servlet自动获取前端页面提交数据
servlet自动获取前端页面jsp提交数据
以下是本人在学习过程中,因前端页面提交参数过多,后台servlet封装实体类过于麻烦而写的一个工具类,应用于jsp/servlet数据提交后,基于MVC+MyBatis进行数据持久化的过程。这里只介绍页面到servlet(controller)提交数据封装对象的过程,MVC+MyBatis访问数据库不在这里介绍。
1.前端页面及代码
1)前端表单页面构建(用于测试简单构建的页面有点丑陋哦~)
2)前端jsp页面代码
这里使用了Ajax异步 get去除缓存方式提交表单。传统方式请自测,本人都已经测试过,在这里不做展示。
注意:在Ajax提交表单部分使用了jQuery的serialize()序列化函数,初学者可参看jQuery的帮助文档。如不理解,可以在data部分使用“字符串”或json对象的方式进行常规方式提交数据。
1 <%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" 2 pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> 3 <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> 4 <html> 5 <head> 6 <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> 7 <title>Insert title here</title> 8 <script type="text/javascript" src="jquery-1.11.1-min.js"></script> 9 <script type="text/javascript"> 10 $(function(){ 11 $("#submitBtn").click(function(){ 12 $.ajax({ 13 url:"${pageContext.request.contextPath }/testPage", 14 data:$("#formId").serialize(), //jQuery中的函数,序列化表单数据 15 type:"get", 16 cache:false, 17 success:function(jsonObj){ 18 alert(jsonObj.msg); 19 $("#formId")[0].reset();//重置表单 20 } 21 }) 22 }); 23 }) 24 25 </script> 26 </head> 27 <body> 28 <form id="formId"> 29 ID:<input id="id" name="id"><br> 30 姓名:<input id="username" name="username"><br> 31 性别:<input id="sex" name="sex" ><br> 32 年龄:<input id="age" name="age" ><br> 33 价格:<input id="price" name="price"><br> 34 <input type="button" value="提交" id="submitBtn"> 35 </form> 36 </body> 37 </html>
2.实体类
5个属性and提供set/get方法
1 package com.domain; 2 3 public class Person { 4 String username; 5 String sex; 6 int age; 7 Double price; 8 Long id; 9 public String getUsername() { 10 return username; 11 } 12 public void setUsername(String username) { 13 this.username = username; 14 } 15 public String getSex() { 16 return sex; 17 } 18 public void setSex(String sex) { 19 this.sex = sex; 20 } 21 public int getAge() { 22 return age; 23 } 24 public void setAge(int age) { 25 this.age = age; 26 } 27 public Double getPrice() { 28 return price; 29 } 30 public void setPrice(Double price) { 31 this.price = price; 32 } 33 public Long getId() { 34 return id; 35 } 36 public void setId(Long id) { 37 this.id = id; 38 } 39 }
3.后台Servlet代码
1)封装实体类对象
这里只讲前端提交数据输出到控制台,证明数据已经获取并封装到对象中。
其中,p = (Person) EncapsulationUtil.getJavaBean(Person.class, request); 使用了封装体工具,为本人为偷懒所写,在后面提供源码。后面做详细解释。
