2D、3D直线鲁棒性拟合(Ransac + SVD)与求近似交点
一、2D直线求交点
用一般式表示直线方程:ax + by + c = 0
1 #include<opencv2/opencv.hpp> 2 #include <iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 /************************************************************************************** 5 6 //function: 2D平面上,求解两条直线交点 7 8 //input: line1: 直线方程:a0 * x + b0 * y + c0 = 0 9 line2: 直线方程:a1 * x + b1 * y + c1 = 0 10 11 //output: point: 交点 12 13 //return: -1: line1平行于line2 14 0: 有交点值返回 15 16 **************************************************************************************/ 17 18 int CalculateIntersectionPoint(const cv::Vec3d& line1, const cv::Vec3d& line2, cv::Point2d& point) 19 { 20 // ... 21 double a0 = line1[0]; 22 double b0 = line1[1]; 23 double c0 = line1[2]; 24 25 double a1 = line2[0]; 26 double b1 = line2[1]; 27 double c1 = line2[2]; 28 29 double D = a0 * b1 - a1 * b0; // ... 30 if (abs(D) < 1e-5) 31 return -1; 32 point.x = (b0 * c1 - b1 * c0) / D; 33 point.y = (a1 * c0 - a0 * c1) / D; 34 return 0; 35 } 36 37 int main() 38 { 39 cv::Vec3d line1(0, 1, -4); 40 cv::Vec3d line2(1, -2, 2); 41 cv::Point2d point; 42 if (CalculateIntersectionPoint(line1, line2, point) == 0) 43 { 44 cout << point.x << "," << point.y; 45 } 46 return 1; 47 }
二、3D直线求交“近似”点,因为有交点的概率几乎为0。

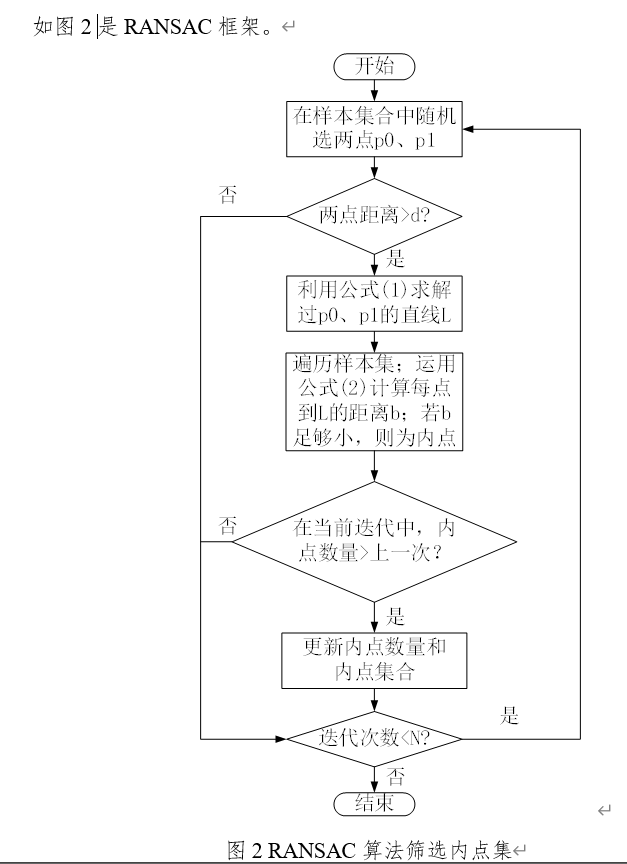
1、直线拟合
首先3D直线方程一般有三种:1、用两个平面交线表示;2、用两个点表示;3、用一个点(x0 y0 z0) 和一个向量(a b c)表示,
即:(x - x0) / a = (y - y0) / b = (z - z0) / c , 本博客选用第三种。
对于3D点的直线拟合有两种方式1:SVD分解法 2:先用ransac选择内点集合,然后再用SVD分解法拟合内点集合
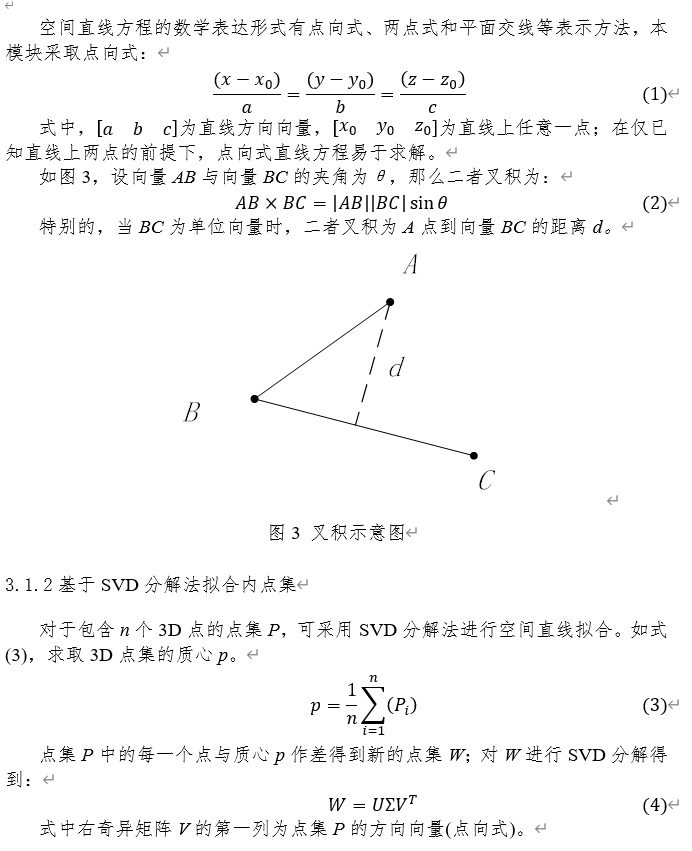
如图是以下Matlab代码拟合的结果:
1 clc; 2 clear all; 3 close all; 4 % 随机生成一组点,这写点距离直线l比较近,l的过点[1,1,1],方向向量为[1,2,3] 5 lineData=bsxfun(@plus, [1,1,1], (-1:.1:1).'*[1,2,3]); 6 Noise=rand(size(lineData))*.1; 7 lineData=lineData+Noise; 8 scatter3(lineData(:,1), lineData(:,2), lineData(:,3),'filled') 9 hold on; 10 11 % 拟合的直线必过所有坐标的算数平均值 12 xyz0=mean(lineData,1); 13 14 % 协方差矩阵奇异变换,与拟合平面不同的是 15 % 所得直线的方向实际上与最大奇异值对应的奇异向量相同 16 centeredLine=bsxfun(@minus,lineData,xyz0); % 去除质心 17 [U,S,V]=svd(centeredLine);% SVD 18 direction=V(:,1); 19 20 % 画图 21 t=-8:0.1:8; 22 xx=xyz0(1)+direction(1)*t; 23 yy=xyz0(2)+direction(2)*t; 24 zz=xyz0(3)+direction(3)*t; 25 plot3(xx,yy,zz)
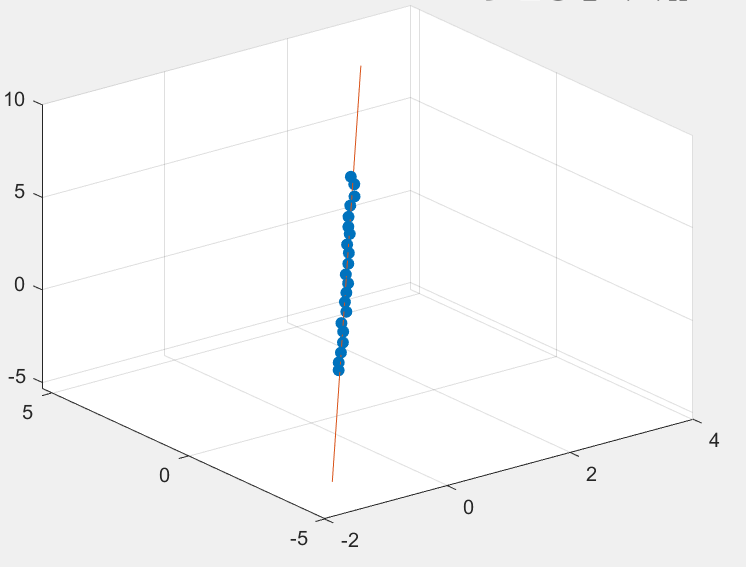
下图是基于Ransac框架下的空间直线拟合,左边有杂点,通过随机抽样抽出符合条件的点,即:内点,下图右边是对内点采用SVD分解拟合的效果。Ransac也没什么好说的,精髓在于:1、内点集比例要高,2、累计误差足够小就行。代码如下:
test2_Fit3dLineRansac.m (这个是主函数,读取数据、执行Ransac + SVD流程)

1 clc; 2 clear all; 3 close all; 4 5 %% <2> 实测数据测试 6 % 竖直 7 data = []; 8 % % % left 9 data = [data; importdata('TestData2/竖直方向/Point3D_V_Left20200311163646.csv')]; 10 data = [data; importdata('TestData2/竖直方向/Point3D_V_Left20200311163759.csv')]; 11 data = [data; importdata('TestData2/竖直方向/Point3D_V_Left20200311163840.csv')]; 12 data = [data; importdata('TestData2/竖直方向/Point3D_V_Left20200311163927.csv')]; 13 data = [data; importdata('TestData2/竖直方向/Point3D_V_Left20200311164009.csv')]; 14 data = [data; importdata('TestData2/竖直方向/Point3D_V_Left20200311164045.csv')]; 15 16 % % right 17 % data = [data; importdata('TestData2/竖直方向/Point3D_V_Right20200311163646.csv')]; 18 % data = [data; importdata('TestData2/竖直方向/Point3D_V_Right20200311163759.csv')]; 19 % data = [data; importdata('TestData2/竖直方向/Point3D_V_Right20200311163840.csv')]; 20 % data = [data; importdata('TestData2/竖直方向/Point3D_V_Right20200311163927.csv')]; 21 % data = [data; importdata('TestData2/竖直方向/Point3D_V_Right20200311164009.csv')]; 22 % data = [data; importdata('TestData2/竖直方向/Point3D_V_Right20200311164045.csv')]; 23 24 % 水平 25 % data = [data; importdata('TestData2/水平方向/Point3D_H20200311163646.csv')]; 26 % data = [data; importdata('TestData2/水平方向/Point3D_H20200311163759.csv')]; 27 % data = [data; importdata('TestData2/水平方向/Point3D_H20200311163840.csv')]; 28 % data = [data; importdata('TestData2/水平方向/Point3D_H20200311163927.csv')]; 29 % data = [data; importdata('TestData2/水平方向/Point3D_H20200311164009.csv')]; 30 % data = [data; importdata('TestData2/水平方向/Point3D_H20200311164045.csv')]; 31 32 data = data(:,1:3); % 取出前三维 33 figure(1); 34 subplot(121); plot3(data(:,1), data(:,2), data(:,3), 'k.'); 35 % ransac挑选内点 36 [diatance_vec, itr_num, paraN,point,inLier_Index, outLier_Index] = Fit3DLineRansac(data, 0.0000005, 50, 0.01); 37 data_line=data(inLier_Index,:); 38 39 subplot(122); plot3(data_line(:,1),data_line(:,2),data_line(:,3),'g*'); grid on; hold on; 40 41 % 拟合内点 42 [direction, xyz] = Fit3DLine(data_line); 43 t=-0.2:0.001:0.2; 44 x=xyz(1)+direction(1)*t; 45 y=xyz(2)+direction(2)*t; 46 z=xyz(3)+direction(3)*t; 47 plot3(x,y,z, 'm.'); hold on; 48 49 % X=[point(1)-20*paraN(1) point(1)+20*paraN(1)]; 50 % Y=[point(2)-20*paraN(2) point(2)+20*paraN(2)]; 51 % Z=[point(3)-20*paraN(3) point(3)+20*paraN(3)]; 52 % plot3(X,Y,Z,'b');grid on; 53 % 内点比例、SSE、SSE平均值 54 SSE = sum(diatance_vec); 55 SSE_mean = mean(diatance_vec); 56 radio = length(data_line) / length(data); 57 sprintf('内点比例 = %f, SSE = %f,SSE_mean = %f ', radio, SSE, SSE_mean) 58 59 a = (direction/norm(direction))'
Fit3DLineRansac.m(Ransac 选出内点集)

1 function [diatance, i, paraN,point,inLier_Index, outLier_Index] = Fit3DLineRansac(data, Threshold, Max_Iter, delta) 2 % Threshold=0.3; 3 % Max_Iter=5000; 4 5 %输出参数分别为拟合的直线的方向向量,经过的点,所有的内点,以及内点的索引号 6 num_points=size(data,1); 7 pretotal=0; 8 9 for i=1:Max_Iter 10 idx = randperm(num_points,2);% [1, num_points]区间中随机选两个数 11 sample=data(idx,:);%随机选择两个点 12 x=sample(:,1); y=sample(:,2); z=sample(:,3); 13 %判断距离是否过近 排除距离过近的情况 14 n12=[x(1)-x(2),y(1)-y(2),z(1)-z(2)]; 15 dist12=norm(n12); 16 if dist12 < delta % 0.01 有待商榷????????<1>取点尽量分开 <2> 不重复取点 17 continue 18 end 19 %拟合直线 20 %计算点到直线的距离 21 p_p0=data-[x(1) y(1) z(1)]; % 所有data 对应的方向向量集合 22 n12=n12/norm(n12); % sample对应的归一化方向向量 23 nAll=repmat(n12,num_points,1);% n12拷贝num_points次 24 % 设点p(x(1) y(1) z(1)) 25 % 每一个样本点和p作叉积,叉积公式:a×b = |a|*|b|*sin(theta) 26 % 由于n12归一化了,即:|a| = 1,所以 a×b 就是垂线段,即:点到直线距离 27 cross_value=cross(p_p0,nAll); 28 Distance=sum(cross_value.*cross_value,2);% 所有样本点到直线距 离的平方 的集合 29 inLierIndex=find(Distance < Threshold); 30 outLierIndex=find(Distance >= Threshold); 31 32 total=size(inLierIndex,1); 33 if total > pretotal 34 pretotal=total; % 更新内点数量 35 paraN=n12; % 更新方向向量 36 point=[x(1) y(1) z(1)]; % 画图用 37 inLier_Index = inLierIndex;% 更新内点索引 38 outLier_Index = outLierIndex; 39 % data_line=data(inLier_Index,:); % 不合理 40 diatance = Distance(inLierIndex); 41 end 42 end
Fit3DLine.m (利用SVD分解法对上述内点集进行拟合)

1 function [direction, xyz0] = Fit3DLine(lineData) 2 %3DLINEFIT 三维点直线拟合 3 % direction:方向向量, 4 % xyz0:所有样本点质心 5 xyz0 = mean(lineData,1); 6 % 协方差矩阵奇异变换,与拟合平面不同的是 7 % 所得直线的方向实际上与最大奇异值对应的奇异向量相同 8 centeredLine=bsxfun(@minus,lineData,xyz0); % 每一个样本减去质心 9 [U,S,V]=svd(centeredLine);% SVD分解 10 direction=V(:,1); 11 end
2、直线求交点
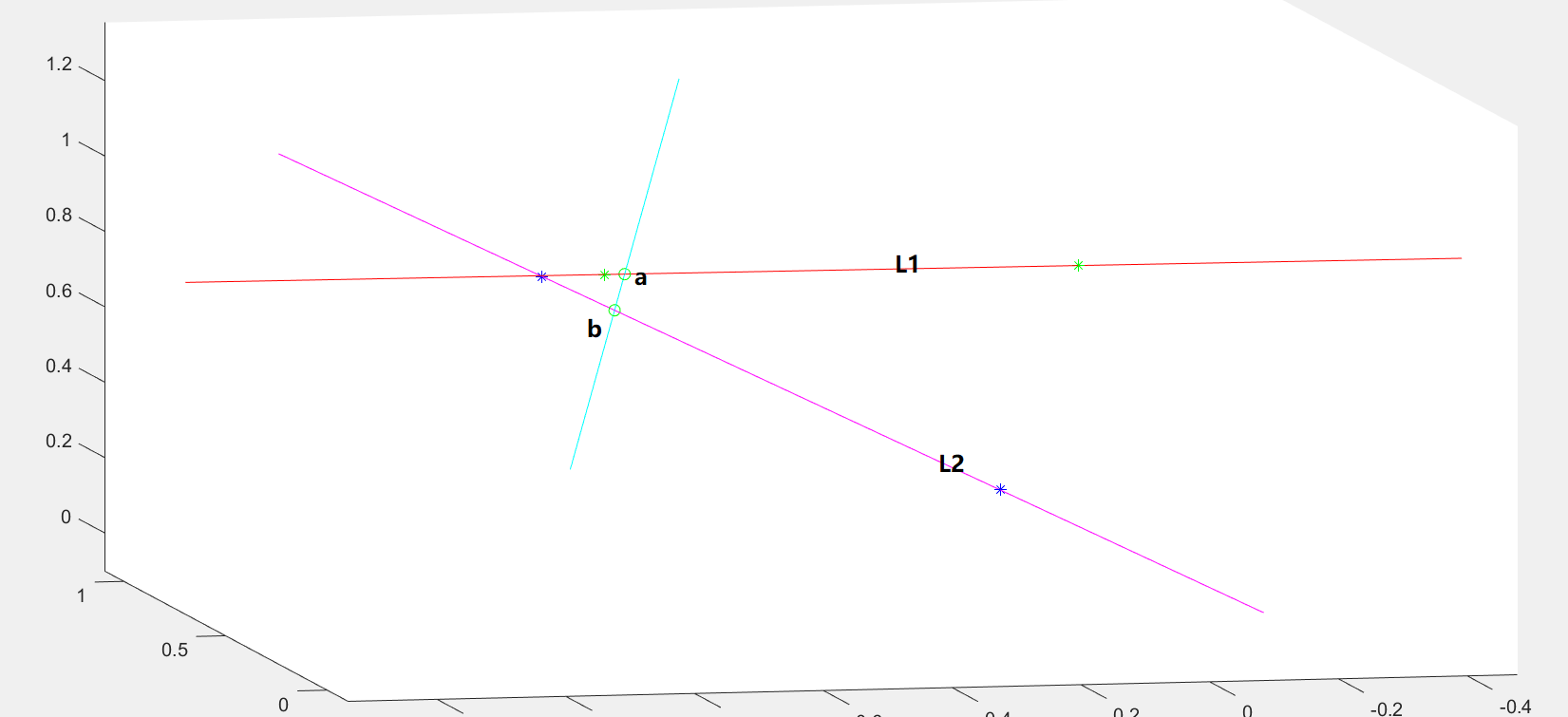
由于工程上,两根空间直线大概率没有严格意义的交点,那我们只能求解近似交点。 如图,3D直线L1、L2没有严格意义交点,于是我们可以找到L1、L2的公共垂线,求得垂线分别与L1、L2的交点为a、b。对a、b求平均值就是“近似交点”。
近似交点的数学问题推导如下图:

上述的推导用Matlab实现了。
Intersection3DPoint.m(3D直线求交点):

1 function [direction2,p0, p1] = Intersection3DPoint(direction0,xyz0, direction1, xyz1) 2 %求两条不共线、不平行且不相交的直线的近似交点 3 4 % 功能:用3D直线的方向向量和一点表示直线方程 5 % direction: 3D直线方向向量; 6 % xyz: 3D直线上一点 7 % (注:xyz为方向向量,由定义可知,每一个分量不能为0,否则下面矩阵A不可逆; 8 % 故:当xyz中存在0的时候,可以认为给定一个极小量,使其不为零) 9 10 % 直线1: (x - x0)/a0 = (y - y0)/b0 = (z - z0)/c0 11 a0 = direction0(1, 1); 12 b0 = direction0(1, 2); 13 c0 = direction0(1, 3); 14 x0 = xyz0(1, 1); 15 y0 = xyz0(1, 2); 16 z0 = xyz0(1, 3); 17 18 % 直线2: (x - x1)/a1 = (y - y1)/b1 = (z - z1)/c1 19 a1 = direction1(1, 1); 20 b1 = direction1(1, 2); 21 c1 = direction1(1, 3); 22 x1 = xyz1(1, 1); 23 y1 = xyz1(1, 2); 24 z1 = xyz1(1, 3); 25 26 % 求公垂线方向向量 27 direction2 = cross(direction0, direction1); 28 a2 = direction2(1, 1); 29 b2 = direction2(1, 2); 30 c2 = direction2(1, 3); 31 32 % ... 33 % ... 34 % ... 35 % 求解方程Ax = b, (x = [β;α]) 36 A = [a1 * b2 - a2 * b1 a2 * b0 - a0 * b2; ... 37 b1 * c2 - b2 * c1 b2 * c0 - b0 * c2]; 38 b = [a2 * (y1 - y0) + b2 * (x0 - x1);b2 * (z1 - z0) + c2 * (y0 - y1)]; 39 40 x = A\b; 41 42 alpha = x(2, 1); % α 43 beta = x(1, 1); 44 45 p0 = [alpha * a0 + x0 alpha * b0 + y0 alpha * c0 + z0]; 46 p1 = [beta * a1 + x1 beta * b1 + y1 beta * c1 + z1]; 47 end
