openstack neutron 开启vxlan
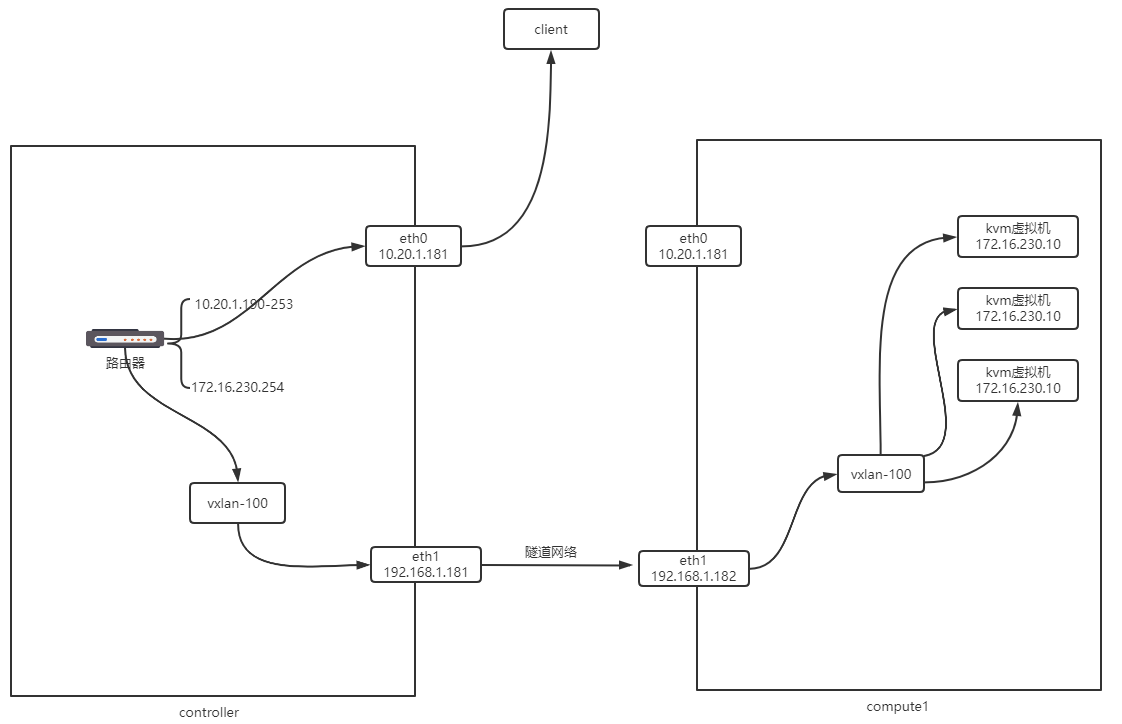
controller配置
[root@controller ~]# cat /etc/neutron/neutron.conf [DEFAULT] core_plugin = ml2 service_plugins = router allow_overlapping_ips = true transport_url = rabbit://openstack:RABBIT_PASS@controller auth_strategy = keystone notify_nova_on_port_status_changes = true notify_nova_on_port_data_changes = true [cors] [database] connection = mysql+pymysql://neutron:NEUTRON_DBPASS@controller/neutron [keystone_authtoken] www_authenticate_uri = http://controller:5000 auth_url = http://controller:5000 memcached_servers = controller:11211 auth_type = password project_domain_name = default user_domain_name = default project_name = service username = neutron password = NEUTRON_PASS [oslo_concurrency] lock_path = /var/lib/neutron/tmp [oslo_messaging_amqp] [oslo_messaging_kafka] [oslo_messaging_notifications] [oslo_messaging_rabbit] [oslo_middleware] [oslo_policy] [privsep] [ssl] [nova] auth_url = http://controller:5000 auth_type = password project_domain_name = default user_domain_name = default region_name = RegionOne project_name = service username = nova password = NOVA_PASS
[root@controller ~]# cat /etc/neutron/plugins/ml2/linuxbridge_agent.ini [DEFAULT] [linux_bridge] physical_interface_mappings = provider:eth0 [vxlan] enable_vxlan = true local_ip = 192.168.1.181 l2_population = true [securitygroup] enable_security_group = true firewall_driver = neutron.agent.linux.iptables_firewall.IptablesFirewallDriver
[root@controller ~]# cat /etc/neutron/plugins/ml2/ml2_conf.ini [DEFAULT] [ml2] type_drivers = flat,vlan,vxlan tenant_network_types = vxlan mechanism_drivers = linuxbridge,l2population extension_drivers = port_security [ml2_type_flat] flat_networks = provider [securitygroup] enable_ipset = true [ml2_type_vxlan] vni_ranges = 1:1000
[root@controller ~]# cat /etc/neutron/l3_agent.ini
[DEFAULT]
