Numpy基础学习笔记3
5.线性代数
线性代数(Linear algebra)相关相关的有一个np.linalg可以解决这些问题。

import numpy as np
a = np.arange(1,10)
np.diag(a) # 以a的元素作为对角线值得方阵,其余值为0
Out[3]:
array([[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 3, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 4, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 5, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 6, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 7, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 8, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 9]])
arr1 = np.array([[2,3,4],[2,5,3]])
arr2 = np.array([[2,4],[-3,4],[5,2]])
arr1.dot(arr2) #计算两个矩阵的内积
Out[6]:
array([[15, 28],
[ 4, 34]])
np.dot(arr1,arr2)
Out[8]:
array([[15, 28],
[ 4, 34]])
np.trace(np.diag(a)) #计算对角线之和
Out[9]: 45
arr3 = np.array([[1,2,3],[2,3,4],[5,4,2]])
np.linalg.det(arr3) # 求行列式
Out[12]: 0.99999999999999956
np.linalg.eig(arr3) # 求特征值和特征向量
Out[13]:
(array([ 8.75449624, -0.04211316, -2.71238309]),
array([[-0.41765986, -0.48871005, -0.42701284],
[-0.61198699, 0.79469434, -0.41357144],
[-0.67158928, -0.3600325 , 0.80412605]]))
arr4 = np.linalg.inv(arr3) #求逆矩阵m
arr4.dot(arr3) # 验证矩阵与逆矩阵的积
Out[17]:
array([[ 1.00000000e+00, -7.10542736e-15, -8.88178420e-15],
[ 3.55271368e-15, 1.00000000e+00, 2.66453526e-15],
[ 0.00000000e+00, -1.77635684e-15, 1.00000000e+00]])
np.linalg.solve(arr3,[2,5,4]) #求arr3和[2,5,4]的线性方程组的解
Out[19]: array([ 16., -25., 12.])
6.随机数
Numpy中有np.random作为python内置random模块的补充,增加了一些高效的函数。
Numpy的random模块不仅能生成1个样本值,也能产生大量样本值。
In [1]: import numpy as np #numpy库
In [2]: from random import normalvariate #python标准库
In [3]: %timeit samples = [normalvariate(0,1) for _ in range(1000000)]
1 loop, best of 3: 1.42 s per loop
In [4]: %timeit np.random.normal(size=1000000)
10 loops, best of 3: 39 ms per loop
可以看出,np.random要快很多。