注意:前端提交数据和我们需要保存到数据库的数据不完全时,在servlet中拿到封装对象后可手动进行设置,如:数据的主键id一般我们采用UUID进行后台生成需要手动set进行设置。

1 package com.controller; 2 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 import java.util.HashMap; 5 import java.util.Map; 6 7 import javax.servlet.ServletException; 8 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; 9 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; 10 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; 11 12 import com.domain.Person; 13 import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper; 14 import com.utils.EncapsulationUtil; 15 16 public class testPage extends HttpServlet { 17 18 protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { 19 //定义数据封装体的对象 20 Person p; 21 //定义用于返回json的数据存放集合 22 Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>(); 23 24 try { 25 //获取前端页面表单提交的数据 26 p = (Person) EncapsulationUtil.getJavaBean(Person.class, request); 27 //打印封装体中的数据结果 28 System.out.println("ID---->"+p.getId()+"<-----"); 29 System.out.println("姓名:---->"+p.getUsername()+"<-----"); 30 System.out.println("年龄:---->"+p.getAge()+"<-----"); 31 System.out.println("性别:"+p.getSex()); 32 System.out.println("价格:"+p.getPrice()); 33 map.put("msg", "提交成功"); 34 35 } catch (Exception e1) { 36 e1.printStackTrace(); 37 //当前的提交数据类型和实体类中数据格式不一致时,抛出异常 38 System.err.println("getMessage"+e1.getMessage()); 39 //将异常信息保存到集合中,返回到前端 40 map.put("msg", e1.getMessage()); 41 } 42 43 //jackson插件,用于将map集合转化为json字符串 44 ObjectMapper ob = new ObjectMapper(); 45 //返回json 46 request.setAttribute("json",ob.writeValueAsString(map) ); 47 request.getRequestDispatcher("/json.jsp").forward(request, response); 48 49 50 /* Map<String,Object> conditionMap = EncapsulationUtil.getMap(request); 51 52 Set ketSet = conditionMap.keySet(); 53 for (Object object : ketSet) { 54 String key = (String) object; 55 System.out.println(conditionMap.get(key)); 56 }*/ 57 } 58 59 protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { 60 doGet(request, response); 61 } 62 63 }
2)封装map集合对象(因在MVC+Mybatis中可能用到map结合,所以提供此方法)
解释:a.这里不再展示如何使用此工具类封装map集合,实现比较简单。
b.如想测试,将doGet方法中注释掉的代码放开,上面的代码注释掉即可,同样为数据到控制台。
c.重点!此工具虽然定义了Map<String,Object> 由于页面通过http协议提交的参数通过request.getParameter()获取后为String类型,实际保存在map对象中的数据为Map<String,String>,如需要在后台获取String类型之外的数据格式,需要单独进行获取后转换类型。下面举一个分页查询中的小例子作为补充。其中利用到了Map即可中key相同时,value会覆盖的特性,以保证我们拿到的map集合对象是数据类型满足要求的。
