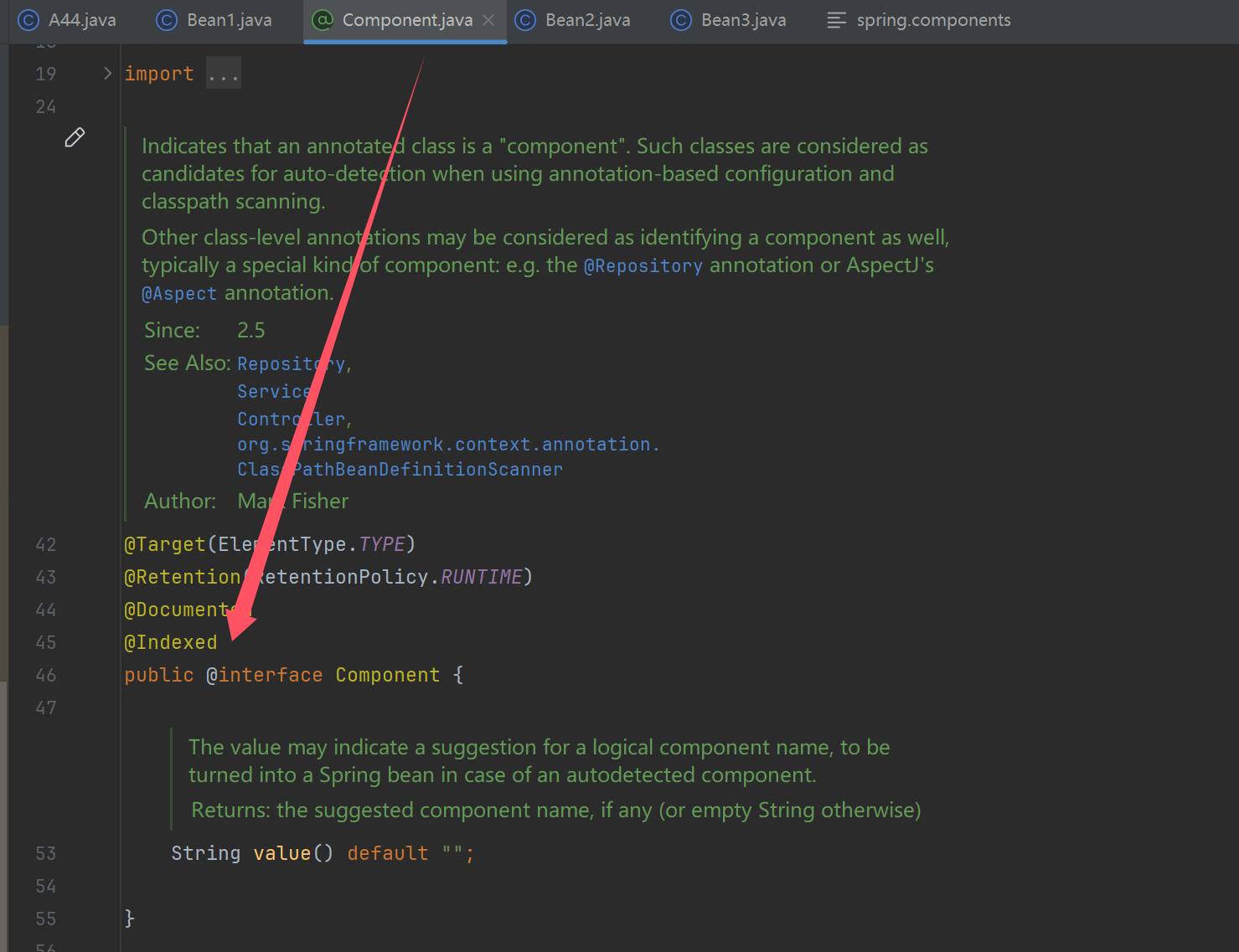
/*
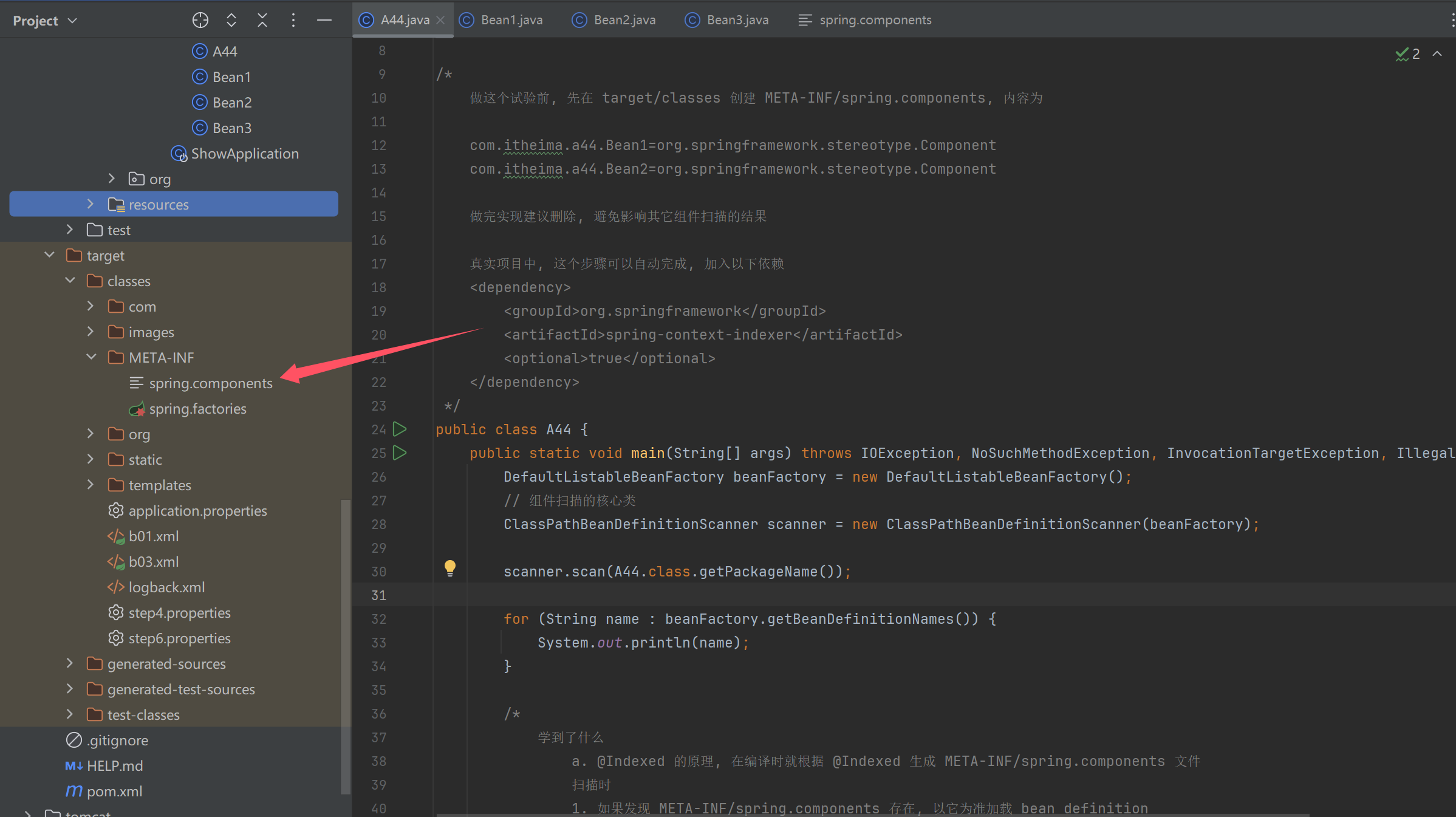
做这个试验前, 先在 target/classes 创建 META-INF/spring.components, 内容为
com.itheima.a44.Bean1=org.springframework.stereotype.Component
com.itheima.a44.Bean2=org.springframework.stereotype.Component
做完实现建议删除, 避免影响其它组件扫描的结果
真实项目中, 这个步骤可以自动完成, 加入以下依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context-indexer</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
*/
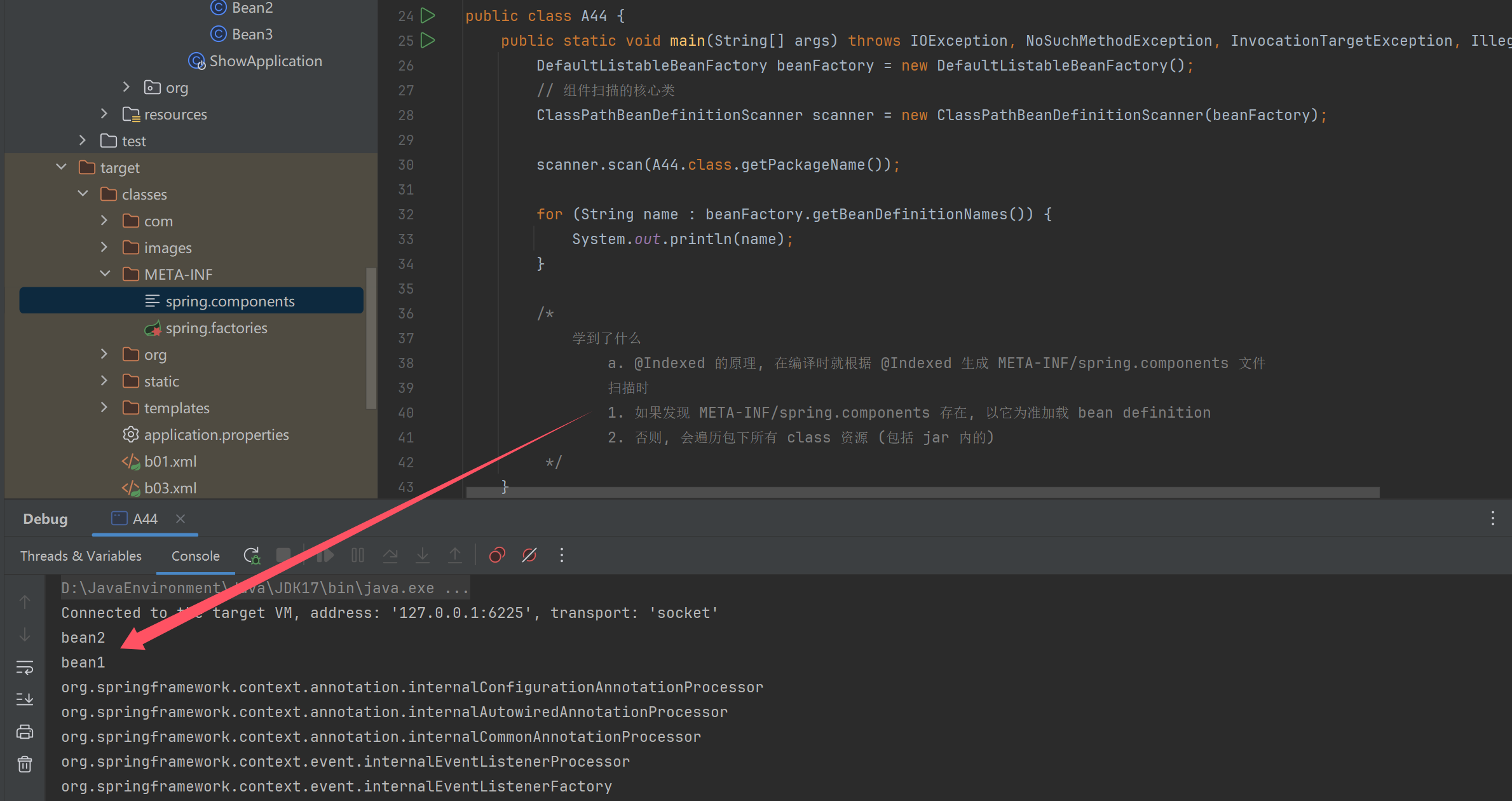
public class A44 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
// 组件扫描的核心类
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(beanFactory);
scanner.scan(A44.class.getPackageName());
for (String name : beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println(name);
}
/*
学到了什么
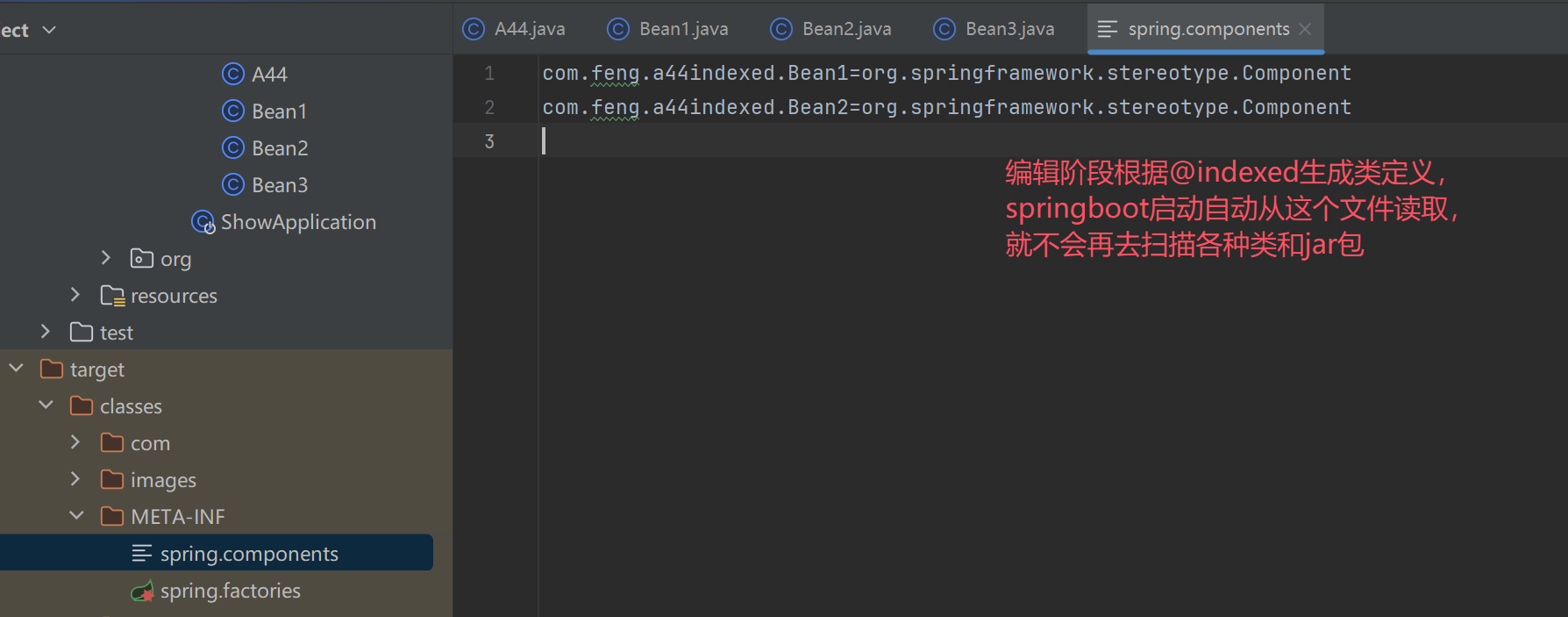
a. @Indexed 的原理, 在编译时就根据 @Indexed 生成 META-INF/spring.components 文件
扫描时
1. 如果发现 META-INF/spring.components 存在, 以它为准加载 bean definition
2. 否则, 会遍历包下所有 class 资源 (包括 jar 内的)
*/
}
}
示例代码
真实项目中,只需要加入以下依赖即可
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context-indexer</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
收获💡
- 在编译时就根据 @Indexed 生成 META-INF/spring.components 文件
- 扫描时
- 如果发现 META-INF/spring.components 存在, 以它为准加载 bean definition
- 否则, 会遍历包下所有 class 资源 (包括 jar 内的)
- 解决的问题,在编译期就找到 @Component 组件,节省运行期间扫描 @Component 的时间
2.3 代理进一步理解
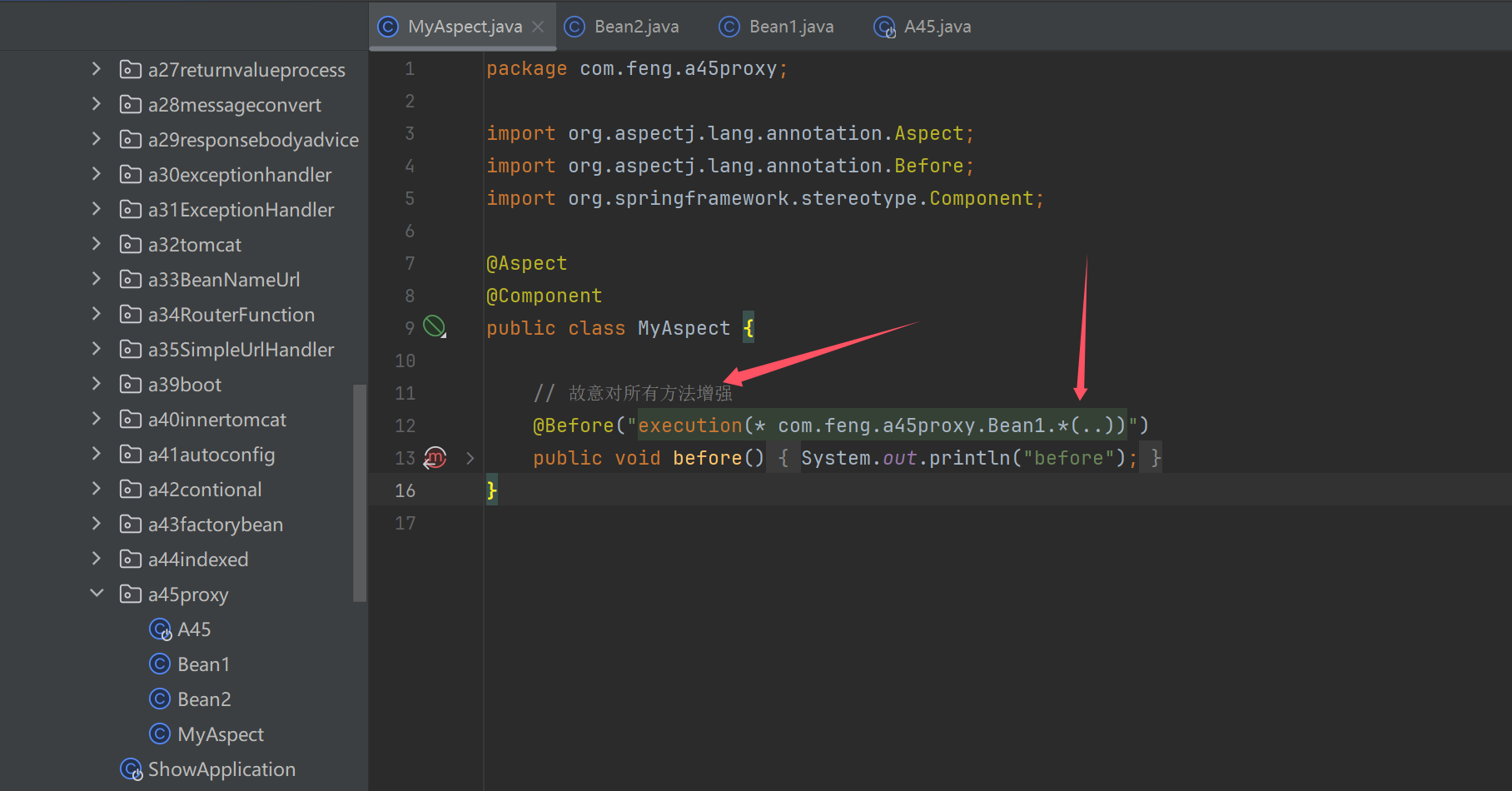
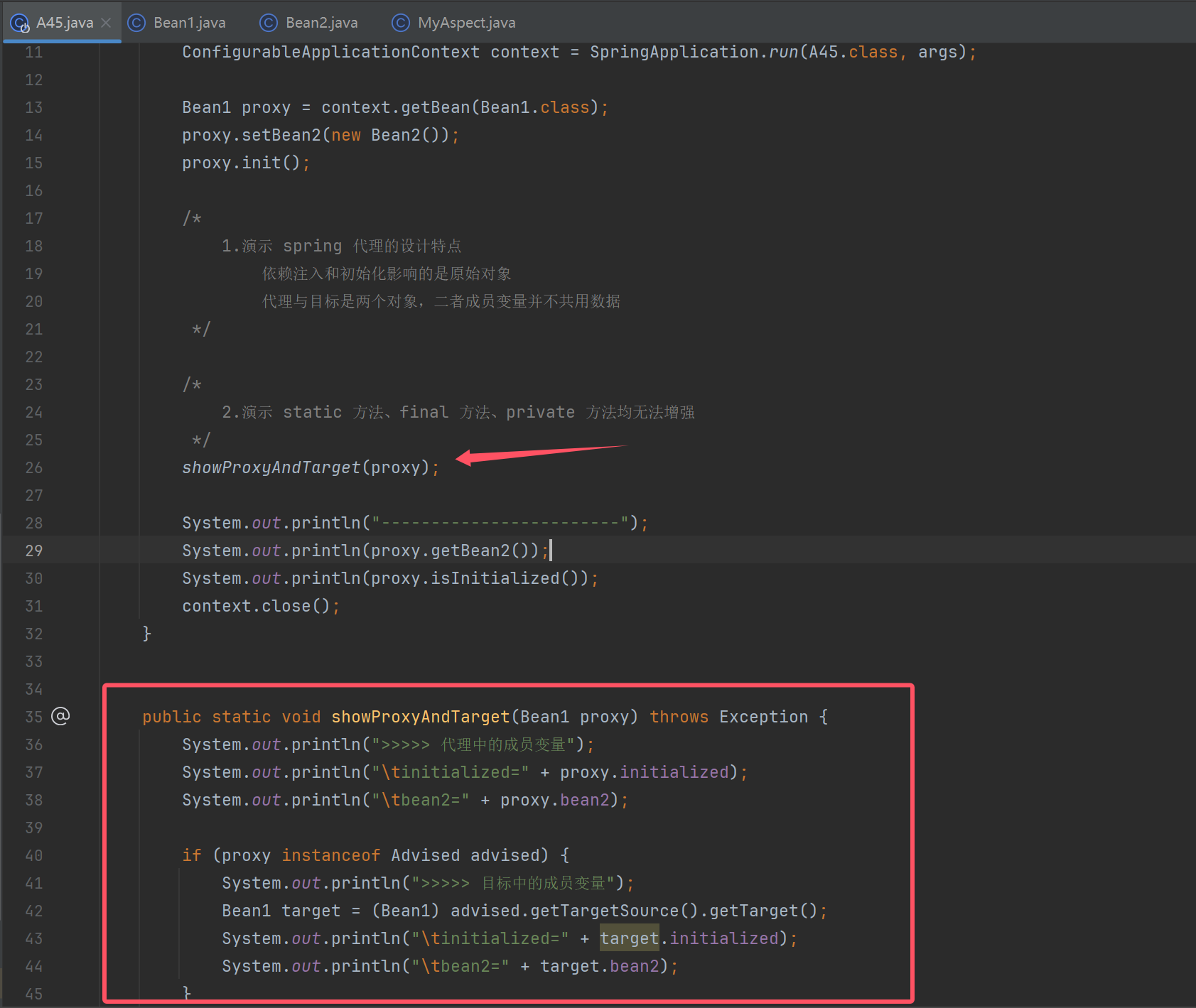
@SpringBootApplication
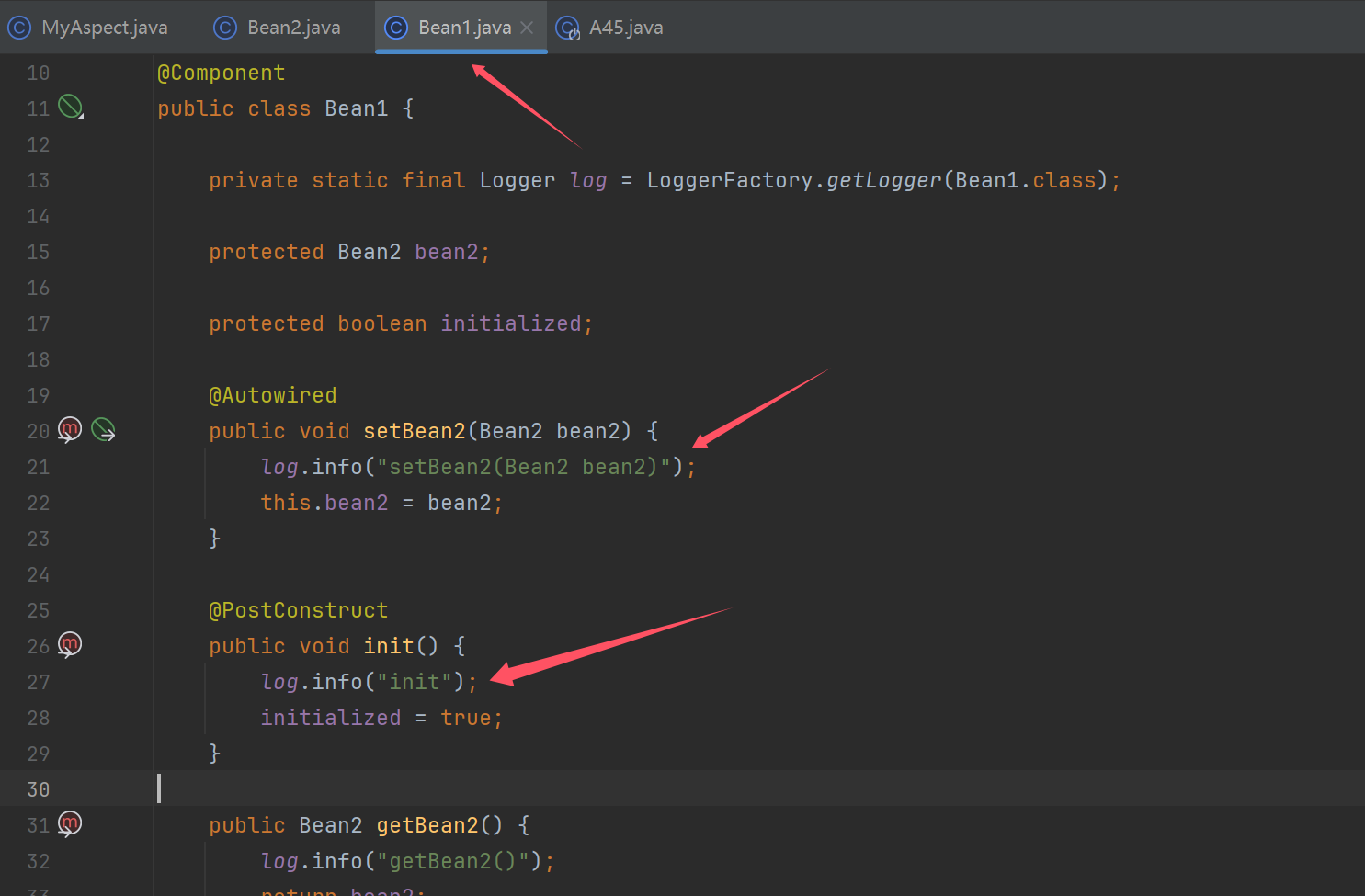
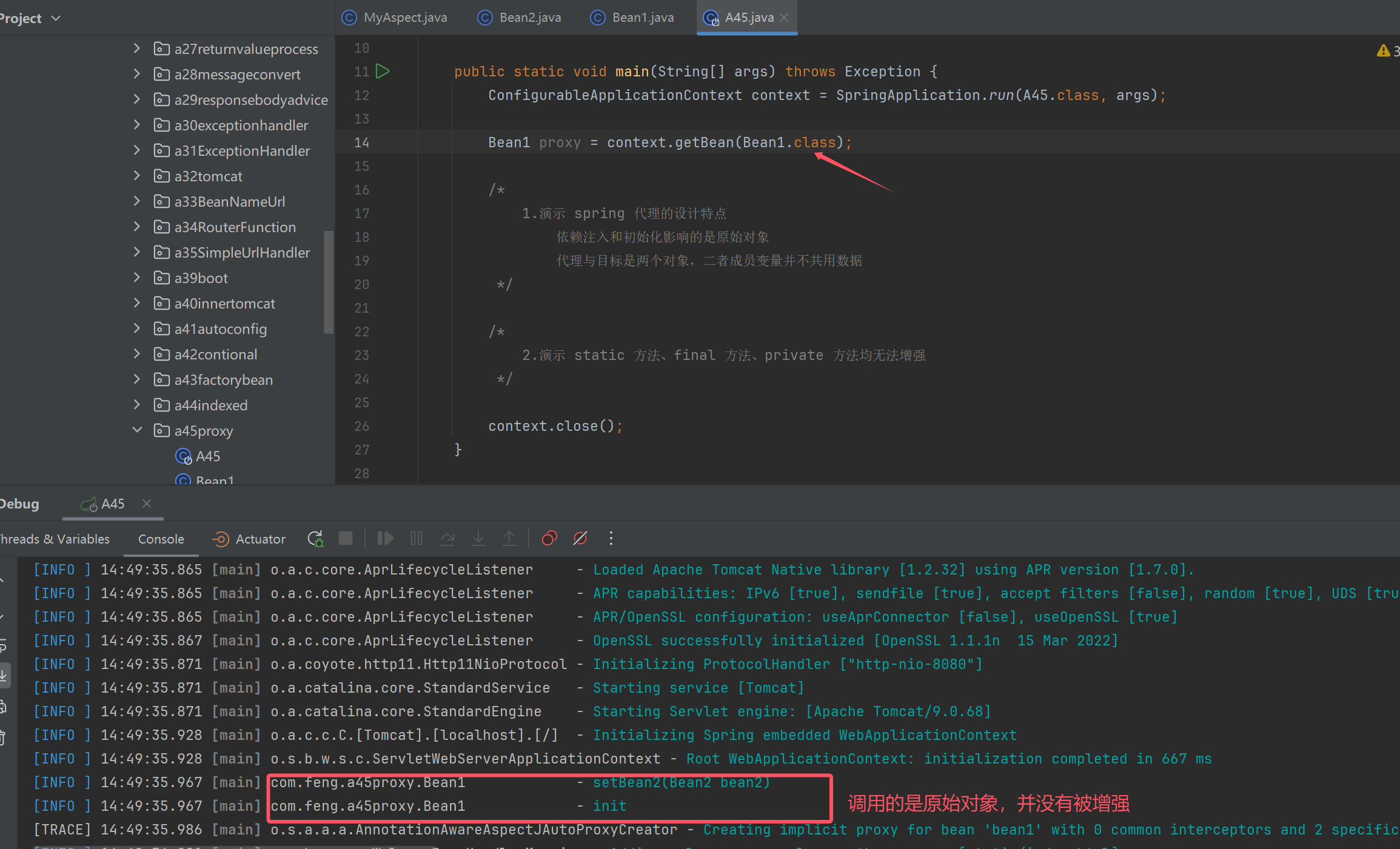
public class A45 {
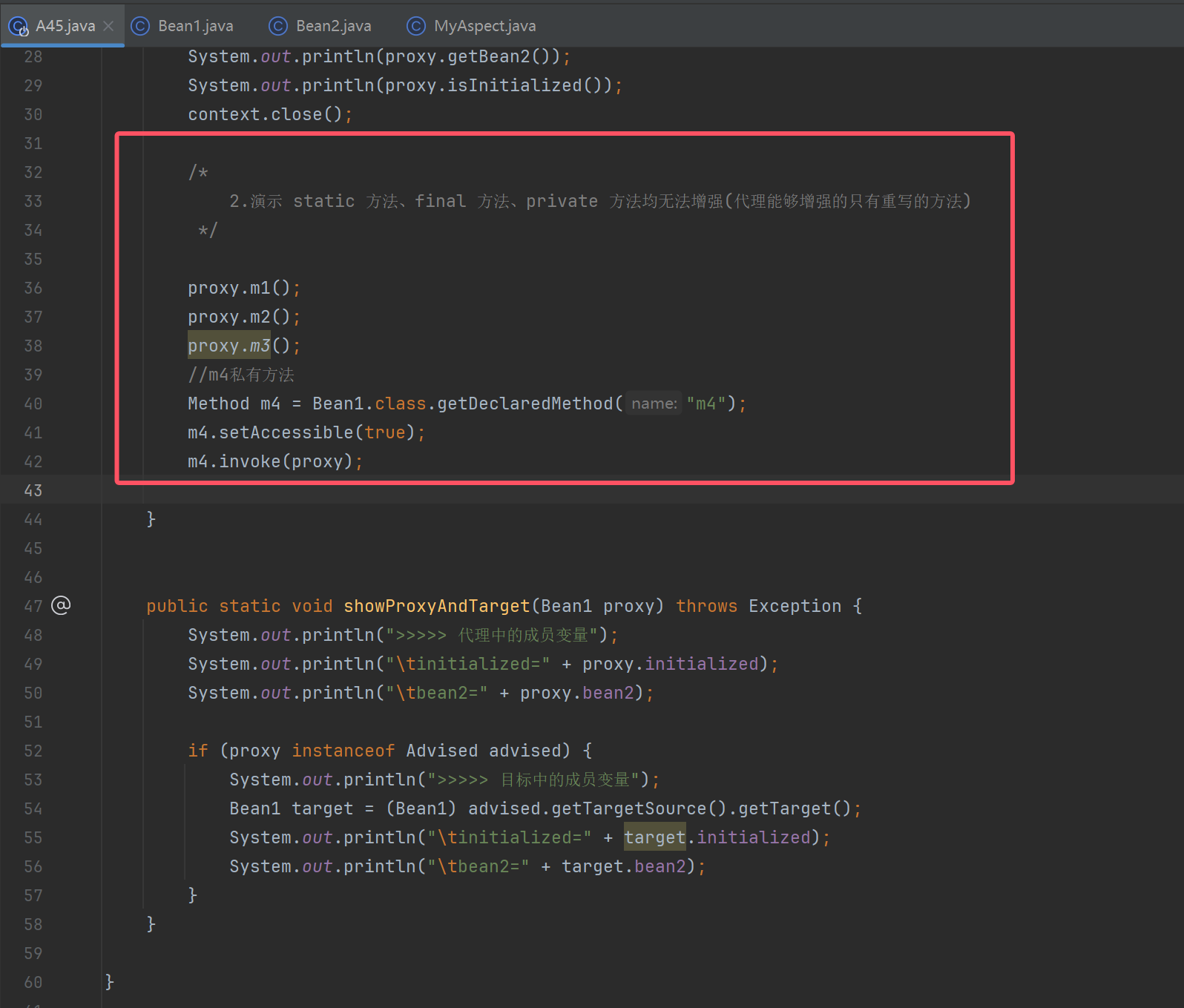
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(A45.class, args);
Bean1 proxy = context.getBean(Bean1.class);
proxy.setBean2(new Bean2());
proxy.init();
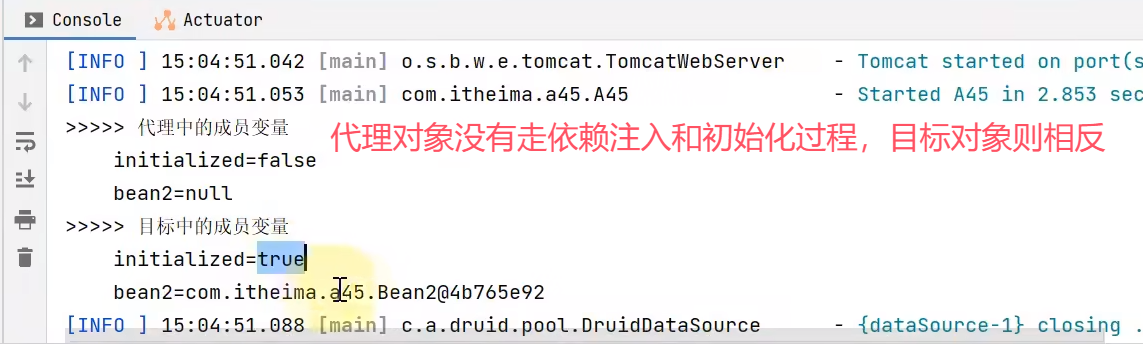
/*
1.演示 spring 代理的设计特点
依赖注入和初始化影响的是原始对象
代理与目标是两个对象,二者成员变量并不共用数据
*/
/*
2.演示 static 方法、final 方法、private 方法均无法增强
*/
showProxyAndTarget(proxy);
System.out.println("------------------------");
System.out.println(proxy.getBean2());
System.out.println(proxy.isInitialized());
context.close();
}
public static void showProxyAndTarget(Bean1 proxy) throws Exception {
System.out.println(">>>>> 代理中的成员变量");
System.out.println("\tinitialized=" + proxy.initialized);
System.out.println("\tbean2=" + proxy.bean2);
if (proxy instanceof Advised advised) {
System.out.println(">>>>> 目标中的成员变量");
Bean1 target = (Bean1) advised.getTargetSource().getTarget();
System.out.println("\tinitialized=" + target.initialized);
System.out.println("\tbean2=" + target.bean2);
}
}
}
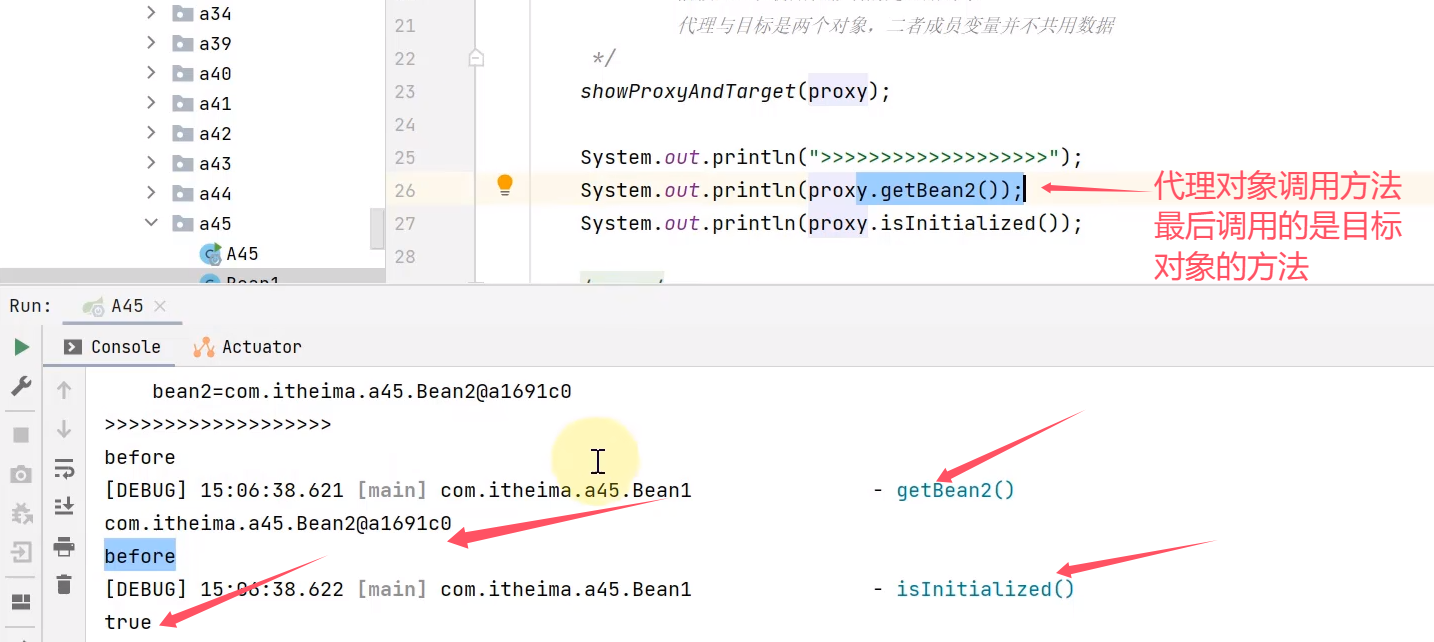
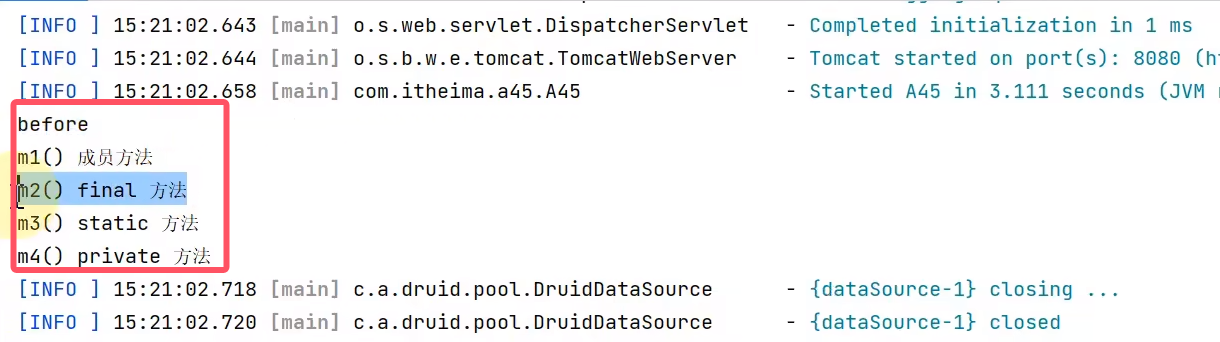
只有成员方法进行了增强
收获💡
-
spring 代理的设计特点
-
依赖注入和初始化影响的是原始对象
- 因此 cglib 不能用 MethodProxy.invokeSuper()
-
代理与目标是两个对象,二者成员变量并不共用数据
-
-
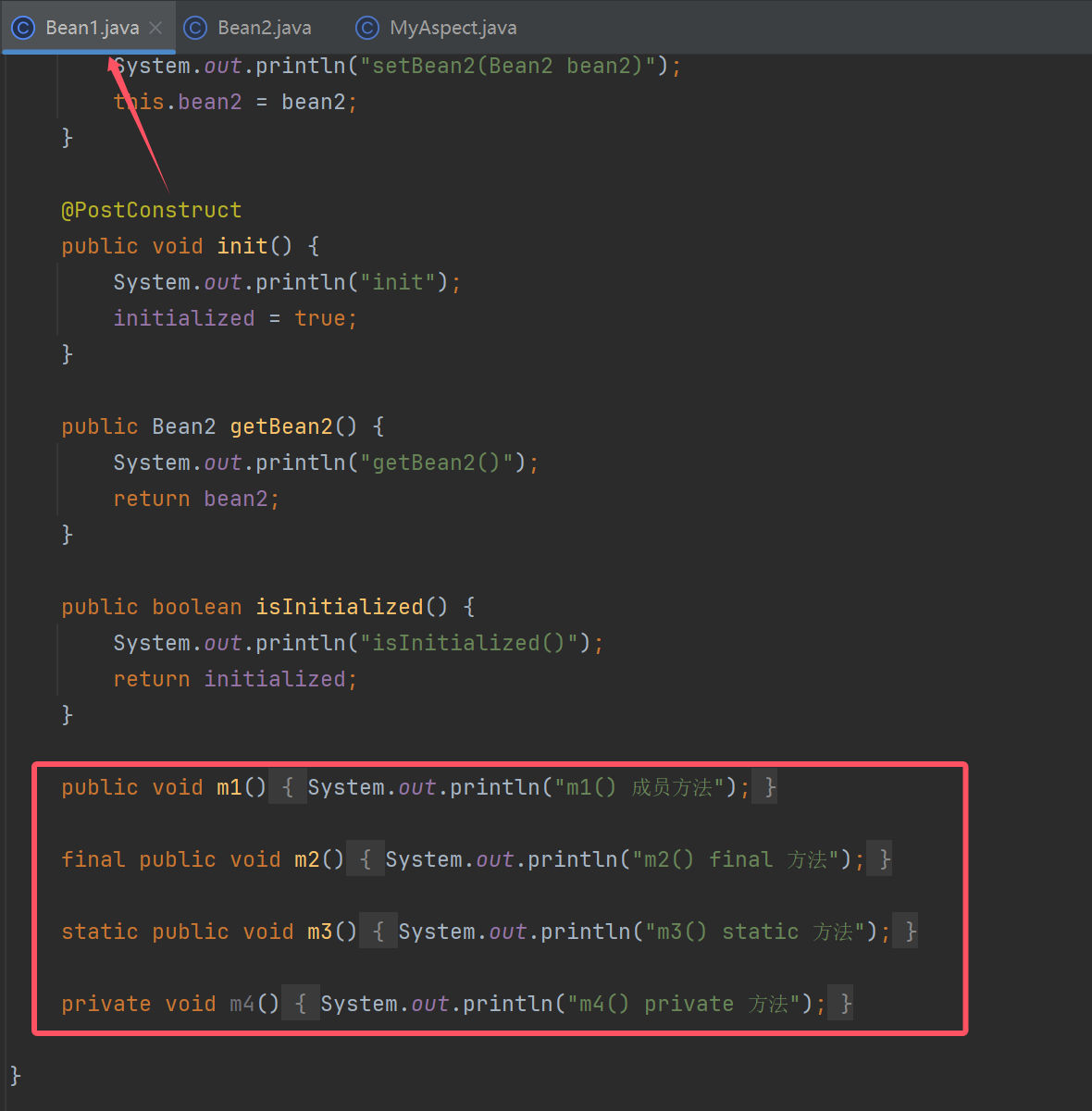
static 方法、final 方法、private 方法均无法增强
- 进一步理解代理增强基于方法重写
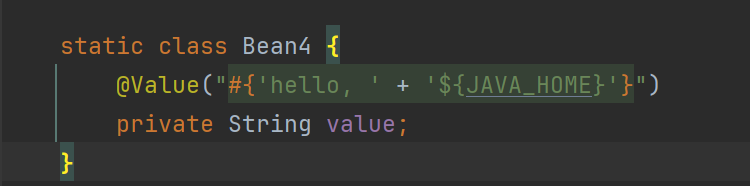
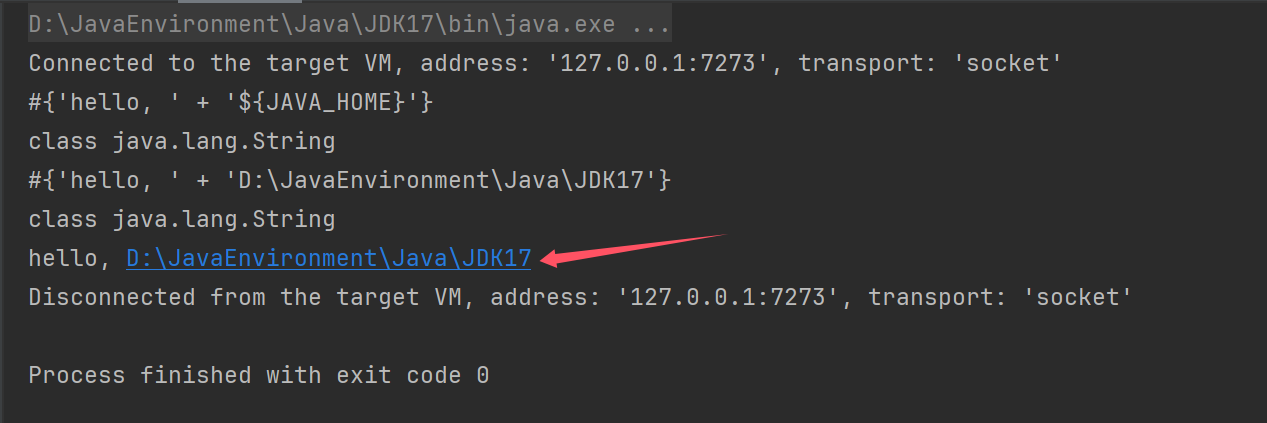
2.4 @Value 装配底层
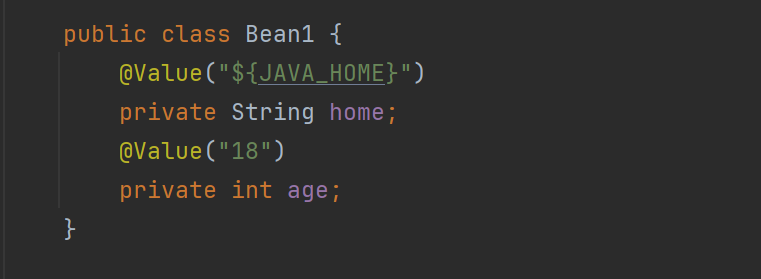
解析${}
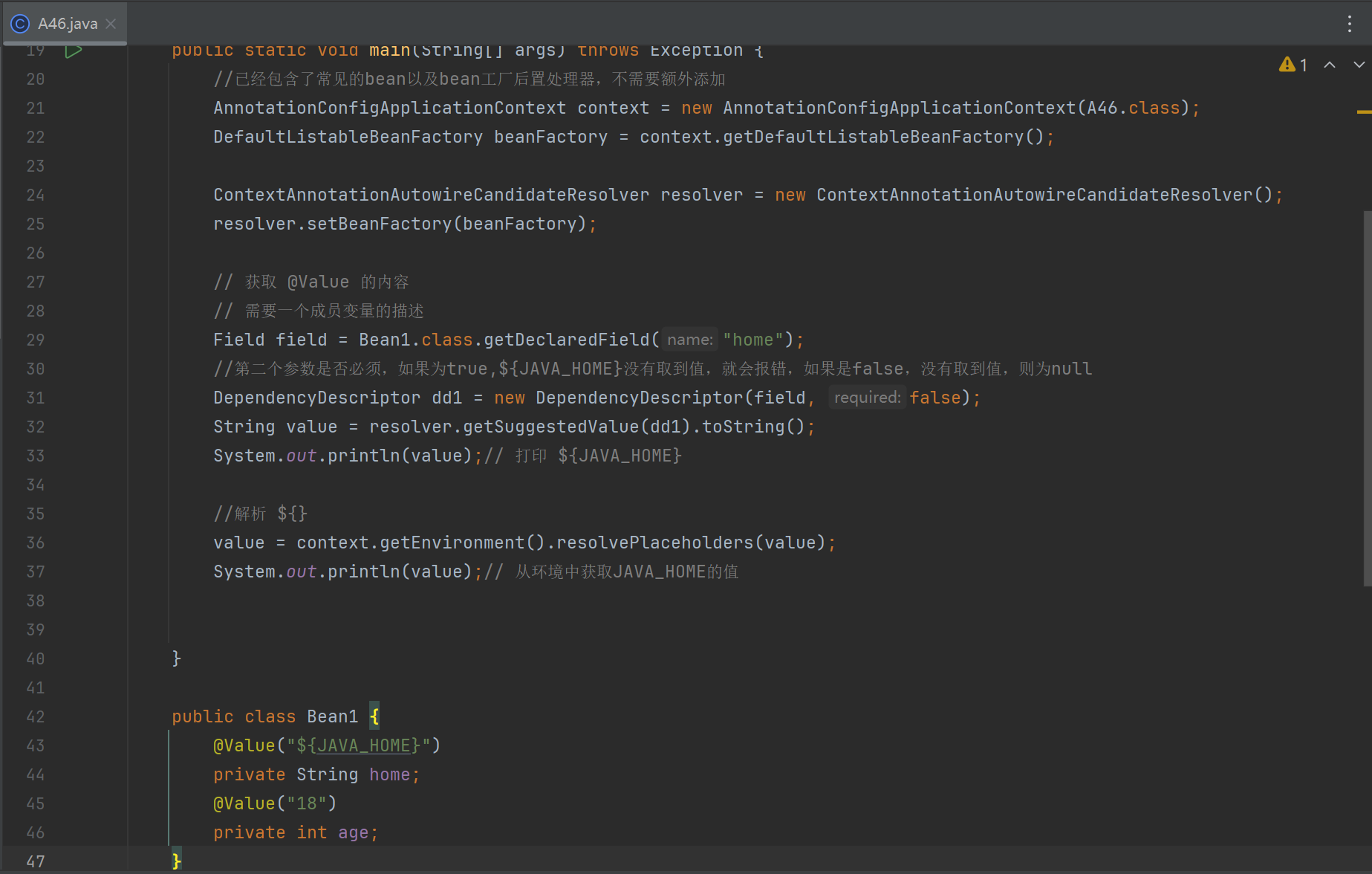
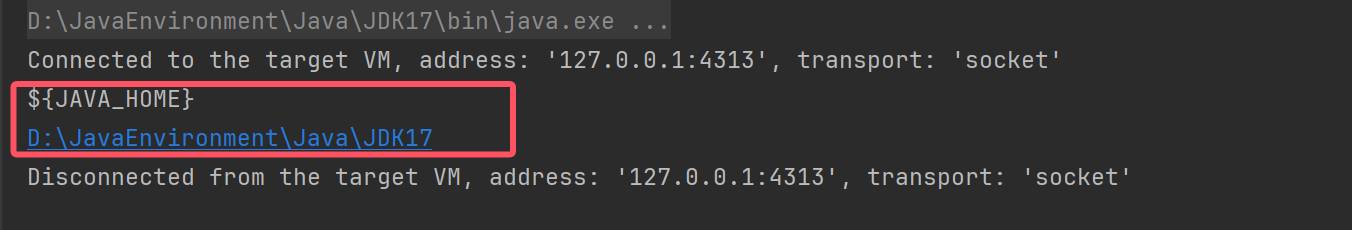
解析值类型转换
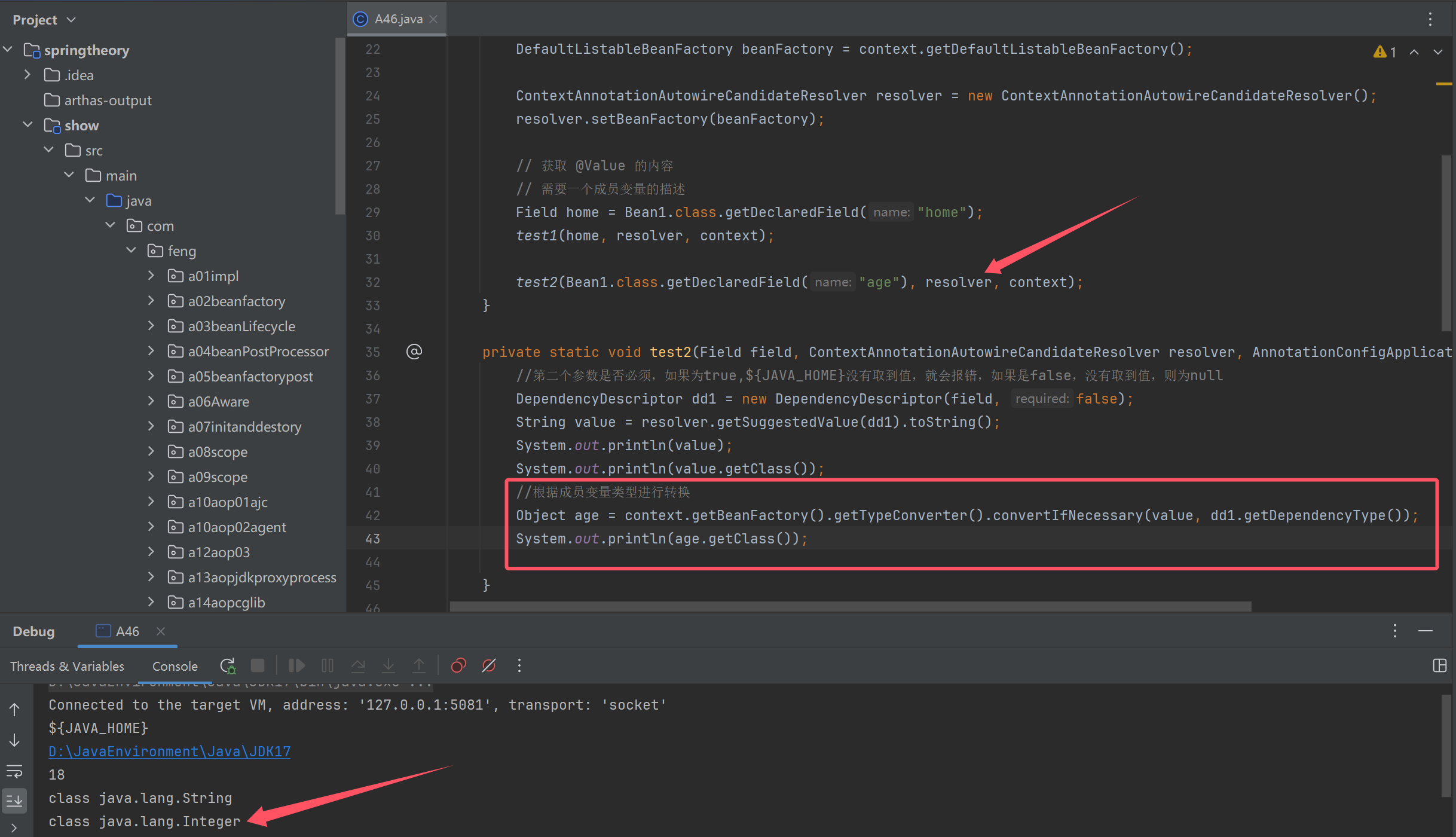
解析注入bean

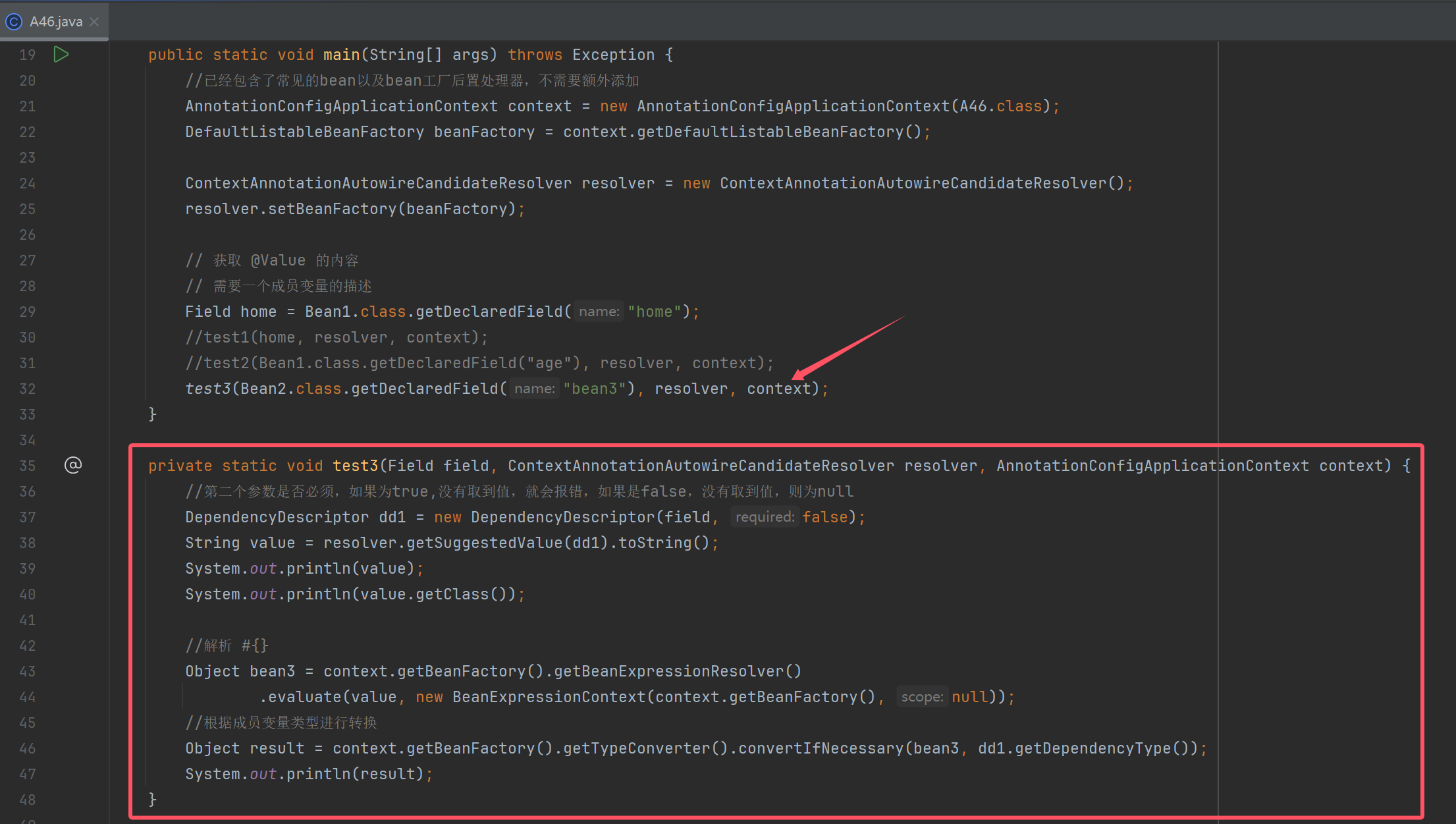
底层默认解析组合数据
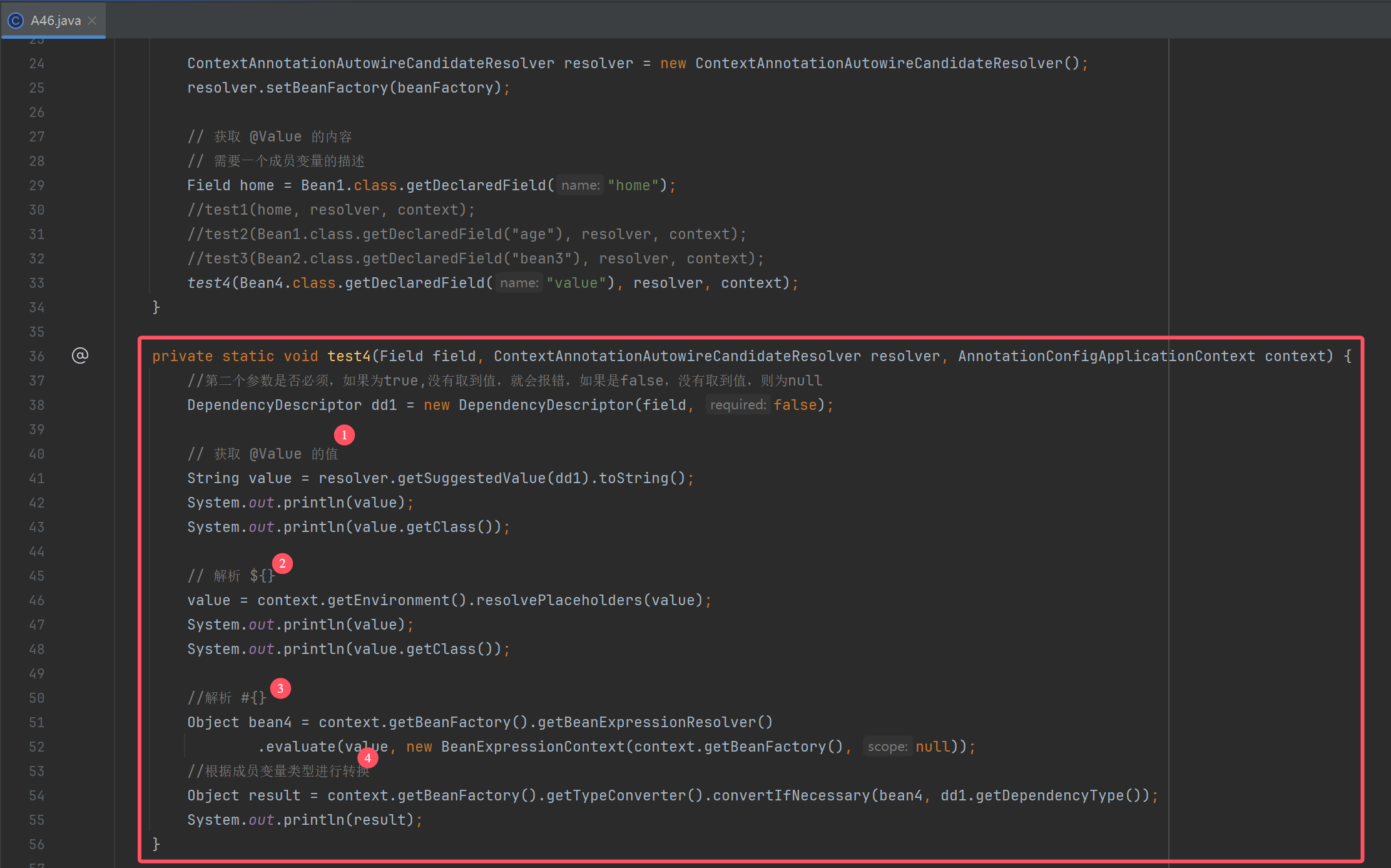
按类型装配的步骤
- 查看需要的类型是否为 Optional,是,则进行封装(非延迟),否则向下走
- 查看需要的类型是否为 ObjectFactory 或 ObjectProvider,是,则进行封装(延迟),否则向下走
- 查看需要的类型(成员或参数)上是否用 @Lazy 修饰,是,则返回代理,否则向下走
- 解析 @Value 的值
- 如果需要的值是字符串,先解析 ${ },再解析 #
- 不是字符串,需要用 TypeConverter 转换
- 看需要的类型是否为 Stream、Array、Collection、Map,是,则按集合处理,否则向下走
- 在 BeanFactory 的 resolvableDependencies 中找有没有类型合适的对象注入,没有向下走
