泡泡一分钟:Stabilize an Unsupervised Feature Learning for LiDAR-based Place Recognition
Stabilize an Unsupervised Feature Learning for LiDAR-based Place Recognition
Peng Yin, Lingyun Xu, Zhe Liu, Lu Li, Hadi Salman, Yuqing He
Abstract— Place recognition is one of the major challenges for the LiDAR-based effective localization and mapping task.Traditional methods are usually relying on geometry matching to achieve place recognition, where a global geometry map need to be restored. In this paper, we accomplish the place recognition task based on an end-to-end feature learning framework with the LiDAR inputs. This method consists of two core modules, a dynamic octree mapping module that generates local 2D maps with the consideration of the robot’s motion; and an unsupervised place feature learning module which is an improved adversarial feature learning network with additional assistance for the long-term place recognition requirement. More specially, in place feature learning, we present an additional Generative Adversarial Network with a designed Conditional Entropy Reduction module to stabilize the feature learning process in an unsupervised manner. We evaluate the proposed method on the Kitti dataset and North Campus Long-Term LiDAR dataset. Experimental results show that the proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art in place recognition tasks under long-term applications. What’s more,the feature size and inference efficiency in the proposed method are applicable in real-time performance on practical robotic platforms.
位置识别是基于LiDAR的有效定位和建图任务的主要挑战之一。传统方法通常依赖于几何匹配来实现位置识别,其中需要恢复全局几何图。在本文中,我们基于具有LiDAR输入的端到端特征学习框架完成了位置识别任务。该方法由两个核心模块组成,一个动态八叉树映射模块,在考虑机器人运动的情况下生成局部二维映射; 和一个无监督的地方特色学习模块,它是一个改进的对抗性特征学习网络,为长期地点识别要求提供额外帮助。更具体地说,就位置特征学习,我们提出了一个额外的生成对抗网络,其具有设计的条件熵减少模块,以无人监督的方式稳定特征学习过程。我们在Kitti数据集和North Campus长期LiDAR数据集上评估所提出的方法。实验结果表明,该方法在长期应用中优于现有技术的识别任务。 而且,所提出的方法中的特征尺寸和推理效率适用于实际机器人平台上的实时性能。
在本文中,我们提出了一种基于端到端的基于LiDAR的特征学习框架,用于长期地点识别任务,其中地点识别是通过低维特征匹配而不是几何匹配来实现的。所提出的方法结合了两个核心模块,一个动态八叉树映射模块,它考虑到机器人的运动产生鸟类的局部视图,以及一个地点特征推理模块,它捕获有限数据样本的唯一地图特征映射。更具体地说,就位置特征学习,我们以完全无监督的方式稳定特征学习过程。在Kitti和North Campus长期LiDAR数据集上进行的实验表明,所提出的框架在变体视点差异下优于现有的最先进技术方法。
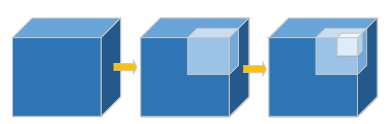
图1 八叉树结构。 每个节点被分成具有相等子空间的八个子节点。

图2 动态八叉树建图结果的示例。 第一行显示原始点云数据; 第二行显示基于所提出的动态八叉树建图的累积占用图; 第三行显示投影的鸟瞰2D地图。
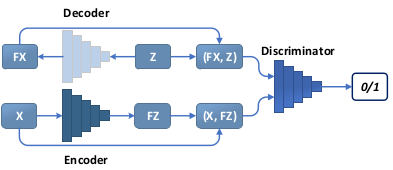
图3 双向生成对抗网络。

图4 稳定对抗特征学习的框架。
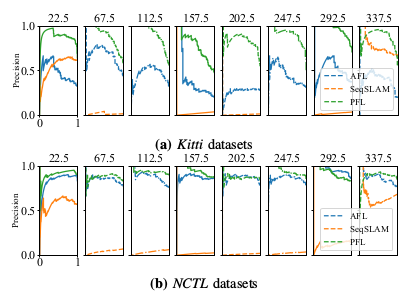
图5 不同方向角度下不同方法的精确回忆曲线。 从第一列到最后一列,航向取向差异分别为22.5°到337.5°。
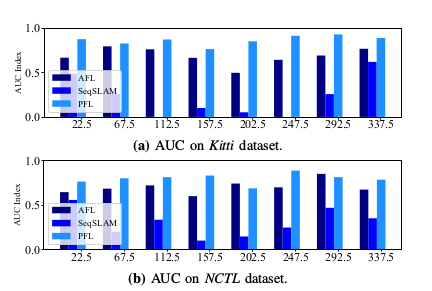
图6 不同航向取向情况下地点识别结果的AUC指数。