mainV1.m(3D直线SVD拟合 + 直线求交点 测试比较理想数据)

1 %% note: 确保严谨,代码后续加入:1、判定是否同一根线; 2、是否平行; 3、是否真的相交 4、方向向量不能为0 2 clc; 3 clear all; 4 close all; 5 %% <1> 数据读取、处理 6 % 竖直 7 points3d_v = []; 8 points3d_v = [points3d_v; importdata('TestData1/竖直方向/Point3D20200226164534.csv')]; 9 points3d_v = [points3d_v; importdata('TestData1/竖直方向/Point3D20200226165026.csv')]; 10 points3d_v = [points3d_v; importdata('TestData1/竖直方向/Point3D20200226165100.csv')]; 11 points3d_v = points3d_v(:,1:3); % 取出前三维 12 % 水平 13 points3d_h = []; 14 points3d_h = [points3d_h; importdata('TestData1/水平方向/Point3D20200226163545.csv')]; 15 points3d_h = [points3d_h; importdata('TestData1/水平方向/Point3D20200226163621.csv')]; 16 points3d_h = [points3d_h; importdata('TestData1/水平方向/Point3D20200226163654.csv')]; 17 points3d_h = points3d_h(:,1:3); % 取出前三维 18 % 显示 19 figure; 20 plot3(points3d_v(:,1), points3d_v(:,2), points3d_v(:,3), 'g.'); hold on; 21 plot3(points3d_h(:,1), points3d_h(:,2), points3d_h(:,3), 'b.'); hold on; 22 23 %% <2> 拟合 24 25 % direction: 方向向量 26 % xyz:3D直线上一点 27 28 % 3D直线L1拟合(横向) 29 [direction_v, xyz_v] = Fit3DLine(points3d_v); 30 tv=-1:0.1:1; 31 xv=xyz_v(1)+direction_v(1)*tv; 32 yv=xyz_v(2)+direction_v(2)*tv; 33 zv=xyz_v(3)+direction_v(3)*tv; 34 plot3(xv,yv,zv, 'r'); hold on; 35 36 % 3D直线L2拟合(纵向) 37 [direction_h, xyz_h] = Fit3DLine(points3d_h); 38 th=-1:0.1:1; 39 xh=xyz_h(1)+direction_h(1)*th; 40 yh=xyz_h(2)+direction_h(2)*th; 41 zh=xyz_h(3)+direction_h(3)*th; 42 plot3(xh,yh,zh, 'm'); hold on; 43 44 %% <3> 求公垂线L 45 % 数学问题描述: 46 % 空间中,找一根线L;直线满足以下两个条件 47 % 1、垂直于直线L1、L2(已经L1与L2不平行、不相交、不重合且L1、L2方向向量中不能有0分量) 48 % 2、与向量L1 和 L2都有交点 49 50 [direction_, p0, p1] = Intersection3DPoint(direction_v', xyz_v, direction_h', xyz_h) 51 t=-1:0.1:1; 52 x_=p0(1)+direction_(1)*t; 53 y_=p0(2)+direction_(2)*t; 54 z_=p0(3)+direction_(3)*t; 55 plot3(x_,y_,z_, 'c'); hold on; % 画线 56 57 % 画点 58 plot3(p0(1,1), p0(1,2), p0(1,3), 'go'); hold on; 59 plot3(p1(1,1), p1(1,2), p1(1,3), 'go'); hold on;
mainV2.m(3D直线SVD拟合 + 直线求交点 测试离群点较多理想数据)

1 %% note: 确保严谨,代码后续加入:1、判定是否同一根线; 2、是否平行; 3、是否真的相交 4、方向向量不能为0 2 3 % 针对离群点:1、聚类(点云库有api,opencv也有); 2、ransac(注意停止迭代的概率公式补上去) 4 5 clc; 6 clear all; 7 close all; 8 %% <1> 数据读取、处理 9 % 竖直 10 points3d_v = []; 11 % left 12 points3d_v = [points3d_v; importdata('TestData2/竖直方向/Point3D_V_Left20200311163646.csv')]; 13 points3d_v = [points3d_v; importdata('TestData2/竖直方向/Point3D_V_Left20200311163759.csv')]; 14 points3d_v = [points3d_v; importdata('TestData2/竖直方向/Point3D_V_Left20200311163840.csv')]; 15 points3d_v = [points3d_v; importdata('TestData2/竖直方向/Point3D_V_Left20200311163927.csv')]; 16 points3d_v = [points3d_v; importdata('TestData2/竖直方向/Point3D_V_Left20200311164009.csv')]; 17 points3d_v = [points3d_v; importdata('TestData2/竖直方向/Point3D_V_Left20200311164045.csv')]; 18 % right 19 % points3d_v = [points3d_v; importdata('TestData2/竖直方向/Point3D_V_Right20200311163646.csv')]; 20 % points3d_v = [points3d_v; importdata('TestData2/竖直方向/Point3D_V_Right20200311163759.csv')]; 21 % points3d_v = [points3d_v; importdata('TestData2/竖直方向/Point3D_V_Right20200311163840.csv')]; 22 % points3d_v = [points3d_v; importdata('TestData2/竖直方向/Point3D_V_Right20200311163927.csv')]; 23 % points3d_v = [points3d_v; importdata('TestData2/竖直方向/Point3D_V_Right20200311164009.csv')]; 24 % points3d_v = [points3d_v; importdata('TestData2/竖直方向/Point3D_V_Right20200311164045.csv')]; 25 26 points3d_v = points3d_v(:,1:3); % 