- 在 BeanFactory 及父工厂中找类型匹配的 bean 进行筛选,筛选时会考虑 @Qualifier 及泛型
- 结果个数为 0 抛出 NoSuchBeanDefinitionException 异常
- 如果结果 > 1,再根据 @Primary 进行筛选
- 如果结果仍 > 1,再根据成员名或变量名进行筛选
- 结果仍 > 1,抛出 NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException 异常
收获💡
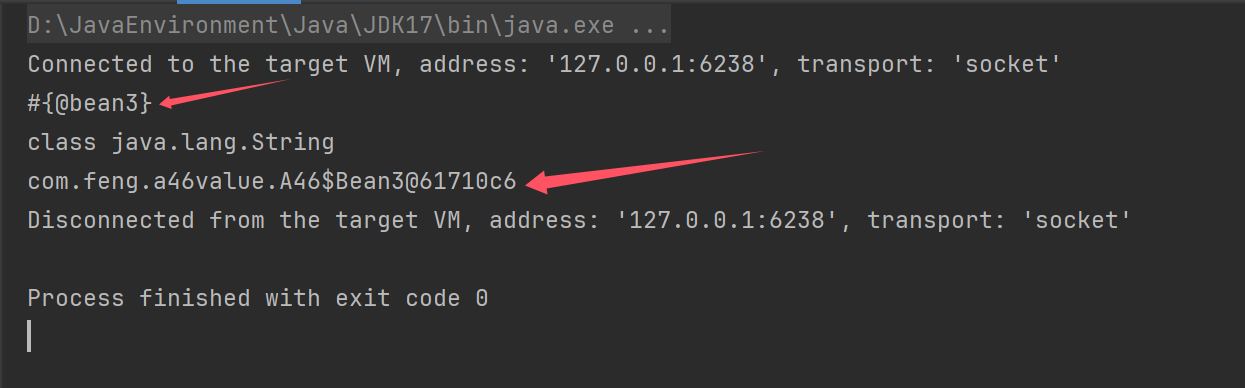
- ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver 作用之一,获取 @Value 的值
- 了解 ${ } 对应的解析器
- 了解 #{ } 对应的解析器
- TypeConvert 的一项体现
2.5 @Autowired 装配底层
演示 - @Autowired 装配过程
根据成员变量的类型注入
根据参数的类型注入
结果包装为 Optional
结果包装为 ObjectProvider,ObjectFactory
对 @Lazy 的处理
@Configuration
public class A47_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, NoSuchMethodException {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(A47_1.class);
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getDefaultListableBeanFactory();
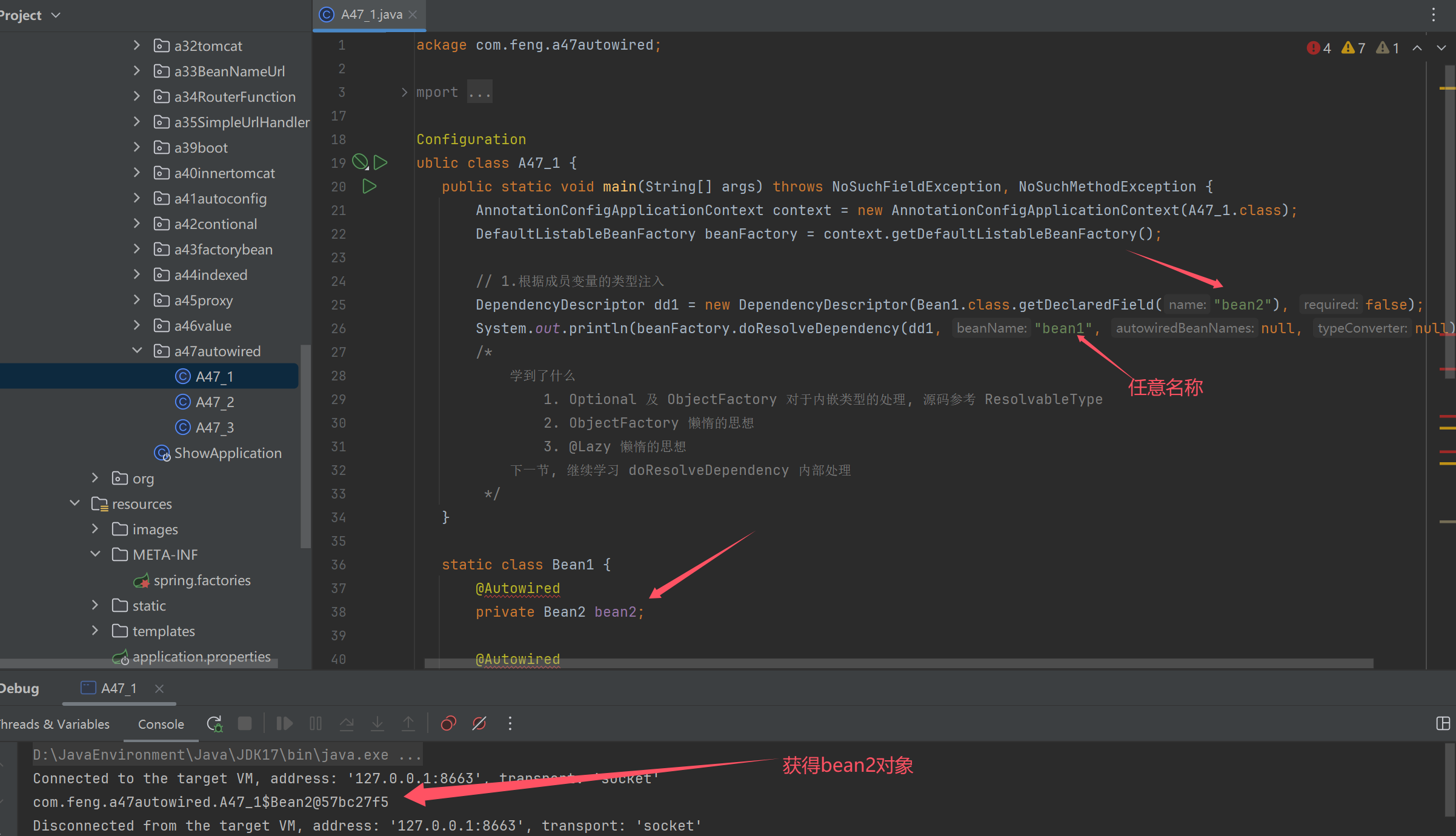
// 1.根据成员变量的类型注入
DependencyDescriptor dd1 = new DependencyDescriptor(Bean1.class.getDeclaredField("bean2"), false);
System.out.println(beanFactory.doResolveDependency(dd1, "bean1", null, null));
System.out.println("------------------------");
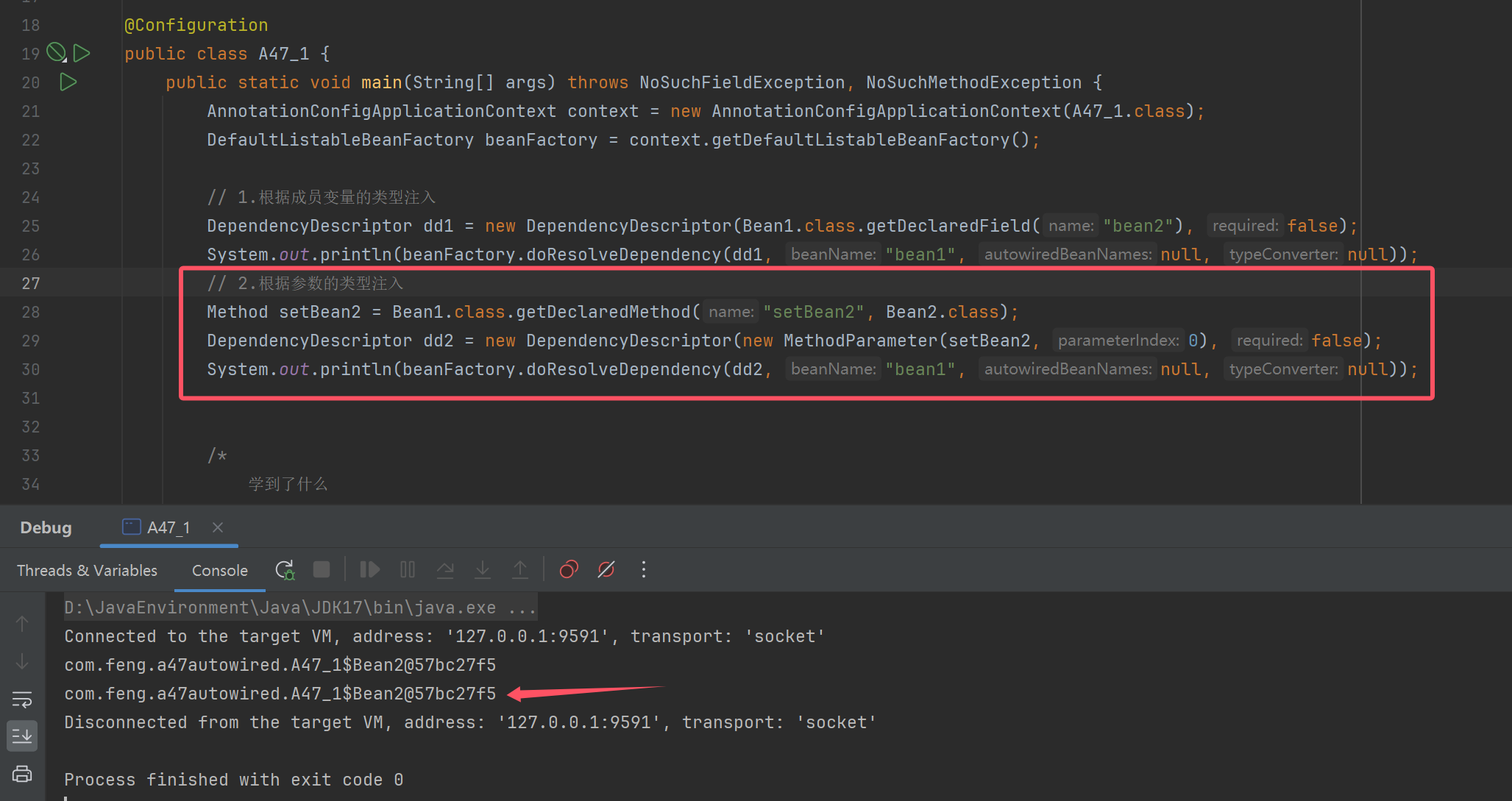
// 2.根据参数的类型注入
Method setBean2 = Bean1.class.getDeclaredMethod("setBean2", Bean2.class);
DependencyDescriptor dd2 = new DependencyDescriptor(new MethodParameter(setBean2, 0), false);
System.out.println(beanFactory.doResolveDependency(dd2, "bean1", null, null));
System.out.println("------------------------");
// 3.结果包装为 Optional<Bean2>
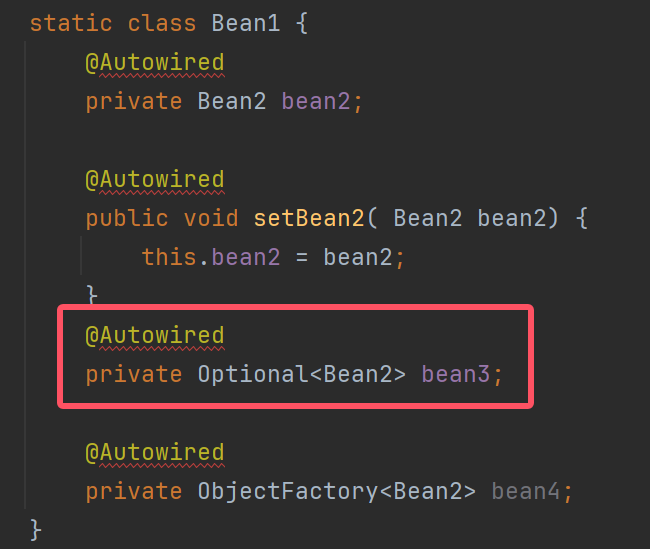
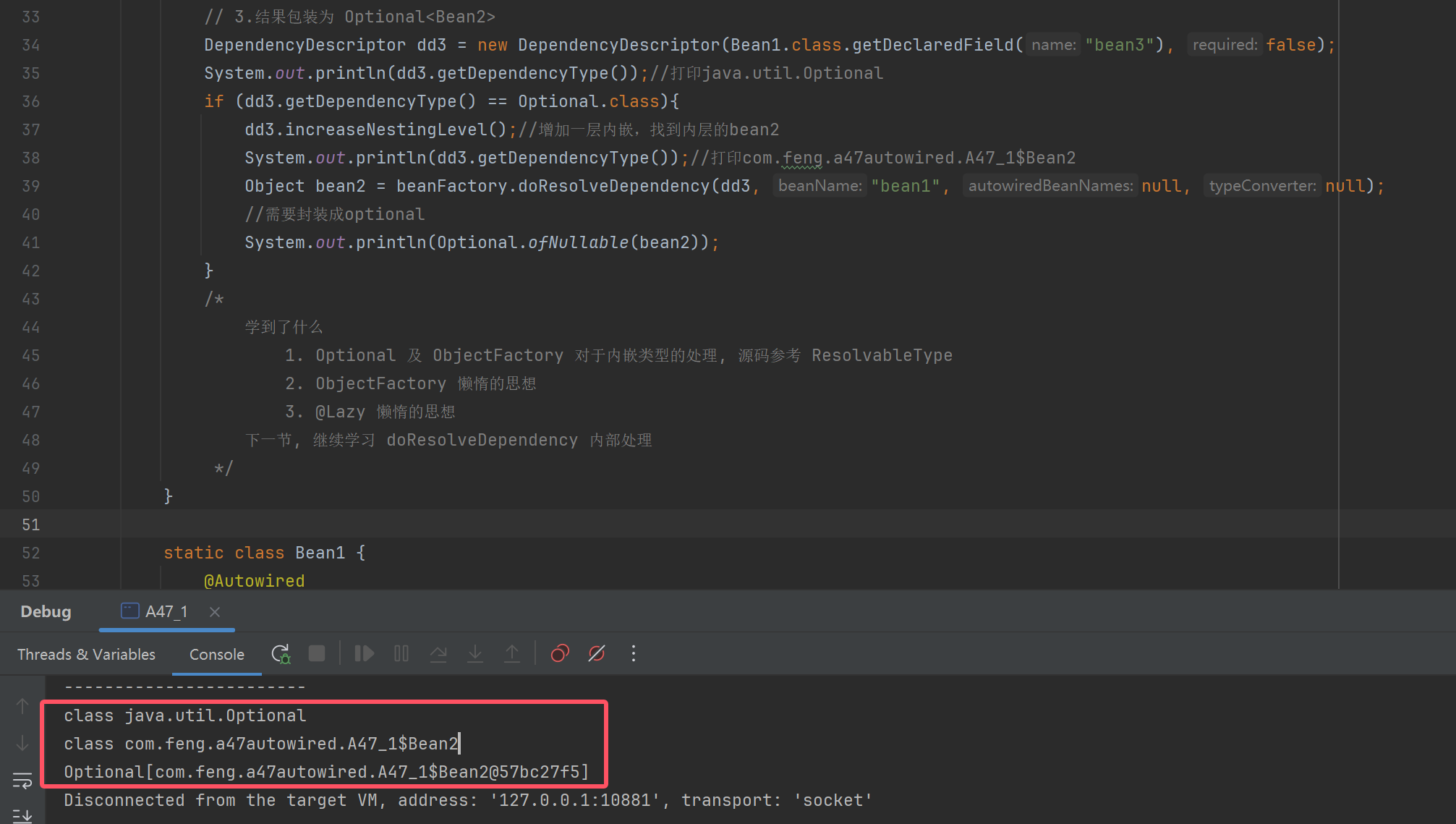
DependencyDescriptor dd3 = new DependencyDescriptor(Bean1.class.getDeclaredField("bean3"), false);
System.out.println(dd3.getDependencyType());//打印java.util.Optional
if (dd3.getDependencyType() == Optional.class){
dd3.increaseNestingLevel();//增加一层内嵌,找到内层的bean2
System.out.println(dd3.getDependencyType());//打印com.feng.a47autowired.A47_1$Bean2
Object bean2 = beanFactory.doResolveDependency(dd3, "bean1", null, null);
//需要封装成optional
System.out.println(Optional.ofNullable(bean2));
}
System.out.println("------------------------");
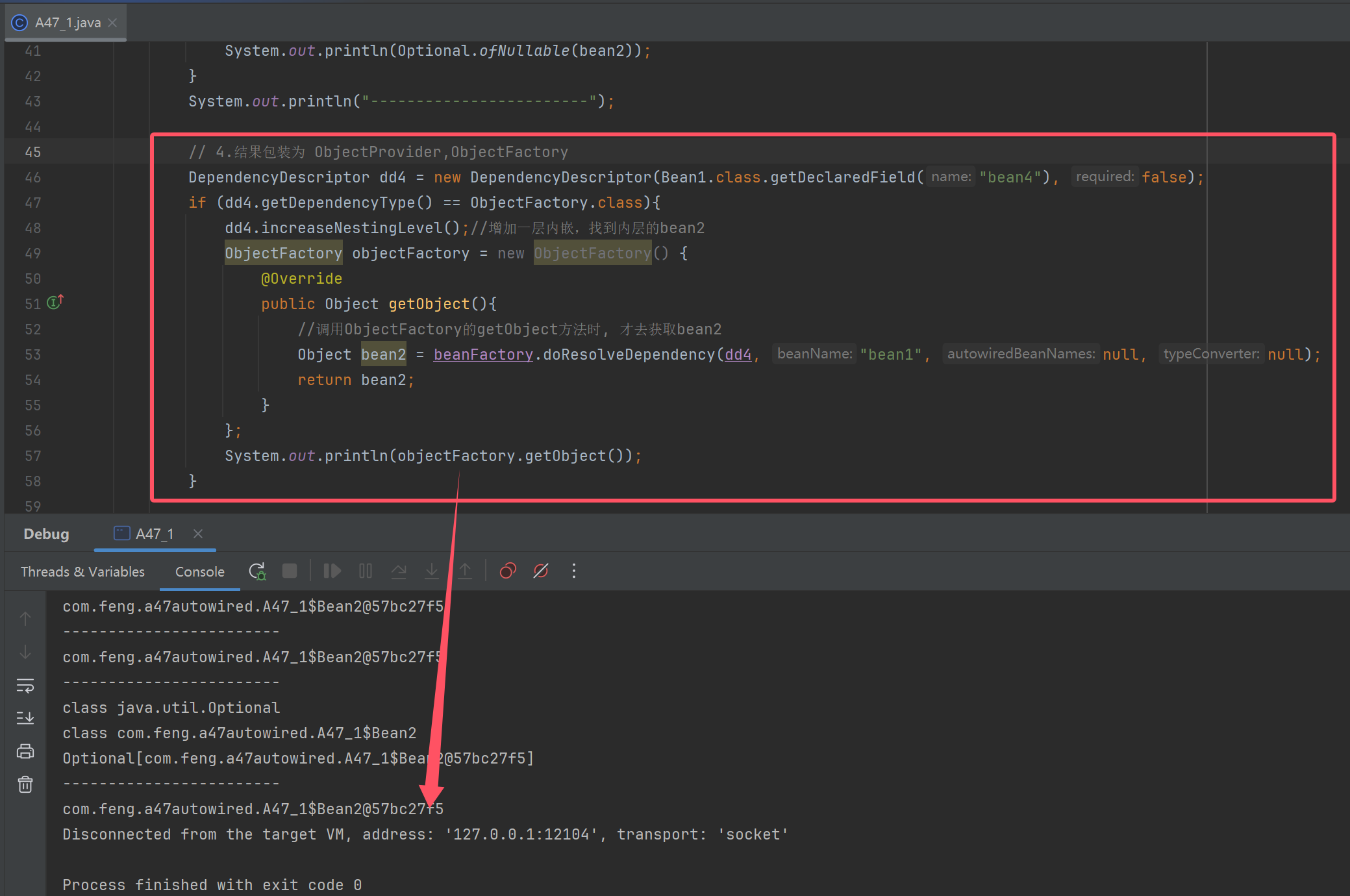
// 4.结果包装为 ObjectProvider,ObjectFactory
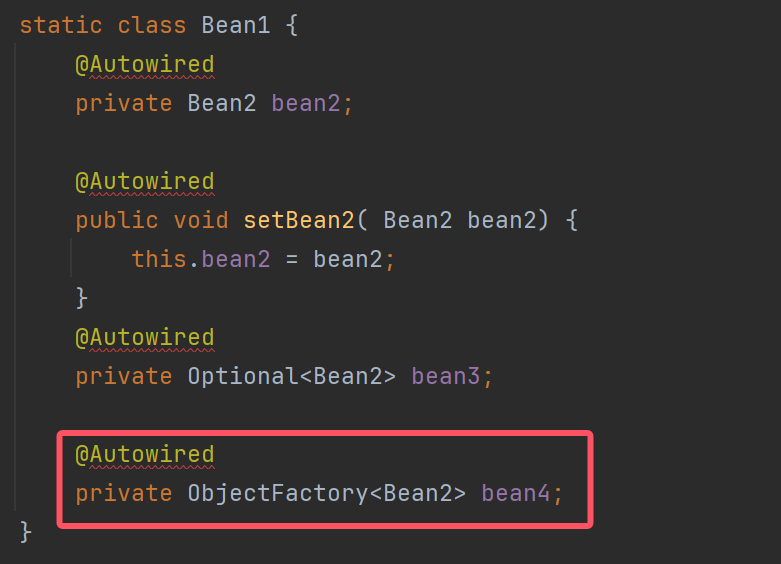
DependencyDescriptor dd4 = new DependencyDescriptor(Bean1.class.getDeclaredField("bean4"), false);
if (dd4.getDependencyType() == ObjectFactory.class){
dd4.increaseNestingLevel();//增加一层内嵌,找到内层的bean2
ObjectFactory objectFactory = new ObjectFactory() {
@Override
public Object getObject(){
//调用ObjectFactory的getObject方法时, 才去获取bean2
Object bean2 = beanFactory.doResolveDependency(dd4, "bean1", null, null);
return bean2;
}
};
System.out.println(objectFactory.getObject());
}
System.out.println("------------------------");
// 5. 对 @Lazy 的处理
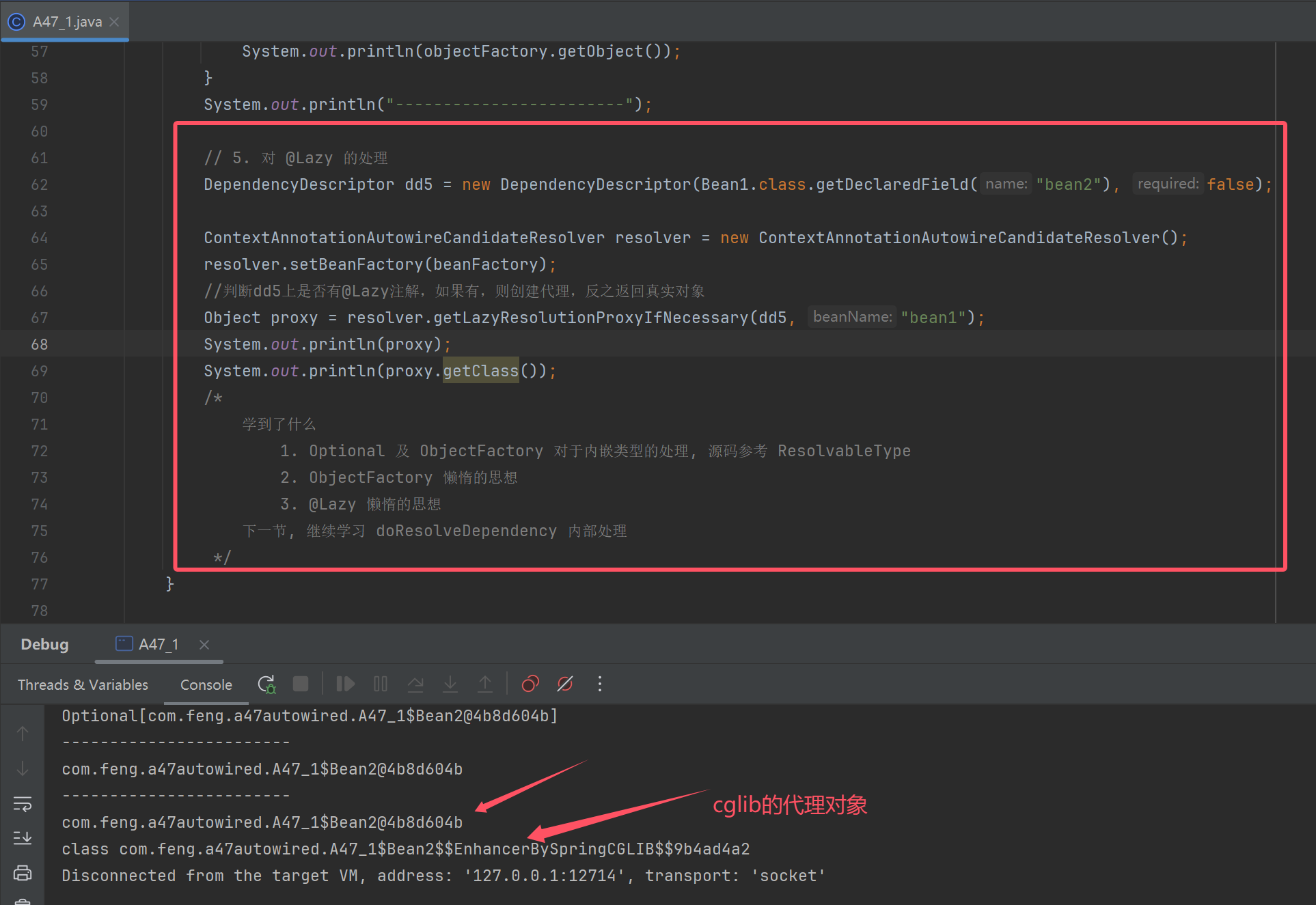
DependencyDescriptor dd5 = new DependencyDescriptor(Bean1.class.getDeclaredField("bean2"), false);
ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver resolver = new ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver();
resolver.setBeanFactory(beanFactory);
//判断dd5上是否有@Lazy注解,如果有,则创建代理,反之返回真实对象
Object proxy = resolver.getLazyResolutionProxyIfNecessary(dd5, "bean1");
System.out.println(proxy);
System.out.println(proxy.getClass());
/*
学到了什么
1. Optional 及 ObjectFactory 对于内嵌类型的处理, 源码参考 ResolvableType
2. ObjectFactory 懒惰的思想
3. @Lazy 懒惰的思想
下一节, 继续学习 doResolveDependency 内部处理
*/
}
static class Bean1 {
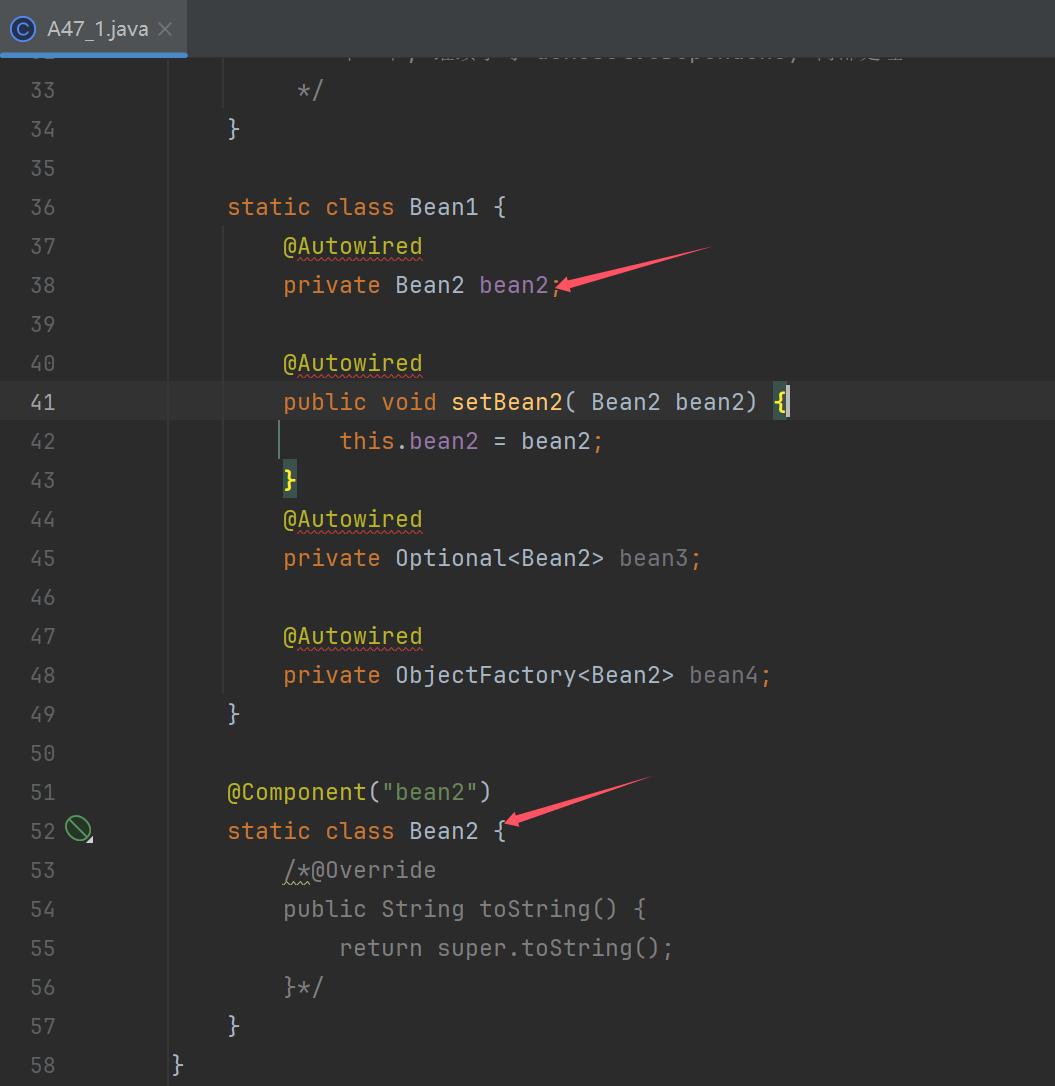
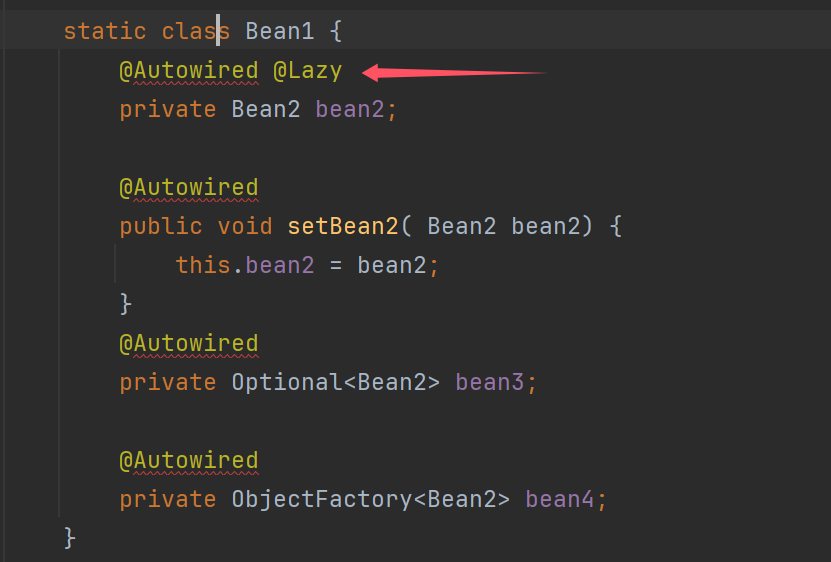
@Autowired @Lazy
private Bean2 bean2;
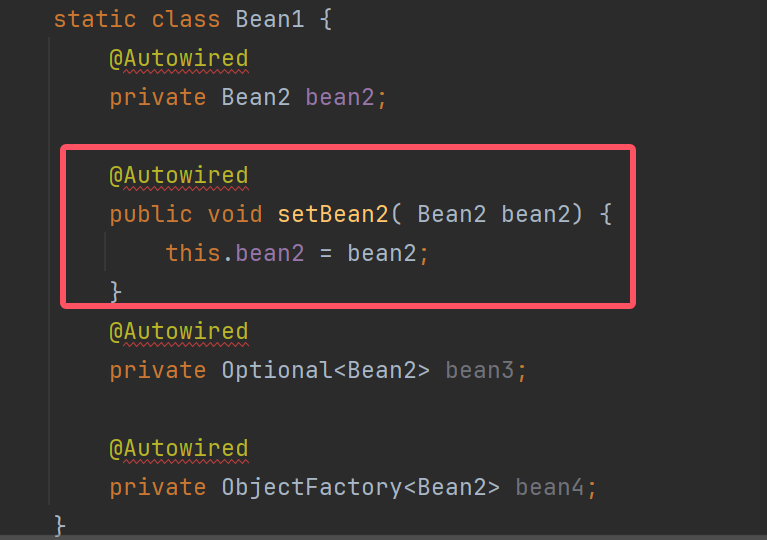
@Autowired
public void setBean2( Bean2 bean2) {
this.bean2 = bean2;
