C#-HTTP-HttpRequest类
一、HttpRequest的作用
HttpRequest的作用是令到Asp.net能够读取客户端发送HTTP值。比如表单、URL、Cookie传递过来的参数。
返回字符串的那些值就不说了,那些基本上都是与HTTP请求报文相关的东西。
现在看看返回NameValueCollection对象的东东,这个对象只是为了存储返回的东西。
1、Request.Headers;
这个东西返回的是什么呢?写个实例:
public ActionResult Index()
{
HttpRequest request = System.Web.HttpContext.Current.Request;
NameValueCollection headersCollect = request.Headers;
string[] headArr = headersCollect.AllKeys;
foreach (string str in headArr)
{
Response.Write(str + ":" + headersCollect.Get(str) + ";<br/>");
}
return View();
}
看看在浏览器输出:

再用火狐看看HTTP请求报文的请求头信息:
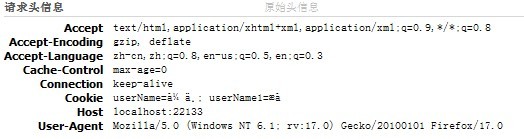
明显可以看到,这个request.Headers返回的就是请求头信息的一个NameValueCollection集合。
2、Request.Form
这个属性获取的是浏览器提交的表单内容,也是返回NameValueCollection对象,这个对象中包含了所有的表单键值对内容。
看前台HTML代码:
<form action="/Home/GetForm" method="post">
<p>姓名:<input type="text" name="Name" /></p> //输入张三
<p>年龄:<input type="text" name="Age" /></p> //输入12
<p>性别:<input type="radio" name="male" value="man" />男 <input type="radio" name="male" value="woman" />女</p> //选择 男
<p><input type="submit" value="提交" /></p>
</form>
后台代码:
public ActionResult GetForm()
{
HttpRequest request = System.Web.HttpContext.Current.Request;
NameValueCollection FormCollect = request.Form;
foreach (string str in FormCollect)
{
Response.Write(str + ": " + FormCollect.Get(str) + "<br/>");
}
return Content("键值对数目:" + FormCollect.Count);
}
浏览器输出:
Name: 张三
Age: 12
male: man
键值对数目:3
3、Request.QueryString
该属性的作用是将URL中的参数全部保存到NameValueCollection集合中。
public ActionResult TestCookie()
{
NameValueCollection nvc = new NameValueCollection();
nvc = System.Web.HttpContext.Current.Request.QueryString;
Response.Write(nvc.Count + " "); //输出路径中参数集合的总数
if (nvc.Count > 0)
{
foreach (string str in nvc.AllKeys)
{
Response.Write(str + ": " + nvc.Get(str) + "; "); //遍历url参数集合,输出参数名与值
}
}
return View();
//当路径为http://localhost:22133/Home/testCookie?id=1&name=张三&Age=23
//输出3 id: 1; name: 张三; Age: 28;
4、Params,Item与QueryString、Forms的区别
- Get请求用QueryString;
- Post请求用Forms;
- Parms与Item可以不区分Get请求还是Post请求;
Params与Item两个属性唯一不同的是:Item是依次访问这4个集合,找到就返回结果,而Params是在访问时,先将4个集合的数据合并到一个新集合(集合不存在时创建), 然后再查找指定的结果。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号