flutter android 开发笔记(二.module集成,混合页面)
1,在as已有的安卓项目中,新建flutter项目
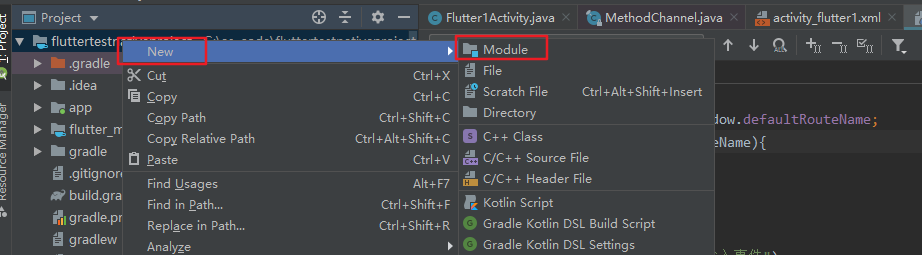
选择新建flutter module
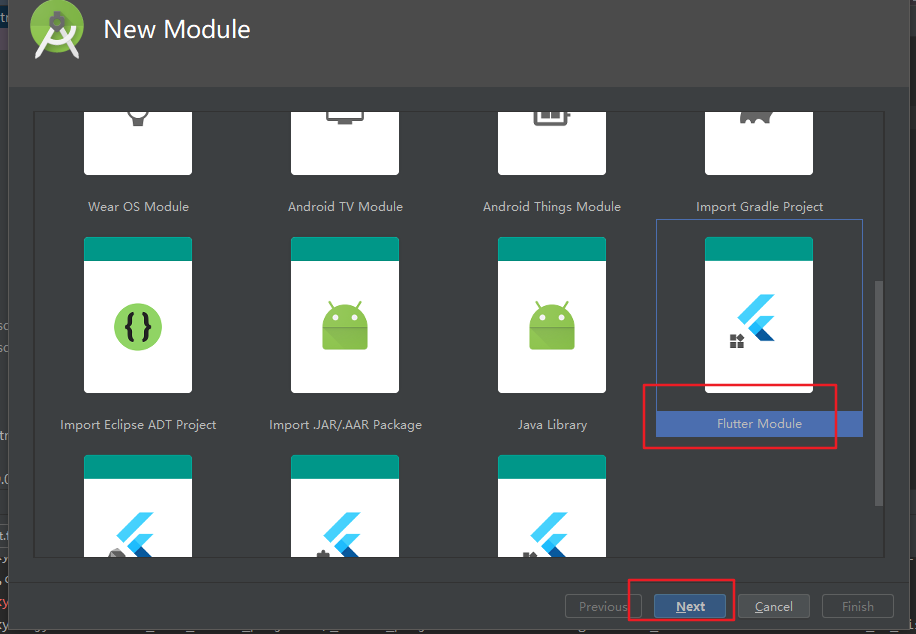
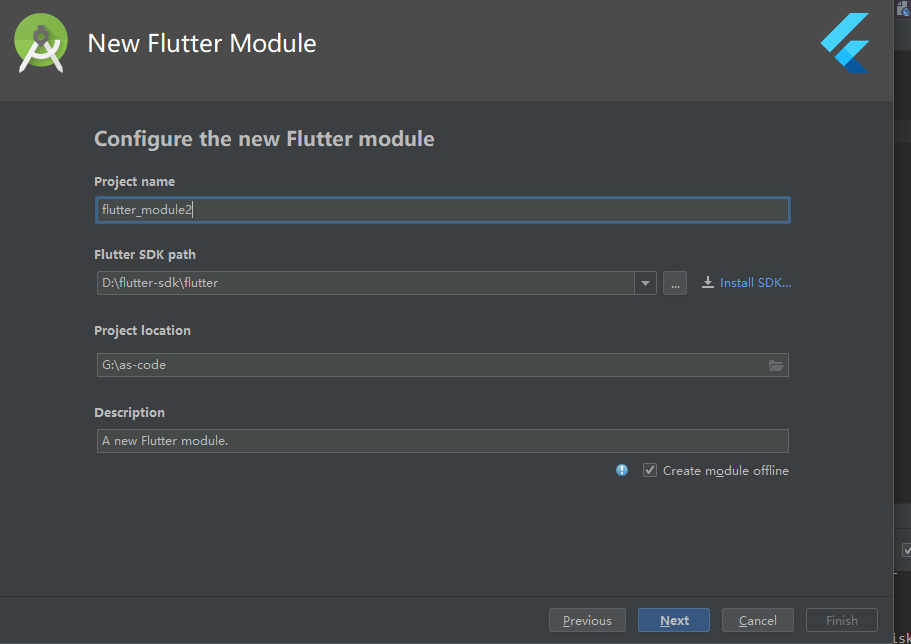
项目的setting.gradle文件已经自动引入flutter_module2,确认下路径是否正确
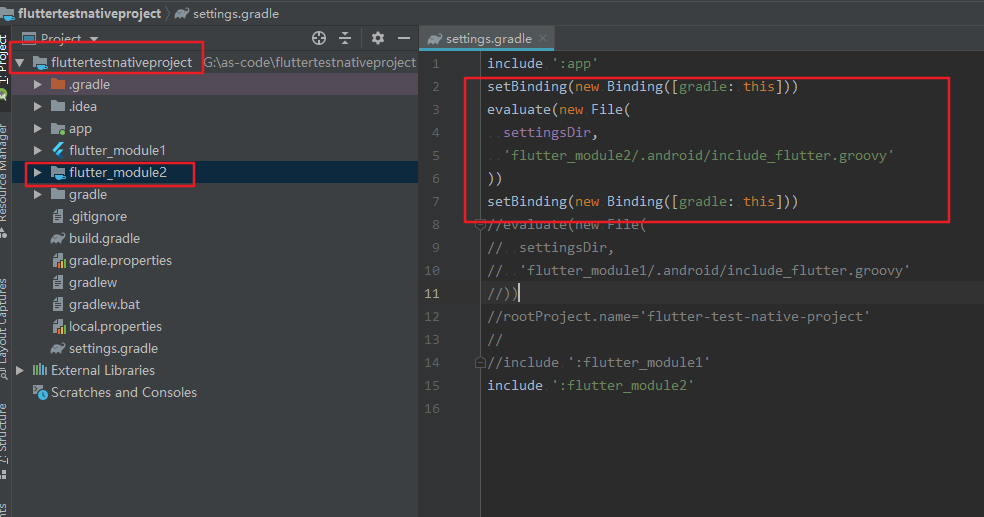
安卓原生代码
2,初始化flutter的控制器
mFlutter1Engine = new FlutterEngine(this);
mFlutter1Engine.getDartExecutor().executeDartEntrypoint(
DartExecutor.DartEntrypoint.createDefault()
);
3,创建flutterview
FlutterView flutterView = new FlutterView(this);
FrameLayout.LayoutParams lp = new FrameLayout.LayoutParams(
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT,
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT);
FrameLayout flContainer = findViewById(R.id.fl_flutter);
flContainer.addView(flutterView, lp);
flContainer.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
FlutterUiDisplayListener listener = new FlutterUiDisplayListener() {
@Override
public void onFlutterUiDisplayed() {
flContainer.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);//当flutter ui展示出来的时候,显示flutterview内容
}
@Override
public void onFlutterUiNoLongerDisplayed() {
}
};
flutterView.addOnFirstFrameRenderedListener(listener);
4,展示flutter
mFlutter1View.attachToFlutterEngine(mFlutter1Engine);
整体android代码
package xyz.djytest.flutter_test_native_project;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.FrameLayout;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import io.flutter.embedding.android.FlutterView;
import io.flutter.embedding.engine.FlutterEngine;
import io.flutter.embedding.engine.FlutterEngineCache;
import io.flutter.embedding.engine.dart.DartExecutor;
import io.flutter.embedding.engine.renderer.FlutterUiDisplayListener;
public class Flutter2Activity extends AppCompatActivity {
FlutterEngine mFlutter1Engine;
FlutterView mFlutter1View;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_flutter2);