}
@Autowired
private Optional<Bean2> bean3;
@Autowired
private ObjectFactory<Bean2> bean4;
}
@Component("bean2")
static class Bean2 {
/*@Override
public String toString() {
return super.toString();
}*/
}
}
对数组的处理
对集合的处理
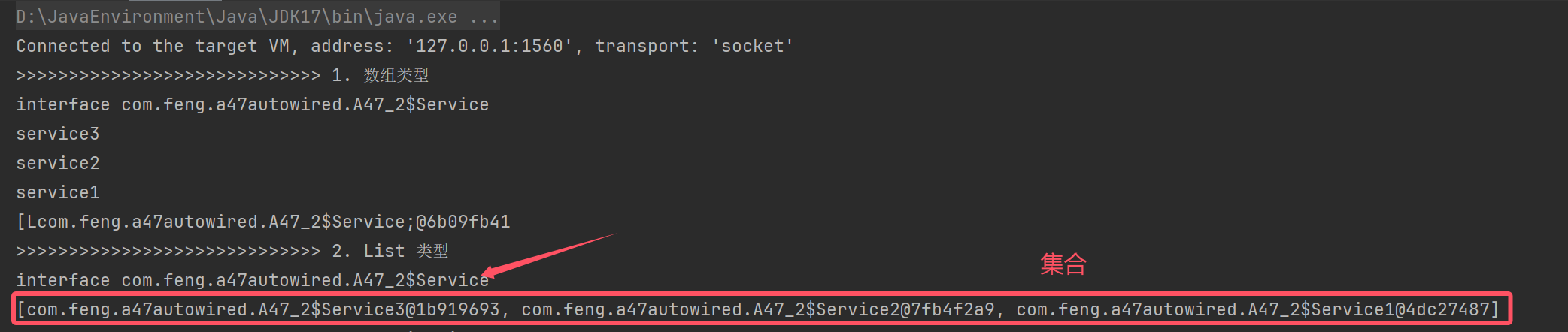
处理ApplicationContext 等特殊类型
处理类型有泛型参数
处理类型有 @Qualifier
@Configuration
public class A47_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(A47_2.class);
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getDefaultListableBeanFactory();
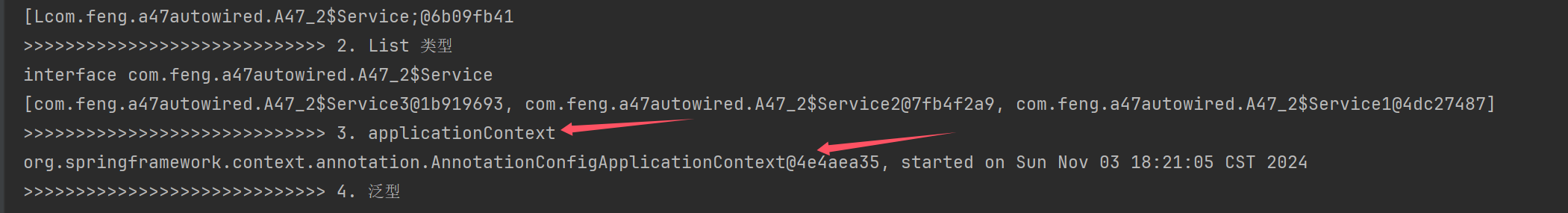
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 1. 数组类型");
testArray(beanFactory);
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 2. List 类型");
testList(beanFactory);
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 3. applicationContext");
testApplicationContext(beanFactory);
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 4. 泛型");
testGeneric(beanFactory);
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 5. @Qualifier");
testQualifier(beanFactory);
/*
学到了什么
1. 如何获取数组元素类型
2. Spring 如何获取泛型中的类型
3. 特殊对象的处理, 如 ApplicationContext, 并注意 Map 取值时的类型匹配问题 (另见 TestMap)
4. 谁来进行泛型匹配 (另见 TestGeneric)
5. 谁来处理 @Qualifier
6. 刚开始都只是按名字处理, 等候选者确定了, 才会创建实例
*/
}
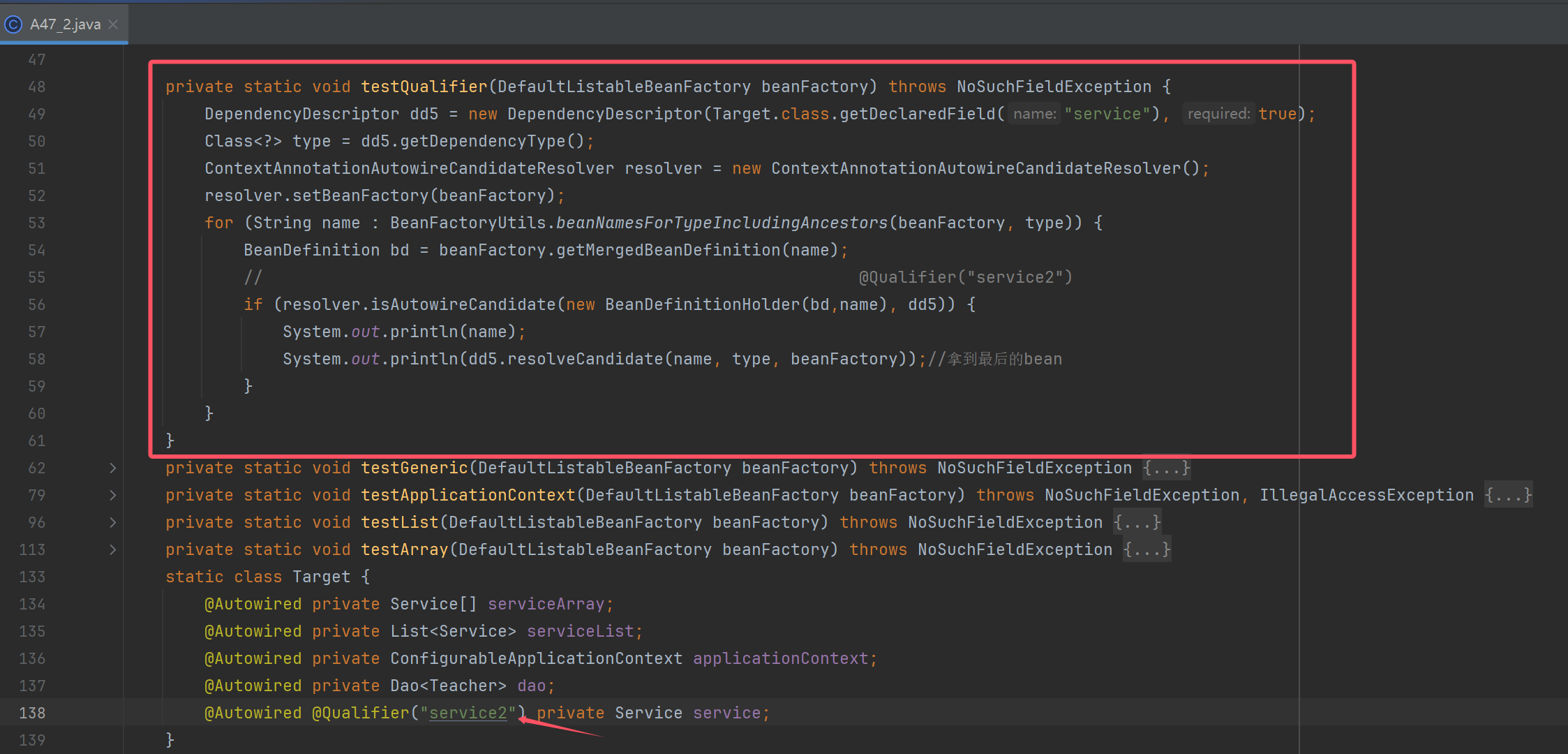
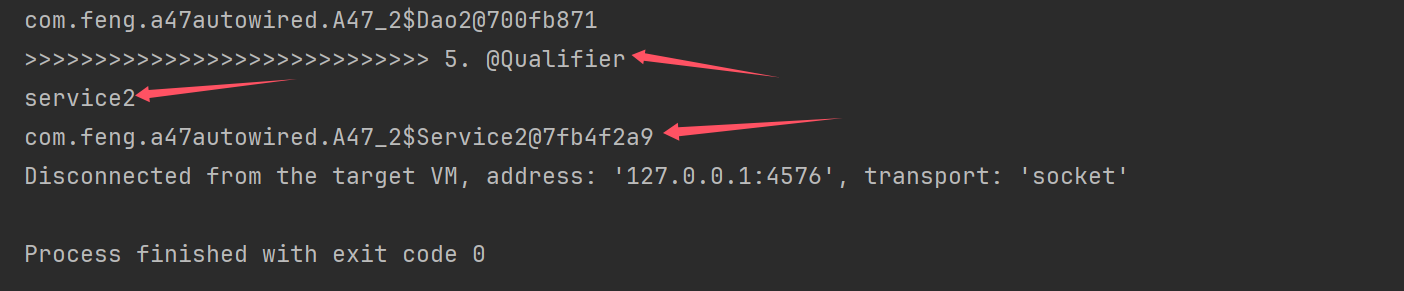
private static void testQualifier(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws NoSuchFieldException {
DependencyDescriptor dd5 = new DependencyDescriptor(Target.class.getDeclaredField("service"), true);
Class<?> type = dd5.getDependencyType();
ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver resolver = new ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver();
resolver.setBeanFactory(beanFactory);
for (String name : BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(beanFactory, type)) {
BeanDefinition bd = beanFactory.getMergedBeanDefinition(name);
// @Qualifier("service2")
if (resolver.isAutowireCandidate(new BeanDefinitionHolder(bd,name), dd5)) {
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(dd5.resolveCandidate(name, type, beanFactory));//拿到最后的bean
}
}
}
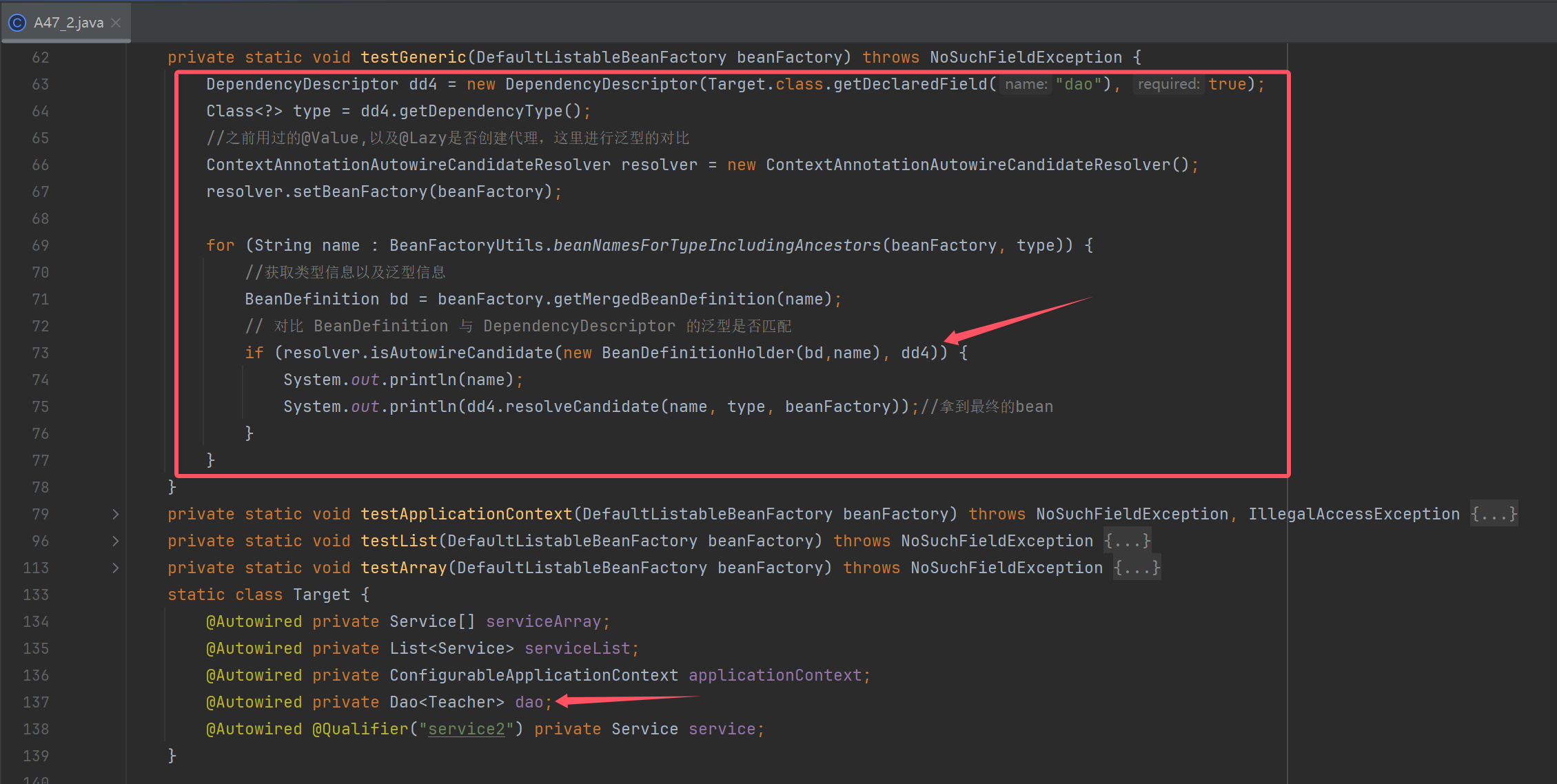
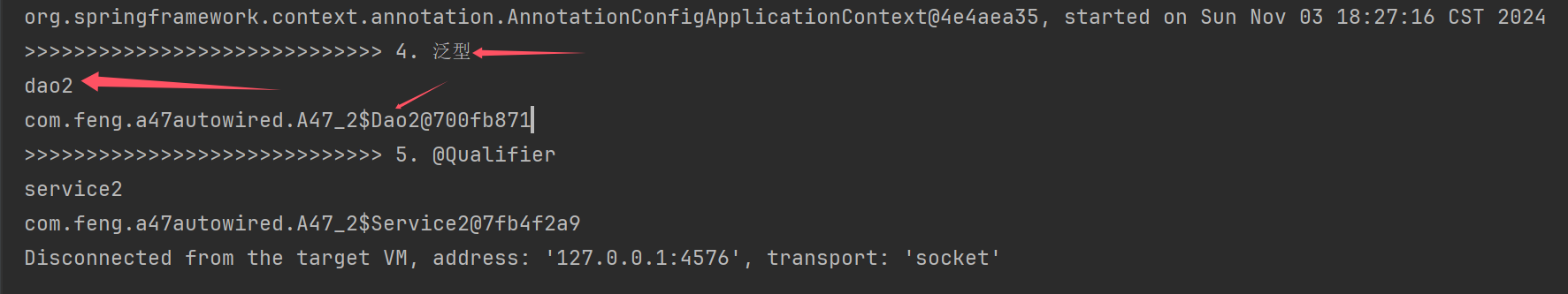
private static void testGeneric(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws NoSuchFieldException {
DependencyDescriptor dd4 = new DependencyDescriptor(Target.class.getDeclaredField("dao"), true);
Class<?> type = dd4.getDependencyType();
//之前用过的@Value,以及@Lazy是否创建代理,这里进行泛型的对比
ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver resolver = new ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver();
resolver.setBeanFactory(beanFactory);
for (String name : BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(beanFactory, type)) {
//获取类型信息以及泛型信息
BeanDefinition bd = beanFactory.getMergedBeanDefinition(name);
// 对比 BeanDefinition 与 DependencyDescriptor 的泛型是否匹配
if (resolver.isAutowireCandidate(new BeanDefinitionHolder(bd,name), dd4)) {
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(dd4.resolveCandidate(name, type, beanFactory));//拿到最终的bean
}
}
}
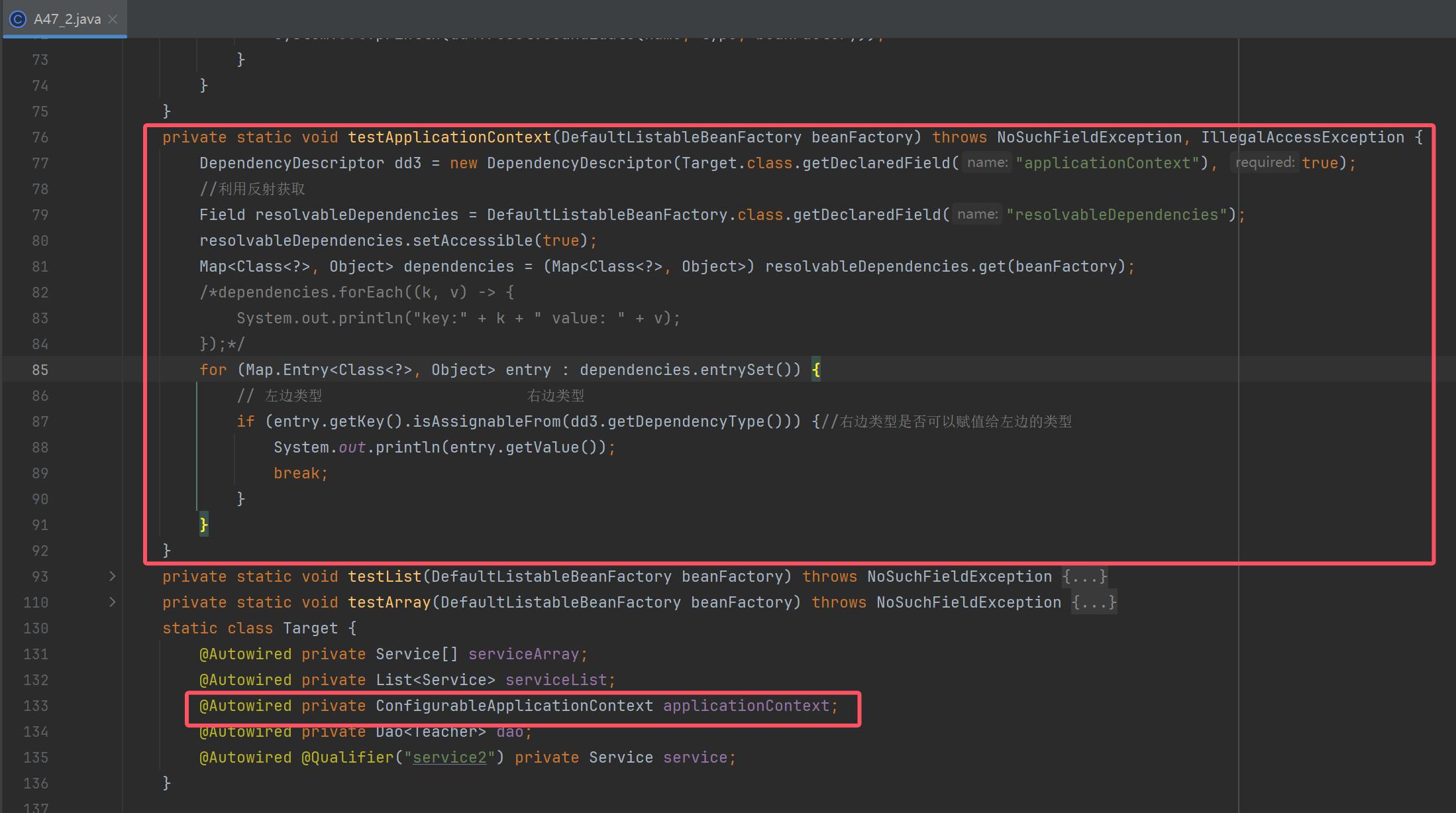
private static void testApplicationContext(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
DependencyDescriptor dd3 = new DependencyDescriptor(Target.class.getDeclaredField("applicationContext"), true);
//利用反射获取
Field resolvableDependencies = DefaultListableBeanFactory.class.getDeclaredField("resolvableDependencies");
resolvableDependencies.setAccessible(true);
Map<Class<?>, Object> dependencies = (Map<Class<?>, Object>) resolvableDependencies.get(beanFactory);