interface_driver = linuxbridge
重启进程
systemctl restart neutron-server.service neutron-linuxbridge-agent.service neutron-dhcp-agent.service neutron-metadata-agent.service systemctl enable neutron-l3-agent.service systemctl start neutron-l3-agent.service
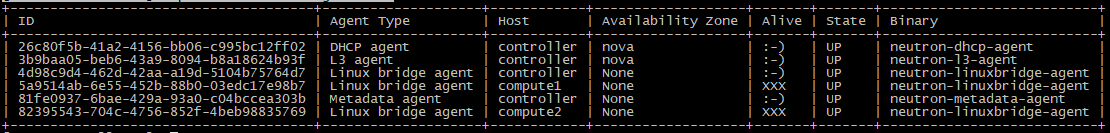
查看neutron网络
[root@controller ~]# openstack network agent list
修改compute1 neutron配置
[root@compute1 ~]# vim /etc/neutron/plugins/ml2/linuxbridge_agent.ini [DEFAULT] [linux_bridge] physical_interface_mappings = provider:eth0 [vxlan] enable_vxlan = true local_ip = 192.168.1.182 l2_population = true [securitygroup] enable_security_group = true firewall_driver = neutron.agent.linux.iptables_firewall.IptablesFirewallDriver
重启
systemctl restart neutron-linuxbridge-agent.service
修改openstack-dashboard 配置文件
'enable_router': False,
修改为
'enable_router': True,
[root@controller openstack-dashboard]# cat /etc/openstack-dashboard/local_settings # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # ---------------------------------------------------------------------- # NOTE: The default values of the settings are defined in # openstack_dashboard/defaults.py. Prevously most available settings # were listed in this example file, but it is no longer true. # For available settings, see openstack_dashboard/defaults.py and # the horizon setting reference found at # https://docs.openstack.org/horizon/latest/configuration/settings.html. # # Django related settings and HORIZON_CONFIG still exist here. # Keep in my mind that they will be revisit in upcoming releases. # ---------------------------------------------------------------------- import os from django.utils.translation import ugettext_lazy as _ from openstack_dashboard.settings import HORIZON_CONFIG DEBUG = False WEBROOT = '/dashboard/' # This setting controls whether or not compression is enabled. Disabling # compression makes