离线综合案例
目标
v 理解网站点击流数据分析的业务背景
v 理解网站点击流数据分析中常用分析指标的业务含义
v 掌握网站点击流数据分析系统的技术架构
v 掌握网站点击流数据分析系统中各环节的技术实现
v 能独立设计完成一个初步的网站点击流数据分析系统
网站点击流数据分析,业务知识,推荐书籍:
《网站分析实战——如何以数据驱动决策,提升网站价值》王彦平,吴盛锋编著
1. 网站点击流数据分析项目业务背景
1.1 什么是点击流数据
1.1.1 WEB访问日志
即指用户访问网站时的所有访问、浏览、点击行为数据。比如点击了哪一个链接,在哪个网页停留时间最多,采用了哪个搜索项、总体浏览时间等。而所有这些信息都可被保存在网站日志中。通过分析这些数据,可以获知许多对网站运营至关重要的信息。采集的数据越全面,分析就能越精准。
² 日志的生成渠道:
1)是网站的web服务器所记录的web访问日志;
2)是通过在页面嵌入自定义的js代码来获取用户的所有访问行为(比如鼠标悬停的位置,点击的页面组件等),然后通过ajax请求到后台记录日志;这种方式所能采集的信息最全面;
3)通过在页面上埋点1像素的图片,将相关页面访问信息请求到后台记录日志;
² 日志数据内容详述:
在实际操作中,有以下几个方面的数据可以被采集:
1) 访客的系统属性特征。比如所采用的操作系统、浏览器、域名和访问速度等。
2) 访问特征。包括停留时间、点击的URL等。
3) 来源特征。包括网络内容信息类型、内容分类和来访URL等。
4) 产品特征。包括所访问的产品编号、产品类别、产品颜色、产品价格、产品利润、产品数量和特价等级等。
以电商某东为例,其点击日志格式如下:
|
GET /log.gif?t=item.010001&m=UA-J2011-1&pin=-&uid=1679790178&sid=1679790178|12&v=je=1$sc=24-bit$sr=1600x900$ul=zh-cn$cs=GBK$dt=【云南白药套装】云南白药牙膏 180g×3 (留兰香型)【行情报价价格评测】-京东$hn=item.jd.com$fl=16.0 r0$os=win$br=chrome$bv=39.0.2171.95$wb=1437269412$xb=1449548587$yb=1456186252$zb=12$cb=4$usc=direct$ucp=-$umd=none$uct=-$ct=1456186505411$lt=0$tad=-$sku=1326523$cid1=1316$cid2=1384$cid3=1405$brand=20583$pinid=-&ref=&rm=1456186505411 HTTP/1.1 |
1.1.2 点击流数据模型
点击流概念
点击流这个概念更注重用户浏览网站的整个流程,网站日志中记录的用户点击就像是图上的“点”,而点击流更像是将这些“点”串起来形成的“线”。也可以把“点”认为是网站的Page,而“线”则是访问网站的Session。所以点击流数据是由网站日志中整理得到的,它可以比网站日志包含更多的信息,从而使基于点击流数据统计得到的结果更加丰富和高效。
点击流模型生成
点击流数据在具体操作上是由散点状的点击日志数据梳理所得,从而,点击数据在数据建模时应该存在两张模型表(Pageviews和visits):
1、用于生成点击流的访问日志表
|
时间戳 |
IP地址 |
Cookie |
Session |
请求URL |
Referal |
|
2012-01-01 12:31:12 |
101.0.0.1 |
User01 |
S001 |
/a/... |
somesite.com |
|
2012-01-01 12:31:16 |
201.0.0.2 |
User02 |
S002 |
/a/... |
- |
|
2012-01-01 12:33:06 |
101.0.0.2 |
User03 |
S002 |
/b/... |
baidu.com |
|
2012-01-01 15:16:39 |
234.0.0.3 |
User01 |
S003 |
/c/... |
google.com |
|
2012-01-01 15:17:11 |
101.0.0.1 |
User01 |
S004 |
/d/... |
/c/... |
|
2012-01-01 15:19:23 |
101.0.0.1 |
User01 |
S004 |
/e/... |
/d/.... |
2、页面点击流模型Pageviews表
|
Session |
userid |
时间 |
访问页面URL |
停留时长 |
第几步 |
|
S001 |
User01 |
2012-01-01 12:31:12 |
/a/.... |
30 |
1 |
|
S002 |
User02 |
2012-01-01 12:31:16 |
/a/.... |
10 |
1 |
|
S002 |
User02 |
2012-01-01 12:33:06 |
/b/.... |
110 |
2 |
|
S002 |
User02 |
2012-01-01 12:35:06 |
/e/.... |
30 |
3 |
3、点击流模型Visits表
|
Session |
起始时间 |
结束时间 |
进入页面 |
离开页面 |
访问页面数 |
IP |
cookie |
referal |
|
S001 |
2012-01-01 12:31:12 |
2012-01-01 12:31:12 |
/a/... |
/a/... |
1 |
101.0.0.1 |
User01 |
somesite.com |
|
S002 |
2012-01-01 12:31:16 |
2012-01-01 12:35:06 |
/a/... |
/e/... |
3 |
201.0.0.2 |
User02 |
- |
|
S003 |
2012-01-01 12:35:42 |
2012-01-01 12:35:42 |
/c/... |
/c/... |
1 |
234.0.0.3 |
User03 |
baidu.com |
|
S003 |
2012-01-01 15:16:39 |
2012-01-01 15:19:23 |
/c/... |
/e/... |
3 |
101.0.0.1 |
User01 |
google.com |
|
…… |
…… |
…… |
…… |
…… |
…… |
…… |
…… |
…… |
这就是点击流模型。当WEB日志转化成点击流数据的时候,很多网站分析度量的计算变得简单了,这就是点击流的“魔力”所在。基于点击流数据我们可以统计出许多常见的网站分析度量
1.2网站流量数据分析的意义
网站流量统计分析,可以帮助网站管理员、运营人员、推广人员等实时获取网站流量信息,并从流量来源、网站内容、网站访客特性等多方面提供网站分析的数据依据。从而帮助提高网站流量,提升网站用户体验,让访客更多的沉淀下来变成会员或客户,通过更少的投入获取最大化的收入。
如下表:
|
网站的眼睛 |
网站的神经 |
网站的大脑 |
|
访问者来自哪里? 访问者在寻找什么? 哪些页面最受欢迎? 访问者从哪里进入?
|
网页布局合理吗? 网站导航清晰吗? 哪些功能存在问题 网站内容有效吗 转化路径靠谱吗? |
如何分解目标? 如何分配广告预算? 如何衡量产品表现? 哪些产品需要优化? 哪些指标需要关注? |
点击流分析的意义可分为两大方面:
1、技术上
可以合理修改网站结构及适度分配资源,构建后台服务器群组,比如
辅助改进网络的拓扑设计,提高性能
在有高度相关性的节点之间安排快速有效的访问路径
帮助企业更好地设计网站主页和安排网页内容
2、业务上
1) 帮助企业改善市场营销决策,如把广告放在适当的Web页面上。
2) 优化页面及业务流程设计,提高流量转化率。
3) 帮助企业更好地根据客户的兴趣来安排内容。
4) 帮助企业对客户群进行细分,针对不同客户制定个性化的促销策略等。
终极目标是:改善网站(电商、社交、电影、小说)的运营,获取更高投资回报率(ROI)
1.3 如何进行网站流量分析
流量分析整体来说是一个内涵非常丰富的体系,其整体过程是一个金字塔结构:
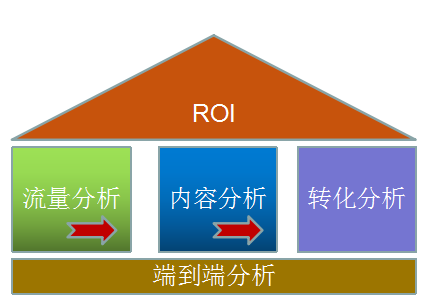
1.3.1 流量分析模型举例
通常有以下几大类的分析需求:
1)网站流量质量分析
流量对于每个网站来说都是很重要,但流量并不是越多越好,应该更加看重流量的质量,换句话来说就是流量可以为我们带来多少收入。
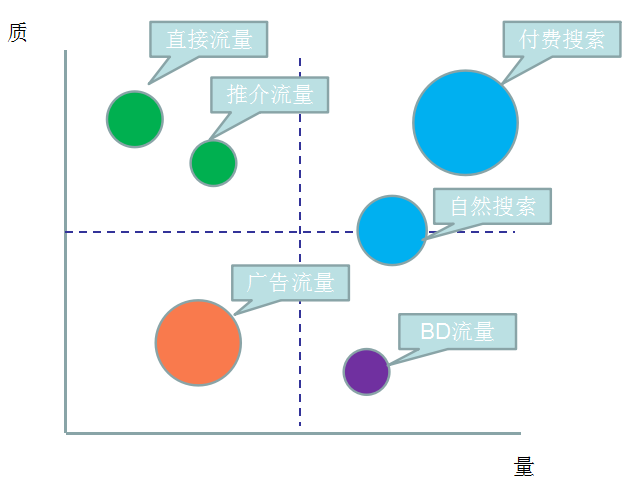
2)网站流量多维度细分
细分是指通过不同维度对指标进行分割,查看同一个指标在不同维度下的表现,进而找出有问题的那部分指标,对这部分指标进行优化。
3)网站内容及导航分析
对于所有网站来说,页面都可以被划分为三个类别:
v 导航页
v 功能页
v 内容页
首页和列表页都是典型的导航页;
站内搜索页面、注册表单页面和购物车页面都是典型的功能页,
而产品详情页、新闻和文章页都是典型的内容页。
比如从内容导航分析中,以下两类行为就是网站运营者不希望看到的行为:
第一个问题:访问者从导航页进入,在还没有看到内容页面之前就从导航页离开网站,需要分析导航页造成访问者中途离开的原因。
第二个问题:访问者从导航页进入内容页后,又返回到导航页,说明需要分析内容页的最初设计,并考虑中内容页提供交叉的信息推荐
4)网站转化及漏斗分析
所谓转化,即网站业务流程中的一个封闭渠道,引导用户按照流程最终实现业务目标(比如商品成交);而漏斗模型则是指进入渠道的用户在各环节递进过程中逐渐流失的形象描述;
对于转化渠道,主要进行两部分的分析:
访问者的流失和迷失
1、阻力和流失

造成流失的原因很多,如:
不恰当的商品或活动推荐
对支付环节中专业名词的解释、帮助信息等内容不当
2、迷失
造成迷失的主要原因是转化流量设计不合理,访问者在特定阶段得不到需要的信息,并且不能根据现有的信息作出决策
总之,网站流量分析是一门内容非常丰富的学科,本课程中主要关注网站分析过程中的技术运用,更多关于网站流量分析的业务知识可学习推荐资料。
1.3.2 流量分析常见指标
课程中涉及的分析指标主要位于以下几大方面:
1)基础分析(PV,IP,UV)
- 趋势分析:根据选定的时段,提供网站流量数据,通过流量趋势变化形态,为您分析网站访客的访问规律、网站发展状况提供参考。
- 对比分析:根据选定的两个对比时段,提供网站流量在时间上的纵向对比报表,帮您发现网站发展状况、发展规律、流量变化率等。
- 当前在线:提供当前时刻站点上的访客量,以及最近15分钟流量、来源、受访、访客变化情况等,方便用户及时了解当前网站流量状况。
- 访问明细:提供最近7日的访客访问记录,可按每个PV或每次访问行为(访客的每次会话)显示,并可按照来源、搜索词等条件进行筛选。 通过访问明细,用户可以详细了解网站流量的累计过程,从而为用户快速找出流量变动原因提供最原始、最准确的依据。
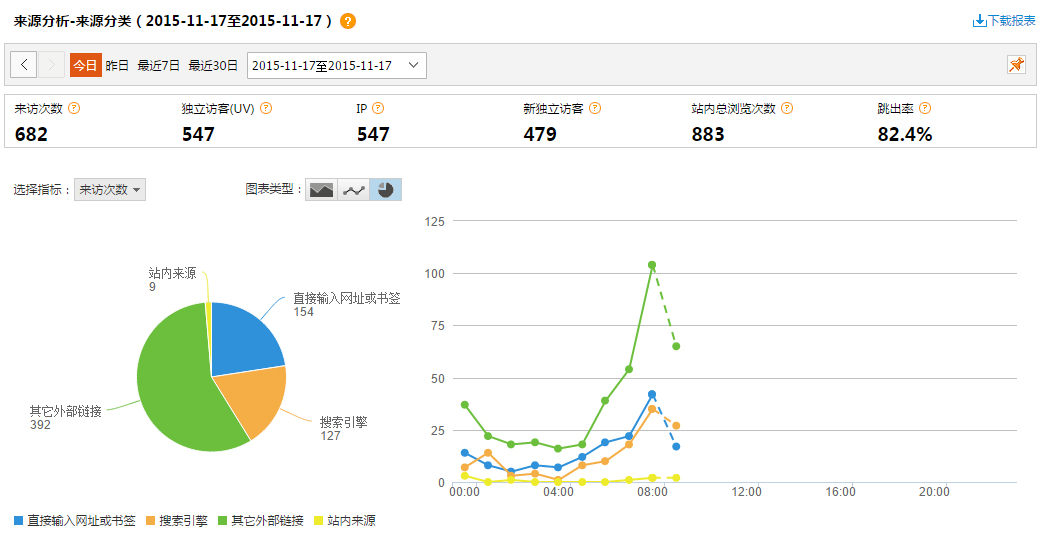
- 来源分类:提供不同来源形式(直接输入、搜索引擎、其他外部链接、站内来源)、不同来源项引入流量的比例情况。通过精确的量化数据,帮助用户分析什么类型的来路产生的流量多、效果好,进而合理优化推广方案。
- 搜索引擎:提供各搜索引擎以及搜索引擎子产品引入流量的比例情况。从搜索引擎引入流量的的角度,帮助用户了解网站的SEO、SEM效果,从而为制定下一步SEO、SEM计划提供依据。
- 搜索词:提供访客通过搜索引擎进入网站所使用的搜索词,以及各搜索词引入流量的特征和分布。帮助用户了解各搜索词引入流量的质量,进而了解访客的兴趣关注点、网站与访客兴趣点的匹配度,为优化SEO方案及SEM提词方案提供详细依据。
- 最近7日的访客搜索记录,可按每个PV或每次访问行为(访客的每次会话)显示,并可按照访客类型、地区等条件进行筛选。为您搜索引擎优化提供最详细的原始数据。
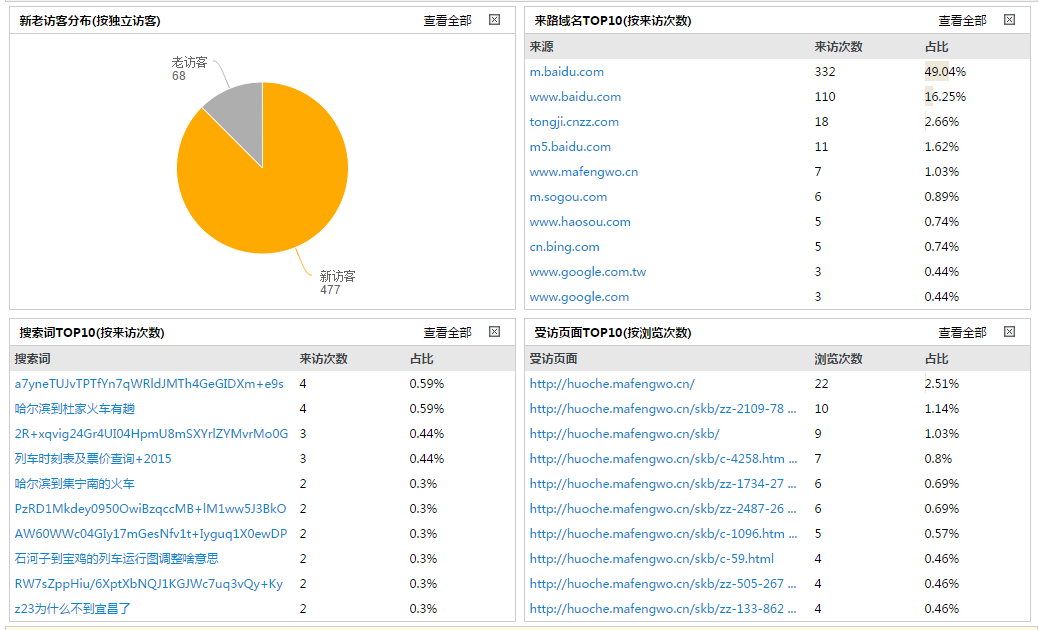
- 来路域名:提供具体来路域名引入流量的分布情况,并可按“社会化媒体”、“搜索引擎”、“邮箱”等网站类型对来源域名进行分类。 帮助用户了解哪类推广渠道产生的流量多、效果好,进而合理优化网站推广方案。
- 来路页面:提供具体来路页面引入流量的分布情况。 尤其对于通过流量置换、包广告位等方式从其他网站引入流量的用户,该功能可以方便、清晰地展现广告引入的流量及效果,为优化推广方案提供依据。
- 来源升降榜:提供开通统计后任意两日的TOP10000搜索词、来路域名引入流量的对比情况,并按照变化的剧烈程度提供排行榜。 用户可通过此功能快速找到哪些来路对网站流量的影响比较大,从而及时排查相应来路问题。
2)来源分析
- 来源分类:提供不同来源形式(直接输入、搜索引擎、其他外部链接、站内来源)、不同来源项引入流量的比例情况。通过精确的量化数据,帮助用户分析什么类型的来路产生的流量多、效果好,进而合理优化推广方案。
- 搜索引擎:提供各搜索引擎以及搜索引擎子产品引入流量的比例情况。从搜索引擎引入流量的的角度,帮助用户了解网站的SEO、SEM效果,从而为制定下一步SEO、SEM计划提供依据。
