07.C语言:结构体、共用体、枚举
一、结构体
是一种复合的数据类型,由多个不同类型的数据(为结构体的成员)组成的集合。
在c语言中没有给出结构体这种类型具体的形式(名称),但是给出类定义该结构体类型的方法(格式)。
在使用结构体类型时,必须先定义机构体具体的类型,然后用定义好的类型来定义变量,进而使用变量。
综上,结构体是一种自定义的复合数据类型,在结构体空间中每个成员都有各自的空间。
1.结构体的类型定义:

1 struct [结构体标签]{ 2 类型名 成员名; 3 类型名 成员名; 4 ... ... 5 类型名 成员名; 6 }; 7 8 9 struct student{ 10 int sno; 11 char name[20]; 12 float high; 13 float score; 14 };
2.结构体变量的定义:

1 //1.常规方式定义 2 struct student1{ 3 int sno; 4 char name[20]; 5 float high; 6 float score; 7 }; 8 struct student1 st1; 9 10 //2.与类型同时定义 11 struct student2{ 12 int sno; 13 char name[20]; 14 float high; 15 float score; 16 }st2; 17 18 //3.直接定义 19 struct{ 20 int sno; 21 char name[20]; 22 float high; 23 float score; 24 }st3;
3.结构体变量的初始化:
1》完全初始化:按定义成员的先后顺序依次给结构体变量中的每一个成员赋值的过程:struct student st = {1001, "刘德华",1.80,99.9};
2》部分初始化:按定义成员的先后顺序依次给结构体变量中的前若干个成员赋值的过程:struct student st = {1001, "刘德华", 1.80};
3》指定成员初始化:不按成员的定义顺序赋值,而是指定结构体变量中的某一些成员赋值的过程:struct student st = {.name = "刘德华", 1.80, .sno = 1001};//指定成员初始化
4.结构体的使用:
1》不能只能赋值,例如:
struct student st;
st = {1001, "刘德华", 1.80, 99.9};//error
2》相同类型结构体变量之间可以相互赋值,例如:
struct student st1 = {1001,"刘德华", 1.80, 99.9};
struct student st2;
st2 = st1;//OK
3》结构体中的成员只能单独使用,例如:

1 /******************************************************************* 2 * > File Name: 33-struct.c 3 * > Author: fly 4 * > Mail: XXXXXXXX@icode.com 5 * > Create Time: Sun 08 Oct 2017 11:48:04 AM CST 6 ******************************************************************/ 7 8 #include <stdio.h> 9 #include <string.h> 10 11 struct student{ 12 int sno; 13 char name[20]; 14 float high; 15 float score; 16 }; 17 18 int main(int argc, char* argv[]) 19 { 20 struct student st1 = {1001, "刘德华", 1.80, 99.9};//完全初始化 21 struct student st2; 22 23 st2.sno = 1002; 24 strcpy(st2.name, "peter"); 25 st2.high = 1.89; 26 st2.score = 98.4; 27 printf("%d\t%s\t%.2f\t%.2f\n", st1.sno, st1.name, st1.high, st1.score); 28 printf("%d\t%s\t%.2f\t%.2f\n", st2.sno, st2.name, st2.high, st2.score); 29 30 return 0; 31 }
5.结构体数组:
元素为结构体类型的数组称之为结构体数组。

1 /******************************************************************* 2 * > File Name: 34-structArr.c 3 * > Author: fly 4 * > Mail: XXXXXXXX@icode.com 5 * > Create Time: Sun 08 Oct 2017 03:58:37 PM CST 6 ******************************************************************/ 7 8 #include <stdio.h> 9 10 struct student{ 11 int sno; 12 char name[20]; 13 float high; 14 float score; 15 }; 16 17 int main(int argc, char* argv[]) 18 { 19 struct student st[5]; 20 int i; 21 22 for(i = 0; i< 5; i++){ 23 printf("Pls input NO[%d]:\n", i); 24 scanf("%d%s%f%f", &st[i].sno, st[i].name, &st[i].high, &st[i].score); 25 } 26 27 for(i = 0; i< 5; i++){ 28 printf("%d\t%s\t%.2f\t%.2f\n", st[i].sno, st[i].name, st[i].high, st[i].score); 29 } 30 31 return 0; 32 }
6.结构体指针:
指向结构体变量的指针称为结构体指针。