Horizon considerably slower, but makes it much easier # to debug JS and CSS changes #COMPRESS_ENABLED = not DEBUG # This setting controls whether compression happens on the fly, or offline # with `python manage.py compress` # See https://django-compressor.readthedocs.io/en/latest/usage/#offline-compression # for more information #COMPRESS_OFFLINE = not DEBUG # If horizon is running in production (DEBUG is False), set this # with the list of host/domain names that the application can serve. # For more information see: # https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/dev/ref/settings/#allowed-hosts ALLOWED_HOSTS = ['*',] # Set SSL proxy settings: # Pass this header from the proxy after terminating the SSL, # and don't forget to strip it from the client's request. # For more information see: # https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/dev/ref/settings/#secure-proxy-ssl-header #SECURE_PROXY_SSL_HEADER = ('HTTP_X_FORWARDED_PROTO', 'https') # If Horizon is being served through SSL, then uncomment the following two # settings to better secure the cookies from security exploits #CSRF_COOKIE_SECURE = True #SESSION_COOKIE_SECURE = True # If provided, a "Report Bug" link will be displayed in the site header # which links to the value of this setting (ideally a URL containing # information on how to report issues). #HORIZON_CONFIG["bug_url"] = "http://bug-report.example.com" # Show backdrop element outside the modal, do not close the modal # after clicking on backdrop. #HORIZON_CONFIG["modal_backdrop"] = "static" # Specify a regular expression to validate user passwords. #HORIZON_CONFIG["password_validator"] = { # "regex": '.