- 搜索词:提供访客通过搜索引擎进入网站所使用的搜索词,以及各搜索词引入流量的特征和分布。帮助用户了解各搜索词引入流量的质量,进而了解访客的兴趣关注点、网站与访客兴趣点的匹配度,为优化SEO方案及SEM提词方案提供详细依据。
- 最近7日的访客搜索记录,可按每个PV或每次访问行为(访客的每次会话)显示,并可按照访客类型、地区等条件进行筛选。为您搜索引擎优化提供最详细的原始数据。
- 来路域名:提供具体来路域名引入流量的分布情况,并可按“社会化媒体”、“搜索引擎”、“邮箱”等网站类型对来源域名进行分类。 帮助用户了解哪类推广渠道产生的流量多、效果好,进而合理优化网站推广方案。
- 来路页面:提供具体来路页面引入流量的分布情况。 尤其对于通过流量置换、包广告位等方式从其他网站引入流量的用户,该功能可以方便、清晰地展现广告引入的流量及效果,为优化推广方案提供依据。
- 来源升降榜:提供开通统计后任意两日的TOP10000搜索词、来路域名引入流量的对比情况,并按照变化的剧烈程度提供排行榜。 用户可通过此功能快速找到哪些来路对网站流量的影响比较大,从而及时排查相应来路问题。
3)受访分析
- 受访域名:提供访客对网站中各个域名的访问情况。 一般情况下,网站不同域名提供的产品、内容各有差异,通过此功能用户可以了解不同内容的受欢迎程度以及网站运营成效。
- 受访页面:提供访客对网站中各个页面的访问情况。 站内入口页面为访客进入网站时浏览的第一个页面,如果入口页面的跳出率较高则需要关注并优化;站内出口页面为访客访问网站的最后一个页面,对于离开率较高的页面需要关注并优化。
- 受访升降榜:提供开通统计后任意两日的TOP10000受访页面的浏览情况对比,并按照变化的剧烈程度提供排行榜。 可通过此功能验证经过改版的页面是否有流量提升或哪些页面有巨大流量波动,从而及时排查相应问题。
- 热点图:记录访客在页面上的鼠标点击行为,通过颜色区分不同区域的点击热度;支持将一组页面设置为"关注范围",并可按来路细分点击热度。 通过访客在页面上的点击量统计,可以了解页面设计是否合理、广告位的安排能否获取更多佣金等。
- 用户视点:提供受访页面对页面上链接的其他站内页面的输出流量,并通过输出流量的高低绘制热度图,与热点图不同的是,所有记录都是实际打开了下一页面产生了浏览次数(PV)的数据,而不仅仅是拥有鼠标点击行为。
- 访问轨迹:提供观察焦点页面的上下游页面,了解访客从哪些途径进入页面,又流向了哪里。 通过上游页面列表比较出不同流量引入渠道的效果;通过下游页面列表了解用户的浏览习惯,哪些页面元素、内容更吸引访客点击。
4)访客分析
- 地区运营商:提供各地区访客、各网络运营商访客的访问情况分布。 地方网站、下载站等与地域性、网络链路等结合较为紧密的网站,可以参考此功能数据,合理优化推广运营方案。
- 终端详情:提供网站访客所使用的浏览终端的配置情况。 参考此数据进行网页设计、开发,可更好地提高网站兼容性,以达到良好的用户交互体验。
- 新老访客:当日访客中,历史上第一次访问该网站的访客记为当日新访客;历史上已经访问过该网站的访客记为老访客。 新访客与老访客进入网站的途径和浏览行为往往存在差异。该功能可以辅助分析不同访客的行为习惯,针对不同访客优化网站,例如为制作新手导航提供数据支持等。
- 忠诚度:从访客一天内回访网站的次数(日访问频度)与访客上次访问网站的时间两个角度,分析访客对网站的访问粘性、忠诚度、吸引程度。 由于提升网站内容的更新频率、增强用户体验与用户价值可以有更高的忠诚度,因此该功能在网站内容更新及用户体验方面提供了重要参考。
- 活跃度:从访客单次访问浏览网站的时间与网页数两个角度,分析访客在网站上的活跃程度。 由于提升网站内容的质量与数量可以获得更高的活跃度,因此该功能是网站内容分析的关键指标之一。
5)转化路径分析
转化定义
·访客在您的网站完成了某项您期望的活动,记为一次转化,如注册或下载。
目标示例
·获得用户目标:在线注册、创建账号等。
·咨询目标:咨询、留言、电话等。
·互动目标:视频播放、加入购物车、分享等。
·收入目标:在线订单、付款等。
转化数据的应用
·在报告的自定义指标中勾选转化指标,实时掌握网站的推广及运营情况。
·结合“全部来源”、“转化路径”、“页面上下游”等报告分析访问漏斗,提高转化率。
·对“转化目标”设置价值,预估转化收益,衡量ROI。
路径分析:根据设置的特定路线,监测某一流程的完成转化情况,算出每步的转换率和流失率数据,如注册流程,购买流程等。
转化类型:
1、页面

2、事件

2 整体技术流程及架构
2.1 数据处理流程
该项目是一个纯粹的数据分析项目,其整体流程基本上就是依据数据的处理流程进行,依此有以下几个大的步骤:
1) 数据采集
首先,通过页面嵌入JS代码的方式获取用户访问行为,并发送到web服务的后台记录日志
然后,将各服务器上生成的点击流日志通过实时或批量的方式汇聚到HDFS文件系统中
当然,一个综合分析系统,数据源可能不仅包含点击流数据,还有数据库中的业务数据(如用户信息、商品信息、订单信息等)及对分析有益的外部数据。
2) 数据预处理
通过mapreduce程序对采集到的点击流数据进行预处理,比如清洗,格式整理,滤除脏数据等
3) 数据入库
将预处理之后的数据导入到HIVE仓库中相应的库和表中
4) 数据分析
项目的核心内容,即根据需求开发ETL分析语句,得出各种统计结果
5) 数据展现
将分析所得数据进行可视化
2.2 项目结构
由于本项目是一个纯粹数据分析项目,其整体结构亦跟分析流程匹配,并没有特别复杂的结构,如下图:
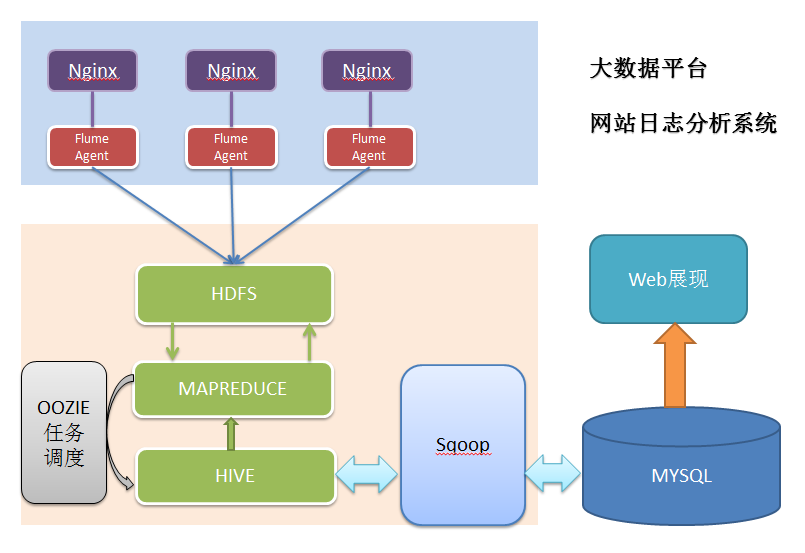
其中,需要强调的是:
系统的数据分析不是一次性的,而是按照一定的时间频率反复计算,因而整个处理链条中的各个环节需要按照一定的先后依赖关系紧密衔接,即涉及到大量任务单元的管理调度,所以,项目中需要添加一个任务调度模块
2.3 数据展现
数据展现的目的是将分析所得的数据进行可视化,以便运营决策人员能更方便地获取数据,更快更简单地理解数据
3 模块开发——数据采集
3.1 需求
数据采集的需求广义上来说分为两大部分。
1)是在页面采集用户的访问行为,具体开发工作:
1、开发页面埋点js,采集用户访问行为
2、后台接受页面js请求记录日志
此部分工作也可以归属为“数据源”,其开发工作通常由web开发团队负责
2)是从web服务器上汇聚日志到HDFS,是数据分析系统的数据采集,此部分工作由数据分析平台建设团队负责,具体的技术实现有很多方式:
² Shell脚本
优点:轻量级,开发简单
缺点:对日志采集过程中的容错处理不便控制
² Java采集程序
优点:可对采集过程实现精细控制
缺点:开发工作量大
² Flume日志采集框架
成熟的开源日志采集系统,且本身就是hadoop生态体系中的一员,与hadoop体系中的各种框架组件具有天生的亲和力,可扩展性强
3.2 技术选型
在点击流日志分析这种场景中,对数据采集部分的可靠性、容错能力要求通常不会非常严苛,因此使用通用的flume日志采集框架完全可以满足需求。
本项目即使用flume来实现日志采集。
3.3 Flume日志采集系统搭建
1、数据源信息
本项目分析的数据用nginx服务器所生成的流量日志,存放在各台nginx服务器上,如:
/var/log/httpd/access_log.2015-11-10-13-00.log
/var/log/httpd/access_log.2015-11-10-14-00.log
/var/log/httpd/access_log.2015-11-10-15-00.log
/var/log/httpd/access_log.2015-11-10-16-00.log
2、数据内容样例
数据的具体内容在采集阶段其实不用太关心。
|
58.215.204.118 - - [18/Sep/2013:06:51:35 +0000] "GET /wp-includes/js/jquery/jquery.js?ver=1.10.2 HTTP/1.1" 304 0 "http://blog.fens.me/nodejs-socketio-chat/" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 5.1; rv:23.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/23.0" |
字段解析:
1、访客ip地址: 58.215.204.118
2、访客用户信息: - -
3、请求时间:[18/Sep/2013:06:51:35 +0000]
4、请求方式:GET
5、请求的url:/wp-includes/js/jquery/jquery.js?ver=1.10.2
6、请求所用协议:HTTP/1.1
7、响应码:304
8、返回的数据流量:0
9、访客的来源url:http://blog.fens.me/nodejs-socketio-chat/
10、访客所用浏览器:Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 5.1; rv:23.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/23.0
3、日志文件生成规律
基本规律为:
当前正在写的文件为access_log;
文件体积达到64M,或时间间隔达到60分钟,即滚动重命名切换成历史日志文件;
形如: access_log.2015-11-10-13-00.log
当然,每个公司的web服务器日志策略不同,可在web程序的log4j.properties中定义,如下:
|
log4j.appender.logDailyFile = org.apache.log4j.DailyRollingFileAppender log4j.appender.logDailyFile.layout = org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout log4j.appender.logDailyFile.layout.ConversionPattern = [%-5p][%-22d{yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ssS}][%l]%n%m%n log4j.appender.logDailyFile.Threshold = DEBUG log4j.appender.logDailyFile.ImmediateFlush = TRUE log4j.appender.logDailyFile.Append = TRUE log4j.appender.logDailyFile.File = /var/logs/access_log log4j.appender.logDailyFile.DatePattern = '.'yyyy-MM-dd-HH-mm'.log' log4j.appender.logDailyFile.Encoding = UTF-8 |
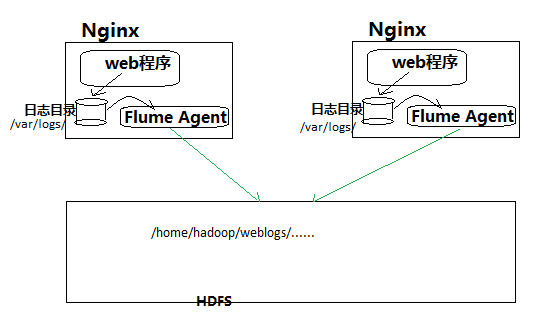
4、Flume采集实现
Flume采集系统的搭建相对简单:
1、在个web服务器上部署agent节点,修改配置文件
2、启动agent节点,将采集到的数据汇聚到指定的HDFS目录中
如下图:
² 版本选择:apache-flume-1.6.0
² 采集规则设计:
1、 采集源:nginx服务器日志目录
2、 存放地:hdfs目录/home/hadoop/weblogs/
² 采集规则配置详情
|
agent1.sources = source1 agent1.sinks = sink1 agent1.channels = channel1
# Describe/configure spooldir source1 #agent1.sources.source1.type = spooldir #agent1.sources.source1.spoolDir = /var/logs/nginx/ #agent1.sources.source1.fileHeader = false
# Describe/configure tail -F source1 #使用exec作为数据源source组件 agent1.sources.source1.type = exec #使用tail -F命令实时收集新产生的日志数据 agent1.sources.source1.command = tail -F /var/logs/nginx/access_log agent1.sources.source1.channels = channel1
#configure host for source #配置一个拦截器插件 agent1.sources.source1.interceptors = i1 agent1.sources.source1.interceptors.i1.type = host #使用拦截器插件获取agent所在服务器的主机名 agent1.sources.source1.interceptors.i1.hostHeader = hostname