取出前三维 27 % 水平 28 points3d_h = []; 29 points3d_h = [points3d_h; importdata('TestData2/水平方向/Point3D_H20200311163646.csv')]; 30 points3d_h = [points3d_h; importdata('TestData2/水平方向/Point3D_H20200311163759.csv')]; 31 points3d_h = [points3d_h; importdata('TestData2/水平方向/Point3D_H20200311163840.csv')]; 32 points3d_h = [points3d_h; importdata('TestData2/水平方向/Point3D_H20200311163927.csv')]; 33 points3d_h = [points3d_h; importdata('TestData2/水平方向/Point3D_H20200311164009.csv')]; 34 points3d_h = [points3d_h; importdata('TestData2/水平方向/Point3D_H20200311164045.csv')]; 35 points3d_h = points3d_h(:,1:3); % 取出前三维 36 37 % 显示 38 figure; 39 plot3(points3d_v(:,1), points3d_v(:,2), points3d_v(:,3), 'g.'); hold on; 40 plot3(points3d_h(:,1), points3d_h(:,2), points3d_h(:,3), 'b.'); hold on; 41 42 %% <2> 拟合 43 44 % direction: 方向向量 45 % xyz:3D直线上一点 46 47 % 3D直线L1拟合(横向) 48 [direction_v, xyz_v] = Fit3DLine(points3d_v); 49 tv=-1:0.1:1; 50 xv=xyz_v(1)+direction_v(1)*tv; 51 yv=xyz_v(2)+direction_v(2)*tv; 52 zv=xyz_v(3)+direction_v(3)*tv; 53 plot3(xv,yv,zv, 'r'); hold on; 54 55 % 3D直线L2拟合(纵向) 56 [direction_h, xyz_h] = Fit3DLine(points3d_h); 57 th=-1:0.1:1; 58 xh=xyz_h(1)+direction_h(1)*th; 59 yh=xyz_h(2)+direction_h(2)*th; 60 zh=xyz_h(3)+direction_h(3)*th; 61 plot3(xh,yh,zh, 'm'); hold on; 62 63 %% <3> 求公垂线L 64 % 数学问题描述: 65 % 空间中,找一根线L;直线满足以下两个条件 66 % 1、垂直于直线L1、L2(已经L1与L2不平行、不相交、不重合且L1、L2方向向量中不能有0分量) 67 % 2、与向量L1 和 L2都有交点 68 69 [direction_, p0, p1] = Intersection3DPoint(direction_v', xyz_v, direction_h', xyz_h) 70 t=-1:0.1:1; 71 x_=p0(1)+direction_(1)*t; 72 y_=p0(2)+direction_(2)*t; 73 z_=p0(3)+direction_(3)*t; 74 plot3(x_,y_,z_, 'c'); hold on; % 画线 75 76 % 画点 77 plot3(p0(1,1), p0(1,2), p0(1,3), 'go'); hold on; 78 plot3(p1(1,1), p1(1,2), p1(1,3), 'go'); hold on;
整个Matlab代码工程放进百度云了。C++版本后续上传。
链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1htim99dlfz56UNblh6e_Pw 提取码: bmfj 复制这段内容后打开百度网盘手机App,操作更方便哦
以下是3D直线的拟合算法(ransac选点 + SVD拟合内点集,注:依赖Eigen337)
文件:FitSpaceLineRansacTest.cpp(拟合测试)
1 // FitSpaceLineRansacTest.cpp : 此文件包含 "main" 函数。程序执行将在此处开始并结束。 2 // 3 4 #include"FitSpaceLineRansac.h" 5 6 int main() 7 { 8 Eigen::MatrixXd pointsMatrix(12, 3); // 3D点数量最少四个点 9 pointsMatrix << 10 // 内点 11 0, 0, 0, 12 1, 1, 1, 13 2, 2, 2, 14 3, 3, 3, 15 4, 4, 4, 16 5, 5, 5, 17 6, 6, 6, 18 7, 7, 7, 19 //外点 20 3, 4, 5, 21 4, 5, 6, 22 5, 4, 3, 23 4, 4, 7; 24 25 FitSpaceLineRansac fitLine(pointsMatrix, 0.0000005, 50, 0.01); 26 fitLine.compute(); 27 cout << fitLine.getModel() << endl; 28 29 // TODO 30 return -1; 31 }
这里是输出为:0.57735 0.57735 0.57735 3.5 3.5 3.5 ,前三个为方向向量,后三个为一个点(3.5 3.5 3.5)
文件:FitSpaceLineRansac.h(拟合函数头文件)
1 #pragma once 2 #ifndef FITSPACELINERANSAC_H 3 #define FITSPACELINERANSAC_H 4 5 #include<iostream> 6 #include<vector> 7 #include<ctime> 8 using namespace std; 9 10 #include"Eigen/Core" 11 #include"Eigen/Geometry" 12 13 /******************************************************************************************************* 14 ** 功能描述:鲁棒性空间3D点直线拟合 15 ** 1、基于RANSAC算法的3D样本点集筛选 16 ** 2、基于SVD分解的直线拟合 17 ** 3、本模块依赖Eigen算法库,使用前需配置Eigen 18 ******************************************************************************************************** 19 ** 模块名:基于RANSAC和SVD分解的3D点直线拟合 20 ** 输 入:_pointsMatrix 3D点集 21 ** _threshold 若点到直线距离为d;如果d < sqrt(threshold), 则该点为内点,反之为外点 22 ** _maxIterNum 最大迭代次数 23 ** _delta 随机选取两点距离必须大于 delta 24 ** 输 出:_V 直线方向向量 25 ** (_centerX _centerY _centerZ) 3D样本点集质心坐标 26 ** 全局变量: 27 ** 调用模块: Eigen/Core, Eigen/Geometry. 