*', # "help_text": _("Your password does not meet the requirements."), #} # Turn off browser autocompletion for forms including the login form and # the database creation workflow if so desired. #HORIZON_CONFIG["password_autocomplete"] = "off" # Setting this to True will disable the reveal button for password fields, # including on the login form. #HORIZON_CONFIG["disable_password_reveal"] = False LOCAL_PATH = '/tmp' # Set custom secret key: # You can either set it to a specific value or you can let horizon generate a # default secret key that is unique on this machine, e.i. regardless of the # amount of Python WSGI workers (if used behind Apache+mod_wsgi): However, # there may be situations where you would want to set this explicitly, e.g. # when multiple dashboard instances are distributed on different machines # (usually behind a load-balancer). Either you have to make sure that a session # gets all requests routed to the same dashboard instance or you set the same # SECRET_KEY for all of them. SECRET_KEY='632ad08cc2fe739de836' # We recommend you use memcached for development; otherwise after every reload # of the django development server, you will have to login again. To use # memcached set CACHES to something like below. # For more information, see # https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/1.11/topics/http/sessions/. #CACHES = { # 'default': { # 'BACKEND': 'django.core.cache.backends.memcached.MemcachedCache', # 'LOCATION': '127.0.0.1:11211', # }, #} # If you use ``tox -e runserver`` for developments,then configure # SESSION_ENGINE to django.contrib.sessions.backends.signed_cookies # as shown below: #SESSION_ENGINE = 'django.contrib.sessions.backends.signed_cookies' ESSION_ENGINE = 'django.contrib.sessions.backends.cache' CACHES = { 'default': { 'BACKEND': 'django.core.cache.backends.memcached.MemcachedCache', 'LOCATION': 'controller:11211', } } # Send email to the console by default EMAIL_BACKEND = 'django.core.mail.backends.console.EmailBackend' # Or send them to /dev/null #EMAIL_BACKEND = 'django.core.mail.backends.dummy.EmailBackend' # Configure