数论学习
初等数论笔记
整除(小学奥数内容)
有关性质: 传递性、同乘性、以及一些显然的性质。
还有b|0对于所有b≠0成立。
若(a,b)=1,a|n,b|n,则(ab)|n;
相关姿势:求出x的所有因子。这个应该没有更好的复杂度了。

void getd(int x){ for(int i=1;i*i<=x;++i) if(x%i==0){ d[++tot]=i; if(i*i!=x)d[++tot]=x/i; } //sort(d+1,d+tot+1); }
余数和同余(小学奥数内容)
定义;模意义;
有关性质:传递性、同加减乘,不同除,以及一些显然的性质。
试着证明一下:a%p=x,a%q=x,(p,q)=1 => a%(pq)=x;
尝试用到上面的定理。
快速幂,龟速乘等等;
中国剩余定理;
相关题目:
某校内OJ1272 就是板子对吧。
HDU1788 思维不要江僵化了。
有关题目:
一些小处理就可以啦。
2.膜法数字:
n个数中必定含有1,2,3,4四个数字。求一种排列方式使其膜7为0(显然的SPJ)。
思考一下:信息学最重要的三种思想是什么?
这也许江会是你们今天最大的收获!
大胆猜想 不用证明 打表输出
素数与合数
定理;1都不是;2是唯一的偶质数。
筛法:素数的线性筛法。
分解质因子;spqt(n);
判定:对于小数,sqrt(n);
对于大数,非完美算法 miller-rabin;对于(a,p)=1,有:
费马小定理:如果p是质数,那么a^(p-1)≡1(mod p);
你会发现这远远不够,比如说561=3*11*17,1105=5*13*17,但无论怎样它们都...
补充定理:如果p是质数,那么a*a≡1(mod p)的解只有a=1或p-1。试用初中数学证明。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
#include <ctime>
#define LL long long int
#define ls (x << 1)
#define rs (x << 1 | 1)
using namespace std;
int n;
int gi()
{
int x=0,res=1;char ch=getchar();
while(ch>'9'||ch<'0'){if(ch=='-')res*=-1;ch=getchar();}
while(ch<='9'&&ch>='0')x=x*10+ch-48,ch=getchar();
return x*res;
}
int Qpow(int d,int z,int mod)
{
int ans=1;
for(;z;z>>=1,d=d*d%mod)
if(z&1)ans=ans*d%mod;
return ans;
}
bool check(int a,int n,int t,int u)
{
int x=Qpow(a,u,n);
while(t--)
{
int y=x*x%n;
if(y==1 && x!=1 && x!=n-1)
return true;
x=y;
}
return x!=1;
}
// check: return [n must not be a prime];
bool Mr(int n)
{
if(n==1)return false;
if(n==2||n==3||n==5||n==7||n==11)return true;
if(n==4||n==6||n==8||n==9||n==10)return false;
int m=n-1,j=0;
while(!(m&1))m>>=1,++j; //n=1+m*2^j
for(int t=1;t<=10;++t) //judge 10 times
{
int a=rand()%(n-2)+1;
if(check(a,n,j,m))return false;
}
return true;
}
int main()
{
srand(time(NULL));
n=gi(),printf("%s\n",Mr(n)?"Yes":"No");
return 0;
}
因数分解;唯一分解定理。
威尔逊定理。逆定理。
费马小定理;与欧拉定理之间的关系。(记住欧拉定理就阔以了)。
因子个数;因子和(其实这个阔以筛出来);
求大整数因子算法:Fermat;Pollard Rho;
乘法逆元
定义;
性质(用途);证明;
求法;单个;线性求(必须是质数);
A[i]=-(p/i)*A[p%i];
NOIP2012 其实并不喜欢这种知道就是闭着眼切不知道就是玩蛋的题
哦对三行扩展欧几里得代码。理解什么的没必要了。( 反正我是hh 想看的话网上一大堆)
int exgcd(int a,int b,int &x,int &y)
{
if(!b){x=1;y=0;return a;}
exgcd(b,a%b,y,x);
y-=a/b*x;
}
int main()
{
int gcd=exgcd(a,b,x,y);
// 把 ax+by=gcd(a,b) 的解存储在x,y中。
}
乘法逆元是都要会求的,考点颇多。数论题和组合数学题很多都要用到它。
GCD与LCM
定义;
性质;i*j=gcd(i,j)*lcm(i,j);
GCD的求法;LCM的求法;
看上去不难,但实际上... ...下面来做一道思维题
【题目名:密码 strongbox】 【64MB】 【4s】
【题目描述】
有一个密码箱,0—n-1中的某些整数是它的密码。
满足:如果a和b都是它的密码,那么(a+b)%n也是它的密码(a=b是合法情况)。
欧洲皇帝QT试了k次密码,前k-1次都失败了,最后一次成功了。
请问:该密码箱最多可能有多少种不同的密码。
【输入格式】
输入第一行有两个正整数,分别表示n,k。
第二行为k个非负整数,表示每次试的密码。
保证存在合法解。
【输出格式】
一行一个整数,表示结果。
【输入样例1】
42 5
28 31 10 38 24