部分例子:
In [6]: np.random.rand()
Out[6]: 0.7802183895038862
In [7]: np.random.rand(10)
Out[7]:
array([ 0.90918046, 0.90886419, 0.00794304, 0.64984129, 0.58132135,
0.9343964 , 0.19191809, 0.1478791 , 0.24818389, 0.36123808])
In [8]: np.random.randint(1,100)
Out[8]: 80
In [9]: np.random.randint(1,100,100)
Out[9]:
array([71, 47, 87, 16, 74, 96, 16, 82, 83, 6, 58, 60, 52, 79, 41, 14, 6,
28, 52, 7, 68, 61, 28, 26, 94, 42, 77, 26, 84, 61, 4, 71, 46, 72,
47, 8, 25, 43, 19, 63, 8, 69, 21, 56, 78, 98, 88, 60, 75, 41, 18,
21, 74, 25, 20, 71, 81, 91, 95, 12, 68, 15, 54, 75, 38, 51, 15, 79,
34, 34, 79, 28, 58, 56, 17, 44, 32, 58, 1, 16, 45, 74, 10, 15, 45,
14, 97, 36, 65, 61, 25, 55, 45, 78, 2, 99, 50, 14, 6, 6])
In [11]: np.random.randn(3,3)
Out[11]:
array([[ 0.31982232, -0.63358435, 0.05103954],
[-0.11613672, -0.8113278 , 0.29019726],
[-0.13409391, -0.81745446, 0.12032746]])
In [13]: np.random.binomial(0,1)
Out[13]: 0
In [16]: np.random.normal(10)
Out[16]: 9.555706096455244
seed()用于指定随机数生成时所用算法开始的整数值,如果使用相同的seed()值,则每次生成的随即数都相同,如果不设置这个值,则系统根据时间来自己选择这个值,此时每次生成的随机数因时间差异而不同。
In [17]: np.random.seed(0)
In [18]: np.random.randn(2,2)
Out[18]:
array([[ 1.76405235, 0.40015721],
[ 0.97873798, 2.2408932 ]])
In [19]: np.random.seed(0)
In [20]: np.random.randn(2,2)
Out[20]:
array([[ 1.76405235, 0.40015721],
[ 0.97873798, 2.2408932 ]])
# 两次生成的随机数居然相同
In [21]: np.random.randn(2,2)
Out[21]:
array([[ 1.86755799, -0.97727788],
[ 0.95008842, -0.15135721]])
# 第三次变了。
7.范例:随机漫步
随机漫步:从0开始,每次走一步,步长为1或者-1,概率相同。用python和numpy两种方式来实现。
7.1 用纯python实现
用纯python实现1000步的随机漫步。
import random
def random_walk_python(N):
postion = 0
walk = [postion]
for i in range(N):
step = 1 if random.randint(0,1) else -1
postion += step
walk.append(postion)
return walk
y = random_walk_python(1000)
#画个图看看,
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
x = np.arange(1001) #注意值个数
plt.plot(x,y)
plt.title("Random Walk")
plt.xlabel("x")
plt.ylabel("y")
plt.show()
结果图:
7.2 用numpy来实现
用numpy.random模块实现1000步随机漫步。
import numpy as np
def random_walk_numpy(N):
draws = np.random.randint(0,2,N) #创建0或1的1000个元素的随机一维数组
steps = np.where(draws > 0, 1,-1) #调整为1或-1的数组
walks = steps.cumsum() #计算累加和
return walks
yy = random_walk_numpy(1000)
#画图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
xx = np.arange(1000)
plt.plot(xx,yy)
plt.title("Random Walk")
plt.xlabel("x")
plt.ylabel("y")
plt.show()
结果图:
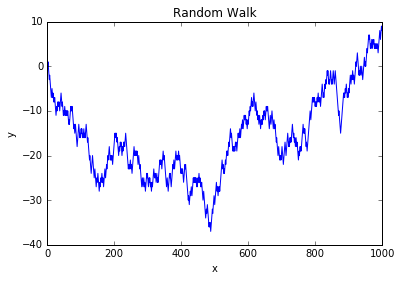
而且,我们很容易算出最大值,最小值。
yy.max() #最大值
Out[12]: 9
yy.min() #最小值
Out[13]: -37
yy.argmax() #最大值所在位置
Out[14]: 998
yy.argmin() #最小值所在位置
Out[15]: 488
7.2 同时实现多个随机漫步
比如一下子产生5000个随机漫步,每个随机漫步步数为1000。
In [22]: draws = np.random.randint(0,2,(5000,1000))
In [23]: steps = np.where(draws>0,1,-1)
# In [24]: walks = steps.cumsum()
In [32]: walks = steps.cumsum(axis= 1) # 按行累加
In [33]: walks
Out[33]:
array([[ -1, -2, -3, ..., 2, 1, 2],
[ 1, 2, 1, ..., 28, 27, 28],
[ 1, 0, 1, ..., 50, 49, 50],
...,
[ -1, -2, -3, ..., -36, -37, -38],
[ -1, -2, -3, ..., -2, -1, -2],
[ 1, 2, 1, ..., -40, -41, -40]], dtype=int32)
计算最大值和最小值
In [34]: walks.max()
Out[34]: 115
In [35]: walks.min()
Out[35]: -128
如果想要得到这五千个随机漫步达到30或-30的平均时间(步数),该如何计算?
In [37]: np.abs(walks)>= 30 #绝对值大于30的都为True
Out[37]:
array([[False, False, False, ..., False, False, False],
[False, False, False, ..., False, False, False],
[False, False, False, ..., True, True, True],
...,
[False, False, False, ..., True, True, True],
[False, False, False, ..., False, False, False],
[False, False, False, ..., True, True, True]], dtype=bool)
In [38]: (np.abs(walks)>= 30).any(1) #选出有绝对值大于30的行
Out[38]: array([ True, True, True, ..., True, True, True], dtype=bool)
In [39]: hit30s = (np.abs(walks)>= 30).any(1)
In [40]: hit30s.sum() # 有3386行
Out[40]: 3386
In [41]: walks[hit30s] #选出这3386行
Out[41]:
array([[ -1, -2, -3, ..., 2, 1, 2],
[ 1, 2, 1, ..., 28, 27, 28],
[ 1, 0, 1, ..., 50, 49, 50],
...,
[ -1, -2, -3, ..., -36, -37, -38],
[ -1, -2, -3, ..., -2, -1, -2],
[ 1, 2, 1, ..., -40, -41, -40]], dtype=int32)
In [42]: np.abs(walks[hit30s])>=30
Out[42]:
array([[False, False, False, ..., False, False, False],
[False, False, False, ..., False, False, False],
[False, False, False, ..., True, True, True],
...,
[False, False, False, ..., True, True, True],
[False, False, False, ..., False, False, False],
[False, False, False, ..., True, True, True]], dtype=bool)
In [43]: (np.abs(walks[hit30s])>=30).shape
Out[43]: (3386, 1000)
#这些行中最大值所在位置,最大值就是1,也就是True,argmax会求出第一个最大值所在的位置。
In [44]: (np.abs(walks[hit30s])>=30).argmax(1)
Out[44]: array([701, 599, 667, ..., 103, 251, 671], dtype=int64)
In [46]: crossing_times = (np.abs(walks[hit30s])>=30).argmax(1)
In [47]: crossing_times.mean() #求这些最大值得平均值
Out[47]: 497.68340224453635

 Numpy基础学习笔记,记录了《利用python进行数据分析》学习过程和笔记。本部分为线性代数和产生随机数的相关内容。
Numpy基础学习笔记,记录了《利用python进行数据分析》学习过程和笔记。本部分为线性代数和产生随机数的相关内容。

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号