these for your outgoing email host #EMAIL_HOST = 'smtp.my-company.com' #EMAIL_PORT = 25 #EMAIL_HOST_USER = 'djangomail' #EMAIL_HOST_PASSWORD = 'top-secret!' OPENSTACK_HOST = "controller" OPENSTACK_KEYSTONE_URL = "http://%s:5000/v3" % OPENSTACK_HOST # The OPENSTACK_NEUTRON_NETWORK settings can be used to enable optional # services provided by neutron. Options currently available are load # balancer service, security groups, quotas, VPN service. OPENSTACK_NEUTRON_NETWORK = { 'enable_auto_allocated_network': False, 'enable_distributed_router': False, 'enable_fip_topology_check': False, 'enable_ha_router': False, 'enable_ipv6': False, 'enable_lb': False, 'enable_firewall': False, 'enable_vpn': False, # TODO(amotoki): Drop OPENSTACK_NEUTRON_NETWORK completely from here. # enable_quotas has the different default value here. 'enable_quotas': False, 'enable_rbac_policy': True, 'enable_router': True, 'default_dns_nameservers': [], 'supported_provider_types': ['*'], 'segmentation_id_range': {}, 'extra_provider_types': {}, 'supported_vnic_types': ['*'], 'physical_networks': [], } # The timezone of the server. This should correspond with the timezone # of your entire OpenStack installation, and hopefully be in UTC. TIME_ZONE = "Asia/Shanghai" # Change this patch to the appropriate list of tuples containing # a key, label and static directory containing two files: # _variables.scss and _styles.scss #AVAILABLE_THEMES = [ # ('default', 'Default', 'themes/default'), # ('material', 'Material', 'themes/material'), # ('example', 'Example', 'themes/example'), #] LOGGING = { 'version': 1, # When set to True this will disable all logging except # for loggers specified in this configuration dictionary. Note that # if nothing is specified here and disable_existing_loggers is True, # django.db.backends will still log unless it is disabled explicitly. 