1 /******************************************************************* 2 * > File Name: 35-structPoint.c 3 * > Author: fly 4 * > Mail: XXXXXXXX@icode.com 5 * > Create Time: Sun 08 Oct 2017 04:08:58 PM CST 6 ******************************************************************/ 7 8 #include <stdio.h> 9 10 struct student{ 11 int sno; 12 char name[20]; 13 float high; 14 float score; 15 }; 16 17 int main(int argc, char* argv[]) 18 { 19 struct student st1 = {1001, "刘德华", 1.80, 99.9}; 20 struct student *ps;//ps为结构体指针 21 22 ps = &st1; 23 24 printf("%d\t%s\t%.2f\t%.2f\n", st1.sno, st1.name, st1.high, st1.score); 25 puts(""); 26 printf("%d\t%s\t%.2f\t%.2f\n", (*ps).sno, (*ps).name, (*ps).high, (*ps).score); 27 puts(""); 28 printf("%d\t%s\t%.2f\t%.2f\n", ps -> sno, ps -> name, ps -> high, ps -> score); 29 30 return 0; 31 }
二、共用体
一种复合的数据类型,它是由多个不同类型的数据组成的集合,这些不同类型的数据称为该共用体的成员。
在C语言中没有给出共用体这种类型具体的形式(名称),但是给出类定义该共用体类型的方法(方法),在使用共用体类型时,必须先定义共用体具体的类型,然后用定义好的类型来定义变量,进而使用变量。
1.共用体类型定义:

1 /******************************************************************* 2 * > File Name: 36-unionTypeDefine.c 3 * > Author: fly 4 * > Mail: XXXXXXXX@icode.com 5 * > Create Time: Sun 08 Oct 2017 04:34:53 PM CST 6 ******************************************************************/ 7 8 #include <stdio.h> 9 10 #if (0) 11 union [结构体标签]{ 12 类型名 成员名; 13 类型名 成员名; 14 ... ...; 15 类型名 成员名; 16 }; 17 #else//egg 18 union student{ 19 int sno; 20 char name[20]; 21 float high; 22 float score; 23 }; 24 #endif 25 26 int main(int argc, char* argv[]) 27 { 28 return 0; 29 }
2.共用体变量的定义:

1 /******************************************************************* 2 * > File Name: 37-unionVarDefine.c 3 * > Author: fly 4 * > Mail: XXXXXXXX@icode.com 5 * > Create Time: Sun 08 Oct 2017 04:40:50 PM CST 6 ******************************************************************/ 7 8 #include <stdio.h> 9 10 //1》.常规定义 11 union student{ 12 int sno; 13 char name[20]; 14 float high; 15 float score; 16 }; 17 union student un; 18 //2》.与类型同时定义 19 union student{ 20 int sno; 21 char name[20]; 22 float high; 23 float score; 24 }un; 25 //3》.直接定义 26 union{ 27 int sno; 28 char name[20]; 29 float high; 30 float score; 31 }un; 32 33 int main(int argc, char* argv[]) 34 { 35 return 0; 36 }
3.使用:
1》不能整体赋值,例如:
union student un;
un = {1001, "刘德华", 1.80, 99.9};//error
2》同类型的共用体之间可以相互赋值,例如:
union student un1, un2;
un1.sno = 1001;
un2 = un1;//OK
3》共用体中的成员只能单独使用,例如:

