coap 协议 和 code
The CoAP resource directory provides a way to discover the properties of the nodes on your network.
CoAP has been designed to work on microcontrollers with as low as 10 KiB of RAM and 100 KiB of code space
协议
https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc7228
https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc7252
Resource discovery is important for machine-to-machine interactions and is supported using the CoRE Link Format [RFC6690] as discussed in Section 7.
https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc6690
Block-Wise Transfers in the Constrained Application Protocol (CoAP)
https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc7959.html
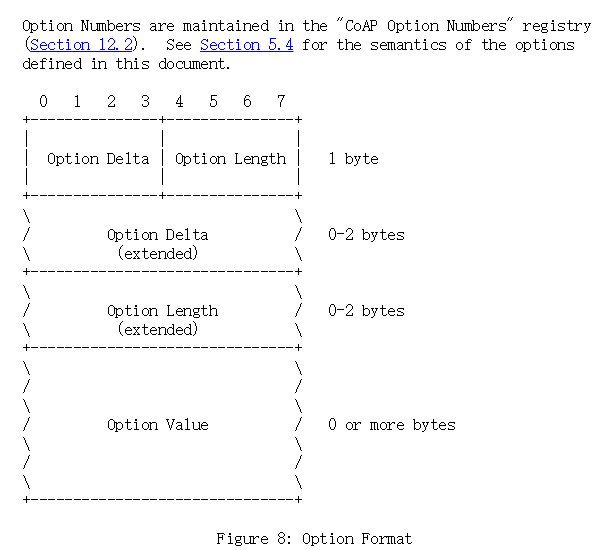
Option Format
CoAP defines a number of options that can be included in a message.
Each option instance in a message specifies the Option Number of the
defined CoAP option, the length of the Option Value, and the Option
Value itself.
Options
Both requests and responses may include a list of one or more
options. For example, the URI in a request is transported in several
options, and metadata that would be carried in an HTTP header in HTTP
is supplied as options as well.
CoAP defines a single set of options that are used in both requests
and responses:
o Content-Format
o ETag
o Location-Path
o Location-Query
o Max-Age
o Proxy-Uri
o Proxy-Scheme
o Uri-Host
o Uri-Path
o Uri-Port
o Uri-Query
o Accept
o If-Match
o If-None-Match
o Size1
length
If the Path MTU is not known for a destination, an IP MTU of 1280
bytes SHOULD be assumed; if nothing is known about the size of the
headers, good upper bounds are 1152 bytes for the message size and
1024 bytes for the payload size.




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号