【输出样例1】
14
【数据规膜】
对于10%的数据:n≤10^4,k≤100;
另有10%的数据:n≤10^9,k≤100;
另有10%的数据:n≤10^9,k=1;
对于前60%的数据:k≤1000;
对于100%的数据:1≤k≤250,000≤n≤10^14;
这道题确实思维难度颇高。我就把解题报告讲(kuai)一讲(kuai)。
首先你得推出2个东西。
1.如果x是密码,那么gcd(x,n)也是密码。
具体证明联系"扩展欧几里得"知识。
2.如果x,y是密码,那么gcd(x,y)也是密码。
具体证明同上。
然后我们对密码进行分析。
记尝试密码集合为a;
1.对于密码集合A,里面所有元素的gcd记作X,有X∈A;
证明:引理2;
2.X是A中最小的元素,且X|gcd(a[k],n);
证明:引理2,引理1;
3.其他的元素是2X,3X,4X...⌊n/x⌋*x;
证明:显而易见;
4.X可能有多个解,但多个解不能同时存在。所以X取解集的最小值。
证明:引理1,答案要求;
5.X与a[j](1≤j<k)互质;
证明:显而易见;
6.最后的答案就是⌊n/x⌋;
具体代码实现步骤是什么呢?
1.读入a后,a[k]=gcd(n,a[k]);
2.a[j]=gcd(a[j],a[k]);
这是为了方便我们节省复杂度。
3.处理出a[k]的所有因子,制造答案可能集;
4.把所有不符合上述结论的因子删掉;
5.找到最小的答案,并输出。
具体代码我就不打了,你们想做也做不了,只能嘴巴一下。 为什么呢? 给你一句伤心的话: Please contact lydsy2012@163.com!
欧拉函数及欧拉定理
欧拉函数:定义;
性质;积性函数;尝试求出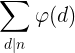 ;
;
计算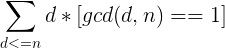 和
和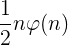
欧拉函数的线性筛(积性);O(sqrt(n))求单个欧拉函数值。
欧拉定理与费马小定理;
引子:求分母小于等于n的最简真分数的个数。
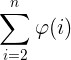 不要思维江化了啊
不要思维江化了啊
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
#define LL long long int
#define ls (x << 1)
#define rs (x << 1 | 1)
using namespace std;
LL n,Ans;
LL gL()
{
LL x=0,res=1;char ch=getchar();
while(ch>'9'||ch<'0'){if(ch=='-')res*=-1;ch=getchar();}
while(ch<='9'&&ch>='0')x=x*10+ch-48,ch=getchar();
return x*res;
}
LL get(LL x)
{
LL ans=x;
for(LL i=2;i*i<=x;++i)
if(x%i==0)
{
ans=ans/i*(i-1);
while(x%i==0)x/=i;
}
if(x!=1)ans=ans/x*(x-1);
return ans;
}
int main()
{
n=gL();
for(LL i=1;i*i<=n;++i)
if(n%i==0)
{
if(i*i==n)Ans+=i*get(i);
else Ans+=(i*get(n/i)+(n/i)*get(i));
}
printf("%lld\n",Ans);
return 0;
}
所以有的省的省选还是有很水的题的,不像某南。
2. BZOJ2818 BZOJ2190 所以这两题很水咯。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
#define LL long long int
#define Inc i*Prime[j]
using namespace std;
const int N = 10010000;
int n,Prime[N],tot,ph[N],vis[N];
LL Q[N],Ans;
int gi()
{
int x=0,res=1;char ch=getchar();
while(ch>'9'||ch<'0'){if(ch=='-')res*=-1;ch=getchar();}
while(ch<='9'&&ch>='0')x=x*10+ch-48,ch=getchar();
return x*res;
}
LL gl()
{
LL x=0,res=1;char ch=getchar();
while(ch>'9'||ch<'0'){if(ch=='-')res*=-1;ch=getchar();}
while(ch<='9'&&ch>='0')x=x*10+ch-48,ch=getchar();
return x*res;
}
void prepare()
{
ph[1]=1;
for(int i=2;i<=n;++i)
{
if(!vis[i]){Prime[++tot]=i;ph[i]=i-1;}
for(int j=1;j<=tot;++j)
{
if(Inc>N)break;vis[Inc]=1;
if(i%Prime[j])ph[Inc]=ph[i]*ph[Prime[j]];
else{ph[Inc]=ph[i]*Prime[j];break;}
}
}
for(int i=2;i<=n;++i)
Q[i]=Q[i-1]+(LL)ph[i];
}
int main()
{
n=gi();prepare();
for(int i=1;i<=tot;++i)
Ans+=(2*(Q[n/Prime[i]])+1);