'disable_existing_loggers': False, # If apache2 mod_wsgi is used to deploy OpenStack dashboard # timestamp is output by mod_wsgi. If WSGI framework you use does not # output timestamp for logging, add %(asctime)s in the following # format definitions. 'formatters': { 'console': { 'format': '%(levelname)s %(name)s %(message)s' }, 'operation': { # The format of "%(message)s" is defined by # OPERATION_LOG_OPTIONS['format'] 'format': '%(message)s' }, }, 'handlers': { 'null': { 'level': 'DEBUG', 'class': 'logging.NullHandler', }, 'console': { # Set the level to "DEBUG" for verbose output logging. 'level': 'DEBUG' if DEBUG else 'INFO', 'class': 'logging.StreamHandler', 'formatter': 'console', }, 'operation': { 'level': 'INFO', 'class': 'logging.StreamHandler', 'formatter': 'operation', }, }, 'loggers': { 'horizon': { 'handlers': ['console'], 'level': 'DEBUG', 'propagate': False, }, 'horizon.operation_log': { 'handlers': ['operation'], 'level': 'INFO', 'propagate': False, }, 'openstack_dashboard': { 'handlers': ['console'], 'level': 'DEBUG', 'propagate': False, }, 'novaclient': { 'handlers': ['console'], 'level': 'DEBUG', 'propagate': False, }, 'cinderclient': { 'handlers': ['console'], 'level': 'DEBUG', 'propagate': False, }, 'keystoneauth': { 'handlers': ['console'], 'level': 'DEBUG', 'propagate': False, }, 'keystoneclient': { 'handlers': ['console'], 'level': 'DEBUG', 'propagate': False, }, 'glanceclient': { 'handlers': ['console'], 'level': 'DEBUG', 'propagate': False, }, 'neutronclient': { 'handlers': ['console'], 'level': 'DEBUG', 'propagate': False, }, 'swiftclient': { 'handlers': ['console'], 'level': 'DEBUG', 'propagate': False, }, 'oslo_policy': { 'handlers': ['console'], 'level': 'DEBUG', 'propagate': False, }, 'openstack_auth': { 'handlers': ['console'], 'level': 'DEBUG', 'propagate': False, }, 'django': { 'handlers': ['console'], 'level': 'DEBUG', 'propagate': False, }, # Logging from django.db.backends is VERY verbose, send to null # by default. 