以下为分页查询中的例子,页码pageNo, 每页显示记录条数pageSize,跳过的记录数skipNo 应均为Integer类型而不是String类型,所以需要做特殊处理。如下 A 和 B 的对比
A.传统手动接收参数进行封装(找的其他项目中的代码,只为展示使用方法)

1 protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { 2 //获取页面数据 3 Integer pageNo=Integer.parseInt(request.getParameter("pageNo")); 4 Integer pageSize =Integer.parseInt(request.getParameter("pageSize")); 5 String name = request.getParameter("name"); 6 String owner = request.getParameter("owner"); 7 String type = request.getParameter("type"); 8 String state = request.getParameter("state"); 9 String startDate = request.getParameter("startDate"); 10 String endDate = request.getParameter("endDate"); 11 Integer skipNo = (pageNo-1)*pageSize; 12 13 //封装数据集合 14 Map<String,Object> conditionMap = new HashMap<>(); 15 conditionMap.put("pageNo", pageNo); 16 conditionMap.put("pageSize", pageSize); 17 conditionMap.put("name", name); 18 conditionMap.put("owner", owner); 19 conditionMap.put("type", type); 20 conditionMap.put("state", state); 21 conditionMap.put("startDate", startDate); 22 conditionMap.put("endDate", endDate); 23 conditionMap.put("skipNo", skipNo); 24 }
B.封装工具进行接收参数

1 @Override 2 protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) 3 throws ServletException, IOException { 4 //获取页面数据 5 Integer pageNo = Integer.parseInt(request.getParameter("pageNo")); 6 Integer pageSize = Integer.parseInt(request.getParameter("pageSize")); 7 Map<String,Object> conditionMap = EncapsulationUtil.getMap(request); 8 conditionMap.put("pageSize", pageSize); 9 conditionMap.put("skipNo", (pageNo-1)*pageSize); 10 11 //创建Service代理对象 12 TransactionService ts = (TransactionService) ServiceFactory.getServiceProxy(new TransactionServiceImpl()); 13 PaginationVO<Transaction> pv = ts.getPaginationVO(conditionMap); 14 //响应json 15 ResponseJSON.out(pv, request, response); 16 17 }
4.封装体工具类
1).工具类中已经对前端页面提交数据两端可能存在空白进行了处理,减少页面处理过程
2). 重点!前端提交表单时,要求URL中name=value&name=value...中name部分(或者说表单中name属性的值)要和实体类中属性字段名保持一致,因为工具中封装原理是调用实体类中的set方法,因此实体类中需要提供标准的set方法。
3).getJavaBean()方法可能会抛出异常,异常发生在前端提交数据和实体中字段类型不一致。如:实体类中年龄为int/Integer,前端提交时输入了“张三”等非法数据。因此最好在前端做表单验证,以保证数据的合法性。