28 ** 作 者: shiruiyu 29 ** 日 期: 2020-03-24 30 ** 修 改: 31 ** 日 期: 32 ** 版 本: 1.0 33 ******************************************************************************************************** 34 ** 备 注: 当输入3D点数量小于4时,成员函数getModel() 输出为0向量 35 *******************************************************************************************************/ 36 class FitSpaceLineRansac 37 { 38 public: 39 FitSpaceLineRansac(const Eigen::MatrixXd& pointsMatrix, const double& threshold, const int& maxIterNum, const double&delta); 40 ~FitSpaceLineRansac(); 41 // 执行拟合流程 42 void compute(); 43 // 获取拟合结果 44 Eigen::Matrix<double, 1, 6> getModel() const; 45 46 private: 47 // 获取随机数 48 int randIndex(const int& min, const int& max); 49 // 基于RANSAC算法的3D样本点集筛选 50 int selectInliersRansac(const Eigen::MatrixXd& pointsMatrix, const double& threshold, const int& maxIterNum, const double&delta, vector<int>& inLierVec); 51 // 基于SVD分解的直线拟合 52 void spacialLineFitting(const Eigen::MatrixXd& pointsMatrix, Eigen::Matrix3d& V, double& centerX, double& centerY, double& centerZ); 53 54 private: 55 // 输入 56 Eigen::MatrixXd _pointsMatrix; // 3D点样本集 57 double _threshold; // 若点到直线距离为d; d < sqrt(_threshold),则该点为内点 58 int _maxIterNum; // 最大迭代次数 59 double _delta; // 随机选取两点距离必须大于 _delta 60 61 vector<int> _inLierVec; // 内点集合inlierPointsMatrix在_pointsMatrix中的索引集 62 Eigen::MatrixXd _inlierPointsMatrix; // 内点集合 63 64 // 输出直线方程参数,直线方程:(x - x0)/a = (y - y0)/b = (z - z0)/c 65 Eigen::Matrix3d _V; // V.col(0) = [a b c] 66 double _centerX; // x0 67 double _centerY; // y0 68 double _centerZ; // z0 69 }; 70 71 #endif // !FITSPACELINERANSAC_H
文件:FitSpaceLineRansac.cpp(拟合函数具体实现)
1 #include "FitSpaceLineRansac.h" 2 3 FitSpaceLineRansac::FitSpaceLineRansac(const Eigen::MatrixXd& pointsMatrix, const double& threshold, const int& maxIterNum, const double&delta) : 4 _pointsMatrix(pointsMatrix), 5 _threshold(threshold), 6 _maxIterNum(maxIterNum), 7 _delta(delta) 8 {} 9 10 FitSpaceLineRansac::~FitSpaceLineRansac() 11 {} 12 13 // ********************************************************************* // 14 // 功能:执行拟合流程 15 // 输入:空 16 // 输出:空 17 // 备注:无 18 // ********************************************************************* // 19 void FitSpaceLineRansac::compute() 20 { 21 // <1> 选内点集 22 if (this->selectInliersRansac(this->_pointsMatrix, this->_threshold, this->_maxIterNum, this->_delta, this->_inLierVec) != 0) 23 return; 24 25 // <2> 深拷贝数据 26 this->_inlierPointsMatrix.resize(this->_inLierVec.size(), 3); 27 for (int i = 0; i < this->_inLierVec.size(); i++) 28 { 29 this->_inlierPointsMatrix.row(i) = this->_pointsMatrix.row(this->_inLierVec[i]); 30 } 31 32 // <3> 拟合 33 this->_centerX = 0.0; 34 this->_centerY = 0.0; 35 this->_centerZ = 0.0; 36 this->spacialLineFitting(this->_inlierPointsMatrix, this->_V, this->_centerX, this->_centerY, this->_centerZ); 37 } 38 39 // ********************************************************************* // 40 // 功能:获取拟合结果 41 // 输入:空 42 // 输出:直线方程参数 [a b c x0 y0 z0] 43 // 备注:直线方程 (x - x0)/a = (y - y0)/b = (z - z0)/c 44 // ********************************************************************* // 45 Eigen::Matrix<double, 1, 6> FitSpaceLineRansac::getModel() const 46 { 47 Eigen::Matrix<double, 1, 6> model; 48 model <<(this->_V)(0, 0), // a 49 (this->_V)(1, 0), // b 50 (this->_V)(2, 0), // c 51 this->_centerX, // x0 52 this->_centerY, // y0 53 this->_centerZ; // z0 54 return model; 55 } 56 57 // ********************************************************************* // 58 // 功能:获取随机值 59 // 输入:min 区间下限、max 区间上限 60 // 输出:空 61 // 返回:随机值,取值范围 [min, max) 62 // 备注:无 63 // ********************************************************************* // 64 int FitSpaceLineRansac::randIndex(const int & min, const int & max) 65 { 66 return rand() % (max - min) + min; 67 } 68 69 // ********************************************************************* // 70 // 功能:基于RANSAC算法的3D样本点集筛选 71 // 输入:pointsMatrix 3D点集 72 // threshold 若点到直线距离为d;如果d < sqrt(threshold), 则该点为内点,反之为外点 73 // maxIterNum 最大迭代次数 74 // delta 随机选取两点距离必须大于 delta 75 // 输出:inLierVec 内点集合在pointsMatrix中的索引集 76 // 返回:-1 异常 77 // 0 正常 78 // 备注:3D点集至少包含4个点 79 // ********************************************************************* // 80 int