力扣日练-day3
1、验证二叉搜索树
关键:递归,设置区间,当前节点是左子树的上界,右子树的下界

class Solution:
def isValidBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
return self.pd(root,-999999999999,999999999999)
def pd(self,min_value,max_value):
if root == None:
return True
if root.val > min_value and root.val > max_val:
pass
else:
return False
if self.pd(root.left,min_val,root.val) == False: #左子树最大值为当前节点值
return False
if self.pd(root.right,root.val,max_val) == False: #右子树最小值为当前节点值
return False
return True
2、二叉树的层序遍历
关键:(广度优先遍历)使用队列数据结构,每次循环出队当前层节点并把每个节点的左右子树入队作为下一层的循环队列
class Solution:
def levelOrder(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[List[int]]:
res=[]
queue=collections.deque()
queue.append(root)
while queue:
level=[]
size=len(queue) #当前层节点个数
for i in size:
cur=queue.popleft()
if not cur:
continue
level.append(cur.val)
queque.append(cur.left)
queue.append(cur.right)
if not level:
res.append(level)
return res
广度优先遍历模板:


3、前序遍历和中序遍历构造二叉树
关键:在前序遍历和中序遍历都是最后遍历右子树,可以用递归的方法,先构造根节点,再构造左右子树
class Solution:
def buildTree(self, preorder: List[int], inorder: List[int]) -> TreeNode:
if not preorder and not inorder:
return
root=TreeNone(preorder[0])
i=inorder.index(preorder[0])
root.left=self.buildTree(preorder[1:i+1],inorder[:i])
root.right=self.buildTree(preorder[i+1:],inorder[i+1:])
return root
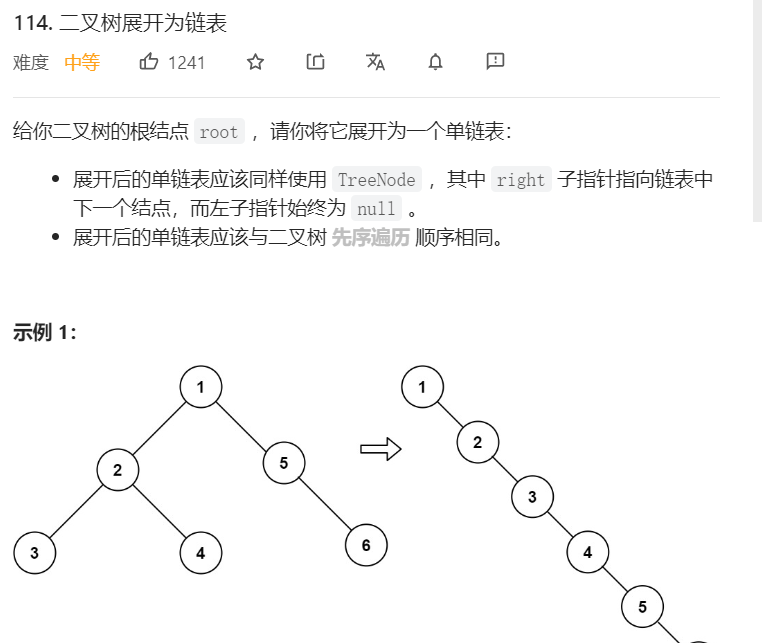
4、二叉树展开为链表
关键:根据题目要求,主要是考察二叉树的前序遍历
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.r=[]