1 package com.utils; 2 import java.lang.reflect.Field; 3 import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException; 4 import java.lang.reflect.Method; 5 import java.util.Enumeration; 6 import java.util.HashMap; 7 import java.util.Map; 8 9 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; 10 11 /** 12 * 获取请求参数封装对象的工具类 13 * 14 */ 15 public class EncapsulationUtil { 16 17 private static int in; 18 private static float fl; 19 private static double d; 20 private static Integer integ; 21 private static Double doub; 22 private static Long lon; 23 /** 24 * 获取一个JavaBean,封装有request请求传递的参数 25 * 26 * @param claz 27 * 封装参数的实体类的Class 28 * @param request 29 * 接收数据的HttpServletRequest请求 30 * @return 封装有请求数据的JavaBean实体类 31 * @throws 当接收到的参数数据类型和实体类对应属性类型不一致时 抛出 32 * 异常信息:“数据格式有误!” 33 */ 34 public static Object getJavaBean(Class<?> claz, HttpServletRequest request) { 35 36 // 1.获取请求中的参数名称 37 Enumeration<String> params = request.getParameterNames(); 38 39 // 2.声明实体类的对象 40 Object jBeanObj = null; 41 42 43 try { 44 jBeanObj = claz.newInstance(); // 初始化实体类对象 45 46 for (Enumeration<String> e = params; e.hasMoreElements();) { 47 // 3.遍历获取某一个参数名(属性) 48 String paramName = e.nextElement().toString(); 49 if("_".equals(paramName)){ 50 continue; 51 } 52 String paramValue = request.getParameter(paramName).trim(); 53 54 // 4.构建set方法方法名 55 String setMethodName = "set" + paramName.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase() + paramName.substring(1); 56 57 // 5.获取属性的Field对象 58 Field field = claz.getDeclaredField(paramName); 59 60 // 6.获取属性的声明类型 61 Class<?> fieldType = field.getType(); 62 63 // 7.获取set方法的Method对象 (方法名,参数类型的Class) 64 Method setMethodObj = claz.getDeclaredMethod(setMethodName, field.getType()); 65 setMethodObj.setAccessible(true); 66 67 // 8.判断属性类型,调用JavaBean的set方法 68 if (Integer.class.equals(fieldType)) { 69 70 if("".equals(paramValue)){ 71 setMethodObj.invoke(jBeanObj,integ); 72 }else{ 73 setMethodObj.invoke(jBeanObj, Integer.valueOf(paramValue)); 74 } 75 76 } else if (Long.class.equals(fieldType)) { 77 78 if("".equals(paramValue)){ 79 setMethodObj.invoke(jBeanObj,lon); 80 }else{ 81 setMethodObj.invoke(jBeanObj, Long.parseLong(paramValue)); 82 } 83 84 } else if (Double.class.equals(fieldType)) { 85 86 if("".equals(paramValue)){ 87 setMethodObj.invoke(jBeanObj,doub); 88 }else{ 89 setMethodObj.invoke(jBeanObj, Double.parseDouble(paramValue)); 90 } 91 92 } else if (String.class.equals(fieldType)){ 93 94 