/*dependencies.forEach((k, v) -> {
System.out.println("key:" + k + " value: " + v);
});*/
for (Map.Entry<Class<?>, Object> entry : dependencies.entrySet()) {
// 左边类型 右边类型
if (entry.getKey().isAssignableFrom(dd3.getDependencyType())) {//右边类型是否可以赋值给左边的类型
System.out.println(entry.getValue());
break;
}
}
}
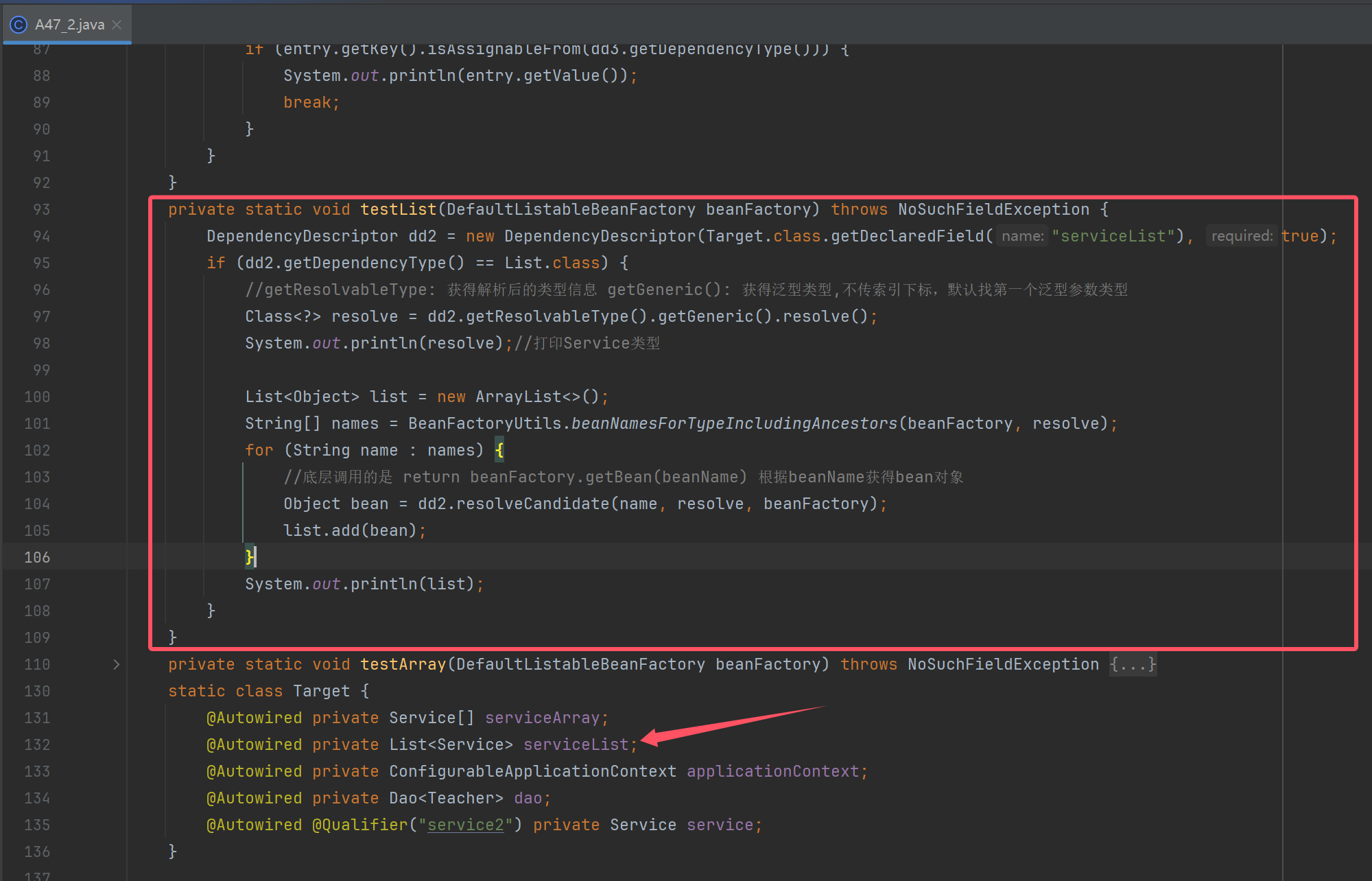
private static void testList(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws NoSuchFieldException {
DependencyDescriptor dd2 = new DependencyDescriptor(Target.class.getDeclaredField("serviceList"), true);
if (dd2.getDependencyType() == List.class) {
//getResolvableType: 获得解析后的类型信息 getGeneric(): 获得泛型类型,不传索引下标,默认找第一个泛型参数类型
Class<?> resolve = dd2.getResolvableType().getGeneric().resolve();
System.out.println(resolve);//打印Service类型
List<Object> list = new ArrayList<>();
String[] names = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(beanFactory, resolve);
for (String name : names) {
//底层调用的是 return beanFactory.getBean(beanName) 根据beanName获得bean对象
Object bean = dd2.resolveCandidate(name, resolve, beanFactory);
list.add(bean);
}
System.out.println(list);
}
}
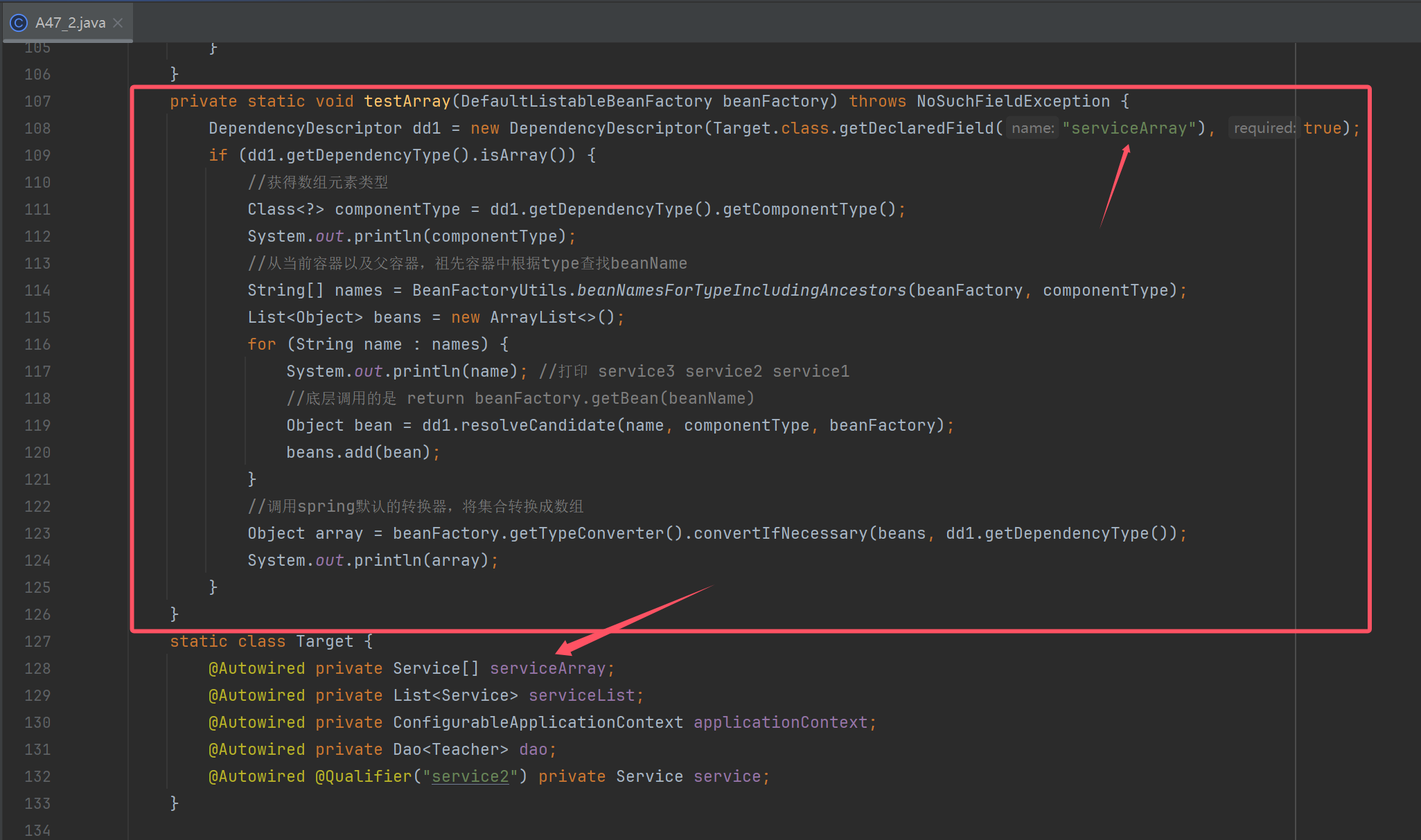
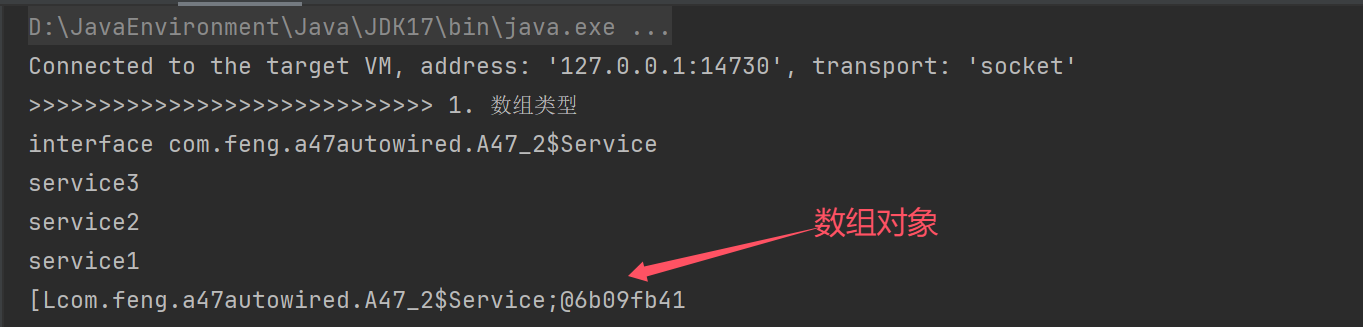
private static void testArray(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws NoSuchFieldException {
DependencyDescriptor dd1 = new DependencyDescriptor(Target.class.getDeclaredField("serviceArray"), true);
if (dd1.getDependencyType().isArray()) {
//获得数组元素类型
Class<?> componentType = dd1.getDependencyType().getComponentType();
System.out.println(componentType);
//从当前容器以及父容器,祖先容器中根据type查找beanName
String[] names = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(beanFactory, componentType);
List<Object> beans = new ArrayList<>();
for (String name : names) {
System.out.println(name); //打印 service3 service2 service1
//底层调用的是 return beanFactory.getBean(beanName)
Object bean = dd1.resolveCandidate(name, componentType, beanFactory);
beans.add(bean);
}
//调用spring默认的转换器,将集合转换成数组
Object array = beanFactory.getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(beans, dd1.getDependencyType());
System.out.println(array);
}
}
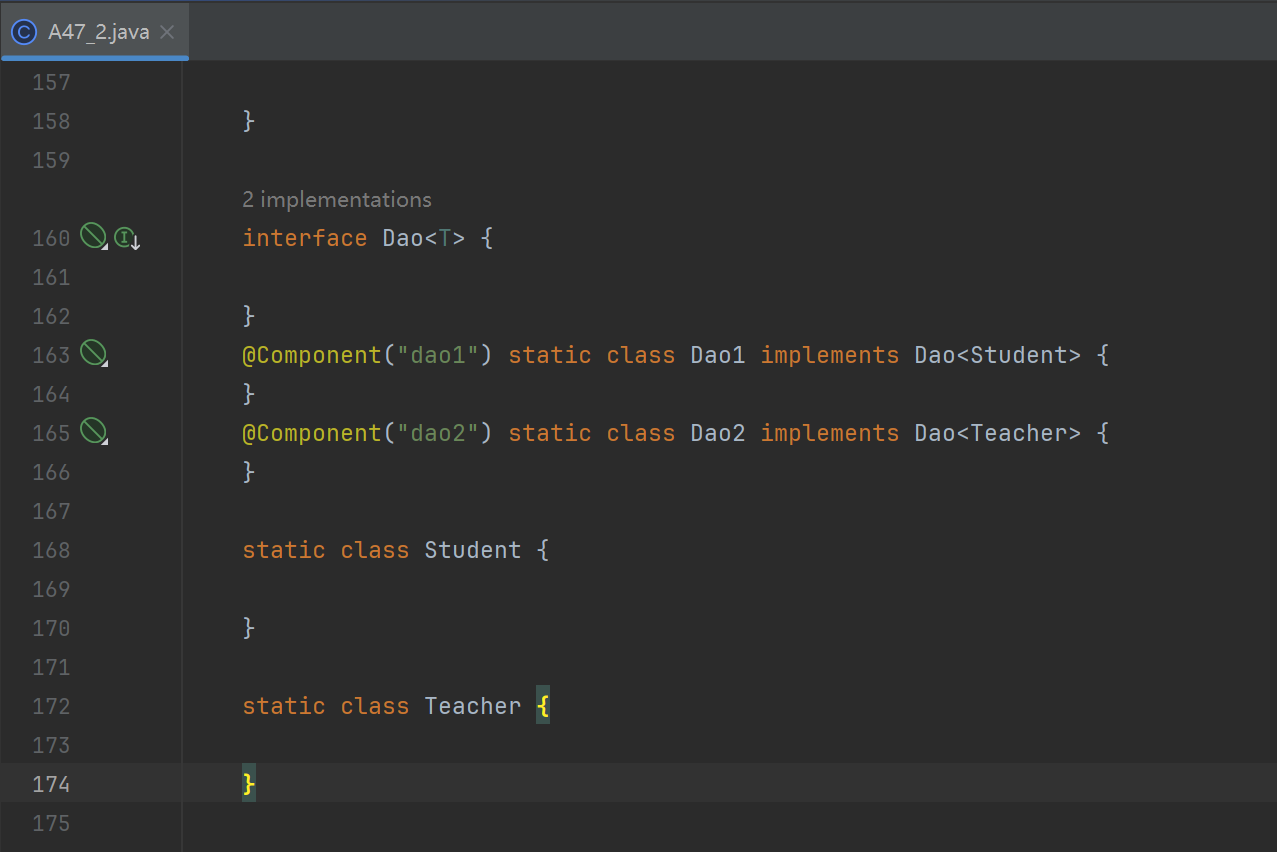
static class Target {
@Autowired private Service[] serviceArray;
@Autowired private List<Service> serviceList;
@Autowired private ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Autowired private Dao<Teacher> dao;
@Autowired @Qualifier("service2") private Service service;
}
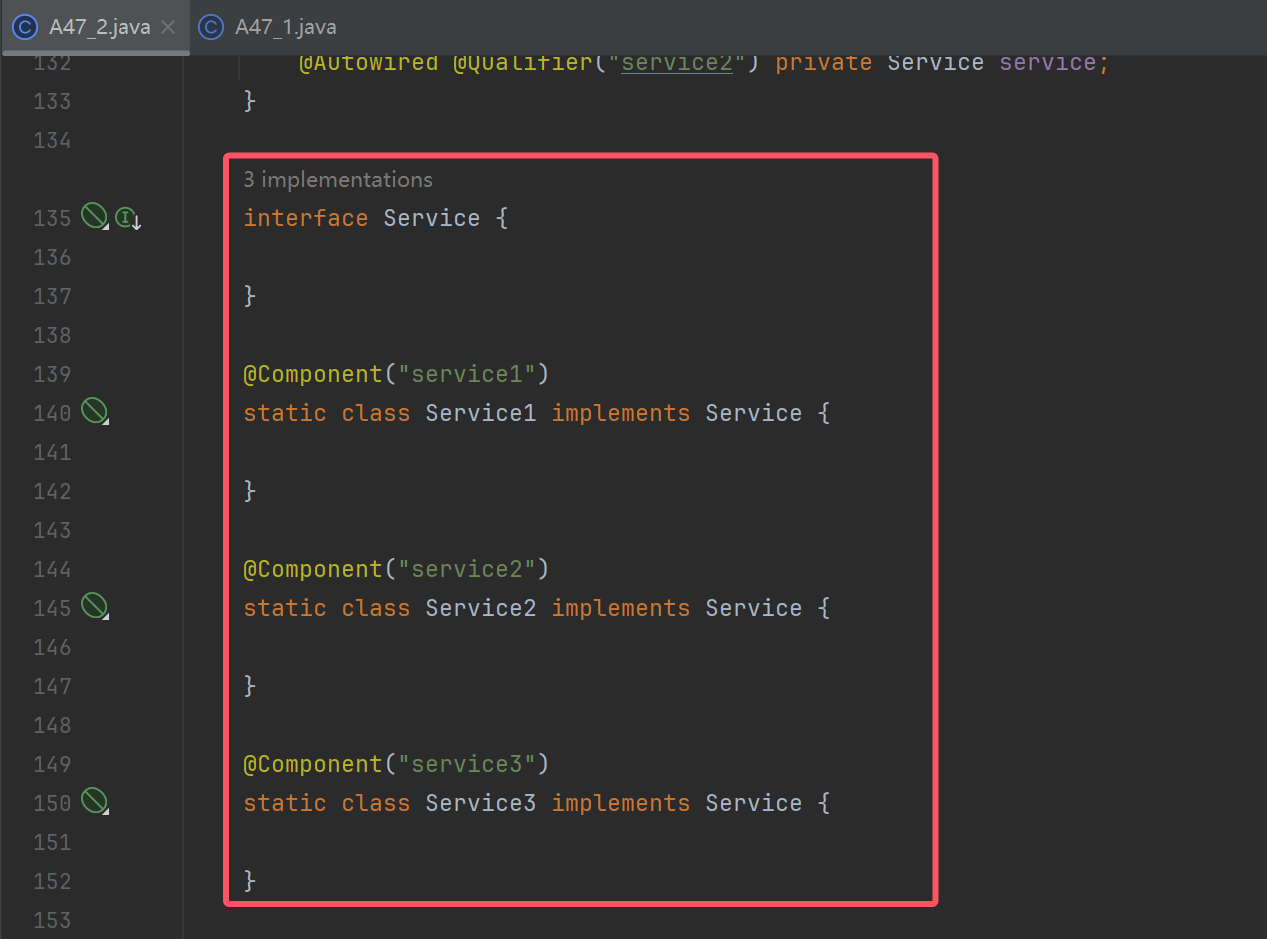
interface Service {
}
@Component("service1")
static class Service1 implements Service {
}
@Component("service2")
static class Service2 implements Service {
}
@Component("service3")
static class Service3 implements Service {
}
interface Dao<T> {
}
@Component("dao1") static class Dao1 implements Dao<Student> {
}
@Component("dao2") static class Dao2 implements Dao<Teacher> {
}
static class Student {
}
static class Teacher {
}
}
@Primary用法
处理默认情况
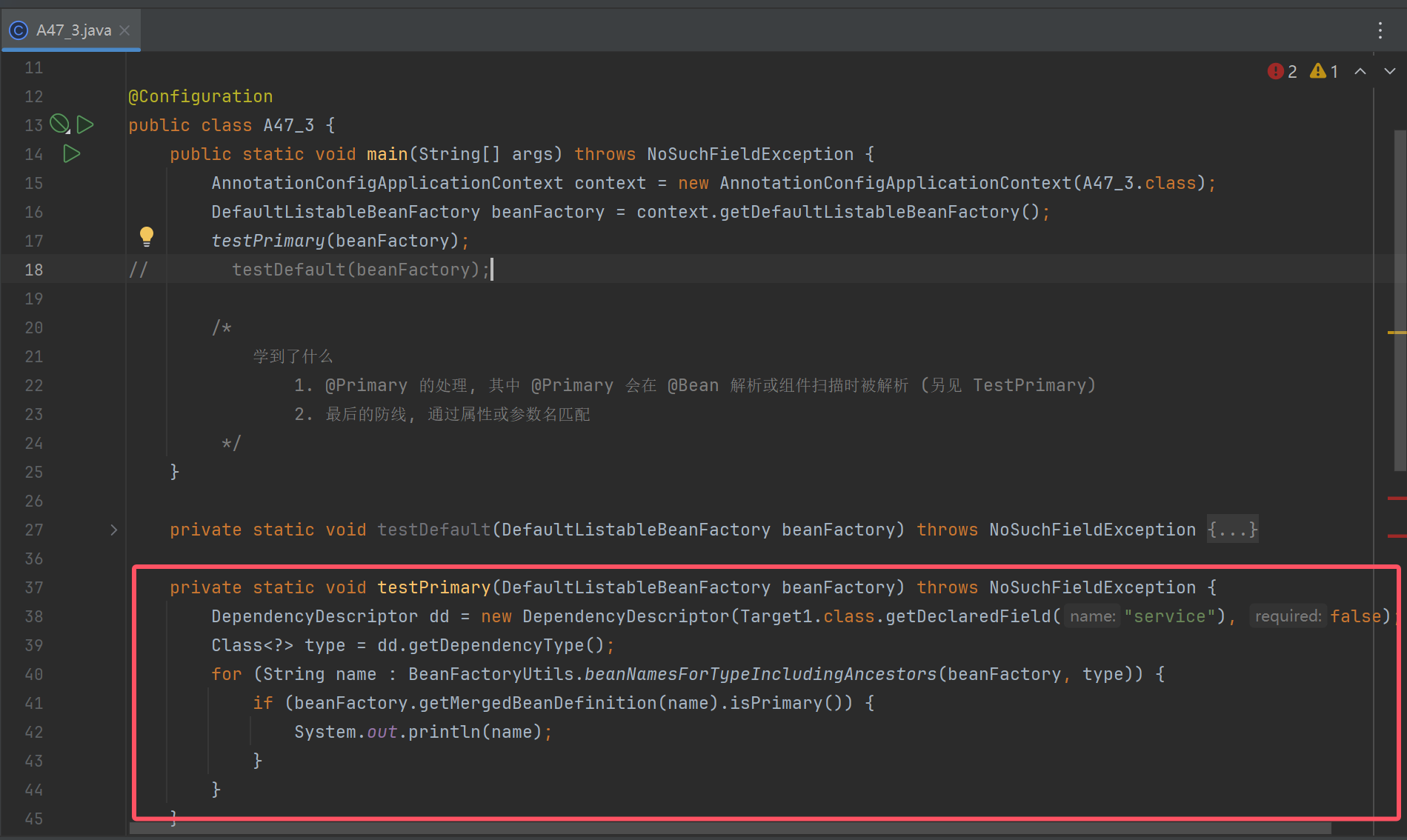
@Configuration
public class A47_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(A47_3.class);
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getDefaultListableBeanFactory();
//testPrimary(beanFactory);
testDefault(beanFactory);
/*
学到了什么
1. @Primary 的处理, 其中 @Primary 会在 @Bean 解析或组件扫描时被解析 (另见 TestPrimary)
2. 最后的防线, 通过属性或参数名匹配
*/
}
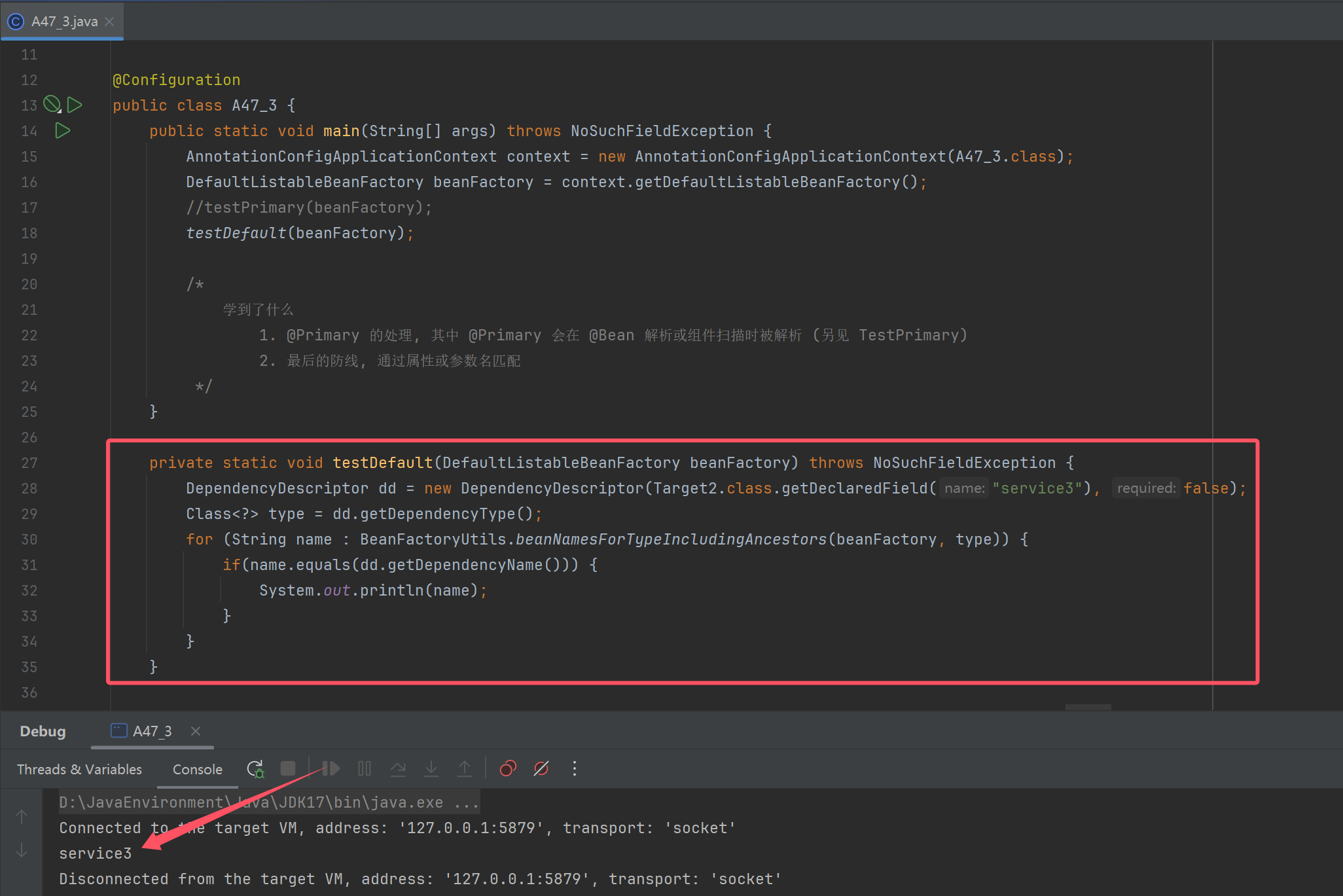
private static void testDefault(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws NoSuchFieldException {
DependencyDescriptor dd = new DependencyDescriptor(Target2.class.getDeclaredField("service3"), false);
Class<?> type = dd.getDependencyType();