printf("%lld",Ans);
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
#define LL long long int
#define Inc i*Prime[j]
using namespace std;
const int N = 40100;
int n,vis[N],Prime[N],ph[N],tot,Ans;
int gi()
{
int x=0,res=1;char ch=getchar();
while(ch>'9'||ch<'0'){if(ch=='-')res*=-1;ch=getchar();}
while(ch<='9'&&ch>='0')x=x*10+ch-48,ch=getchar();
return x*res;
}
void pui(int x)
{
if(x<10)putchar(x+'0');
else pui(x/10),putchar(x%10+'0');
}
void shai()
{
ph[1]=1;
for(int i=2;i<=n;++i)
{
if(!vis[i]){Prime[++tot]=i;ph[i]=i-1;}
for(int j=1;j<=tot;++j)
{
if(Inc>n)break;vis[Inc]=1;
if(i%Prime[j])ph[Inc]=ph[i]*ph[Prime[j]];
else {ph[Inc]=ph[i]*Prime[j];break;}
}
Ans+=ph[i];
}Ans-=ph[n]-1;
}
int main()
{
n=gi();shai();
printf("%d",Ans*2+1);
return 0;
}
3. BZOJ1951 考的比较多,板子合集,还带了一点思维,是道不错的题。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
#define LL long long int
#define ls (x << 1)
#define rs (x << 1 | 1)
using namespace std;
const LL Mod = 999911659;
const int N = 50010;
LL n,g,M[]={0,2ll,3ll,4679ll,35617ll},Y[10];
LL J[N],A[N],Z[10];
void pL(LL x)
{
if(x<10)putchar(x+'0');
else pL(x/10),putchar(x%10+'0');
}
LL gL()
{
LL x=0,res=1;char ch=getchar();
while(ch>'9'||ch<'0'){if(ch=='-')res*=-1;ch=getchar();}
while(ch<='9'&&ch>='0')x=x*10+ch-48,ch=getchar();
return x*res;
}
void prepare(LL x)
{
A[1]=J[0]=J[1]=1;
for(LL i=2;i<x;++i)
J[i]=J[i-1]*i%x,A[i]=((-(x/i)*A[x%i])%x+x)%x;
}
LL C(LL N,LL M,LL P)
{
if(N<M)return 0ll;
LL ans=J[N];
ans*=A[J[M]];ans%=P;
ans*=A[J[N-M]];ans%=P;
return ans;
}
LL Lucas(LL N,LL M,LL P)
{
if(!M)return 1ll;
if(N<P&&M<P)return C(N,M,P);
LL c=C(N%P,M%P,P);if(!c)return 0ll;
LL L=Lucas(N/P,M/P,P);return c*L%P;
}
LL get(LL mod)
{
LL ans=0;
for(LL i=1;i*i<=n;++i)
if(n%i==0)
{
ans+=Lucas(n,i,mod);ans%=mod;
if(i*i!=n)ans+=Lucas(n,n/i,mod),ans%=mod;
}
return ans;
}
LL Qpow(LL d,LL z)
{
LL ans=1;
for(;z;z>>=1,d=d*d%Mod)if(z&1)ans=ans*d%Mod;
return ans;
}
int main()
{
n=gL();g=gL()%Mod;
if(g==0){pL(0);return 0;}
for(int t=1;t<=4;++t)
{
prepare(M[t]);
Y[t]=get(M[t]);
Z[t]=((Mod-1)/M[t])*A[((Mod-1)/M[t])%M[t]];
Y[0]+=Y[t]*Z[t]%(Mod-1);Y[0]%=(Mod-1);
}
return pL(Qpow(g,Y[0])),0;
}
4. BZOJ1408 提示:积性,结合率,递×。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
#define LL long long int
#define ls (x << 1)
#define rs (x << 1 | 1)
using namespace std;
const LL Mod = 10000;
LL F[1010][1010],Ans1,Ans2,m,k;
int gi()
{
int x=0,res=1;char ch=getchar();
while(ch>'9'||ch<'0'){if(ch=='-')res*=-1;ch=getchar();}
while(ch<='9'&&ch>='0')x=x*10+ch-48,ch=getchar();
return x*res;
}
void pL(LL x)
{