#配置sink组件为hdfs agent1.sinks.sink1.type = hdfs #a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1 #agent1.sinks.sink1.hdfs.path=hdfs://hdp-node-01:9000/weblog/flume-collection/%y-%m-%d/%H%M%S #指定文件sink到hdfs上的路径 agent1.sinks.sink1.hdfs.path= hdfs://hdp-node-01:9000/weblog/flume-collection/%y-%m-%d/%H-%M_%hostname #指定文件名前缀 agent1.sinks.sink1.hdfs.filePrefix = access_log agent1.sinks.sink1.hdfs.maxOpenFiles = 5000 #指定每批下沉数据的记录条数 agent1.sinks.sink1.hdfs.batchSize= 100 agent1.sinks.sink1.hdfs.fileType = DataStream agent1.sinks.sink1.hdfs.writeFormat =Text #指定下沉文件按1G大小滚动 agent1.sinks.sink1.hdfs.rollSize = 1024*1024*1024 #指定下沉文件按1000000条数滚动 agent1.sinks.sink1.hdfs.rollCount = 1000000 #指定下沉文件按30分钟滚动 agent1.sinks.sink1.hdfs.rollInterval = 30 #agent1.sinks.sink1.hdfs.round = true #agent1.sinks.sink1.hdfs.roundValue = 10 #agent1.sinks.sink1.hdfs.roundUnit = minute agent1.sinks.sink1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory #使用memory类型channel agent1.channels.channel1.type = memory agent1.channels.channel1.keep-alive = 120 agent1.channels.channel1.capacity = 500000 agent1.channels.channel1.transactionCapacity = 600
# Bind the source and sink to the channel agent1.sources.source1.channels = channel1 agent1.sinks.sink1.channel = channel1 |
启动采集
在部署了flume的nginx服务器上,启动flume的agent,命令如下:
bin/flume-ng agent --conf ./conf -f ./conf/weblog.properties.2 -n agent
注意:启动命令中的 -n 参数要给配置文件中配置的agent名称
4 模块开发——数据预处理
4.1 主要目的:
过滤“不合规”数据
格式转换和规整
根据后续的统计需求,过滤分离出各种不同主题的基础数据
4.2 实现方式:
开发一个mr程序WeblogPreProcess(内容太长,见工程代码)
|
public class WeblogPreProcess { static class WeblogPreProcessMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, NullWritable> { Text k = new Text(); NullWritable v = NullWritable.get(); @Override protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { String line = value.toString(); WebLogBean webLogBean = WebLogParser.parser(line); // WebLogBean productWebLog = WebLogParser.parser2(line); // WebLogBean bbsWebLog = WebLogParser.parser3(line); // WebLogBean cuxiaoBean = WebLogParser.parser4(line); if (!webLogBean.isValid()) return; k.set(webLogBean.toString()); context.write(k, v); // k.set(productWebLog); // context.write(k, v); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration(); Job job = Job.getInstance(conf); job.setJarByClass(WeblogPreProcess.class); job.setMapperClass(WeblogPreProcessMapper.class); job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class); FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0])); FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1])); job.waitForCompletion(true);
} }
|
l 运行mr对数据进行预处理
|
hadoop jar weblog.jar cn.itcast.bigdata.hive.mr.WeblogPreProcess /weblog/input /weblog/preout |
4.3 点击流模型数据梳理
由于大量的指标统计从点击流模型中更容易得出,所以在预处理阶段,可以使用mr程序来生成点击流模型的数据
4.3.1 点击流模型pageviews表
Pageviews表模型数据生成
|
代码见工程
hadoop jar weblogpreprocess.jar \ cn.itcast.bigdata.hive.mr.ClickStreamThree \ /user/hive/warehouse/dw_click.db/test_ods_weblog_origin/datestr=2013-09-20/ /test-click/pageviews/ |
表结构:

(表定义及数据导入见6.2节)
4.3.2 点击流模型visit信息表
注:“一次访问”=“N次连续请求”
直接从原始数据中用hql语法得出每个人的“次”访问信息比较困难,可先用mapreduce程序分析原始数据得出“次”信息数据,然后再用hql进行更多维度统计
用MR程序从pageviews数据中,梳理出每一次visit的起止时间、页面信息
|
代码见工程 hadoop jar weblogpreprocess.jar cn.itcast.bigdata.hive.mr.ClickStreamVisit /weblog/sessionout /weblog/visitout |
然后,在hive仓库中建点击流visit模型表
|
drop table if exist click_stream_visit; create table click_stream_visit( session string, remote_addr string, inTime string, outTime string, inPage string, outPage string, referal string, pageVisits int) partitioned by (datestr string); |
然后,将MR运算得到的visit数据导入visit模型表
|
load data inpath '/weblog/visitout' into table click_stream_visit partition(datestr='2013-09-18'); |
5 模块开发——数据仓库设计
注:采用星型模型
5.1 事实表
|
原始数据表:t_origin_weblog |
||
|
valid |
string |
是否有效 |
|
remote_addr |
string |
访客ip |
|
remote_user |
string |
访客用户信息 |
|
time_local |
string |
请求时间 |
|
request |
string |
请求url |
|
status |
string |
响应码 |
|
body_bytes_sent |
string |
响应字节数 |
|
http_referer |
string |
来源url |
|
http_user_agent |
string |
访客终端信息 |
|
|
|
|
|
ETL中间表:t_etl_referurl |
||
|
valid |
string |
是否有效 |
|
remote_addr |
string |
访客ip |
|
remote_user |
string |
访客用户信息 |
|
time_local |
string |
请求时间 |
|
request |
string |
请求url |
|
request_host |
string |
请求的域名 |
|
status |
string |
响应码 |
|
body_bytes_sent |
string |
响应字节数 |
|
http_referer |
string |
来源url |
|
http_user_agent |
string |
访客终端信息 |
|
valid |
string |
是否有效 |
|
remote_addr |
string |
访客ip |
|
remote_user |
string |
访客用户信息 |
|
time_local |
string |
请求时间 |
|
request |
string |
请求url |
|
status |
string |
响应码 |
|
body_bytes_sent |
string |
响应字节数 |
|
http_referer |
string |
外链url |
|
http_user_agent |
string |
访客终端信息 |
|
host |
string |
外链url的域名 |
|
path |
string |
外链url的路径 |
|
query |
string |
外链url的参数 |
|
query_id |
string |
外链url的参数值 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
访问日志明细宽表:t_ods_access_detail |
||
|
valid |
string |
是否有效 |
|
remote_addr |
string |
访客ip |
|
remote_user |
string |
访客用户信息 |
|
time_local |
string |
请求时间 |
|
request |
string |
请求url整串 |
|
request_level1 |
string |
请求的一级栏目 |
|
request_level2 |
string |
请求的二级栏目 |
|
request_level3 |
string |
请求的三级栏目 |
|
status |
string |
响应码 |
|
body_bytes_sent |
string |
响应字节数 |
|
http_referer |
string |
来源url |
|
http_user_agent |
string |
访客终端信息 |
|
valid |
string |
是否有效 |
|
remote_addr |
string |
访客ip |
|
remote_user |
string |
访客用户信息 |
|
time_local |
string |
请求时间 |
|
request |
string |
请求url |
|
status |
string |
响应码 |
|
body_bytes_sent |
string |
响应字节数 |
|
http_referer |
string |
外链url |
|
http_user_agent |
string |
访客终端信息整串 |
|
http_user_agent_browser |
string |
访客终端浏览器 |
|
http_user_agent_sys |
string |
访客终端操作系统 |
|
http_user_agent_dev |
string |