initFlutterEngine();
mFlutter1View = createFlutterView();
mFlutter1View.attachToFlutterEngine(mFlutter1Engine);
}
private FlutterView createFlutterView() {
FlutterView flutterView = new FlutterView(this);
FrameLayout.LayoutParams lp = new FrameLayout.LayoutParams(
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT,
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT);
FrameLayout flContainer = findViewById(R.id.fl_flutter);
flContainer.addView(flutterView, lp);
flContainer.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
FlutterUiDisplayListener listener = new FlutterUiDisplayListener() {
@Override
public void onFlutterUiDisplayed() {
flContainer.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
}
@Override
public void onFlutterUiNoLongerDisplayed() {
}
};
flutterView.addOnFirstFrameRenderedListener(listener);
return flutterView;
}
private void initFlutterEngine() {
mFlutter1Engine = FlutterEngineCache.getInstance().get("flutter");
if (mFlutter1Engine == null){
mFlutter1Engine = new FlutterEngine(this);
mFlutter1Engine.getDartExecutor().executeDartEntrypoint(
DartExecutor.DartEntrypoint.createDefault()
);
FlutterEngineCache.getInstance().put("flutter", mFlutter1Engine);
}
}
}
xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/fl_flutter"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
</FrameLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_gravity="bottom"
android:layout_marginBottom="20dp"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="我是Flutter2Activity的native的text" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:text="修改text内容"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
</LinearLayout>
</FrameLayout>
flutter代码
flutter页面入口
默认页面内容
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: ThemeData(
// This is the theme of your application.