def flatten(self, root: TreeNode) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify root in-place instead.
"""
r=self.f(root)
if r:
for i in r[1:]:
root.left=None
root.right=TreeNode(i)
root=root.right
def f(self,root:TreeNode):
if root ==None:
return
self.r.append(root.val)
self.f(root.left)
self.f(root.right)
return self.r
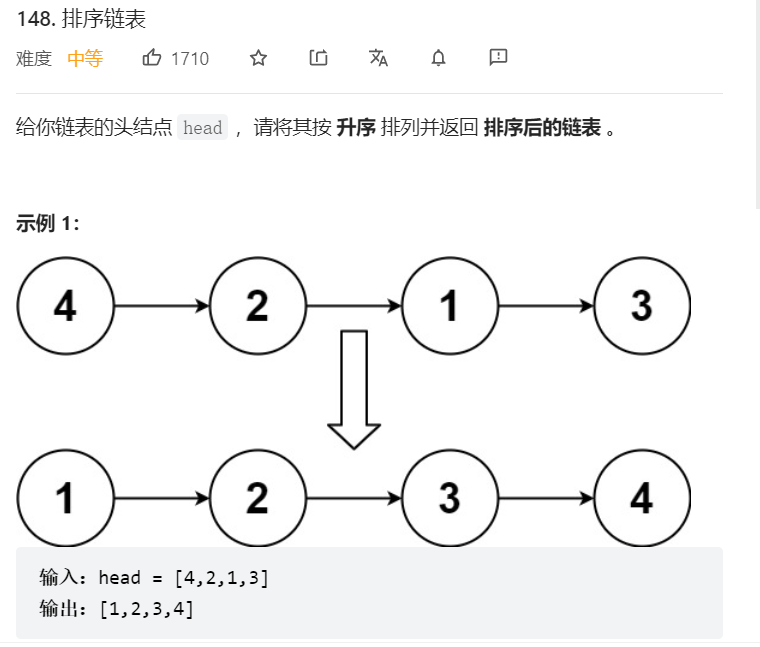
5、排序链表
关键:遍历链表获取链表值,将链表值排序后重新遍历链表赋值
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def sortList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
h1=h2=head
r=[]
if h1 == None:
return head
while h1 != None:
r.append(h1.val)
h1=h1.next
r=sorted(r)
for i in range(len(r)):
h2.val=r[i]
h2=h2.next
return head
6、二叉树的最近公共祖先
关键:递归遍历二叉树左右子树,递归出口为当前节点等于其中一个节点或当前节点为空,根据返回值判断,如果左右子树均返回非空则两节点分别在左右子树,返回root,若左子树或右子树为空则返回相对子树,若两子树都为空则返回root
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root: 'TreeNode', p: 'TreeNode', q: 'TreeNode') -> 'TreeNode':
if not root or root==p or root==q: #递归出口
return root
left=self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q)
left=self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q)
if not left:
return right
if not right:
return left
return root
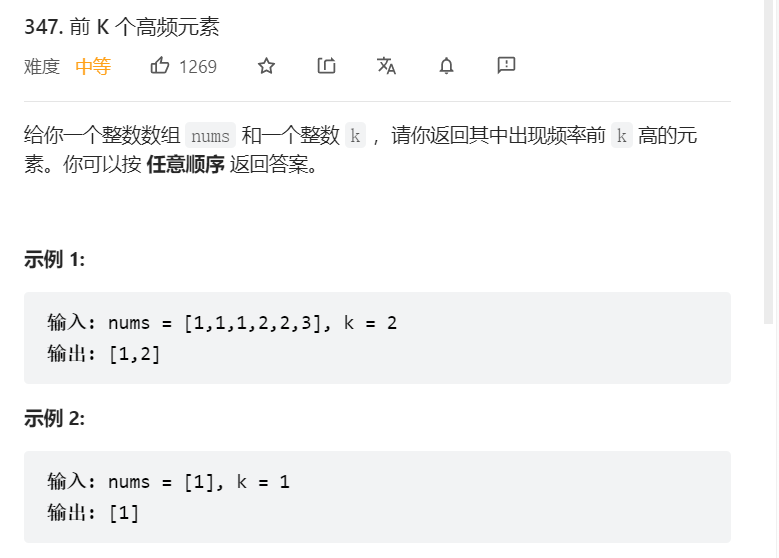
7、前k个高频的元素
关键:先用Counter( )函数统计每个元素出现次数并逆向排序取出前k个,最后遍历Counter对象,取相应值
class Solution:
def topKFrequent(self, nums: List[int], k: int) -> List[int]:
a=Counter(nums).most_common(k)
res=[]
for i,b in a:
res.append(i)
return res


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号