访客终端设备 |
|
host |
string |
外链url的域名 |
|
path |
string |
外链url的路径 |
|
query |
string |
外链url的参数 |
|
query_id |
string |
外链url的参数值 |
|
daystr |
string |
日期整串 |
|
tmstr |
string |
时间整串 |
|
month |
string |
月份 |
|
day |
string |
日 |
|
hour |
string |
时 |
|
minute |
string |
分 |
|
## |
## |
## |
|
mm |
string |
分区字段--月 |
|
dd |
string |
分区字段--日 |
5.2 维度表
|
时间维度 v_year_month_date |
|
year |
|
month |
|
day |
|
hour |
|
minute |
|
访客地域维度t_dim_area |
|
北京 |
|
上海 |
|
广州 |
|
深圳 |
|
河北 |
|
河南 |
|
终端类型维度t_dim_termination |
|
uc |
|
firefox |
|
chrome |
|
safari |
|
ios |
|
android |
|
网站栏目维度 t_dim_section |
|
跳蚤市场 |
|
房租信息 |
|
休闲娱乐 |
|
建材装修 |
|
本地服务 |
|
人才市场 |
6 模块开发——ETL
该项目的数据分析过程在hadoop集群上实现,主要应用hive数据仓库工具,因此,采集并经过预处理后的数据,需要加载到hive数据仓库中,以进行后续的挖掘分析。
6.1创建原始数据表
--在hive仓库中建贴源数据表
|
drop table if exists ods_weblog_origin; create table ods_weblog_origin( valid string, remote_addr string, remote_user string, time_local string, request string, status string, body_bytes_sent string, http_referer string, http_user_agent string) partitioned by (datestr string) row format delimited fields terminated by '\001'; |
点击流模型pageviews表
|
drop table if exists ods_click_pageviews; create table ods_click_pageviews( Session string, remote_addr string, time_local string, request string, visit_step string, page_staylong string, http_referer string, http_user_agent string, body_bytes_sent string, status string) partitioned by (datestr string) row format delimited fields terminated by '\001'; |
时间维表创建
|
drop table dim_time if exists ods_click_pageviews; create table dim_time( year string, month string, day string, hour string) row format delimited fields terminated by ','; |
6.2导入数据
|
导入清洗结果数据到贴源数据表ods_weblog_origin load data inpath '/weblog/preprocessed/16-02-24-16/' overwrite into table ods_weblog_origin partition(datestr='2013-09-18');
0: jdbc:hive2://localhost:10000> show partitions ods_weblog_origin; +-------------------+--+ | partition | +-------------------+--+ | timestr=20151203 | +-------------------+--+
0: jdbc:hive2://localhost:10000> select count(*) from ods_origin_weblog; +--------+--+ | _c0 | +--------+--+ | 11347 | +--------+--+
导入点击流模型pageviews数据到ods_click_pageviews表 0: jdbc:hive2://hdp-node-01:10000> load data inpath '/weblog/clickstream/pageviews' overwrite into table ods_click_pageviews partition(datestr='2013-09-18');
0: jdbc:hive2://hdp-node-01:10000> select count(1) from ods_click_pageviews; +------+--+ | _c0 | +------+--+ | 66 | +------+--+
导入点击流模型visit数据到ods_click_visit表
导入时间维表: load data inpath '/dim_time.txt' into table dim_time; |
6.3 生成ODS层明细宽表
6.3.1 需求概述
整个数据分析的过程是按照数据仓库的层次分层进行的,总体来说,是从ODS原始数据中整理出一些中间表(比如,为后续分析方便,将原始数据中的时间、url等非结构化数据作结构化抽取,将各种字段信息进行细化,形成明细表),然后再在中间表的基础之上统计出各种指标数据
6.3.2 ETL实现
建表——明细表 (源:ods_weblog_origin) (目标:ods_weblog_detail)
|
drop table ods_weblog_detail; create table ods_weblog_detail( valid string, --有效标识 remote_addr string, --来源IP remote_user string, --用户标识 time_local string, --访问完整时间 daystr string, --访问日期 timestr string, --访问时间 month string, --访问月 day string, --访问日 hour string, --访问时 request string, --请求的url status string, --响应码 body_bytes_sent string, --传输字节数 http_referer string, --来源url[dht1] ref_host string, --来源的host ref_path string, --来源的路径 ref_query string, --来源参数query ref_query_id string, --来源参数query的值 http_user_agent string --客户终端标识 ) partitioned by(datestr string); |
--抽取refer_url到中间表 "t_ods_tmp_referurl"
--将来访url分离出host path query query id
|
drop table if exists t_ods_tmp_referurl; create table t_ ods _tmp_referurl as SELECT a.*,b.* FROM ods_origin_weblog a LATERAL VIEW parse_url_tuple(regexp_replace(http_referer, "\"", ""), 'HOST', 'PATH','QUERY', 'QUERY:id') b as host, path, query, query_id; |
--抽取转换time_local字段到中间表明细表 ”t_ ods _detail”
|
drop table if exists t_ods_tmp_detail; create table t_ods_tmp_detail as select b.*,substring(time_local,0,10) as daystr, substring(time_local,11) as tmstr, substring(time_local,5,2) as month, substring(time_local,8,2) as day, substring(time_local,11,2) as hour From t_ ods _tmp_referurl b; |
以上语句可以改写成:
|
insert into table zs.ods_weblog_detail partition(datestr='$day_01') select c.valid,c.remote_addr,c.remote_user,c.time_local, substring(c.time_local,0,10) as daystr, substring(c.time_local,12) as tmstr, substring(c.time_local,6,2) as month, substring(c.time_local,9,2) as day, substring(c.time_local,11,3) as hour, c.request,c.status,c.body_bytes_sent,c.http_referer,c.ref_host,c.ref_path,c.ref_query,c.ref_query_id,c.http_user_agent from (SELECT a.valid,a.remote_addr,a.remote_user,a.time_local, a.request,a.status,a.body_bytes_sent,a.http_referer,a.http_user_agent,b.ref_host,b.ref_path,b.ref_query,b.ref_query_id FROM zs.ods_weblog_origin a LATERAL VIEW parse_url_tuple(regexp_replace(http_referer, "\"", ""), 'HOST', 'PATH','QUERY', 'QUERY:id') b as ref_host, ref_path, ref_query, ref_query_id) c " 0: jdbc:hive2://localhost:10000> show partitions ods_weblog_detail; +---------------------+--+ | partition | +---------------------+--+ | dd=18%2FSep%2F2013 | +---------------------+--+ 1 row selected (0.134 seconds) |
7 模块开发——统计分析
注:每一种统计指标都可以跟各维度表进行叉乘,从而得出各个维度的统计结果
篇幅限制,叉乘的代码及注释信息详见项目工程代码文件
为了在前端展示时速度更快,每一个指标都事先算出各维度结果存入mysql
提前准备好维表数据,在hive仓库中创建相应维表,如:
时间维表:
|
create table v_time(year string,month string,day string,hour string) row format delimited fields terminated by ',';
load data local inpath '/home/hadoop/v_time.txt' into table v_time; |
在实际生产中,究竟需要哪些统计指标通常由相关数据需求部门人员提出,而且会不断有新的统计需求产生,以下为网站流量分析中的一些典型指标示例。
1. PV统计
1.1 多维度统计PV总量
1. 时间维度
|
--计算指定的某个小时pvs select count(*),month,day,hour from dw_click.ods_weblog_detail group by month,day,hour;
--计算该处理批次(一天)中的各小时pvs drop table dw_pvs_hour; create table dw_pvs_hour(month string,day string,hour string,pvs bigint) partitioned by(datestr string);