FitSpaceLineRansac::selectInliersRansac(const Eigen::MatrixXd& pointsMatrix, const double& threshold, const int& maxIterNum, const double&delta, vector<int>& inLierVec) 81 { 82 if (pointsMatrix.data() == nullptr || pointsMatrix.rows() < 4 ||pointsMatrix.cols() != 3) 83 return -1; 84 85 srand((unsigned)time(nullptr)); // seed of time 86 int preTotal = 0; // 上一次迭代内点总数 87 int total = 0; // 当前迭代内点总数 88 89 for (int i = 0; i < maxIterNum; i++) 90 { 91 // <1> 随机取两点p0、p1;p0与p1连线记为L0 92 Eigen::Matrix<double, 2, 3> sample; 93 sample.row(0) = pointsMatrix.row(randIndex(0, pointsMatrix.rows())); // p0(x0 y0 z0) 94 sample.row(1) = pointsMatrix.row(randIndex(0, pointsMatrix.rows())); // p1(x1 y1 z1) 95 96 // <2> 确保p0 p1距离适当 97 Eigen::Vector2d x, y, z; 98 x = sample.col(0); 99 y = sample.col(1); 100 z = sample.col(2); 101 Eigen::Vector3d v01; 102 v01 << x(0) - x(1), y(0) - y(1), z(0) - z(1);// 向量v01 = p0 - p1 103 if (v01.norm() < delta) // p0 p1太近? 104 continue; 105 v01.normalize(); // 归一化 106 107 // <3> 筛选点 108 vector<int> idxVec; 109 for (int i = 0; i < pointsMatrix.rows(); i++) 110 { 111 // pi(xi yi zi) 112 double xi = pointsMatrix.row(i).x(); 113 double yi = pointsMatrix.row(i).y(); 114 double zi = pointsMatrix.row(i).z(); 115 116 // vi0 = pi - p0 117 Eigen::Vector3d vi0(xi - x(0), yi - y(0), zi - z(0)); 118 119 // vi0.cross(v01) : pi 到 直线L0 的距离 120 // norm : 平方根 121 if ((vi0.cross(v01)).norm() < sqrt(threshold)) 122 { 123 idxVec.push_back(i); 124 } 125 } 126 // <4> 更新 127 total = (int)idxVec.size(); 128 if (total > preTotal) 129 { 130 preTotal = total; 131 inLierVec = idxVec; 132 } 133 134 } 135 136 return 0; 137 } 138 139 // ********************************************************************* // 140 // 功能:基于SVD分解的直线拟合 141 // 输入:pointsMatrix 3D点样本集 142 // 输出:V 直线方向向量 143 // (centerX centerY centerZ) 3D样本点集质心坐标 144 // 备注: 145 // ********************************************************************* // 146 void FitSpaceLineRansac::spacialLineFitting(const Eigen::MatrixXd& pointsMatrix, Eigen::Matrix3d& V, double& centerX, double& centerY, double& centerZ) 147 { 148 int r = (int)pointsMatrix.rows(); 149 Eigen::MatrixXd sumMatrixXd(1, 3); 150 sumMatrixXd = pointsMatrix.colwise().sum();//求x,y,z和 151 // <1>、求质心 152 centerX = sumMatrixXd(0, 0) / r; 153 centerY = sumMatrixXd(0, 1) / r; 154 centerZ = sumMatrixXd(0, 2) / r; 155 Eigen::MatrixXd centerdMatrix(r, 3); 156 // <2>、去质心 157 for (int i = 0; i < r; i++) 158 { 159 centerdMatrix.row(i)[0] = pointsMatrix.row(i)[0] - centerX; 160 centerdMatrix.row(i)[1] = pointsMatrix.row(i)[1] - centerY; 161 centerdMatrix.row(i)[2] = pointsMatrix.row(i)[2] - centerZ; 162 } 163 // <3>、SVD分解 164 Eigen::JacobiSVD<Eigen::MatrixXd> svd(centerdMatrix, Eigen::ComputeThinU | Eigen::ComputeThinV); 165 V = svd.matrixV(); 166 }
以下是C++求交点代码
CrossPointTest.cpp(主函数,用于测试)
1 #include"CrossPoint.h" 2 3 4 int test2( Eigen::MatrixXd& pointsMatrix_H, 5 Eigen::MatrixXd& pointsMatrix_V, 6 vector<double>& p0, 7 vector<double>& p1) 8 { 9 // <1> 10 Eigen::Matrix3d V_H; 11 double centerX_H = 0.0, centerY_H = 0.0, centerZ_H = 0.0; 12 spacialLineFitting(pointsMatrix_H, V_H, centerX_H, centerY_H, centerZ_H); // 拟合 13 //cout << V_H(0, 0) << V_H(1, 0) << V_H(2, 0) << endl; 方向 14 vector<double> center_H; // 质心 15 center_H.reserve(3); 16 center_H.push_back(centerX_H); 17 center_H.push_back(centerY_H); 18 center_H.push_back(centerZ_H); 19 // <2> 20 Eigen::Matrix3d V_V; 21 double centerX_V = 0.0, centerY_V = 0.0, centerZ_V = 0.0; 22 spacialLineFitting(pointsMatrix_V, V_V, centerX_V, centerY_V, centerZ_V); 23 //cout << V_V(0, 0) << V_V(1, 0) << V_V(2, 0) << endl; 24 vector<double> center_V; 25 center_V.reserve(3); 26 center_V.push_back(centerX_V); 27 center_V.push_back(centerY_V); 28 center_V.push_back(centerZ_V); 29 // <3> 30 return Intersection3DPoint(V_V, center_V, V_H, center_H, p0, p1); 