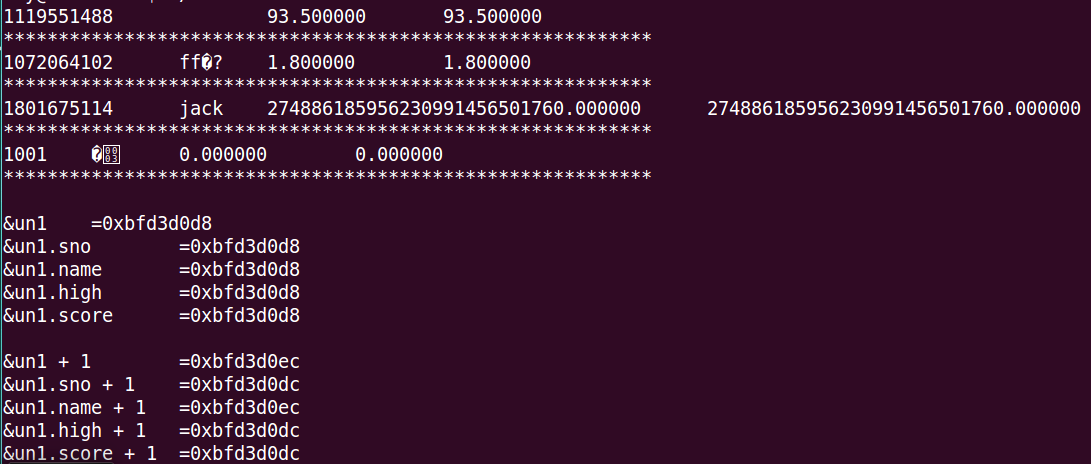
1 /******************************************************************* 2 * > File Name: 38-union.c 3 * > Author: fly 4 * > Mail: XXXXXXXX@icode.com 5 * > Create Time: Sun 08 Oct 2017 04:52:12 PM CST 6 ******************************************************************/ 7 8 #include <stdio.h> 9 #include <string.h> 10 11 //定义一个共用体类型 12 union student{ 13 int sno; 14 char name[20]; 15 float high; 16 float score; 17 }; 18 19 int main(int argc, char* argv[]) 20 { 21 union student un1; 22 23 un1.sno = 1001; 24 strcpy(un1.name, "jack"); 25 un1.high = 1.80; 26 un1.score = 93.5; 27 printf("%d\t%s\t%f\t%f\n", un1.sno, un1.name, un1.high, un1.score); 28 puts("***********************************************************"); 29 30 un1.sno = 1001; 31 strcpy(un1.name, "jack"); 32 un1.score = 93.5; 33 un1.high = 1.80; 34 printf("%d\t%s\t%f\t%f\n", un1.sno, un1.name, un1.high, un1.score); 35 puts("***********************************************************"); 36 37 un1.sno = 1001; 38 un1.high = 1.80; 39 un1.score = 93.5; 40 strcpy(un1.name, "jack"); 41 printf("%d\t%s\t%f\t%f\n", un1.sno, un1.name, un1.high, un1.score); 42 puts("***********************************************************"); 43 44 strcpy(un1.name, "jack"); 45 un1.high = 1.80; 46 un1.score = 93.5; 47 un1.sno = 1001; 48 printf("%d\t%s\t%f\t%f\n", un1.sno, un1.name, un1.high, un1.score); 49 puts("***********************************************************"); 50 51 printf("\n&un1\t=%p\n", &un1); 52 printf("&un1.sno\t=%p\n", &un1.sno); 53 printf("&un1.name\t=%p\n", &un1.name); 54 printf("&un1.high\t=%p\n", &un1.high); 55 printf("&un1.score\t=%p\n", &un1.score); 56 57 printf("\n&un1 + 1\t=%p\n", &un1 + 1); 58 printf("&un1.sno + 1\t=%p\n", &un1.sno + 1); 59 printf("&un1.name + 1\t=%p\n", &un1.name + 1); 60 printf("&un1.high + 1\t=%p\n", &un1.high + 1); 61 printf("&un1.score + 1\t=%p\n", &un1.score + 1); 62 63 return 0; 64 }
运行结果:
三、枚举
属于基本数据类型,本质上为整型。为了提高程序的可读性。
在某些时候需要给一些整型数据一个取值空间,这时如果直接赋值整型常量,它的含义不是特别的明确,从而导致程序的可读性差。
引入枚举类型之后,可以重新定义整型数据的取值空间,这样可以提高程序的可读性。
1.枚举类型的定义

1 /******************************************************************* 2 * > File Name: 39-enum.c 3 * > Author: fly 4 * > Mail: XXXXXXXX@icode.com 5 * > Create Time: Sun 08 Oct 2017 05:35:54 PM CST 6 ******************************************************************/ 7 8 #include <stdio.h> 9 10 #if (枚举类型的定义) 11 enum [枚举标签]{ 12 枚举常量; 13 枚举常量; 14 ......; 15 枚举常量; 16 }; 17 #else 18 /*定义一个枚举类型spectrum*/ 19 enum spectrum{ 20 red, //默认值0 21 blue, //1 22 green, //2 23 yellow //3 24 }color; 25 #endif 26 27 int main(int argc, char* argv[]) 28 { 29 return 0; 30 }
2.枚举类型中枚举、常量的值

1 /******************************************************************* 2 * > File Name: 40-enum.c 3 * > Author: fly 4 * > Mail: XXXXXXXX@icode.com 5 * > Create Time: Sun 08 Oct 2017 05:42:52 PM CST 6 ******************************************************************/ 7 8 #include <stdio.h> 9 10 //1》.枚举常量的默认值 11 enum spectrum{ 12 red, //0 13 blue, //1 14 green, //2 15 yellow //3 16 }color; 17 //2》.枚举常量也可以指定值 18 enum spectrum{ 19 red = 10,//不是赋值,而是指定枚举常量red代表整型常量10 20 blue, //the default value :11 21 green = 9, 22 yellow //the default value :10 23 }color; 24 25 int main(int argc, char* argv[]) 26 { 27 return 0; 28 }
3.使用:

1 /******************************************************************* 2 * > File Name: 41-enum.c 3 * > Author: fly 4 * > Mail: XXXXXXXX@icode.com 5 * > Create Time: Sun 08 Oct 2017 05:51:54 PM CST 6 ******************************************************************/ 7 8 #include <stdio.h> 9 10 enum spectrum{ 11 red, //0 12 blue, //1 13 green, //2 14 yellow //3 15 }color1; 16 17 int main(int argc, char* argv[]) 18 { 19 enum spectrum color2; 20 21 color1 = 0; //可读性差 22 color1 = red; //可读性好 23 printf("color1 = %d\n", color1); 24 25 color2 = 2; 26 color2 = green; 27 printf("color2 = %d\n", color2); 28 29 return 0; 30 }