for (String name : BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(beanFactory, type)) {
if(name.equals(dd.getDependencyName())) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
}
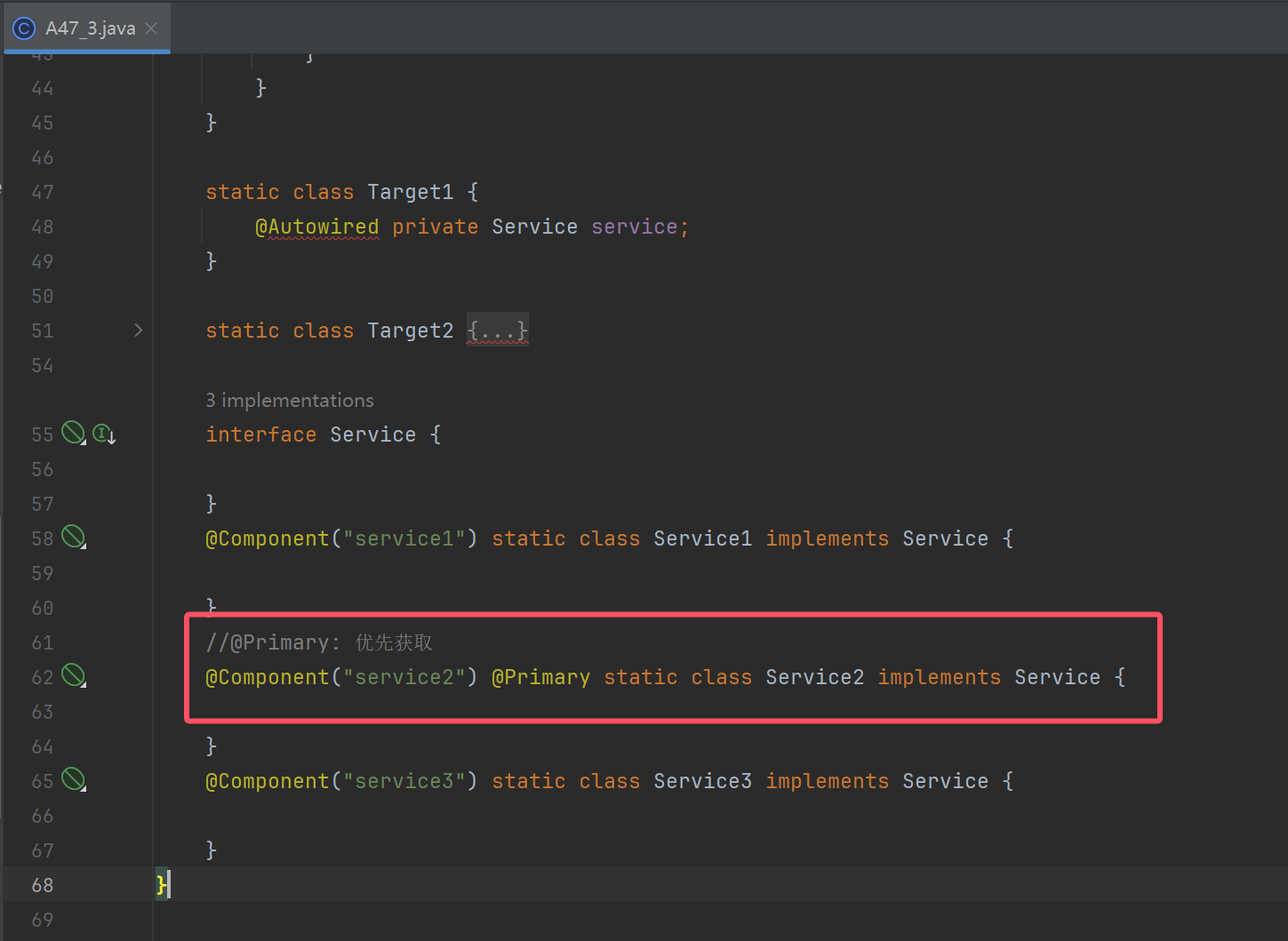
private static void testPrimary(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws NoSuchFieldException {
DependencyDescriptor dd = new DependencyDescriptor(Target1.class.getDeclaredField("service"), false);
Class<?> type = dd.getDependencyType();
for (String name : BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(beanFactory, type)) {
if (beanFactory.getMergedBeanDefinition(name).isPrimary()) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
}
static class Target1 {
@Autowired private Service service;
}
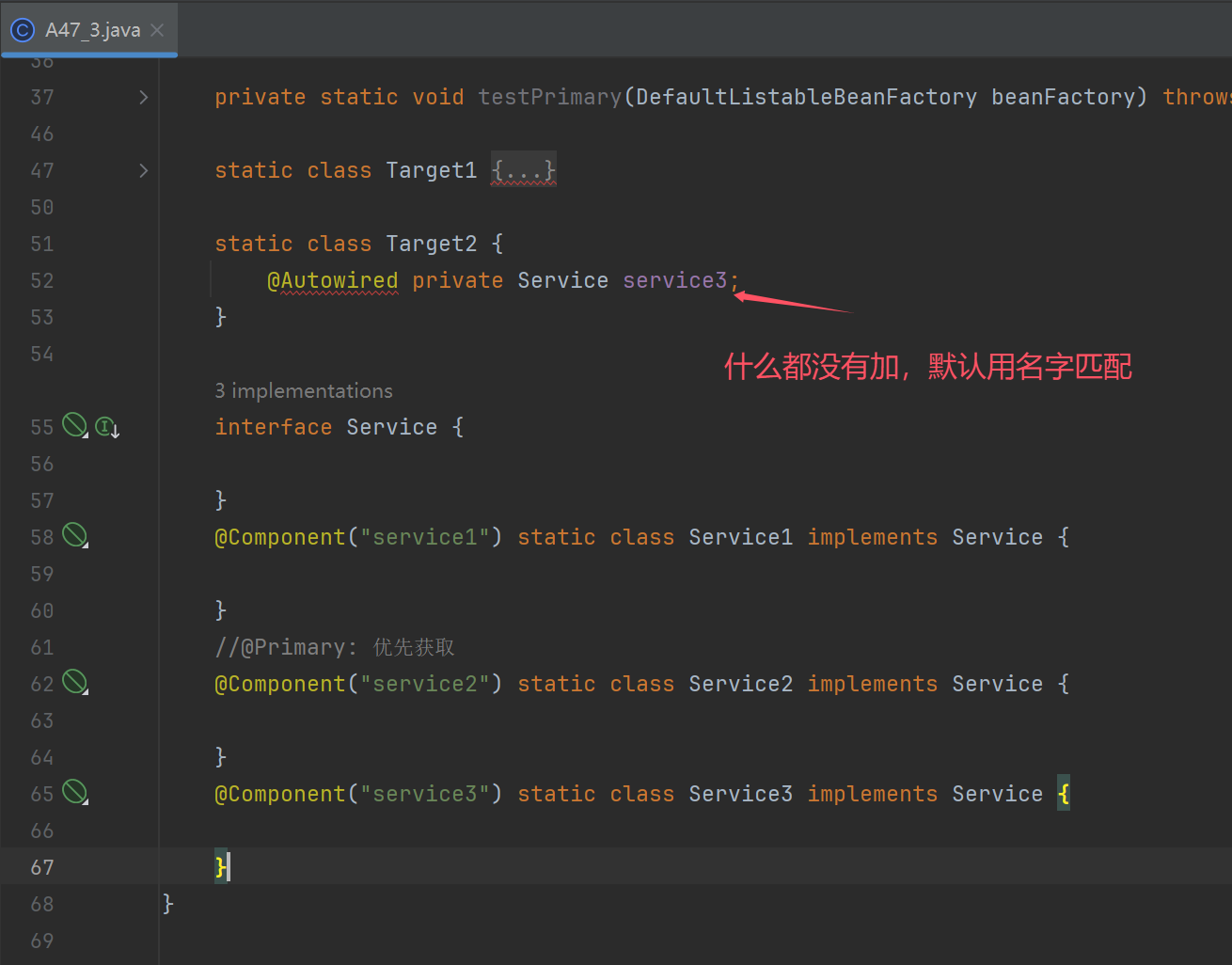
static class Target2 {
@Autowired private Service service3;
}
interface Service {
}
@Component("service1") static class Service1 implements Service {
}
//@Primary: 优先获取
@Component("service2") static class Service2 implements Service {
}
@Component("service3") static class Service3 implements Service {
}
}
收获💡
- @Autowired 本质上是根据成员变量或方法参数的类型进行装配
- 如果待装配类型是 Optional,需要根据 Optional 泛型找到 bean,再封装为 Optional 对象装配
- 如果待装配的类型是 ObjectFactory,需要根据 ObjectFactory 泛型创建 ObjectFactory 对象装配
- 此方法可以延迟 bean 的获取
- 如果待装配的成员变量或方法参数上用 @Lazy 标注,会创建代理对象装配
- 此方法可以延迟真实 bean 的获取
- 被装配的代理不作为 bean
- 如果待装配类型是数组,需要获取数组元素类型,根据此类型找到多个 bean 进行装配
- 如果待装配类型是 Collection 或其子接口,需要获取 Collection 泛型,根据此类型找到多个 bean
- 如果待装配类型是 ApplicationContext 等特殊类型
- 会在 BeanFactory 的 resolvableDependencies 成员按类型查找装配
- resolvableDependencies 是 map 集合,key 是特殊类型,value 是其对应对象
- 不能直接根据 key 进行查找,而是用 isAssignableFrom 逐一尝试右边类型是否可以被赋值给左边的 key 类型
- 如果待装配类型有泛型参数
- 需要利用 ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver 按泛型参数类型筛选
- 如果待装配类型有 @Qualifier
- 需要利用 ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver 按注解提供的 bean 名称筛选
- 有 @Primary 标注的 @Component 或 @Bean 的处理
- 与成员变量名或方法参数名同名 bean 的处理
2.6 事件监听器
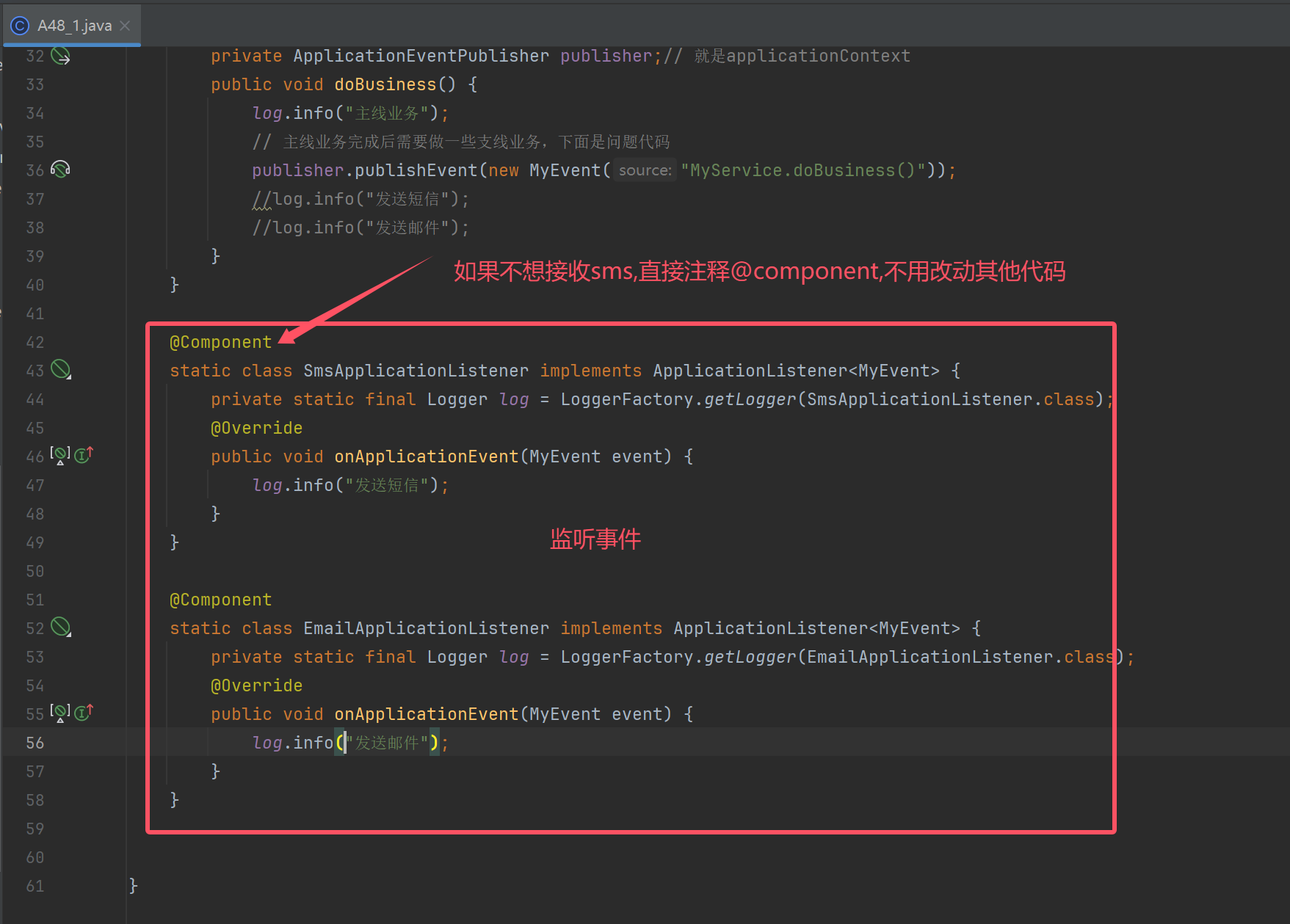
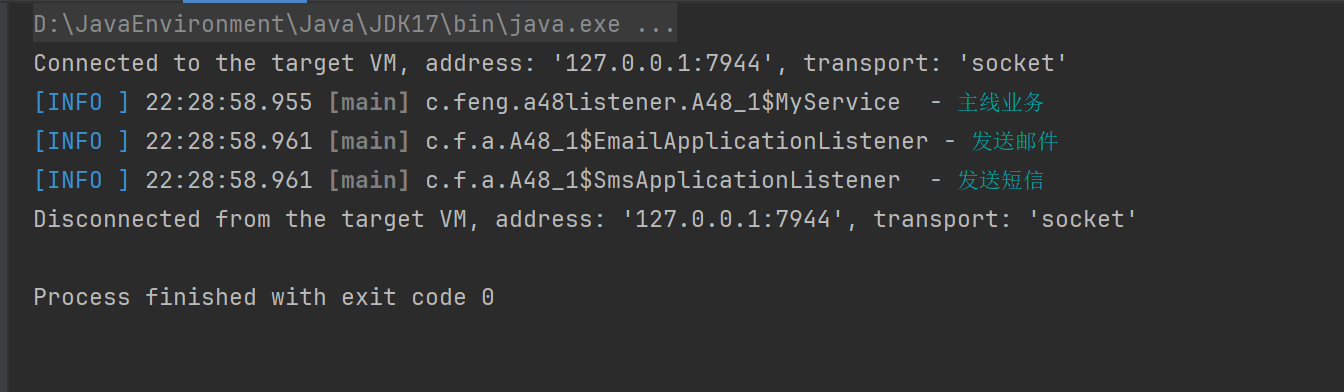
// 事件解耦例子
@Configuration
public class A48_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(A48_1.class);
context.getBean(MyService.class).doBusiness();
context.close();
}
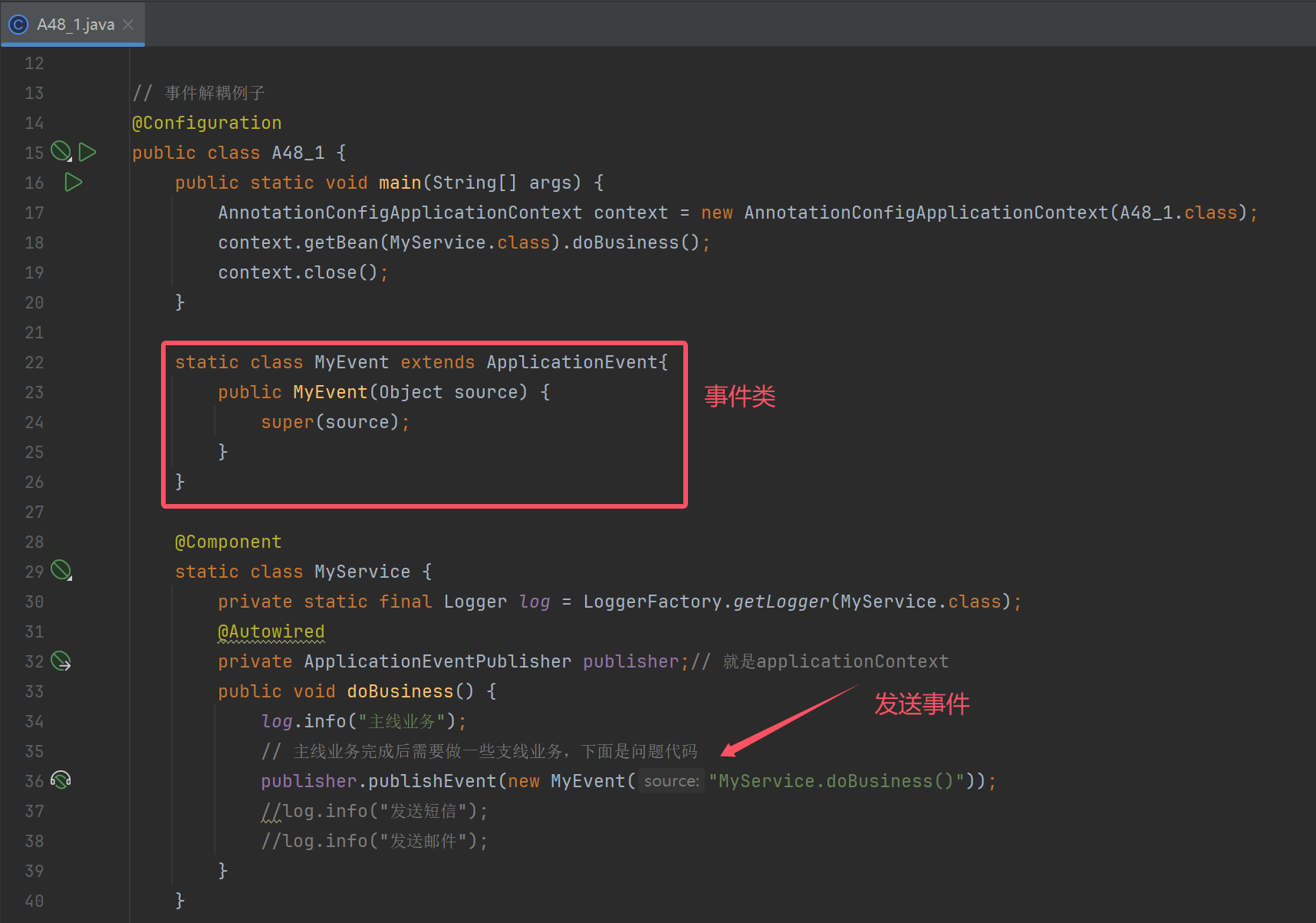
static class MyEvent extends ApplicationEvent{
public MyEvent(Object source) {
super(source);
}
}
@Component
static class MyService {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyService.class);
@Autowired
private ApplicationEventPublisher publisher;// 就是applicationContext
public void doBusiness() {
log.info("主线业务");
// 主线业务完成后需要做一些支线业务,下面是问题代码
publisher.publishEvent(new MyEvent("MyService.doBusiness()"));
//log.info("发送短信");
//log.info("发送邮件");
}
}
@Component
static class SmsApplicationListener implements ApplicationListener<MyEvent> {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SmsApplicationListener.class);
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(MyEvent event) {
log.info("发送短信");
}
}
@Component
static class EmailApplicationListener implements ApplicationListener<MyEvent> {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(EmailApplicationListener.class);
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(MyEvent event) {
log.info("发送邮件");
}
}
}
另外一种方式监听事件
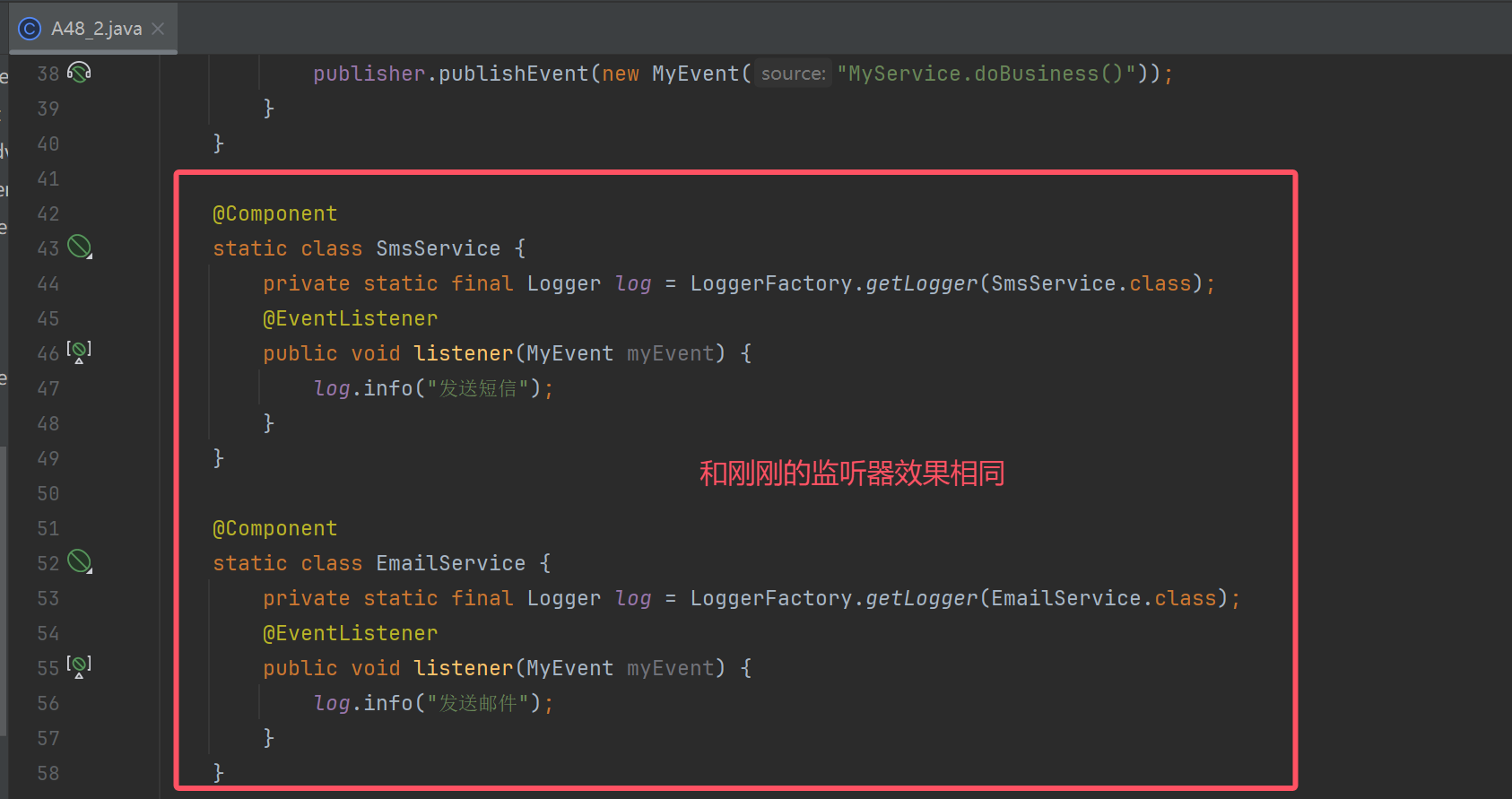
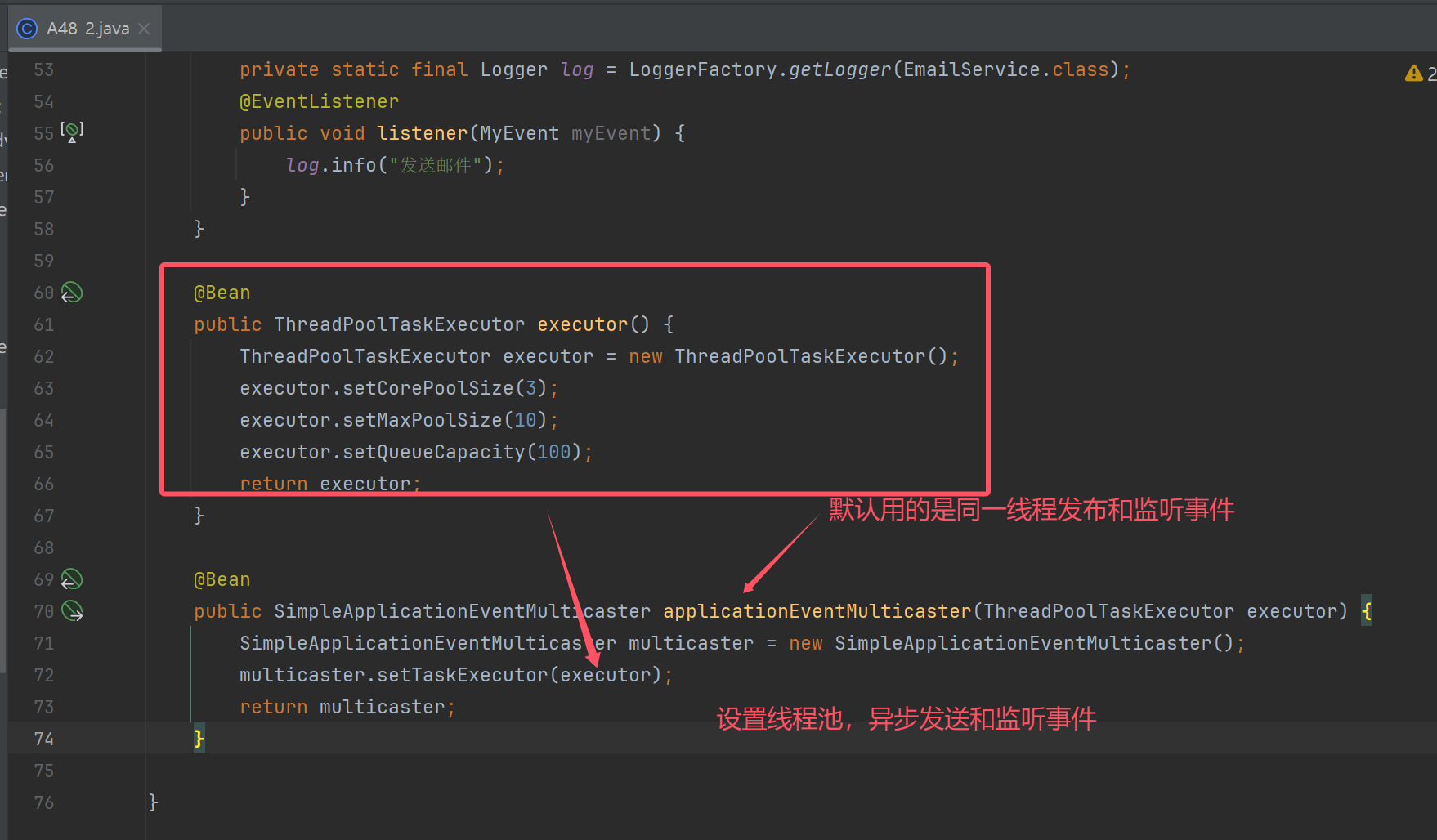
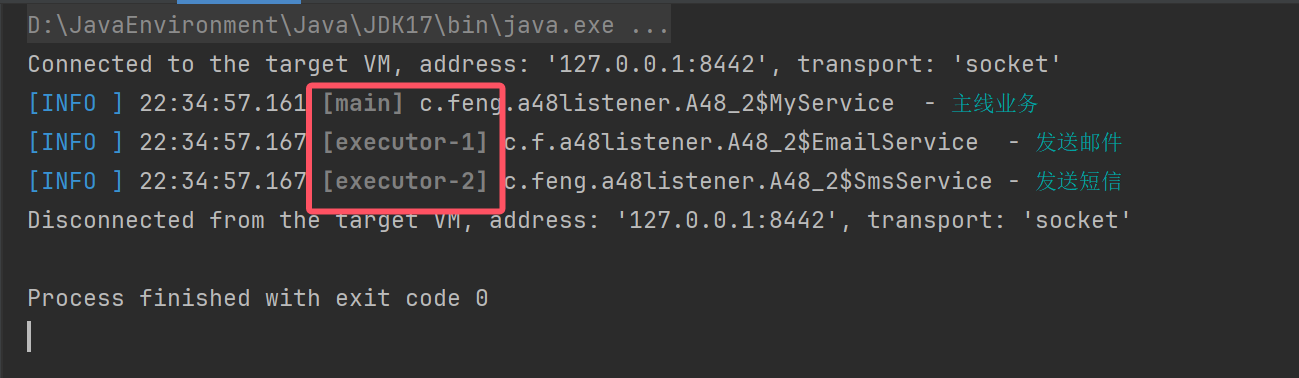
完整代码
@Configuration
public class A48_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(A48_2.class);
context.getBean(MyService.class).doBusiness();
context.close();
}
static class MyEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