'django.db.backends': { 'handlers': ['null'], 'propagate': False, }, 'requests': { 'handlers': ['null'], 'propagate': False, }, 'urllib3': { 'handlers': ['null'], 'propagate': False, }, 'chardet.charsetprober': { 'handlers': ['null'], 'propagate': False, }, 'iso8601': { 'handlers': ['null'], 'propagate': False, }, 'scss': { 'handlers': ['null'], 'propagate': False, }, }, } # 'direction' should not be specified for all_tcp/udp/icmp. # It is specified in the form. SECURITY_GROUP_RULES = { 'all_tcp': { 'name': _('All TCP'), 'ip_protocol': 'tcp', 'from_port': '1', 'to_port': '65535', }, 'all_udp': { 'name': _('All UDP'), 'ip_protocol': 'udp', 'from_port': '1', 'to_port': '65535', }, 'all_icmp': { 'name': _('All ICMP'), 'ip_protocol': 'icmp', 'from_port': '-1', 'to_port': '-1', }, 'ssh': { 'name': 'SSH', 'ip_protocol': 'tcp', 'from_port': '22', 'to_port': '22', }, 'smtp': { 'name': 'SMTP', 'ip_protocol': 'tcp', 'from_port': '25', 'to_port': '25', }, 'dns': { 'name': 'DNS', 'ip_protocol': 'tcp', 'from_port': '53', 'to_port': '53', }, 'http': { 'name': 'HTTP', 'ip_protocol': 'tcp', 'from_port': '80', 'to_port': '80', }, 'pop3': { 'name': 'POP3', 'ip_protocol': 'tcp', 'from_port': '110', 'to_port': '110', }, 'imap': { 'name': 'IMAP', 'ip_protocol': 'tcp', 'from_port': '143', 'to_port': '143', }, 'ldap': { 'name': 'LDAP', 'ip_protocol': 'tcp', 'from_port': '389', 'to_port': '389', }, 'https': { 'name': 'HTTPS', 'ip_protocol': 'tcp', 'from_port': '443', 'to_port': '443', }, 'smtps': { 'name': 'SMTPS', 'ip_protocol': 'tcp', 'from_port': '465', 'to_port': '465', }, 'imaps': { 'name': 'IMAPS', 'ip_protocol': 'tcp', 'from_port': '993', 'to_port': '993', }, 'pop3s': { 'name': 'POP3S', 'ip_protocol': 'tcp', 'from_port': '995', 'to_port': '995', }, 'ms_sql': { 'name': 'MS