insert into table dw_pvs_hour partition(datestr='2016-03-18') select a.month as month,a.day as day,a.hour as hour,count(1) as pvs from ods_weblog_detail a where a.datestr='2016-03-18' group by a.month,a.day,a.hour;
或者用时间维表关联
|
维度:日
|
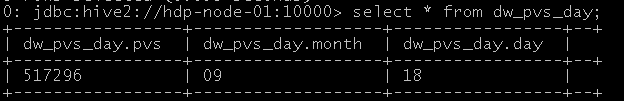
drop table dw_pvs_day; create table dw_pvs_day(pvs bigint,month string,day string);
insert into table dw_pvs_day select count(1) as pvs,a.month as month,a.day as day from dim_time a join ods_weblog_detail b on b.dd='18/Sep/2013' and a.month=b.month and a.day=b.day group by a.month,a.day;
--或者,从之前算好的小时结果中统计 Insert into table dw_pvs_day Select sum(pvs) as pvs,month,day from dw_pvs_hour group by month,day having day='18'; 结果如下:
|
维度:月
|
drop table t_display_pv_month; create table t_display_pv_month (pvs bigint,month string); insert into table t_display_pv_month select count(*) as pvs,a.month from t_dim_time a join t_ods_detail_prt b on a.month=b.month group by a.month; |
2. 按终端维度统计pv总量
注:探索数据中的终端类型
|
select distinct(http_user_agent) from ods_weblog_detail where http_user_agent like '%Mozilla%' limit 200; |
终端维度:uc
|
drop table t_display_pv_terminal_uc; create table t_display_pv_ terminal_uc (pvs bigint,mm string,dd string,hh string); |
终端维度:chrome
|
drop table t_display_pv_terminal_chrome; create table t_display_pv_ terminal_ chrome (pvs bigint,mm string,dd string,hh string); |
终端维度:safari
|
drop table t_display_pv_terminal_safari; create table t_display_pv_ terminal_ safari (pvs bigint,mm string,dd string,hh string); |
3. 按栏目维度统计pv总量
栏目维度:job
栏目维度:news
栏目维度:bargin
栏目维度:lane
1.2 人均浏览页数
需求描述:比如,今日所有来访者,平均请求的页面数
--总页面请求数/去重总人数
|
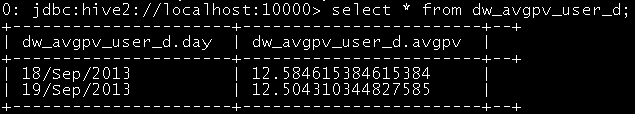
drop table dw_avgpv_user_d; create table dw_avgpv_user_d( day string, avgpv string);
insert into table dw_avgpv_user_d select '2013-09-18',sum(b.pvs)/count(b.remote_addr) from (select remote_addr,count(1) as pvs from ods_weblog_detail where datestr='2013-09-18' group by remote_addr) b;
|
1.3 按referer维度统计pv总量
需求:按照来源及时间维度统计PVS,并按照PV大小倒序排序
-- 按照小时粒度统计,查询结果存入:( "dw_pvs_referer_h" )
|
drop table dw_pvs_referer_h; create table dw_pvs_referer_h(referer_url string,referer_host string,month string,day string,hour string,pv_referer_cnt bigint) partitioned by(datestr string);
insert into table dw_pvs_referer_h partition(datestr='2016-03-18') select http_referer,ref_host,month,day,hour,count(1) as pv_referer_cnt from ods_weblog_detail group by http_referer,ref_host,month,day,hour having ref_host is not null order by hour asc,day asc,month asc,pv_referer_cnt desc; |
按天粒度统计各来访域名的访问次数并排序
|
drop table dw_ref_host_visit_cnts_h; create table dw_ref_host_visit_cnts_h(ref_host string,month string,day string,hour string,ref_host_cnts bigint) partitioned by(datestr string);
insert into table dw_ref_host_visit_cnts_h partition(datestr='2016-03-18') select ref_host,month,day,hour,count(1) as ref_host_cnts from ods_weblog_detail group by ref_host,month,day,hour having ref_host is not null order by hour asc,day asc,month asc,ref_host_cnts desc; |
注:还可以按来源地域维度、访客终端维度等计算
1.4 统计pv总量最大的来源TOPN
需求描述:按照时间维度,比如,统计一天内产生最多pvs的来源topN
需要用到row_number函数
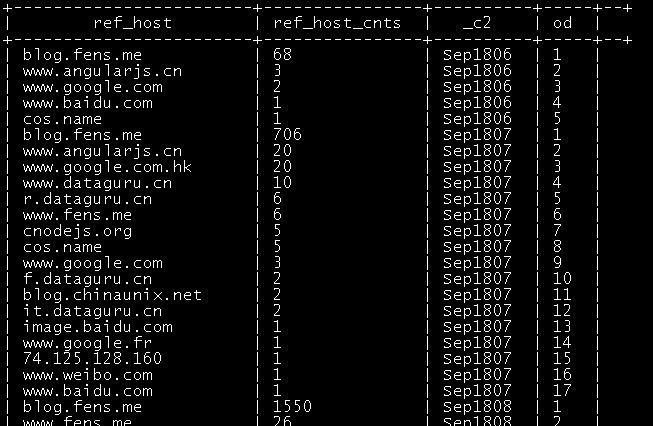
以下语句对每个小时内的来访host次数倒序排序标号,
select ref_host,ref_host_cnts,concat(month,hour,day),
row_number() over (partition by concat(month,hour,day) order by ref_host_cnts desc) as od
from dw_ref_host_visit_cnts_h
效果如下:
根据上述row_number的功能,可编写Hql取各小时的ref_host访问次数topn
|
drop table dw_pvs_refhost_topn_h; create table dw_pvs_refhost_topn_h( hour string, toporder string, ref_host string, ref_host_cnts string ) partitioned by(datestr string);
insert into table zs.dw_pvs_refhost_topn_h partition(datestr='2016-03-18') select t.hour,t.od,t.ref_host,t.ref_host_cnts from (select ref_host,ref_host_cnts,concat(month,day,hour) as hour, row_number() over (partition by concat(month,day,hour) order by ref_host_cnts desc) as od from zs.dw_ref_host_visit_cnts_h) t where od<=3; |
结果如下:
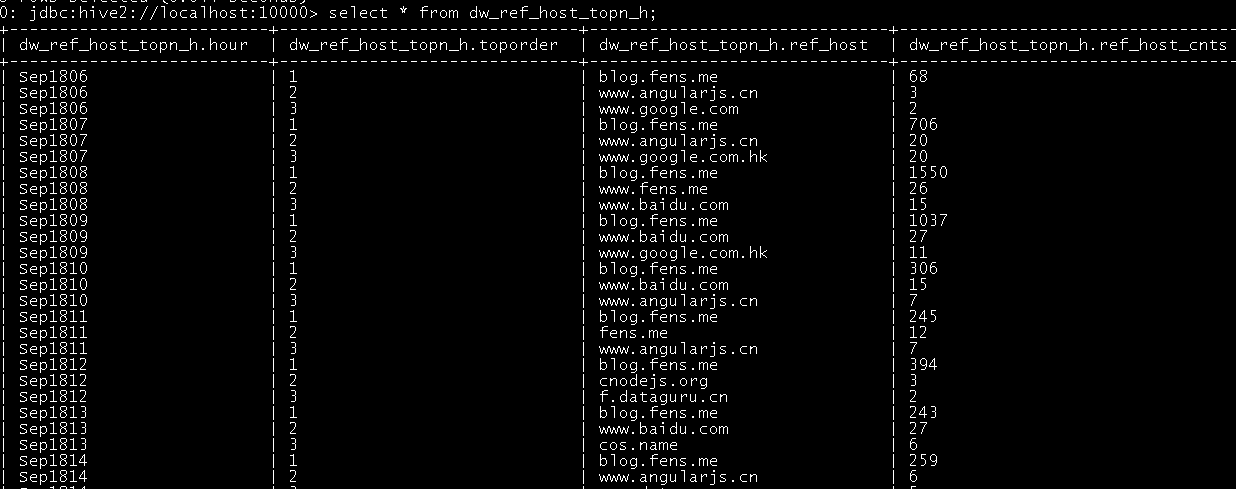
注:还可以按来源地域维度、访客终端维度等计算
2. 受访分析
统计每日最热门的页面top10
|
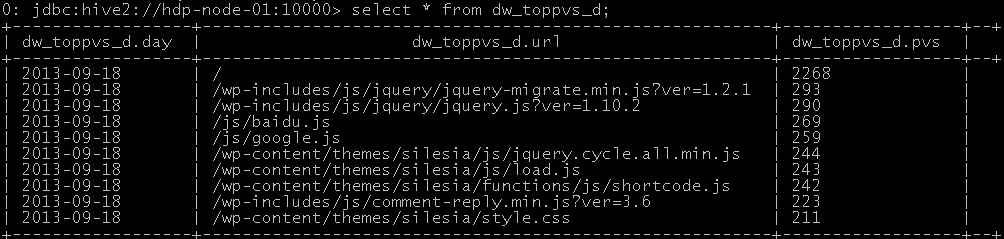
drop table dw_pvs_d; create table dw_pvs_d(day string,url string,pvs string);
insert into table dw_pvs_d select '2013-09-18',a.request,a.request_counts from (select request as request,count(request) as request_counts from ods_weblog_detail where datestr='2013-09-18' group by request having request is not null) a order by a.request_counts desc limit 10; 结果如下:
|
注:还可继续得出各维度交叉结果
3. 访客分析
3.1 独立访客
需求描述:按照时间维度比如小时来统计独立访客及其产生的pvCnts
对于独立访客的识别,如果在原始日志中有用户标识,则根据用户标识即很好实现;
此处,由于原始日志中并没有用户标识,以访客IP来模拟,技术上是一样的,只是精确度相对较低
时间维度:时
|
drop table dw_user_dstc_ip_h; create table dw_user_dstc_ip_h( remote_addr string, pvs bigint, hour string);
insert into table dw_user_dstc_ip_h select remote_addr,count(1) as pvs,concat(month,day,hour) as hour from ods_weblog_detail Where datestr='2013-09-18' group by concat(month,day,hour),remote_addr; |
在此结果表之上,可以进一步统计出,每小时独立访客总数,每小时请求次数topn访客等
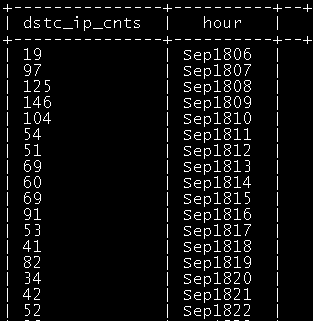
如每小时独立访客总数:
|
select count(1) as dstc_ip_cnts,hour from dw_user_dstc_ip_h group by hour; |
|
练习: 统计每小时请求次数topn的独立访客 |
时间维度:月
|
select remote_addr,count(1) as counts,month from ods_weblog_detail group by month,remote_addr; |
时间维度:日
|
select remote_addr,count(1) as counts,concat(month,day) as day from ods_weblog_detail Where dd='18/Sep/2013' group by concat(month,day),remote_addr; |
注:还可以按来源地域维度、访客终端维度等计算
3.2 每日新访客
需求描述:将每天的新访客统计出来
实现思路:创建一个去重访客累积表,然后将每日访客对比累积表

时间维度:日
|
--历日去重访客累积表 drop table dw_user_dsct_history; create table dw_user_dsct_history( day string, ip string ) partitioned by(datestr string);
--每日新用户追加到累计表 drop table dw_user_dsct_history; create table dw_user_dsct_history( day string, ip string ) partitioned by(datestr string);