if(x<0)putchar('-'),pL(-x);
if(x<10)putchar(x+'0');
else pL(x/10),putchar(x%10+'0');
}
void pc(){putchar('\n');}
LL gL()
{
LL x=0,res=1;char ch=getchar();
while(ch>'9'||ch<'0'){if(ch=='-')res*=-1;ch=getchar();}
while(ch<='9'&&ch>='0')x=x*10+ch-48,ch=getchar();
return x*res;
}
LL Qpow(LL d,LL z)
{
LL ans=1;
for(;z;z>>=1,d=d*d%Mod)if(z&1)ans=ans*d%Mod;
return ans;
}
int main()
{
k=gL();m=1;
for(LL i=1;i<=k;++i)
{
LL p=gL(),e=gL();
m=m*Qpow(p,e)%Mod;
if(p==2)continue;
LL ans1=(Ans1+(Ans2+1)*(p-1))%Mod;
LL ans2=(Ans2+Ans1*(p-1))%Mod;
Ans1=ans1;Ans2=ans2;
}
pL(Ans2);pc();pL(Ans1);pc();pL(((m-Ans1-Ans2-1)%Mod+Mod)%Mod);
return 0;
}
最后来道水题放放松。李电出过的题,大家应该都切过。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
#define LL long long int
using namespace std;
int n,p;
int gi()
{
int x=0,res=1;char ch=getchar();
while(ch>'9'||ch<'0'){if(ch=='-')res*=-1;ch=getchar();}
while(ch<='9'&&ch>='0')x=x*10+ch-48,ch=getchar();
return x*res;
}
void pL(int x)
{
if(x<0)putchar('-'),pL(-x);
if(x<10)putchar(x+'0');
else pL(x/10),putchar(x%10+'0');
}
int Qpow(int d,int z,int Mod)
{
int ans=1;
for(;z;z>>=1,d=(LL)d*d%Mod)if(z&1)ans=(LL)ans*d%Mod;
return ans;
}
int phi(int x)
{
int Txd=x;
for(int i=2;i*i<=x;++i)
if(x%i==0)
{
Txd-=Txd/i;
while(x%i==0)x/=i;
}
if(x>1)Txd-=Txd/x;
return Txd;
}
int f(int p)
{
if(p==1)return 0;int x=phi(p);
return Qpow(2,x+f(x),p);
}
int main()
{
int T=gi();
while(T--)pL(f(gi())),putchar('\n');
return 0;
}
原根与离散对数
先来看看这道题怎么写。
某校内OJ 1508。求 a^x≡1 (mod b)。
当时我做这题时还太naive,现在想想很简单是吧?
介绍一下原根和离散对数。(你们随便听听就够了,有点超)
原根:
对于2个互质的数a,b,由欧拉定理知,必定存在x≤φ(b),使a^x≡1 (mod b);
x记作a对模m的阶,记作δm(a);(应该是长这个吧)
1^1≡1(modn),1对模n的阶为1;
2^2≡1(mod3),2对模3的阶为2;
5^6≡1(mod7),5对模7的阶为6;
2^3≡1(mod7),2对模7的阶为3;
由此,定义Ordm(a)为使得a^x≡1 (mod m) 的最小整数解x;
如果有Ordma=φ(m),则称a是模m的一个原根。
我知道刚刚看完的肯定一脸蒙蔽... ...我也是。
原根的有关性质,我蒯了一点。
(1).具有原根的数一定是:2,4,p^n,2(p^n),其中p为奇素数。
(2).m的最小原根大小是O(m0.25)的。所以有些东西你枚举就够了(惨疼的教训)。
(3).如果模m有原根,那么它有φ(φ(m))个原根。(防止有人出结论题)。
求原根的方法:
你们不是已经知道了吗?
离散对数
初等代数中的对数运算,定义如果有ax=b,则称x是以a为底的对数,记作logab;
在同余关系中也有类似的问题。给定n,a,b,如何求解x使ax≡b (mod n);
这一问题也被称作离散对数问题。我们只讨论n为素数的情况。
先来讨论暴力怎么做?
由欧拉定理,我们知道0~n-1内必有一解,递推即可,复杂度O(n);
但这样并不是很好的算法,下面给出一种O(比n小)的算法。
首先计算出x=0,1,2...m时ax (mod n)的值。
设ak≡b (mod n);设 k=p*m+q(q<m);枚举p;
对于一个枚举出的p,ap*m是一定且可求的。
则可以改写成: ap*m+q≡b (mod n);
继续改: aq*apm≡b (mod n);
再一步: aq*(am)p≡b (mod n);
设T=(am)p,就有:
T*aq≡b (mod n);
你就可以用exgcd求出T;
那么问题就在于求q上。聪明的你可以用很多种方法解决这个问题。。。
这种分块用基本不等式算出m取到sqrt(n)时复杂度最优秀。。。
练习题:
BZOJ2956 模积和;
BZOJ1407 Savage(NOI 2002 荒岛野人);
NOIP2014 Day2T3 解方程,同BZOJ2742 Akai的数学作业;
神题之圆上的整点;
神题之数论之神CJK;
其实上面的题目我一个都不会。