SQL', 'ip_protocol': 'tcp', 'from_port': '1433', 'to_port': '1433', }, 'mysql': { 'name': 'MYSQL', 'ip_protocol': 'tcp', 'from_port': '3306', 'to_port': '3306', }, 'rdp': { 'name': 'RDP', 'ip_protocol': 'tcp', 'from_port': '3389', 'to_port': '3389', }, } # Help URL can be made available for the client. To provide a help URL, edit the # following attribute to the URL of your choice. #HORIZON_CONFIG["help_url"] = "http://openstack.mycompany.org" OPENSTACK_KEYSTONE_MULTIDOMAIN_SUPPORT = True OPENSTACK_API_VERSIONS = { "identity": 3, "image": 2, "volume": 3, } OPENSTACK_KEYSTONE_DEFAULT_DOMAIN = "Default" OPENSTACK_KEYSTONE_DEFAULT_ROLE = "user"
重启http
systemctl restart httpd.service
登录dashboard,配置路由等相关信息
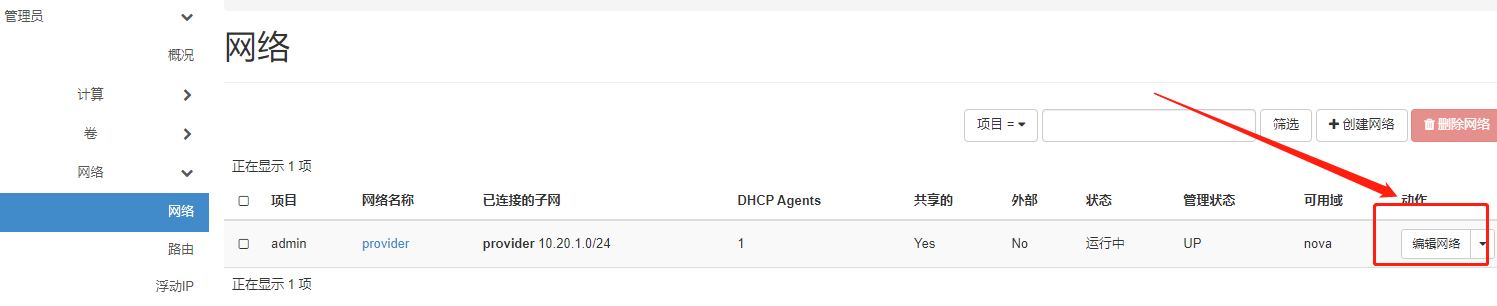
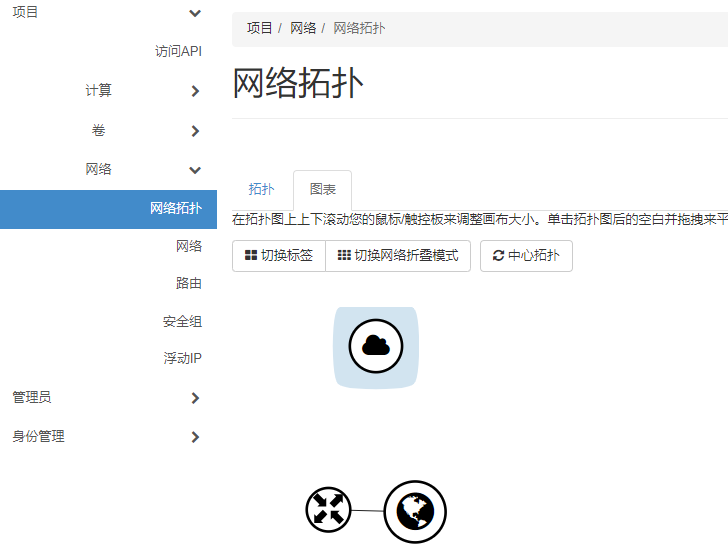
项目-网络拓扑图查看, 默认不是外部网络
管理员---网路-- 编辑网络
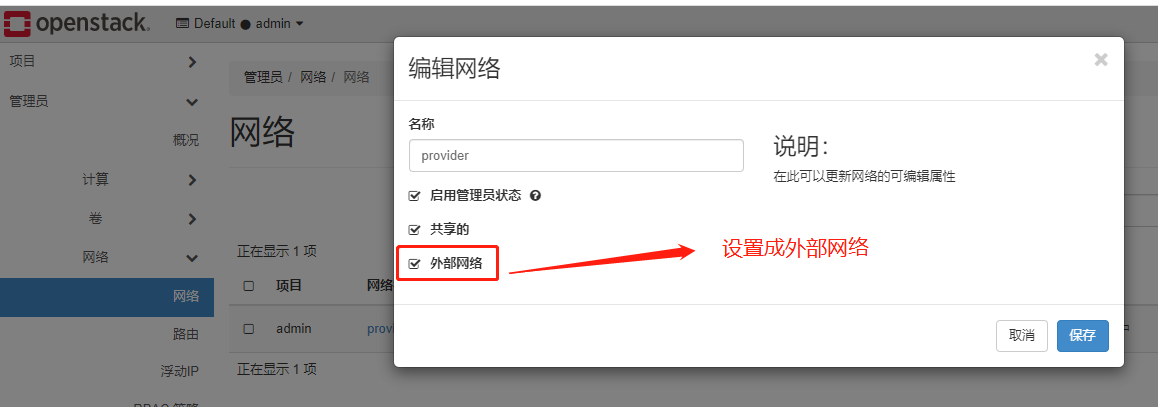
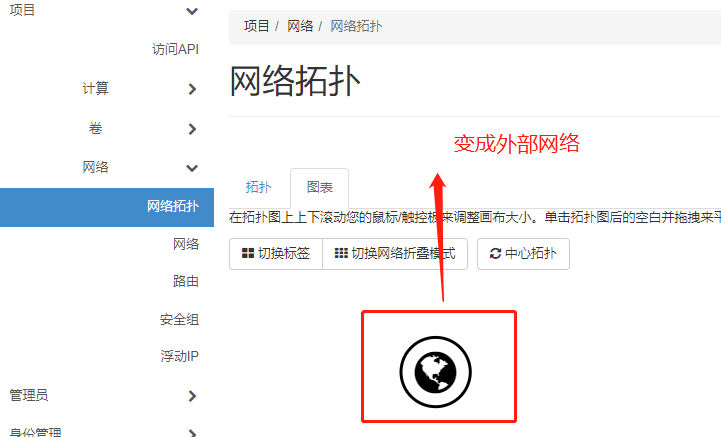
再次在项目-网络中查看
创建私有网络(租户网络)
项目--网络---创建网络
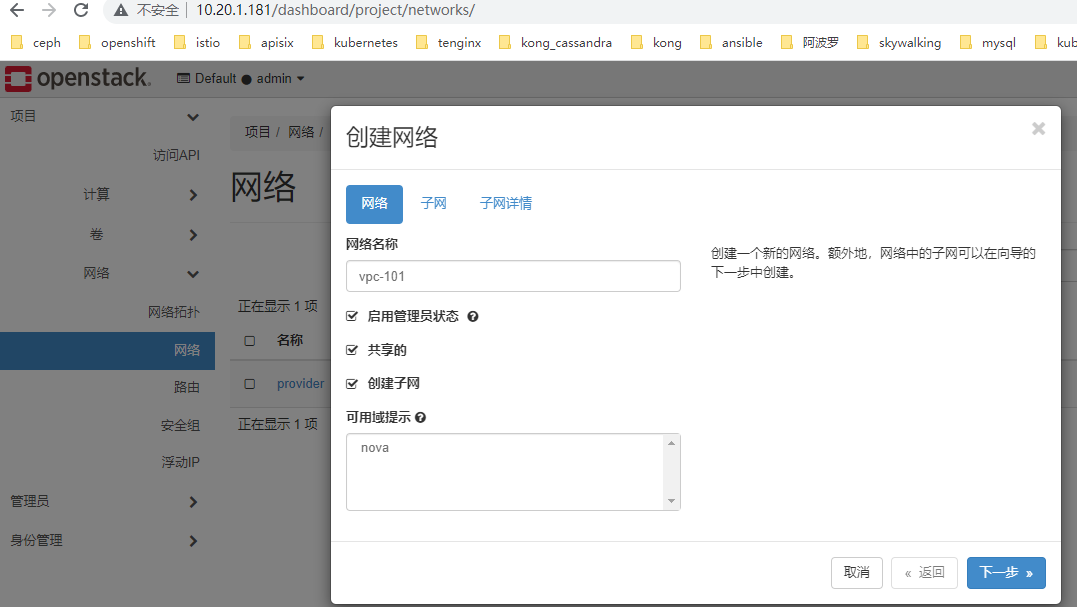
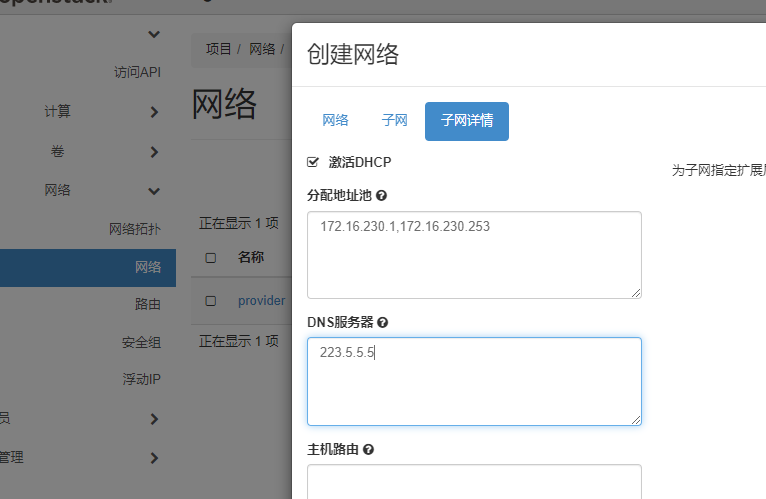
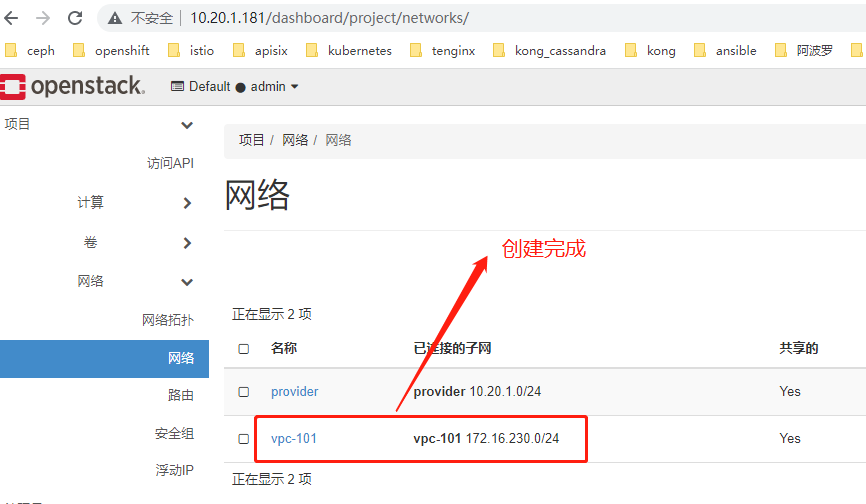
外部网络 与 vpc网络无关联
创建路由器
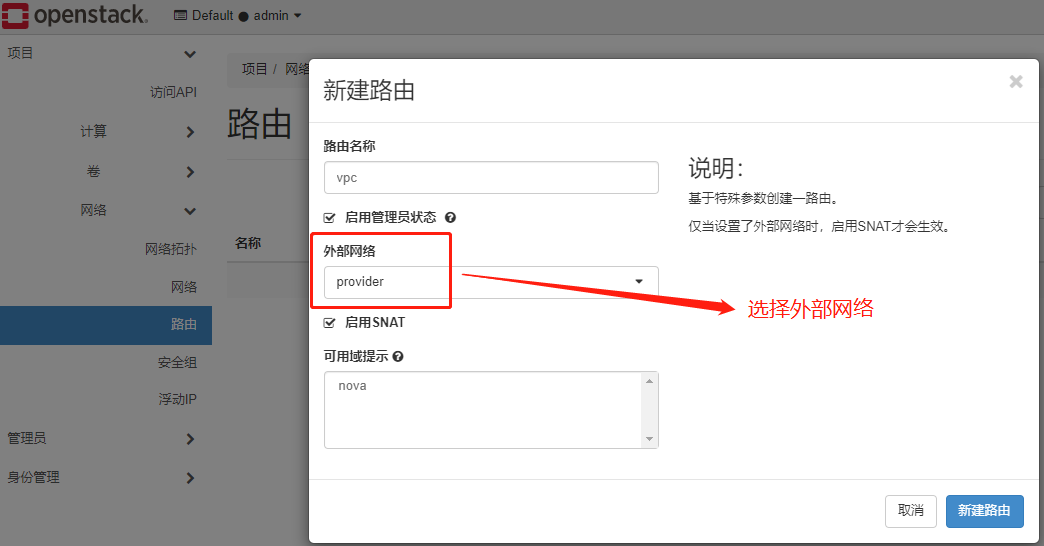
路由器创建完成
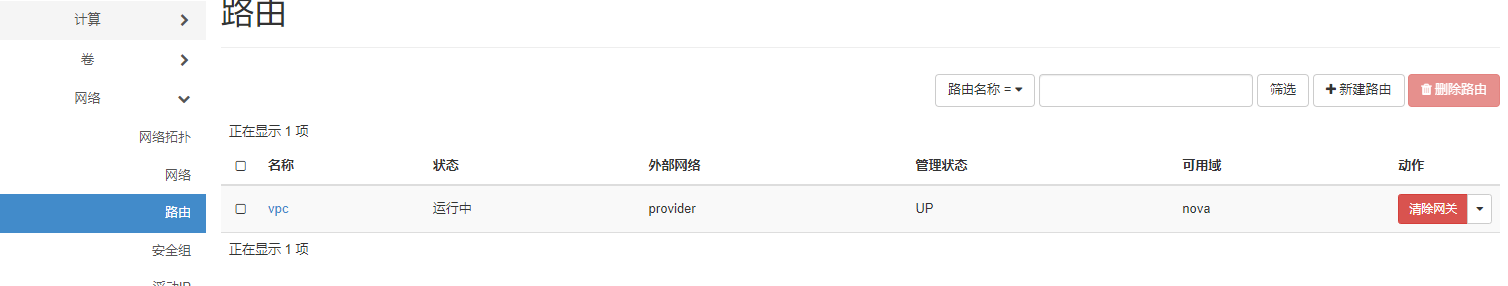
网络拓扑图中,路由器与共有网络已经链接
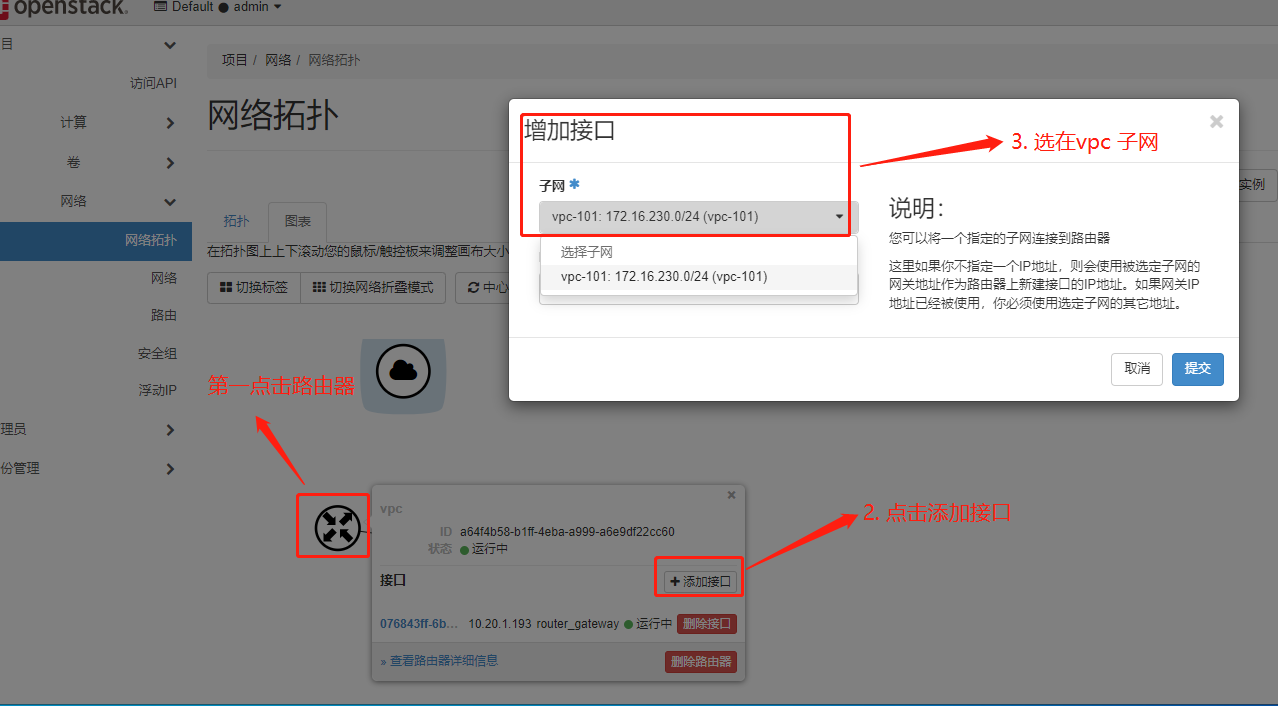
完成后,拓扑图变成 私有网络 - 路由器 -- 外部网络 相互关联
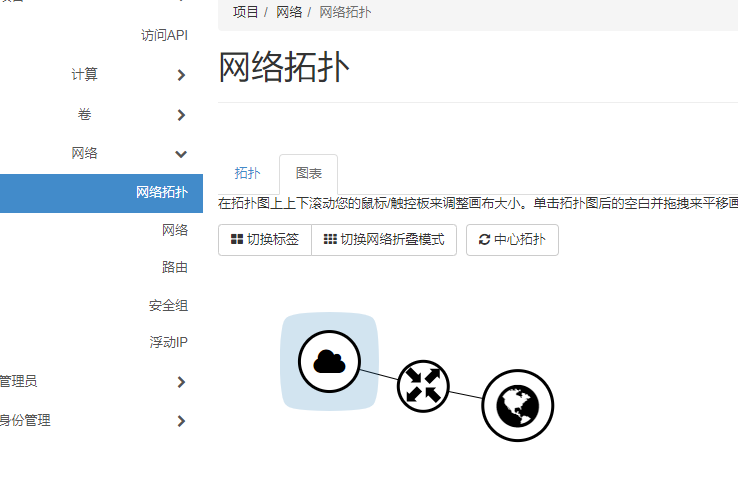
创建实例测试
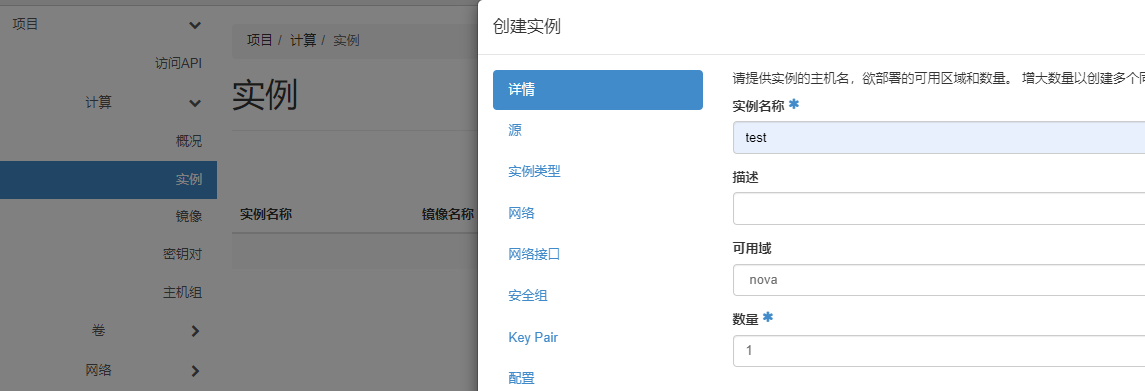
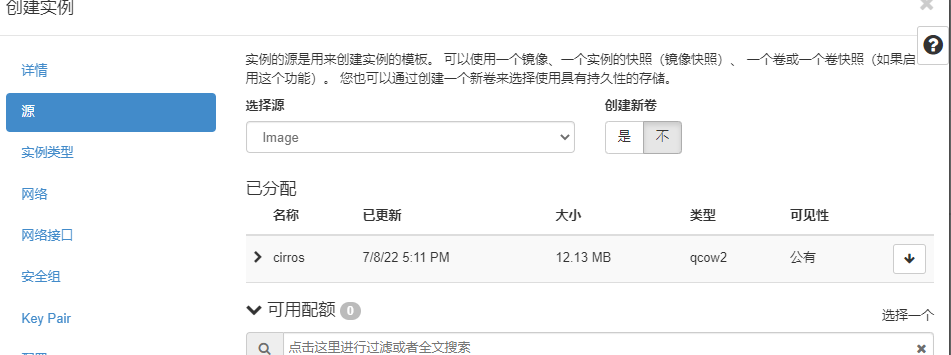
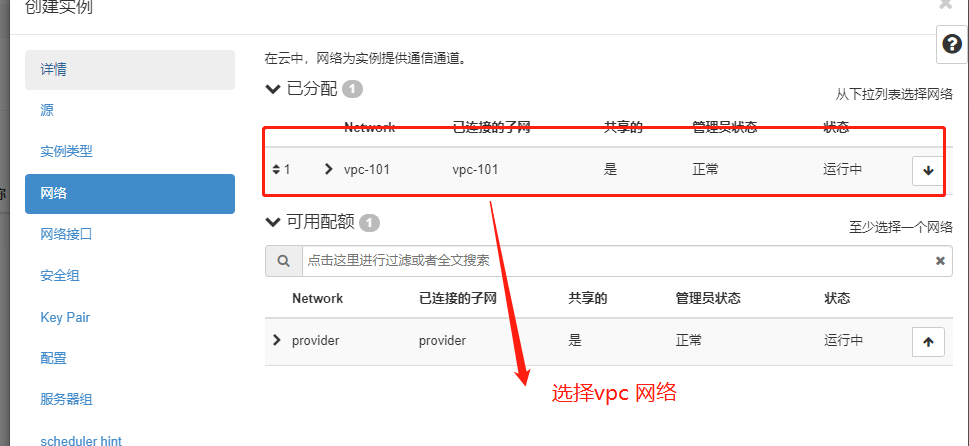
IP地址为172.16.230.162 IP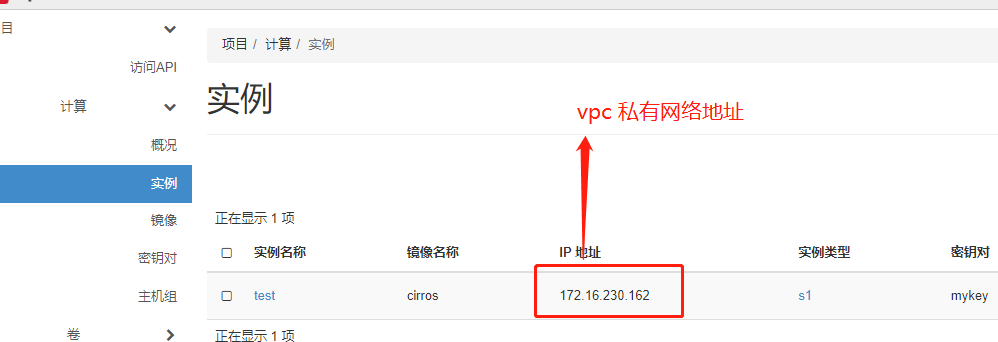
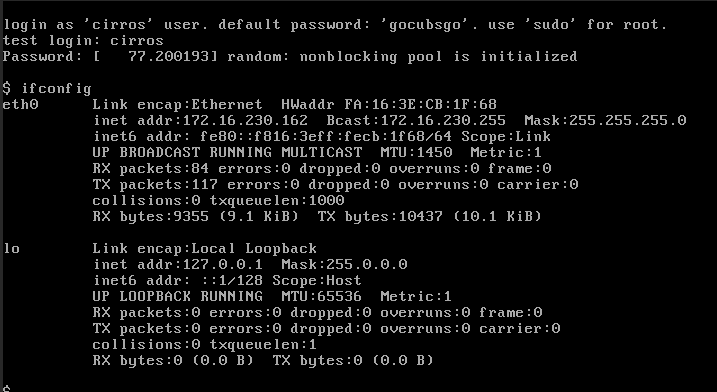
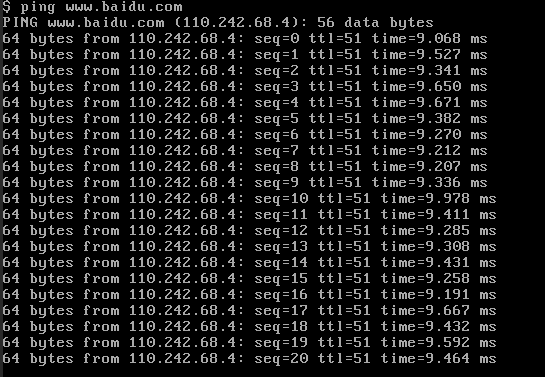
由于外网网络 无法访问 vpc网络地址, 需要绑定浮动IP
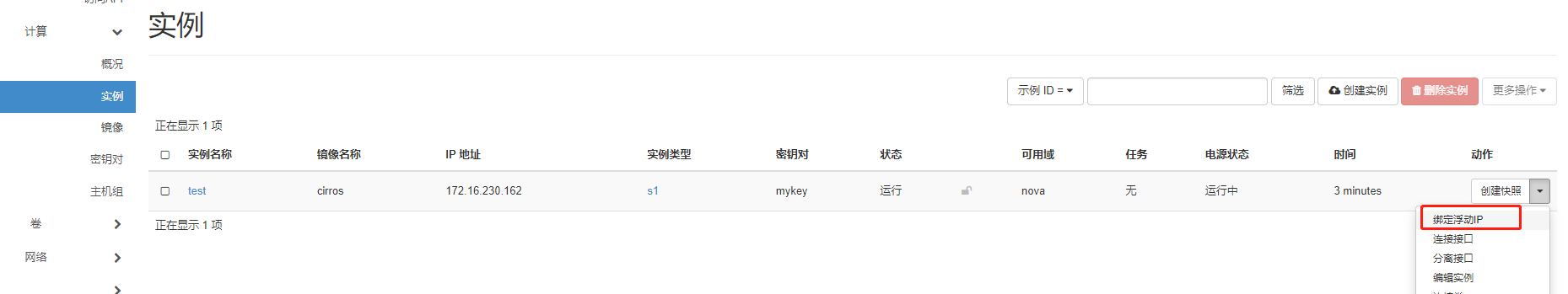
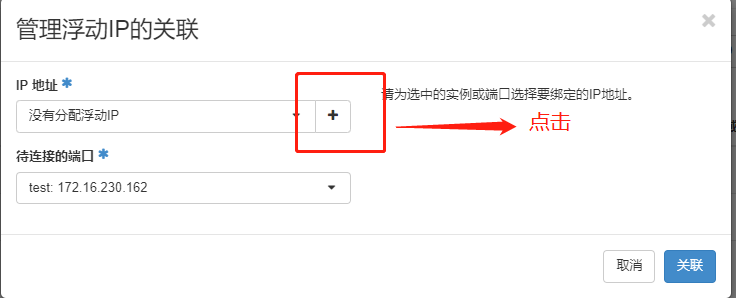
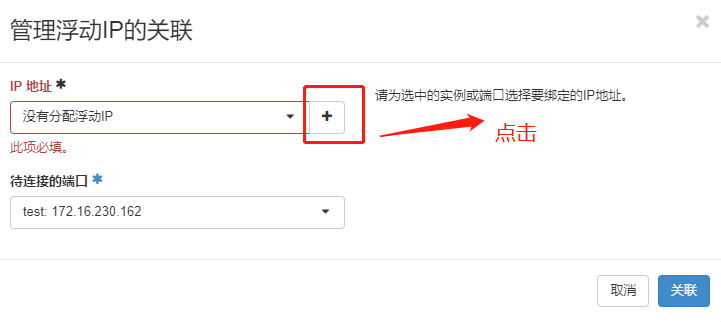
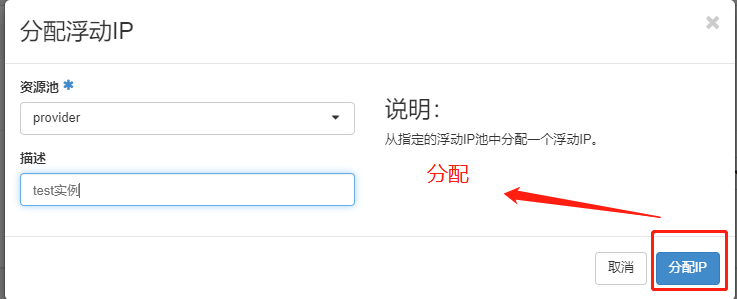
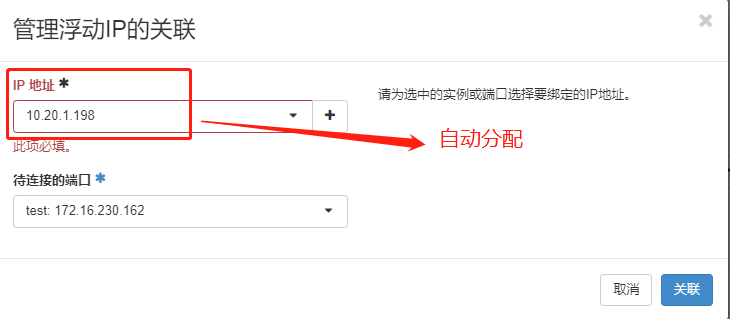
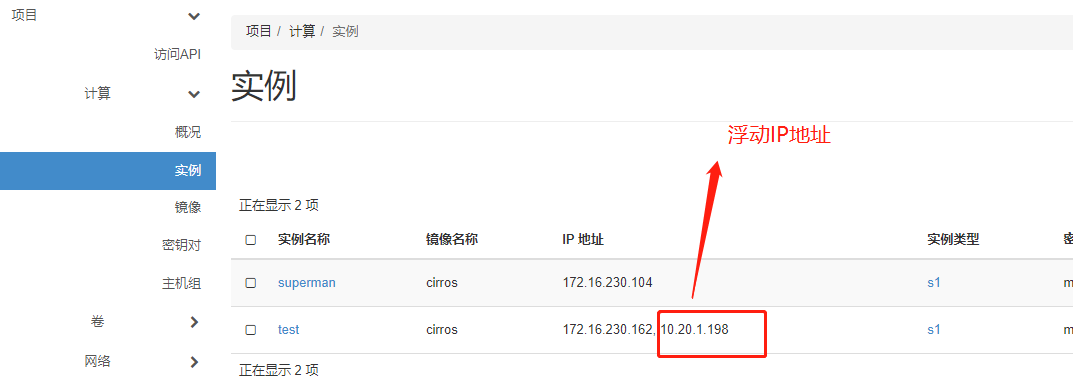
可以登录, 可以ping通