--每日新用户追加到累计表 insert into table dw_user_dsct_history partition(datestr='2013-09-19') select tmp.day as day,tmp.today_addr as new_ip from ( select today.day as day,today.remote_addr as today_addr,old.ip as old_addr from (select distinct remote_addr as remote_addr,"2013-09-19" as day from ods_weblog_detail where datestr="2013-09-19") today left outer join dw_user_dsct_history old on today.remote_addr=old.ip ) tmp where tmp.old_addr is null; |
验证:
|
select count(distinct remote_addr) from ods_weblog_detail; -- 1005
select count(1) from dw_user_dsct_history where prtflag_day='18/Sep/2013'; --845
select count(1) from dw_user_dsct_history where prtflag_day='19/Sep/2013'; --160 |
时间维度:月
|
类似日粒度算法 |
注:还可以按来源地域维度、访客终端维度等计算
4. Visit分析(点击流模型)
4.2 回头/单次访客统计
需求描述:查询今日所有回头访客及其访问次数
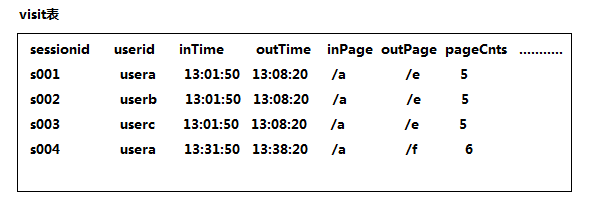
实现思路:上表中出现次数>1的访客,即回头访客;反之,则为单次访客
|
drop table dw_user_returning; create table dw_user_returning( day string, remote_addr string, acc_cnt string) partitioned by (datestr string);
insert overwrite table dw_user_returning partition(datestr='2013-09-18')
select tmp.day,tmp.remote_addr,tmp.acc_cnt from (select '2013-09-18' as day,remote_addr,count(session) as acc_cnt from click_stream_visit group by remote_addr) tmp where tmp.acc_cnt>1; |
4.3 人均访问频次
需求:统计出每天所有用户访问网站的平均次数(visit)
总visit数/去重总用户数
|
select sum(pagevisits)/count(distinct remote_addr) from click_stream_visit partition(datestr='2013-09-18'); |
5. Visit分析另一种实现方式[dht2]
5.1 mr程序识别出访客的每次访问
a.) 首先开发MAPREDUCE程序:UserStayTime
|
注:代码略长,见项目工程代码
|
b.) 提交MAPREDUCE程序进行运算
|
[hadoop@hdp-node-01 ~]$ hadoop jar weblog.jar cn.itcast.bigdata.hive.mr.UserStayTime /weblog/input /weblog/stayout4 --导入hive表("t_display_access_info")中 drop table ods_access_info; create table ods_access_info(remote_addr string,firt_req_time string,last_req_time string,stay_long string) partitioned by(prtflag_day string) row format delimited fields terminated by '\t';
load data inpath '/weblog/stayout4' into table ods_access_info partition(prtflag_day='18/Sep/2013'); 创建表时stay_long使用的string类型,但是在后续过程中发现还是用bigint更好,进行表修改 alter table ods_access_info change column stay_long stay_long bigint; |
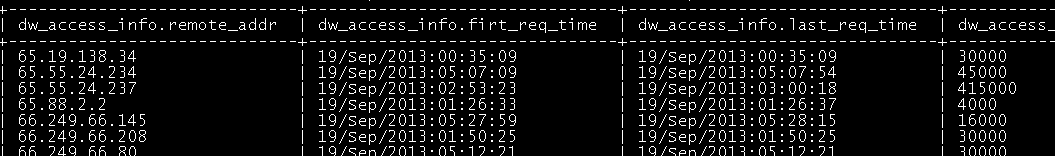
5.2 将mr结果导入访客访问信息表 "t_display_access_info"
由于有一些访问记录是单条记录,mr程序处理处的结果给的时长是0,所以考虑给单次请求的停留时间一个默认市场30秒
|
drop table dw_access_info; create table dw_access_info(remote_addr string,firt_req_time string,last_req_time string,stay_long string) partitioned by(prtflag_day string);
insert into table dw_access_info partition(prtflag_day='19/Sep/2013') select remote_addr,firt_req_time,last_req_time, case stay_long when 0 then 30000 else stay_long end as stay_long from ods_access_info where prtflag_day='18/Sep/2013'; |
在访问信息表的基础之上,可以实现更多指标统计,如:
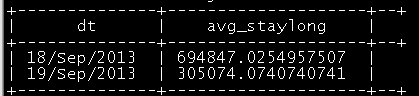
统计所有用户停留时间平均值,观察用户在站点停留时长的变化走势
select prtflag_day as dt,avg(stay_long) as avg_staylong
from dw_access_info group by prtflag_day;
5.3 回头/单次访客统计
注:从上一步骤得到的访问信息统计表“dw_access_info”中查询
--回头访客访问信息表 "dw_access_info_htip"
|
drop table dw_access_info_htip; create table dw_access_info_htip(remote_addr string, firt_req_time string, last_req_time string, stay_long string,acc_counts string) partitioned by(prtflag_day string);
insert into table dw_access_info_htip partition(prtflag_day='18/Sep/2013') select b.remote_addr,b.firt_req_time,b.last_req_time,b.stay_long,a.acc_counts from (select remote_addr,count(remote_addr) as acc_counts from dw_access_info where prtflag_day='18/Sep/2013' group by remote_addr having acc_counts>1) a join dw_access_info b on a.remote_addr = b.remote_addr;
|
--单次访客访问信息表 "dw_access_info_dcip"
|
drop table dw_access_info_dcip; create table dw_access_info_dcip(remote_addr string, firt_req_time string, last_req_time string, stay_long string,acc_counts string) partitioned by(prtflag_day string);
insert into table dw_access_dcip partition(prtflag_day='18/Sep/2013') select b.remote_addr,b.firt_req_time,b.last_req_time,b.stay_long,a.acc_counts from (select remote_addr,count(remote_addr) as acc_counts from dw_access_info where prtflag_day='18/Sep/2013' group by remote_addr having acc_counts<2) a join dw_access_info b on a.remote_addr = b.remote_addr;
|
在回头/单词访客信息表的基础之上,可以实现更多统计指标,如:
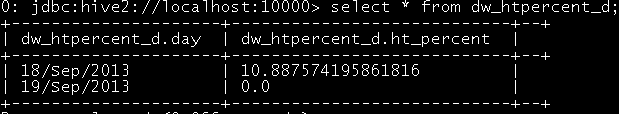
--当日回头客占比
|
drop table dw_htpercent_d; create table dw_htpercent_d(day string,ht_percent float);
Insert into table dw_htpercent_d select '18/Sep/2013',(tmp_ht.ht/tmp_all.amount)*100 from (select count( distinct a.remote_addr) as ht from dw_access_info_htip a where prtflag_day='18/Sep/2013') tmp_ht Join (select count(distinct b.remote_addr) as amount from dw_access_info b where prtflag_day='18/Sep/2013') tmp_all;
|
5.4 人均访问频度
--总访问次数/去重总人数,从访客次数汇总表中查询
|
select avg(user_times.counts) as user_access_freq from (select remote_addr,counts from t_display_htip union all select remote_addr,counts from t_display_access_dcip) user_times;
--或直接从访问信息表 t_display_access_info 中查询 select avg(a.acc_cts) from (select remote_addr,count(*) as acc_cts from dw_access_info group by remote_addr) a; |
6.关键路径转化率分析——漏斗模型
转化:在一条指定的业务流程中,各个步骤的完成人数及相对上一个步骤的百分比
6.1 需求分析
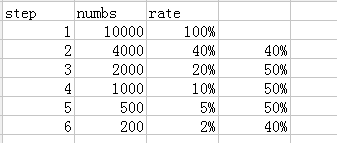
6.2 模型设计
定义好业务流程中的页面标识,下例中的步骤为:
Step1、 /item%
Step2、 /category
Step3、 /order
Step4、 /index
6.3 开发实现
分步骤开发:
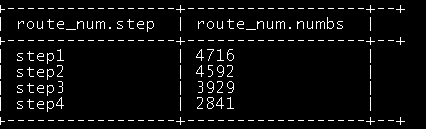
1、查询每一个步骤的总访问人数
|
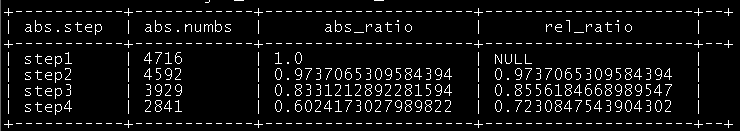
create table route_numbs as select 'step1' as step,count(distinct remote_addr) as numbs from ods_click_pageviews where request like '/item%' union select 'step2' as step,count(distinct remote_addr) as numbs from ods_click_pageviews where request like '/category%' union select 'step3' as step,count(distinct remote_addr) as numbs from ods_click_pageviews where request like '/order%' union select 'step4' as step,count(distinct remote_addr) as numbs from ods_click_pageviews where request like '/index%'; |