31 } 32 33 int main() 34 { 35 cout << "p0、p1分别是公垂线L与直线L0、L1的交点" << endl; 36 37 vector<double> p0, p1;//与两直线交点 38 p0.resize(3); 39 p1.resize(3); 40 41 // 情况1:实测数据 42 /*if (test1(p0, p1) == 0) 43 { 44 cout << "p0(" << p0[0] << "," << p0[1] << "," << p0[2] << ")" << endl; 45 cout << "p1(" << p1[0] << "," << p1[1] << "," << p1[2] << ")" << endl; 46 cout << "************************" << endl; 47 }*/ 48 49 50 // 情况2:方向向量有零分量 51 Eigen::MatrixXd pointsMatrix_H(3, 3); // 3个3D点,水平 52 pointsMatrix_H << 0, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 3, 0, 1; // (0, 0, 1), (2, 0, 1), (3, 0, 1) 53 Eigen::MatrixXd pointsMatrix_V(3, 3); 54 pointsMatrix_V << 0, 0, 4, 0, 2, 4, 0, 9, 4; // (0, 0, 4), (0, 2, 4), (0, 9, 4) 55 56 if (test2(pointsMatrix_H, pointsMatrix_V, p0, p1) == 0) 57 { 58 cout << "p0(" << p0[0] << "," << p0[1] << "," << p0[2] << ")" << endl; // 理论:(0 0 4) 59 cout << "p1(" << p1[0] << "," << p1[1] << "," << p1[2] << ")" << endl; // 理论:(0 0 1) 60 cout << "************************" << endl; 61 } 62 63 64 // 情况3:两直线有交点 65 pointsMatrix_H << 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 7; // (0, 0, 0), (0, 0, 2), (0, 0, 7) 66 pointsMatrix_V << 0, 0, 3, 3, 0, 3, 4, 0, 3; // (0, 0, 3), (3, 0, 3), (4, 0, 3) 67 68 if (test2(pointsMatrix_H, pointsMatrix_V, p0, p1) == 0) 69 { 70 cout << "p0(" << p0[0] << "," << p0[1] << "," << p0[2] << ")" << endl; // 理论:(0 0 3) 71 cout << "p1(" << p1[0] << "," << p1[1] << "," << p1[2] << ")" << endl; // 理论:(0 0 3) 72 cout << "************************" << endl; 73 } 74 75 // 情况4:平行(重合)(既平行,又是零向量,所以要先判断是否平行) 76 pointsMatrix_H << 1.33, 0, 3.21, 1.33, 0, 3.31, 1.33, 0, 4.81; // (1.33, 0, 3.21), (1.33, 0, 3.31), (1.33, 0, 4.81) 77 pointsMatrix_V << 0, 2.3, 3.1, 0, 2.3, 3.2, 0, 2.3, 1.222; // (0, 2.3, 3.1), (0, 2.3, 3.2), (0, 2.3, 1.222) 78 79 if (test2(pointsMatrix_H, pointsMatrix_V, p0, p1) == 0) 80 { 81 cout << "p0(" << p0[0] << "," << p0[1] << "," << p0[2] << ")" << endl; // 理论:由于平行,直接return 82 cout << "p1(" << p1[0] << "," << p1[1] << "," << p1[2] << ")" << endl; // 83 cout << "************************" << endl; 84 } 85 86 87 88 89 system("pause"); 90 return 0; 91 }
CrossPoint.h(空间直线拟合、直线求交点)
1 #pragma once 2 3 #ifndef CROSSPOINT_H 4 #define CROSSPOINT_H 5 6 #include<iostream> 7 #include<fstream> 8 #include<sstream> 9 #include<vector> 10 #include"Eigen/Dense" 11 using namespace std; 12 13 void spacialLineFitting(Eigen::MatrixXd& pointsMatrix, Eigen::Matrix3d& V, double& centerX, double& centerY, double& centerZ); 14 15 void readPoint(string strPath, vector<vector<double>>& pointsVec); 16 17 int Intersection3DPoint(Eigen::Matrix3d dir_V, vector<double> center_V, Eigen::Matrix3d dir_H, vector<double> center_H, vector<double>& p0, vector<double>& p1); 18 19 #endif // !CROSSPOINT_H
CrossPoint.cpp
1 #include"CrossPoint.h" 2 3 // ************************************************************************************************************** 4 5 // 功能:空间直线拟合 6 7 // 输入:pointsMatrix:3D点样本集 8 9 // 输出:V:直线方向向量;(centerX centerY centerZ):3D样本点集质心 10 11 // return: void 12 13 // ************************************************************************************************************** 14 void spacialLineFitting(Eigen::MatrixXd& pointsMatrix, Eigen::Matrix3d& V, double& centerX, double& centerY, double& centerZ) 15 { 16 int r = pointsMatrix.rows(); 17 Eigen::MatrixXd sumMatrixXd(1, 3); 18 sumMatrixXd = pointsMatrix.colwise().sum();//求x,y,z和 19 // <1>、求质心 20 centerX = sumMatrixXd(0, 0) / r; 21 centerY = sumMatrixXd(0, 1) / r; 22 centerZ = sumMatrixXd(0, 2) / r; 23 Eigen::MatrixXd centerdMatrix(r, 3); 24 // <2>、去质心 25 for (int i = 0; i < r; i++) 26 { 27 centerdMatrix.row(i)[0] = pointsMatrix.row(i)[0] - centerX; 28 centerdMatrix.row(i)[1] = pointsMatrix.row(i)[1] - centerY; 29 centerdMatrix.row(i)[2] = pointsMatrix.row(i)[2] - centerZ; 