public MyEvent(Object source) {
super(source);
}
}
@Component
static class MyService {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyService.class);
@Autowired
private ApplicationEventPublisher publisher; // applicationContext
public void doBusiness() {
log.info("主线业务");
// 主线业务完成后需要做一些支线业务,下面是问题代码
publisher.publishEvent(new MyEvent("MyService.doBusiness()"));
}
}
@Component
static class SmsService {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SmsService.class);
@EventListener
public void listener(MyEvent myEvent) {
log.info("发送短信");
}
}
@Component
static class EmailService {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(EmailService.class);
@EventListener
public void listener(MyEvent myEvent) {
log.info("发送邮件");
}
}
@Bean
public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setCorePoolSize(3);
executor.setMaxPoolSize(10);
executor.setQueueCapacity(100);
return executor;
}
@Bean
public SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster applicationEventMulticaster(ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor) {
SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster multicaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster();
multicaster.setTaskExecutor(executor);
return multicaster;
}
}
自定义注解实现@EventListener效果
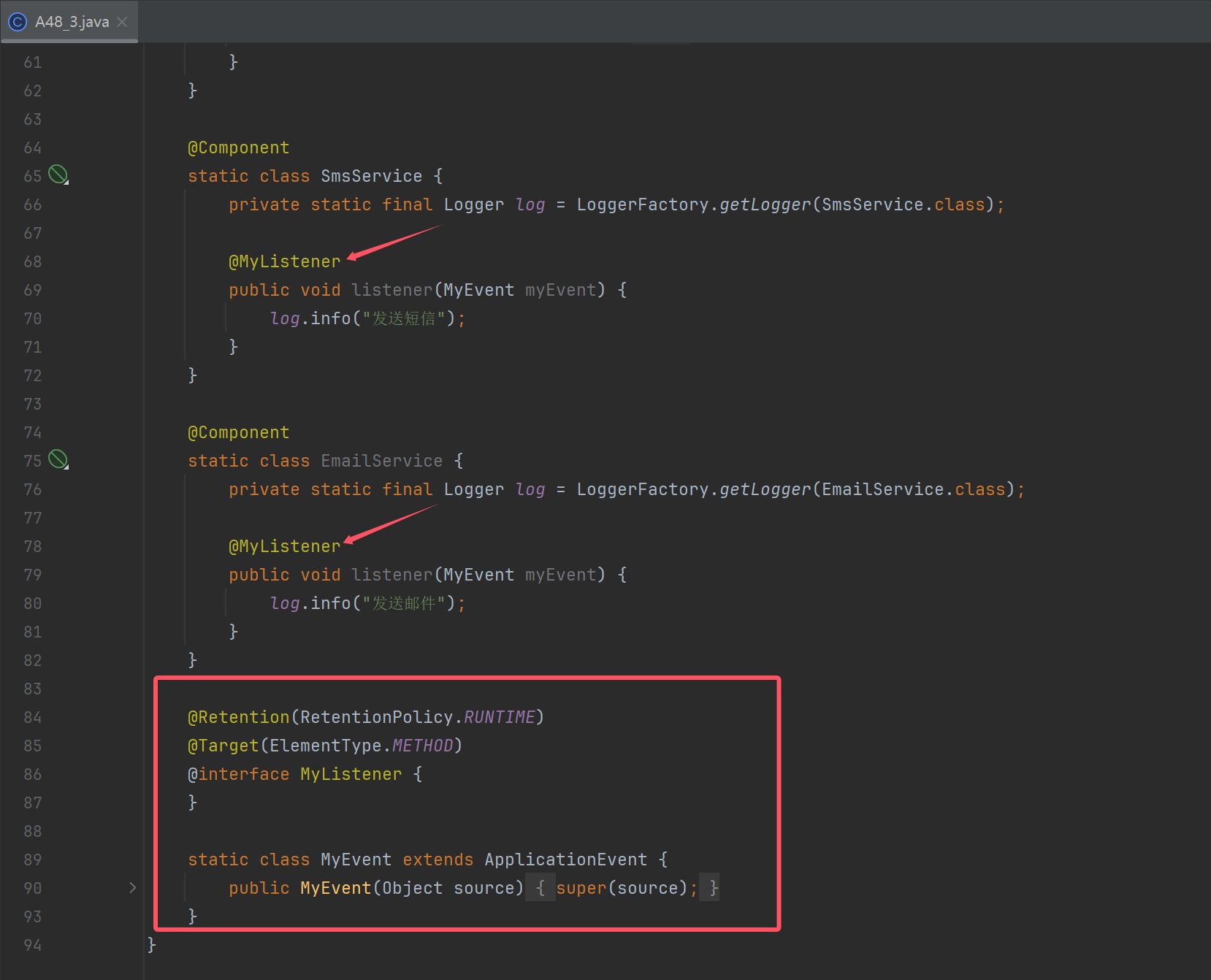
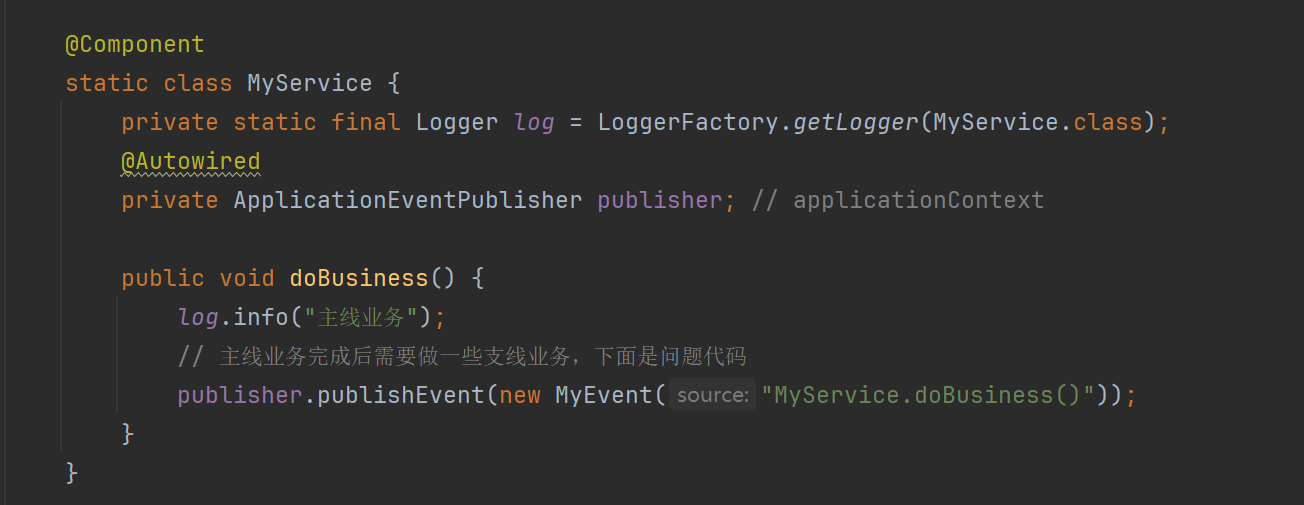
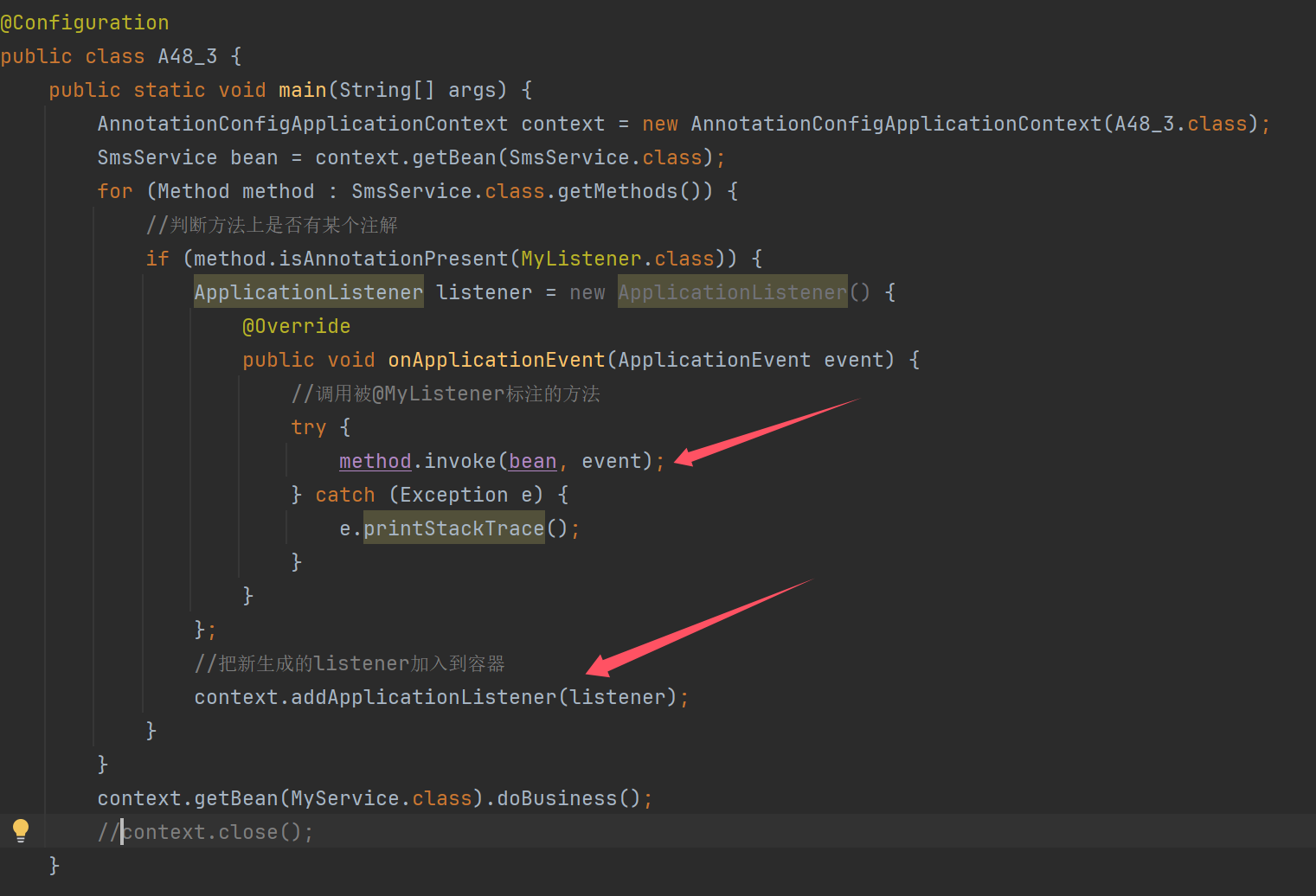
@Configuration
public class A48_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(A48_3.class);
SmsService bean = context.getBean(SmsService.class);
for (Method method : SmsService.class.getMethods()) {
//判断方法上是否有某个注解
if (method.isAnnotationPresent(MyListener.class)) {
ApplicationListener listener = new ApplicationListener() {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
//调用被@MyListener标注的方法
try {
method.invoke(bean, event);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
//把新生成的listener加入到容器
context.addApplicationListener(listener);
}
}
context.getBean(MyService.class).doBusiness();
//context.close();
}
@Component
static class MyService {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyService.class);
@Autowired
private ApplicationEventPublisher publisher; // applicationContext
public void doBusiness() {
log.info("主线业务");
// 主线业务完成后需要做一些支线业务,下面是问题代码
publisher.publishEvent(new MyEvent("MyService.doBusiness()"));
}
}
@Component
static class SmsService {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SmsService.class);
@MyListener
public void listener(MyEvent myEvent) {
log.info("发送短信");
}
}
@Component
static class EmailService {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(EmailService.class);
@MyListener
public void listener(MyEvent myEvent) {
log.info("发送邮件");
}
}
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@interface MyListener {
}
static class MyEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
public MyEvent(Object source) {
super(source);
}
}
}
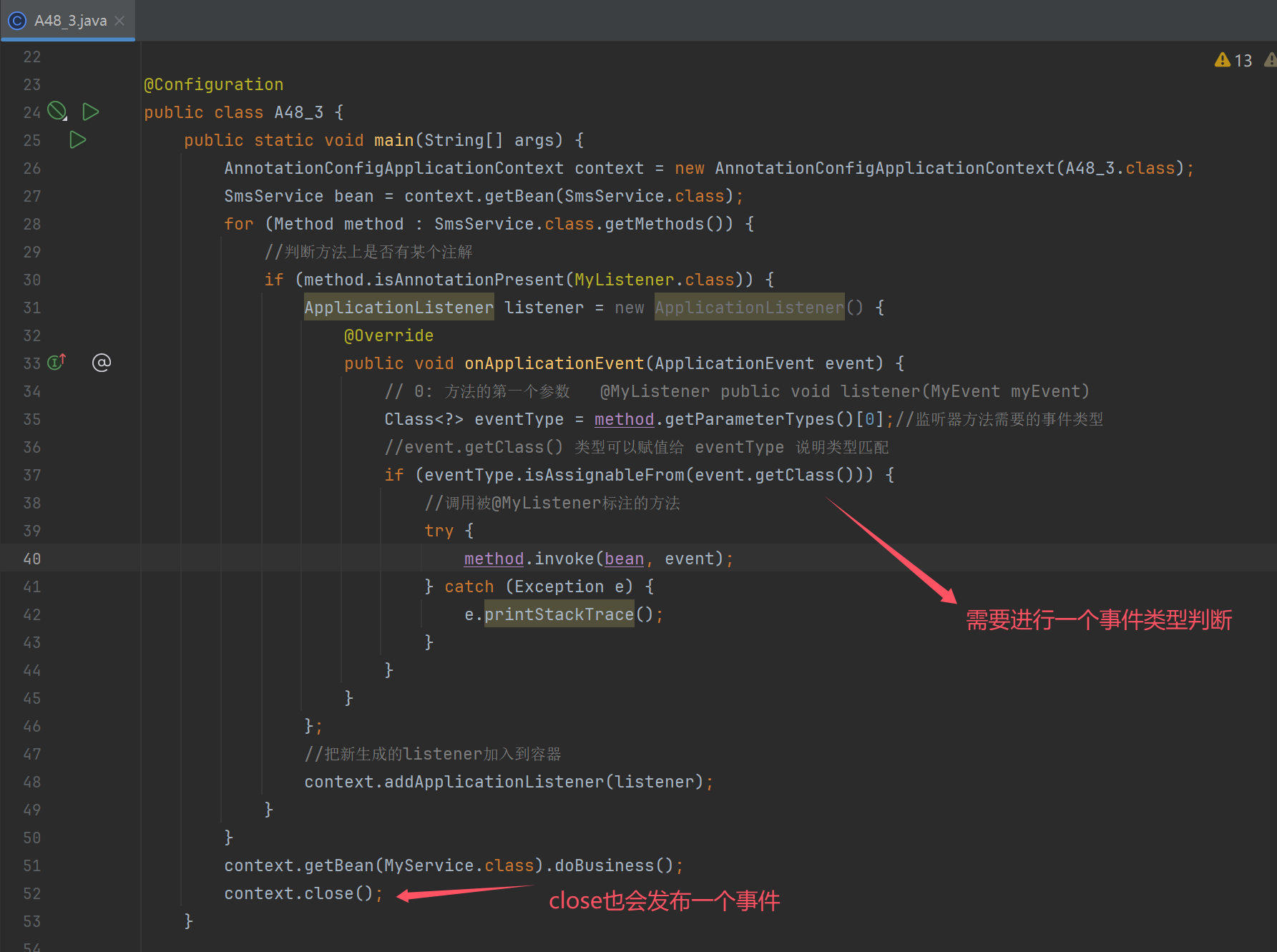
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(A48_3.class);
SmsService bean = context.getBean(SmsService.class);
for (Method method : SmsService.class.getMethods()) {
//判断方法上是否有某个注解
if (method.isAnnotationPresent(MyListener.class)) {
ApplicationListener listener = new ApplicationListener() {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
// 0: 方法的第一个参数 @MyListener public void listener(MyEvent myEvent)
Class<?> eventType = method.getParameterTypes()[0];//监听器方法需要的事件类型
//event.getClass() 类型可以赋值给 eventType 说明类型匹配
if (eventType.isAssignableFrom(event.getClass())) {
//调用被@MyListener标注的方法