setMethodObj.invoke(jBeanObj, paramValue); 95 96 } else if(int.class.equals(fieldType)){ 97 98 if("".equals(paramValue)){ 99 setMethodObj.invoke(jBeanObj,in); 100 }else{ 101 setMethodObj.invoke(jBeanObj, Integer.parseInt(paramValue)); 102 } 103 } else if(float.class.equals(fieldType)){ 104 105 if("".equals(paramValue)){ 106 setMethodObj.invoke(jBeanObj,fl); 107 }else{ 108 setMethodObj.invoke(jBeanObj, Float.parseFloat(paramValue)); 109 } 110 111 } else if(double.class.equals(fieldType)){ 112 113 if("".equals(paramValue)){ 114 setMethodObj.invoke(jBeanObj,d); 115 }else{ 116 setMethodObj.invoke(jBeanObj, Double.parseDouble(paramValue)); 117 } 118 } 119 120 } 121 } catch (IllegalAccessException | IllegalArgumentException | InvocationTargetException | NoSuchMethodException | SecurityException | NoSuchFieldException | InstantiationException e) { 122 e.printStackTrace(); 123 throw new NumberFormatException("数据格式错误,请核对!"); 124 } 125 126 // 9.返回封装对象 127 return jBeanObj; 128 } 129 130 /** 131 * 获取请求数据的Map集合封装体 132 * 133 * @param request 134 * 接收数据的HttpServletRequest请求 135 * @return 返回封装请求中数据的Map<String ,Object> 136 */ 137 public static Map<String, Object> getMap(HttpServletRequest request) { 138 // 0.创建Map集合 139 Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>(); 140 141 // 1.获取请求中的参数名称 142 Enumeration<String> params = request.getParameterNames(); 143 144 for (Enumeration<String> e = params; e.hasMoreElements();) { 145 // 2.遍历获取某一个参数名称 146 String paramName = e.nextElement().toString(); 147 // 3.获取参数值 148 String paramValue = request.getParameter(paramName).trim(); 149 // 4.封装数据 150 map.put(paramName, paramValue); 151 } 152 // 5.返回封装体集合 153 return map; 154 } 155 156 private EncapsulationUtil() { 157 } 158 }
5.工具目录图
其中ajax部分json.jsp如下:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/json; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
${json}
工具目录图(测试一切从简,请勿追问包结构不完整之类问题)
6.效果展示
将工程发布到Tomcat中,进行访问http://localhost:8080/reflect/test.jsp
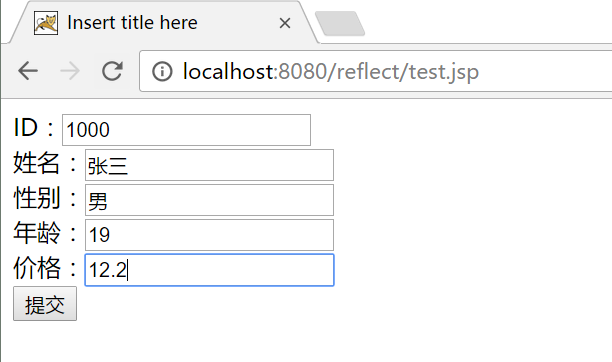
1)前端提交正常数据
前端页面
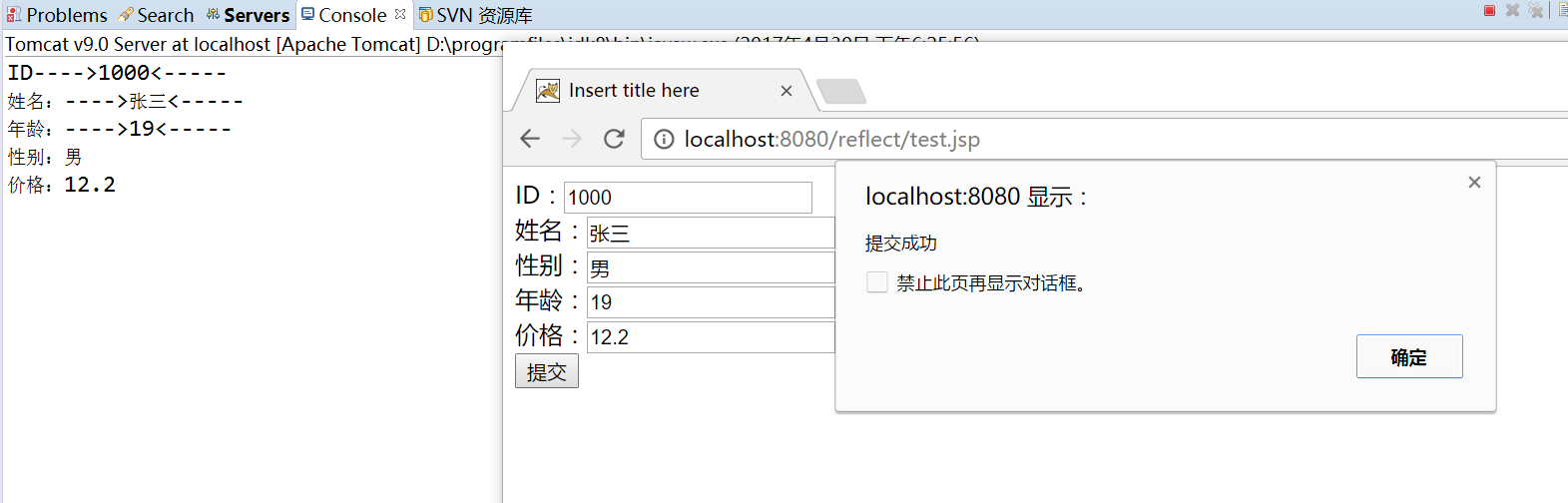
点击提交后,后台控制台输出及前端显示
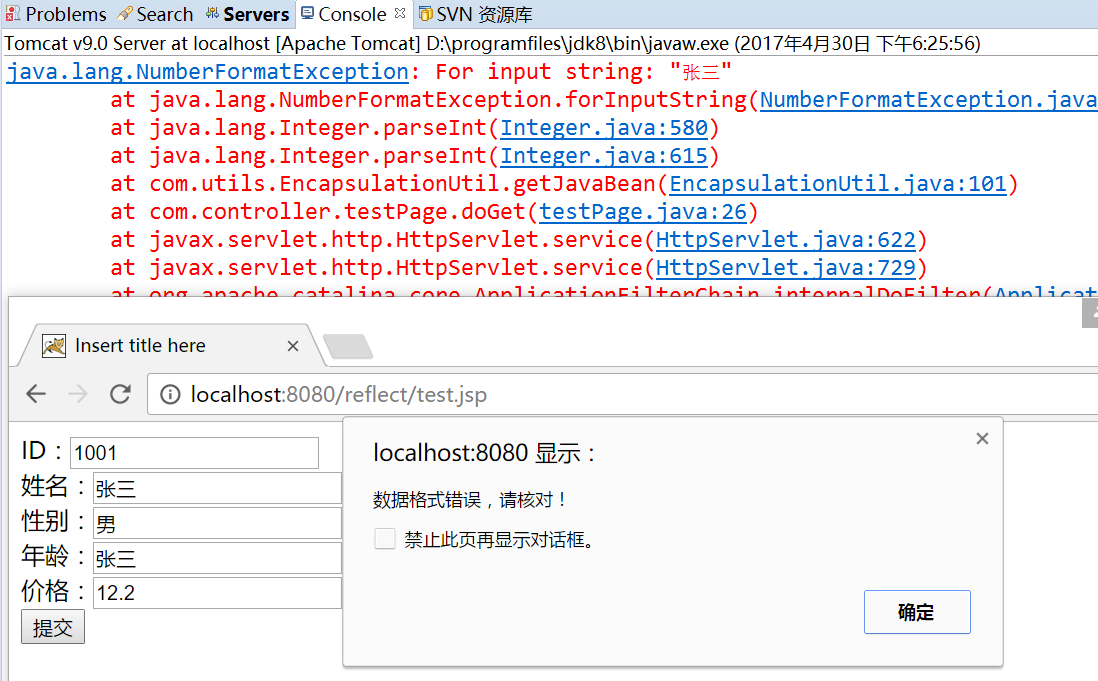
2)前端提交非法数据时(未做表单验证)
年龄应为int类型,底层使用了Integer.valueOf(paramValue)因此会发生数据格式换行异常。这是需要注意的地方!!特殊地方最好做表单验证,这是测试demo就不再丰富。
说明:本例中工具类纯属个人学习过程中在不使用Spring等框架的前提下 为偷懒所写,如使用生产环境发生问题,概不负责!
转载请注明出处,谢谢!^.^