//
// Try running your application with "flutter run". You'll see the
// application has a blue toolbar. Then, without quitting the app, try
// changing the primarySwatch below to Colors.green and then invoke
// "hot reload" (press "r" in the console where you ran "flutter run",
// or press Run > Flutter Hot Reload in a Flutter IDE). Notice that the
// counter didn't reset back to zero; the application is not restarted.
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
home: MyHomePage(title: 'Flutter Demo Home Page'),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatefulWidget {
MyHomePage({Key key, this.title}) : super(key: key);
// This widget is the home page of your application. It is stateful, meaning
// that it has a State object (defined below) that contains fields that affect
// how it looks.
// This class is the configuration for the state. It holds the values (in this
// case the title) provided by the parent (in this case the App widget) and
// used by the build method of the State. Fields in a Widget subclass are
// always marked "final".
final String title;
@override
_MyHomePageState createState() => _MyHomePageState();
}
class _MyHomePageState extends State<MyHomePage> {
int _counter = 0;
void _incrementCounter() {
setState(() {
// This call to setState tells the Flutter framework that something has
// changed in this State, which causes it to rerun the build method below
// so that the display can reflect the updated values. If we changed
// _counter without calling setState(), then the build method would not be
// called again, and so nothing would appear to happen.
_counter++;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
// This method is rerun every time setState is called, for instance as done
// by the _incrementCounter method above.
//
// The Flutter framework has been optimized to make rerunning build methods
// fast, so that you can just rebuild anything that needs updating rather
// than having to individually change instances of widgets.
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
// Here we take the value from the MyHomePage object that was created by
// the App.build method, and use it to set our appbar title.
title: Text(widget.title),
),
body: Center(
// Center is a layout widget. It takes a single child and positions it
// in the middle of the parent.
child: Column(
// Column is also a layout widget. It takes a list of children and
// arranges them vertically. By default, it sizes itself to fit its
// children horizontally, and tries to be as tall as its parent.
//
// Invoke "debug painting" (press "p" in the console, choose the
// "Toggle Debug Paint" action from the Flutter Inspector in Android
// Studio, or the "Toggle Debug Paint" command in Visual Studio Code)
// to see the wireframe for each widget.
//
// Column has various properties to control how it sizes itself and
// how it positions its children. Here we use mainAxisAlignment to
// center the children vertically; the main axis here is the vertical
// axis because Columns are vertical (the cross axis would be
// horizontal).
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
Text(
'You have pushed the button this many times:',
),
Text(
'$_counter',
style: Theme.of(context).textTheme.display1,
),
],
),
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: _incrementCounter,
tooltip: 'Increment',
child: Icon(Icons.add),
), // This trailing comma makes auto-formatting nicer for build methods.
);
}
}
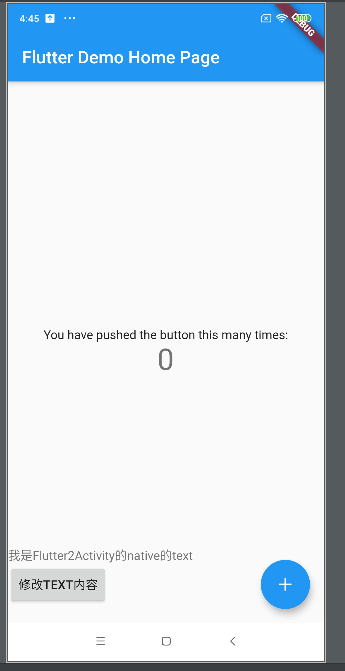
打开Flutter2Activity时的展示效果