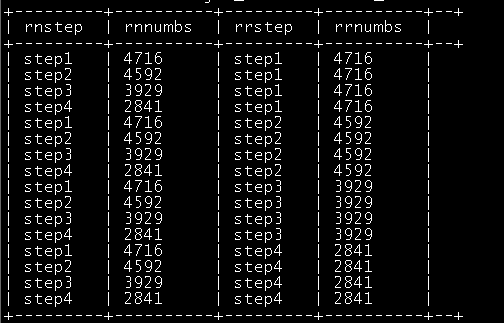
2、查询每一步骤相对于路径起点人数的比例
思路:利用join
|
select rn.step as rnstep,rn.numbs as rnnumbs,rr.step as rrstep,rr.numbs as rrnumbs from route_num rn inner join route_num rr
|
|
select tmp.rnstep,tmp.rnnumbs/tmp.rrnumbs as ratio from ( select rn.step as rnstep,rn.numbs as rnnumbs,rr.step as rrstep,rr.numbs as rrnumbs from route_num rn inner join route_num rr) tmp where tmp.rrstep='step1';
|
3、查询每一步骤相对于上一步骤的漏出率
|
select tmp.rrstep as rrstep,tmp.rrnumbs/tmp.rnnumbs as ration from ( select rn.step as rnstep,rn.numbs as rnnumbs,rr.step as rrstep,rr.numbs as rrnumbs from route_num rn inner join route_num rr) tmp where cast(substr(tmp.rnstep,5,1) as int)=cast(substr(tmp.rrstep,5,1) as int)-1
|
4、汇总以上两种指标
|
select abs.step,abs.numbs,abs.ratio as abs_ratio,rel.ratio as rel_ratio from ( select tmp.rnstep as step,tmp.rnnumbs as numbs,tmp.rnnumbs/tmp.rrnumbs as ratio from ( select rn.step as rnstep,rn.numbs as rnnumbs,rr.step as rrstep,rr.numbs as rrnumbs from route_num rn inner join route_num rr) tmp where tmp.rrstep='step1' ) abs left outer join ( select tmp.rrstep as step,tmp.rrnumbs/tmp.rnnumbs as ratio from ( select rn.step as rnstep,rn.numbs as rnnumbs,rr.step as rrstep,rr.numbs as rrnumbs from route_num rn inner join route_num rr) tmp where cast(substr(tmp.rnstep,5,1) as int)=cast(substr(tmp.rrstep,5,1) as int)-1 ) rel on abs.step=rel.step
|
8 模块开发——结果导出
报表统计结果,由sqoop从hive表中导出,示例如下,详见工程代码
|
sqoop export \ --connect jdbc:mysql://hdp-node-01:3306/webdb --username root --password root \ --table click_stream_visit \ --export-dir /user/hive/warehouse/dw_click.db/click_stream_visit/datestr=2013-09-18 \ --input-fields-terminated-by '\001' |
9 模块开发——工作流调度
注:将整个项目的数据处理过程,从数据采集到数据分析,再到结果数据的导出,一系列的任务分割成若干个oozie的工作流,并用coordinator进行协调
工作流定义示例
Ooize配置片段示例,详见项目工程
1、日志预处理mr程序工作流定义
|
<workflow-app name="weblogpreprocess" xmlns="uri:oozie:workflow:0.4"> <start to="firstjob"/> <action name="firstjob"> <map-reduce> <job-tracker>${jobTracker}</job-tracker> <name-node>${nameNode}</name-node> <prepare> <delete path="${nameNode}/${outpath}"/> </prepare> <configuration> <property> <name>mapreduce.job.map.class</name> <value>cn.itcast.bigdata.hive.mr.WeblogPreProcess$WeblogPreProcessMapper</value> </property>
<property> <name>mapreduce.job.output.key.class</name> <value>org.apache.hadoop.io.Text</value> </property> <property> <name>mapreduce.job.output.value.class</name> <value>org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable</value> </property>
<property> <name>mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.inputdir</name> <value>${inpath}</value> </property> <property> <name>mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.outputdir</name> <value>${outpath}</value> </property> <property> <name>mapred.mapper.new-api</name> <value>true</value> </property> <property> <name>mapred.reducer.new-api</name> <value>true</value> </property>
</configuration> </map-reduce> <ok to="end"/> <error to="kill"/> |
2、数据加载etl工作流定义:
|
<workflow-app xmlns="uri:oozie:workflow:0.5" name="hive2-wf"> <start to="hive2-node"/>
<action name="hive2-node"> <hive2 xmlns="uri:oozie:hive2-action:0.1"> <job-tracker>${jobTracker}</job-tracker> <name-node>${nameNode}</name-node> <configuration> <property> <name>mapred.job.queue.name</name> <value>${queueName}</value> </property> </configuration> <jdbc-url>jdbc:hive2://hdp-node-01:10000</jdbc-url> <script>script.q</script> <param>input=/weblog/outpre2</param> </hive2> <ok to="end"/> <error to="fail"/> </action>
<kill name="fail"> <message>Hive2 (Beeline) action failed, error message[${wf:errorMessage(wf:lastErrorNode())}]</message> </kill> <end name="end"/> </workflow-app> |
3、数据加载工作流所用hive脚本:
|
create database if not exists dw_weblog; use dw_weblog; drop table if exists t_orgin_weblog; create table t_orgin_weblog(valid string,remote_addr string, remote_user string, time_local string, request string, status string, body_bytes_sent string, http_referer string, http_user_agent string) row format delimited fields terminated by '\001'; load data inpath '/weblog/preout' overwrite into table t_orgin_weblog;
drop table if exists t_ods_detail_tmp_referurl; create table t_ods_detail_tmp_referurl as SELECT a.*,b.* FROM t_orgin_weblog a LATERAL VIEW parse_url_tuple(regexp_replace(http_referer, "\"", ""), 'HOST', 'PATH','QUERY', 'QUERY:id') b as host, path, query, query_id;
drop table if exists t_ods_detail; create table t_ods_detail as select b.*,substring(time_local,0,11) as daystr, substring(time_local,13) as tmstr, substring(time_local,4,3) as month, substring(time_local,0,2) as day, substring(time_local,13,2) as hour from t_ods_detail_tmp_referurl b;
drop table t_ods_detail_prt; create table t_ods_detail_prt( valid string, remote_addr string, remote_user string, time_local string, request string, status string, body_bytes_sent string, http_referer string, http_user_agent string, host string, path string, query string, query_id string, daystr string, tmstr string, month string, day string, hour string) partitioned by (mm string,dd string);
insert into table t_ods_detail_prt partition(mm='Sep',dd='18') select * from t_ods_detail where daystr='18/Sep/2013'; insert into table t_ods_detail_prt partition(mm='Sep',dd='19') select * from t_ods_detail where daystr='19/Sep/2013'; |
更多工作流及hql脚本定义详见项目工程
工作流单元测试
1、工作流定义配置上传
|