try {
method.invoke(bean, event);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
};
//把新生成的listener加入到容器
context.addApplicationListener(listener);
}
}
context.getBean(MyService.class).doBusiness();
context.close();
}
对所有bean都进行判断
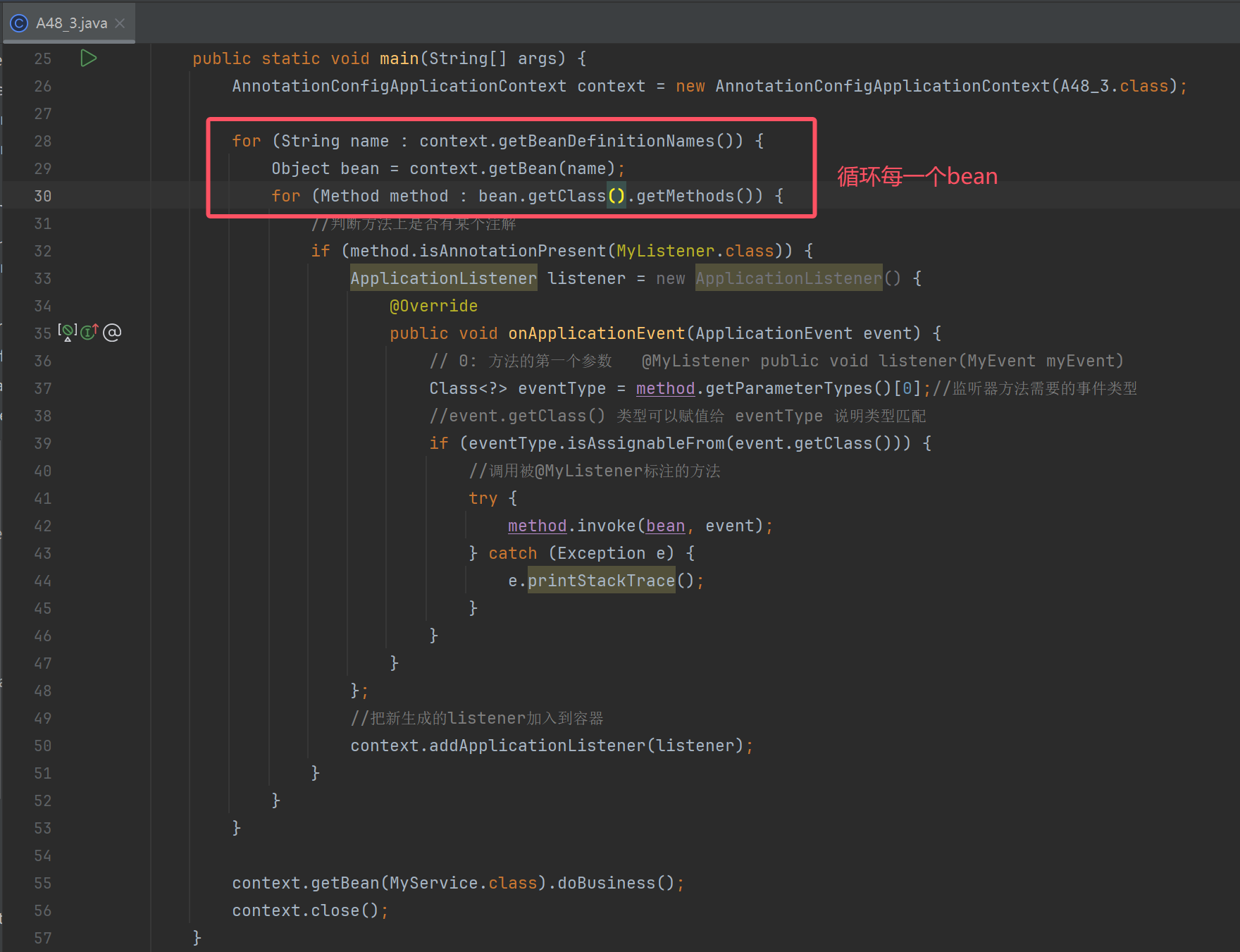
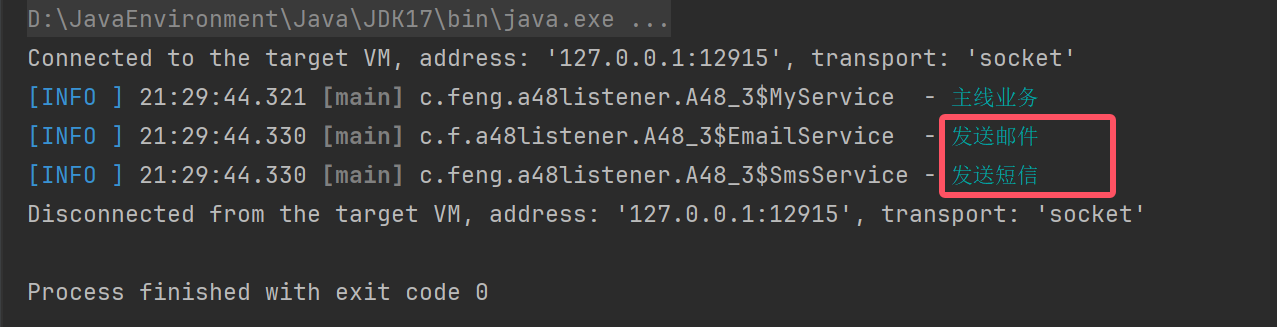
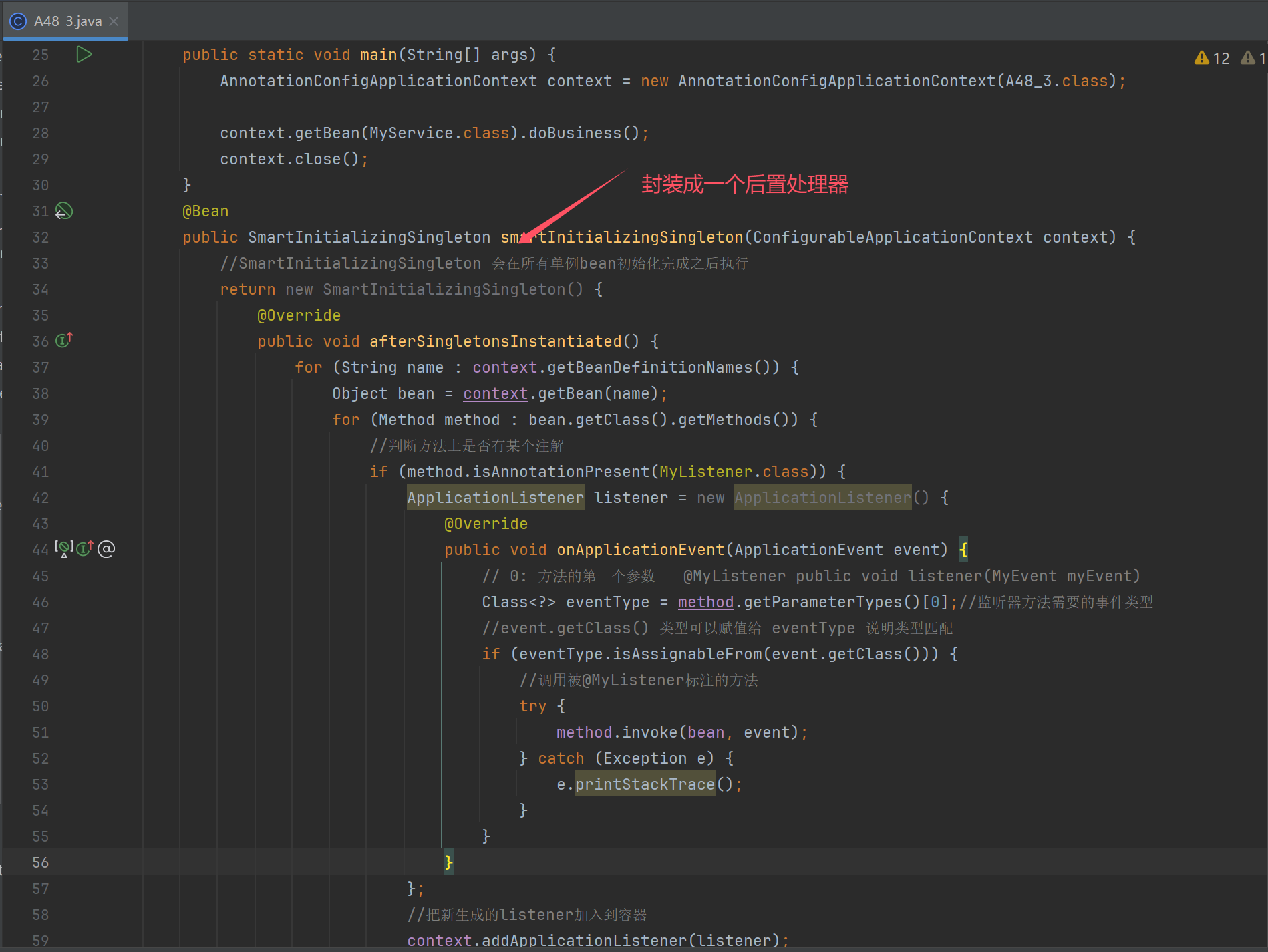
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(A48_3.class);
context.getBean(MyService.class).doBusiness();
context.close();
}
@Bean
public SmartInitializingSingleton smartInitializingSingleton(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
//SmartInitializingSingleton 会在所有单例bean初始化完成之后执行
return new SmartInitializingSingleton() {
@Override
public void afterSingletonsInstantiated() {
for (String name : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
Object bean = context.getBean(name);
for (Method method : bean.getClass().getMethods()) {
//判断方法上是否有某个注解
if (method.isAnnotationPresent(MyListener.class)) {
ApplicationListener listener = new ApplicationListener() {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
// 0: 方法的第一个参数 @MyListener public void listener(MyEvent myEvent)
Class<?> eventType = method.getParameterTypes()[0];//监听器方法需要的事件类型
//event.getClass() 类型可以赋值给 eventType 说明类型匹配
if (eventType.isAssignableFrom(event.getClass())) {
//调用被@MyListener标注的方法
try {
method.invoke(bean, event);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
};
//把新生成的listener加入到容器
context.addApplicationListener(listener);
}
}
}
}
};
}
收获💡
事件监听器的两种方式
- 实现 ApplicationListener 接口
- 根据接口泛型确定事件类型
- @EventListener 标注监听方法
- 根据监听器方法参数确定事件类型
- 解析时机:在 SmartInitializingSingleton(所有单例初始化完成后),解析每个单例 bean
2.7 事件发布器
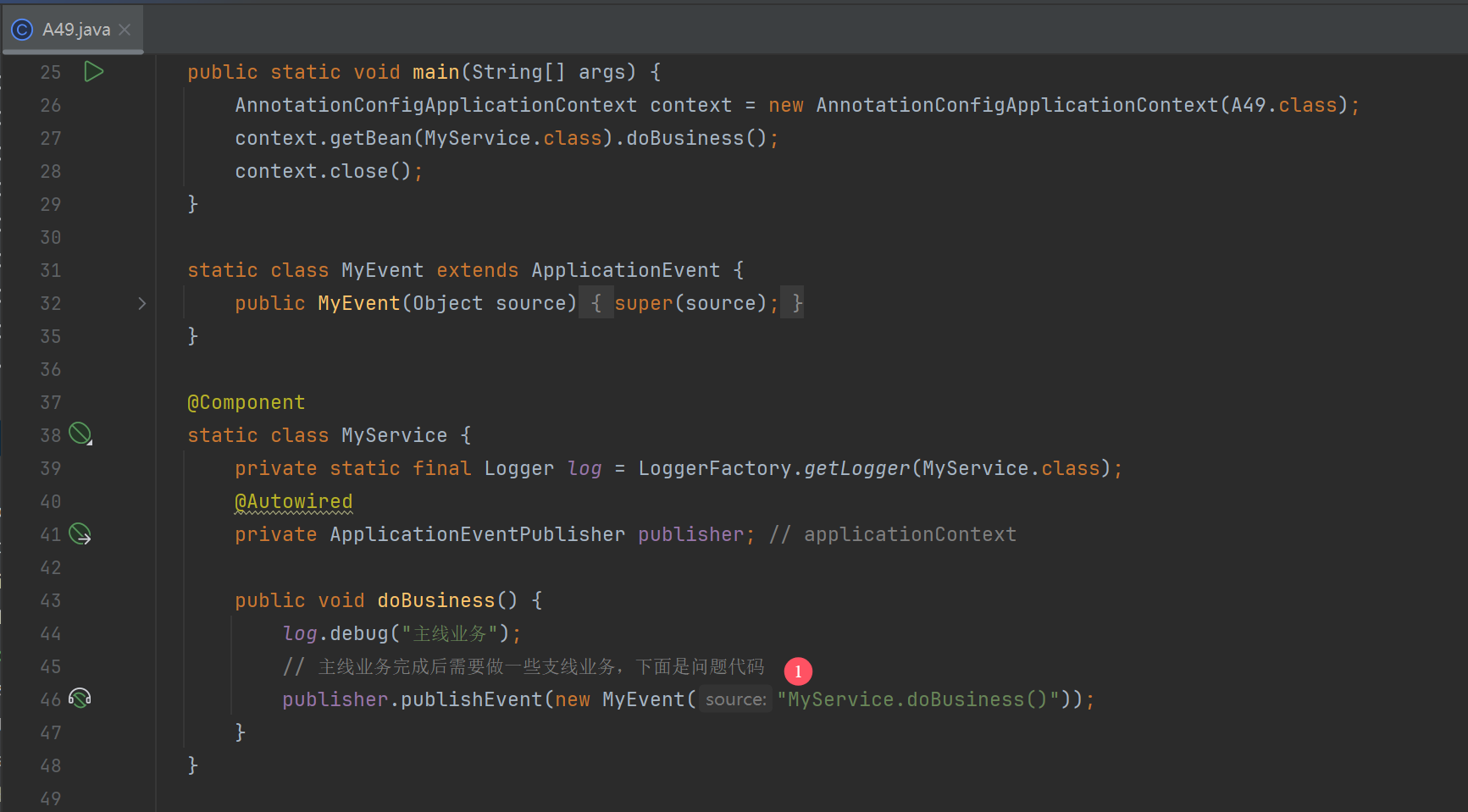
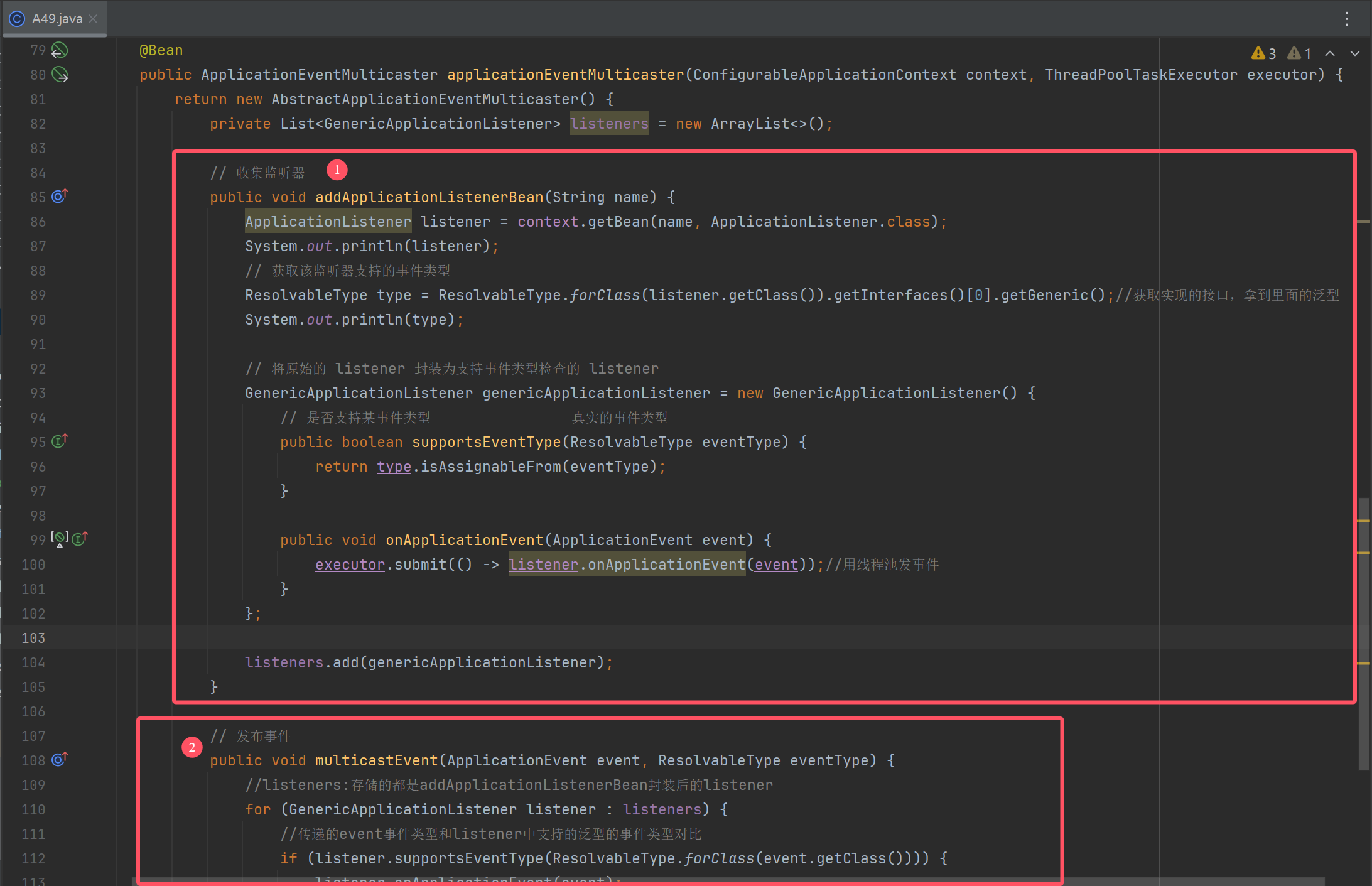
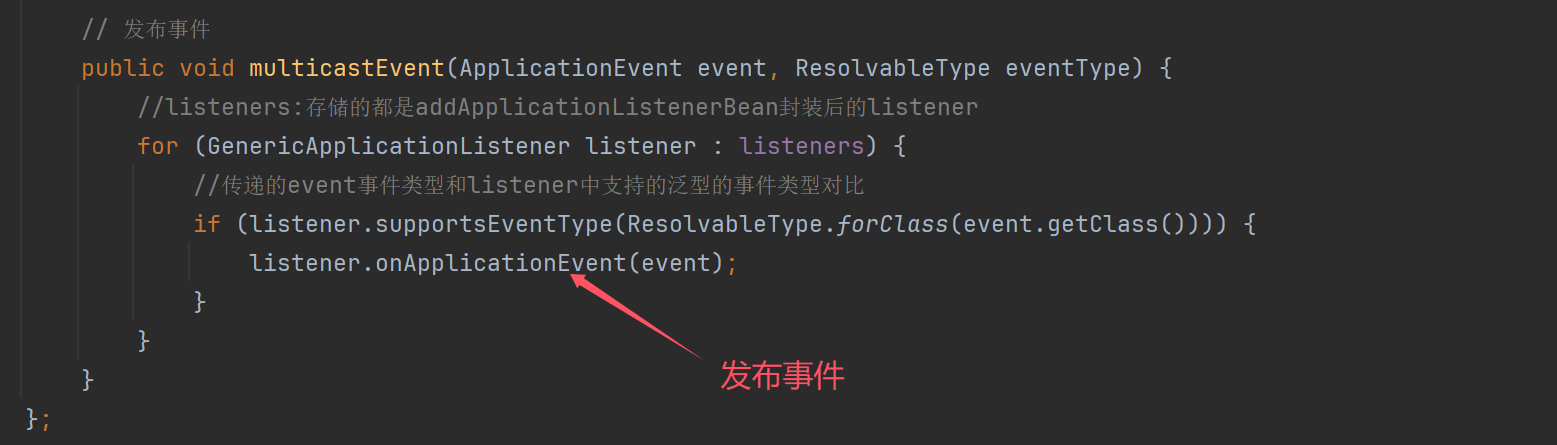
用匿名内部类实现的
@Bean
public ApplicationEventMulticaster applicationEventMulticaster(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor) {
return new AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster() {
private List<GenericApplicationListener> listeners = new ArrayList<>();
// 收集监听器
public void addApplicationListenerBean(String name) {
ApplicationListener listener = context.getBean(name, ApplicationListener.class);
System.out.println(listener);
// 获取该监听器支持的事件类型
ResolvableType type = ResolvableType.forClass(listener.getClass()).getInterfaces()[0].getGeneric();//获取实现的接口,拿到里面的泛型
System.out.println(type);
// 将原始的 listener 封装为支持事件类型检查的 listener
GenericApplicationListener genericApplicationListener = new GenericApplicationListener() {
// 是否支持某事件类型 真实的事件类型
public boolean supportsEventType(ResolvableType eventType) {
return type.isAssignableFrom(eventType);
}
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
executor.submit(() -> listener.onApplicationEvent(event));//用线程池发事件
}
};
listeners.add(genericApplicationListener);
}
// 发布事件
public void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event, ResolvableType eventType) {
//listeners:存储的都是addApplicationListenerBean封装后的listener
for (GenericApplicationListener listener : listeners) {
//传递的event事件类型和listener中支持的泛型的事件类型对比
if (listener.supportsEventType(ResolvableType.forClass(event.getClass()))) {
listener.onApplicationEvent(event);
}
}
}
};
}
完整代码
@Configuration
public class A49 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(A49.class);
context.getBean(MyService.class).doBusiness();
context.close();
}
static class MyEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
public MyEvent(Object source) {
super(source);
}
}
@Component
static class MyService {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyService.class);