30 } 31 // <3>、SVD分解 32 Eigen::JacobiSVD<Eigen::MatrixXd> svd(centerdMatrix, Eigen::ComputeThinU | Eigen::ComputeThinV); 33 V = svd.matrixV(); 34 } 35 //字符转double 36 template <class Type> 37 Type stringToNum(string& str) 38 { 39 istringstream iss(str); 40 Type num; 41 iss >> num; 42 return num; 43 } 44 //读取csv文件点 45 void readPoint(string strPath, vector<vector<double>>& pointsVec) 46 { 47 std::ifstream _csvInput; 48 _csvInput.open(strPath, std::ios::in); 49 std::string _Oneline; 50 std::vector<double> _lineOfstr; 51 vector<vector<double>> verticalLinePoints; 52 while (std::getline(_csvInput, _Oneline)) // 整行读取,换行符“\n”区分,遇到文件尾标志eof终止读取 53 { 54 std::istringstream _Readstr(_Oneline); // 将整行字符串_Oneline读入到字符串流istringstream中 55 std::string _partOfstr; 56 double pointCorr; 57 int i = 0; 58 while (std::getline(_Readstr, _partOfstr, ',')) // 将字符串流_Readstr中的字符读入到_partOfstr字符串中,以逗号为分隔符 59 { 60 if (i < 3) 61 { 62 pointCorr = stringToNum<double>(_partOfstr); 63 _lineOfstr.push_back(pointCorr); // 将刚刚读取的字符串添加到向量_lineOfstr中, 64 } 65 else if (i == 3) 66 { 67 verticalLinePoints.push_back(_lineOfstr); 68 _lineOfstr.clear(); 69 _Readstr.clear(); 70 break; 71 } 72 ++i; 73 } 74 } 75 pointsVec = verticalLinePoints; 76 } 77 78 79 // ************************************************************************************************************** 80 81 // 功能:计算公垂线L与两直线(L0、L1)交点 82 83 // 输入:dir_V:竖向直线(L0)方向向量; center_V:竖向3D点质心 84 // dir_H:横向直线(L1)方向向量; center_H:横向3D点质心 85 86 // 输出:p0: L0与公垂线(L)的交点; p1: L1与公垂线(L)的交点; 87 88 // return: -1: L0、L1平行(重合) 89 // 0: L0、L1不平行(不重合) 90 91 // ************************************************************************************************************** 92 int Intersection3DPoint(Eigen::Matrix3d dir_V, vector<double> center_V, Eigen::Matrix3d dir_H, vector<double> center_H, vector<double>& p0, vector<double>& p1) 93 { 94 //直线1: (x - x0)/a0 = (y - y0)/b0 = (z - z0)/c0 95 double a0 = dir_V(0, 0), b0 = dir_V(1, 0), c0 = dir_V(2, 0); // (a0 b0 c0) 是竖向直线L0的方向向量 96 double x0 = center_V[0], y0 = center_V[1], z0 = center_V[2]; // (x0 y0 z0) 是竖向3D样本点的质心 97 //直线2: (x - x1)/a1 = (y - y1)/b1 = (z - z1)/c1 98 double a1 = dir_H(0, 0), b1 = dir_H(1, 0), c1 = dir_H(2, 0); 99 double x1 = center_H[0], y1 = center_H[1], z1 = center_H[2]; 100 Eigen::Matrix<double, 1, 3> dir_V_, dir_H_; 101 102 // 方向向量零分量补偿 103 if (a0 == 0) // abs(a0 - 1e-5) 104 a0 += 1e-5; 105 if (b0 == 0) 106 b0 += 1e-5; 107 if (c0 == 0) 108 c0 += 1e-5; 109 110 if (a1 == 0) 111 a1 += 1e-5; 112 if (b1 == 0) 113 b1 += 1e-5; 114 if (c1 == 0) 115 c1 += 1e-5; 116 117 //cout << a0 / a1 << endl; 118 //cout << b0 / b1 << endl; 119 //cout << c0 / c1 << endl; 120 // 判断平行(重合) 121 if (a0 / a1 == b0 / b1 == c0 / c1) 122 return -1; 123 124 dir_V_(0, 0) = a0; 125 dir_V_(0, 1) = b0; 126 dir_V_(0, 2) = c0; 127 dir_H_(0, 0) = a1; 128 dir_H_(0, 1) = b1; 129 dir_H_(0, 2) = c1; 130 // <1>、求公垂线方向 131 Eigen::MatrixXd crossM = dir_H_.cross(dir_V_); // (a0 b0 c0) 与 (a1 b1 c1) 作叉积 -> 公垂向量(a2 b2 c2) 132 double a2 = crossM(0, 0); 133 double b2 = crossM(0, 1); 134 double c2 = crossM(0, 2); 135 // <2>、求交点p0、p1(推导见 readme.txt) 136 Eigen::Matrix<double, 2, 2> A; 137 A(0, 0) = a1 * b2 - a2 * b1; 138 A(0, 1) = a2 * b0 - a0 * b2; 139 A(1, 0) = b1 * c2 - b2 * c1; 140 A(1, 1) = b2 * c0 - b0 * c2; 141 Eigen::Matrix<double, 2, 1> B; 142 B(0, 0) = a2 * (y1 - y0) + b2 * (x0 - x1); 143 B(1, 0) = b2 * (z1 - z0) + c2 * (y0 - y1); 144 Eigen::Matrix<double, 2, 1> X; 145 X = A.inverse()*B; // 解方程 A*X = B 146 double alpha = X(1, 0); 147 double beta = X(0, 0); 148 /*p0.resize(3); 149 p1.resize(3);*/ 150 p0[0] = alpha * a0 + x0; 151 p0[1] = alpha * b0 + y0; 152 p0[2] = alpha * c0 + z0; 153 p1[0] = beta * a1 + x1; 154 p1[1] = beta * b1 + y1; 155 p1[2] = beta * c1 + z1; 156 return 0; 157 }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号