[hadoop@hdp-node-01 wf-oozie]$ hadoop fs -put hive2-etl /user/hadoop/oozie/myapps/ [hadoop@hdp-node-01 wf-oozie]$ hadoop fs -put hive2-dw /user/hadoop/oozie/myapps/ [hadoop@hdp-node-01 wf-oozie]$ ll total 12 drwxrwxr-x. 2 hadoop hadoop 4096 Nov 23 16:32 hive2-dw drwxrwxr-x. 2 hadoop hadoop 4096 Nov 23 16:32 hive2-etl drwxrwxr-x. 3 hadoop hadoop 4096 Nov 23 11:24 weblog [hadoop@hdp-node-01 wf-oozie]$ export OOZIE_URL=http://localhost:11000/oozie |
2、工作流单元提交启动
oozie job -D inpath=/weblog/input -D outpath=/weblog/outpre -config weblog/job.properties -run
启动etl的hive工作流
oozie job -config hive2-etl/job.properties -run
启动pvs统计的hive工作流
oozie job -config hive2-dw/job.properties -run
3、工作流coordinator配置(片段)
多个工作流job用coordinator组织协调:
|
[hadoop@hdp-node-01 hive2-etl]$ ll total 28 -rw-rw-r--. 1 hadoop hadoop 265 Nov 13 16:39 config-default.xml -rw-rw-r--. 1 hadoop hadoop 512 Nov 26 16:43 coordinator.xml -rw-rw-r--. 1 hadoop hadoop 382 Nov 26 16:49 job.properties drwxrwxr-x. 2 hadoop hadoop 4096 Nov 27 11:26 lib -rw-rw-r--. 1 hadoop hadoop 1910 Nov 23 17:49 script.q -rw-rw-r--. 1 hadoop hadoop 687 Nov 23 16:32 workflow.xml |
l config-default.xml
|
<configuration> <property> <name>jobTracker</name> <value>hdp-node-01:8032</value> </property> <property> <name>nameNode</name> <value>hdfs://hdp-node-01:9000</value> </property> <property> <name>queueName</name> <value>default</value> </property> </configuration> |
l job.properties
|
user.name=hadoop oozie.use.system.libpath=true oozie.libpath=hdfs://hdp-node-01:9000/user/hadoop/share/lib oozie.wf.application.path=hdfs://hdp-node-01:9000/user/hadoop/oozie/myapps/hive2-etl/ |
l workflow.xml
|
<workflow-app xmlns="uri:oozie:workflow:0.5" name="hive2-wf"> <start to="hive2-node"/>
<action name="hive2-node"> <hive2 xmlns="uri:oozie:hive2-action:0.1"> <job-tracker>${jobTracker}</job-tracker> <name-node>${nameNode}</name-node> <configuration> <property> <name>mapred.job.queue.name</name> <value>${queueName}</value> </property> </configuration> <jdbc-url>jdbc:hive2://hdp-node-01:10000</jdbc-url> <script>script.q</script> <param>input=/weblog/outpre2</param> </hive2> <ok to="end"/> <error to="fail"/> </action>
<kill name="fail"> <message>Hive2 (Beeline) action failed, error message[${wf:errorMessage(wf:lastErrorNode())}]</message> </kill> <end name="end"/> </workflow-app> |
l coordinator.xml
|
<coordinator-app name="cron-coord" frequency="${coord:minutes(5)}" start="${start}" end="${end}" timezone="Asia/Shanghai" xmlns="uri:oozie:coordinator:0.2"> <action> <workflow> <app-path>${workflowAppUri}</app-path> <configuration> <property> <name>jobTracker</name> <value>${jobTracker}</value> </property> <property> <name>nameNode</name> <value>${nameNode}</value> </property> <property> <name>queueName</name> <value>${queueName}</value> </property> </configuration> </workflow> </action> </coordinator-app> |
10 模块开发——数据展示
在企业的数据分析系统中,前端展现工具有很多,
l 独立部署专门系统的方式:以Business Objects(BO,Crystal Report),Heperion(Brio),Cognos等国外产品为代表的,它们的服务器是单独部署的,与应用程序之间通过某种协议沟通信息
l 有WEB程序展现方式:通过独立的或者嵌入式的java web系统来读取报表统计结果,以网页的形式对结果进行展现,如,100%纯Java的润乾报表
本日志分析项目采用自己开发web程序展现的方式
u Web展现程序采用的技术框架:
Jquery + Echarts + springmvc + spring + mybatis + mysql
u 展现的流程:
- 使用ssh从mysql中读取要展现的数据
- 使用json格式将读取到的数据返回给页面
- 在页面上用echarts对json解析并形成图标
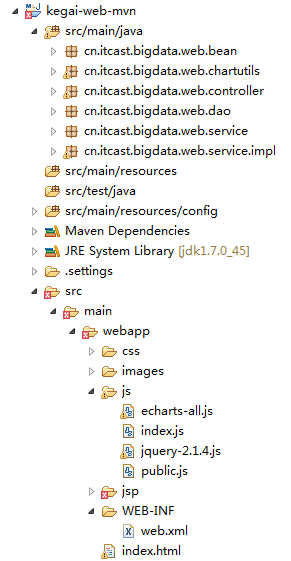
Web程序工程结构
采用maven管理工程,引入SSH框架依赖及jquery+echarts的js库
Web程序的实现代码
采用典型的MVC架构实现
|
页面 |
HTML + JQUERY + ECHARTS |
|
Controller |
SpringMVC |
|
Service |
Service |
|
DAO |
Mybatis |
|
数据库 |
Mysql |
代码详情见项目工程
代码示例:ChartServiceImpl
|
@Service("chartService") public class ChartServiceImpl implements IChartService { @Autowired IEchartsDao iEchartsDao;
public EchartsData getChartsData() { List<Integer> xAxiesList = iEchartsDao.getXAxiesList(""); List<Integer> pointsDataList = iEchartsDao.getPointsDataList("");
EchartsData data = new EchartsData(); ToolBox toolBox = EchartsOptionUtil.getToolBox(); Serie serie = EchartsOptionUtil.getSerie(pointsDataList); ArrayList<Serie> series = new ArrayList<Serie>(); series.add(serie);
List<XAxi> xAxis = EchartsOptionUtil.getXAxis(xAxiesList); List<YAxi> yAxis = EchartsOptionUtil.getYAxis();
HashMap<String, String> title = new HashMap<String, String>(); title.put("text", "pvs"); title.put("subtext", "超级pvs"); HashMap<String, String> tooltip = new HashMap<String, String>(); tooltip.put("trigger", "axis");
HashMap<String, String[]> legend = new HashMap<String, String[]>(); legend.put("data", new String[]{"pv统计"});
data.setTitle(title); data.setTooltip(tooltip); data.setLegend(legend); data.setToolbox(toolBox); data.setCalculable(true); data.setxAxis(xAxis); data.setyAxis(yAxis); data.setSeries(series); return data; }
public List<HashMap<String, Integer>> getGaiKuangList(String date) throws ParseException{
HashMap<String, Integer> gaiKuangToday = iEchartsDao.getGaiKuang(date); SimpleDateFormat sf = new SimpleDateFormat("MMdd"); Date parse = sf.parse(date); Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance(); calendar.setTime(parse); calendar.add(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH, -1); Date before = calendar.getTime(); String beforeString = sf.format(before); System.out.println(beforeString);
HashMap<String, Integer> gaiKuangBefore = iEchartsDao.getGaiKuang(beforeString);
ArrayList<HashMap<String, Integer>> gaiKuangList = new ArrayList<HashMap<String, Integer>>(); gaiKuangList.add(gaiKuangToday); gaiKuangList.add(gaiKuangBefore);
return gaiKuangList;
}
public static void main(String[] args) { ChartServiceImpl chartServiceImpl = new ChartServiceImpl(); EchartsData chartsData = chartServiceImpl.getChartsData(); Gson gson = new Gson(); String json = gson.toJson(chartsData); System.out.println(json);
} } |
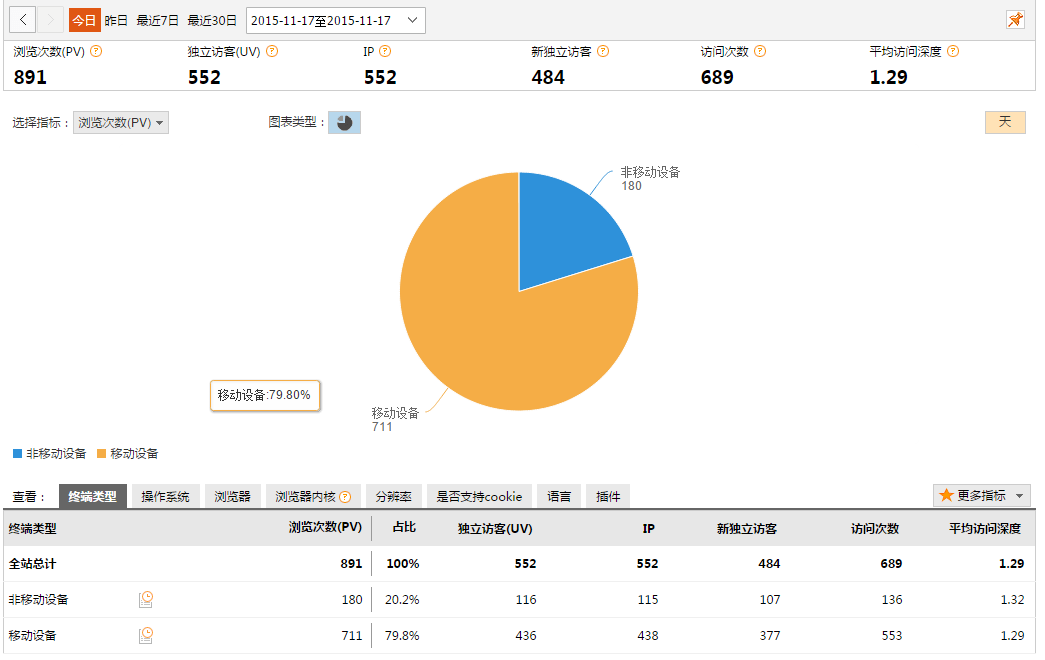
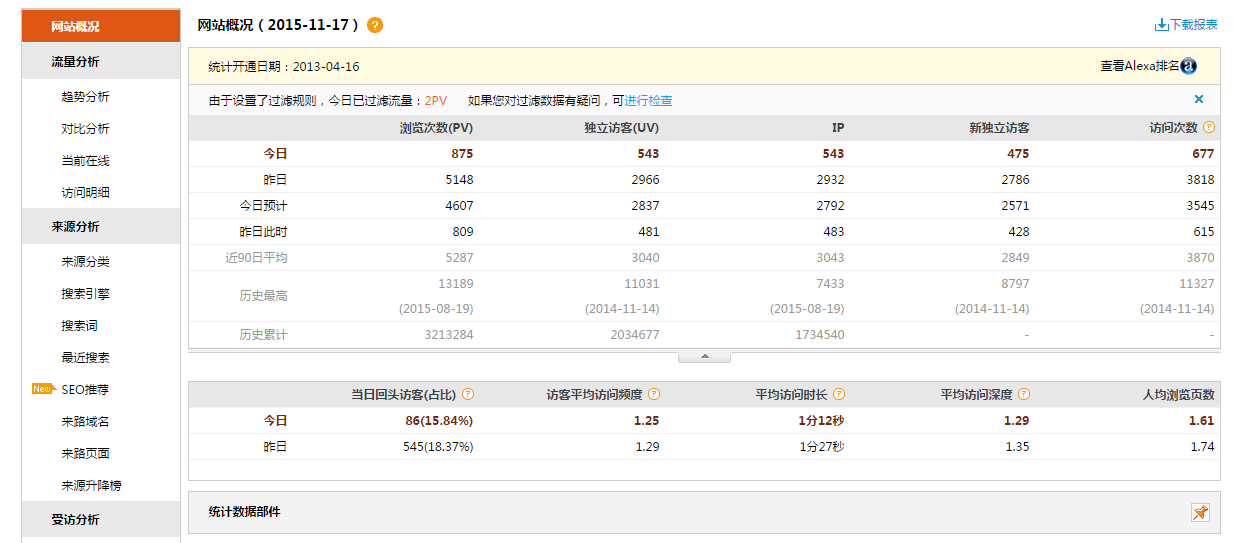
Web程序的展现效果
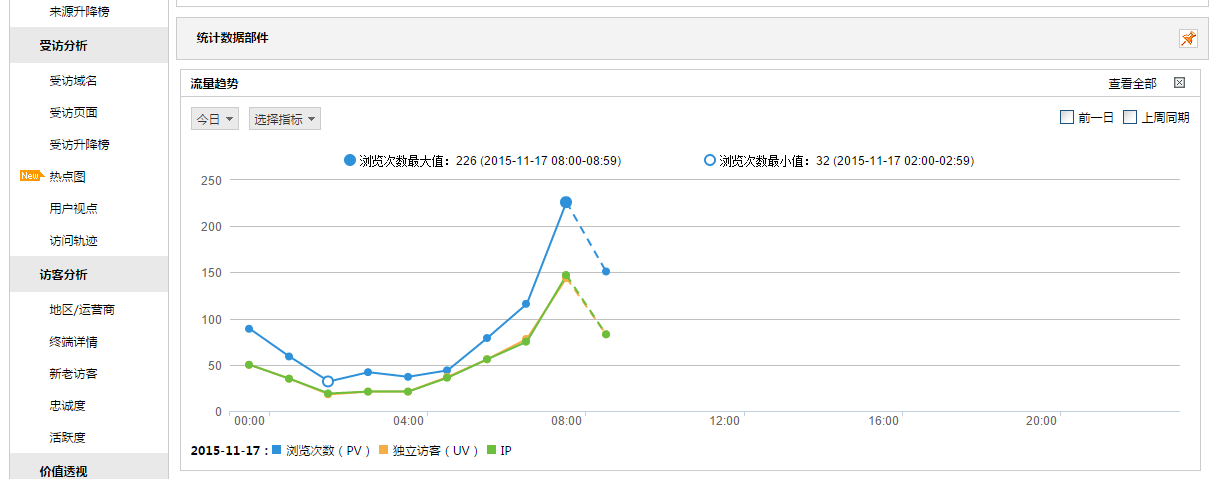
网站概况
流量分析


来源分析
访客分析