@Autowired
private ApplicationEventPublisher publisher; // applicationContext
public void doBusiness() {
log.debug("主线业务");
// 主线业务完成后需要做一些支线业务,下面是问题代码
publisher.publishEvent(new MyEvent("MyService.doBusiness()"));
}
}
@Component
static class SmsApplicationListener implements ApplicationListener<MyEvent> {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SmsApplicationListener.class);
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(MyEvent event) {
log.debug("发送短信");
}
}
@Component
static class EmailApplicationListener implements ApplicationListener<MyEvent> {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(EmailApplicationListener.class);
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(MyEvent event) {
log.debug("发送邮件");
}
}
@Bean
public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setCorePoolSize(3);
executor.setMaxPoolSize(10);
executor.setQueueCapacity(100);
return executor;
}
@Bean
public ApplicationEventMulticaster applicationEventMulticaster(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor) {
return new AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster() {
private List<GenericApplicationListener> listeners = new ArrayList<>();
// 收集监听器
public void addApplicationListenerBean(String name) {
ApplicationListener listener = context.getBean(name, ApplicationListener.class);
System.out.println(listener);
// 获取该监听器支持的事件类型
ResolvableType type = ResolvableType.forClass(listener.getClass()).getInterfaces()[0].getGeneric();//获取实现的接口,拿到里面的泛型
System.out.println(type);
// 将原始的 listener 封装为支持事件类型检查的 listener
GenericApplicationListener genericApplicationListener = new GenericApplicationListener() {
// 是否支持某事件类型 真实的事件类型
public boolean supportsEventType(ResolvableType eventType) {
return type.isAssignableFrom(eventType);
}
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
executor.submit(() -> listener.onApplicationEvent(event));//用线程池发事件
}
};
listeners.add(genericApplicationListener);
}
// 发布事件
public void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event, ResolvableType eventType) {
//listeners:存储的都是addApplicationListenerBean封装后的listener
for (GenericApplicationListener listener : listeners) {
//传递的event事件类型和listener中支持的泛型的事件类型对比
if (listener.supportsEventType(ResolvableType.forClass(event.getClass()))) {
listener.onApplicationEvent(event);
}
}
}
};
}
abstract static class AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster implements ApplicationEventMulticaster {
@Override
public void addApplicationListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener) {
}
@Override
public void addApplicationListenerBean(String listenerBeanName) {
}
@Override
public void removeApplicationListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener) {
}
@Override
public void removeApplicationListenerBean(String listenerBeanName) {
}
@Override
public void removeApplicationListeners(Predicate<ApplicationListener<?>> predicate) {
}
@Override
public void removeApplicationListenerBeans(Predicate<String> predicate) {
}
@Override
public void removeAllListeners() {
}
@Override
public void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
}
@Override
public void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event, ResolvableType eventType) {
}
}
}
收获💡
事件发布器模拟实现
- addApplicationListenerBean 负责收集容器中的监听器
- 监听器会统一转换为 GenericApplicationListener 对象,以支持判断事件类型
- multicastEvent 遍历监听器集合,发布事件
- 发布前先通过 GenericApplicationListener.supportsEventType 判断支持该事件类型才发事件
- 可以利用线程池进行异步发事件优化
- 如果发送的事件对象不是 ApplicationEvent 类型,Spring 会把它包装为 PayloadApplicationEvent 并用泛型技术解析事件对象的原始类型
- 视频中未讲解

