「Python实用秘技02」给Python函数定“闹钟”
本文完整示例代码及文件已上传至我的
Github仓库https://github.com/CNFeffery/PythonPracticalSkills
这是我的系列文章「Python实用秘技」的第2期,本系列立足于笔者日常工作中使用Python辅助办公的心得体会,每一期为大家带来一个3分钟即可学会的简单小技巧。
作为系列第2期,我们即将学习的是:为Python函数添加执行超时检查功能。

某些常用的库如requests的get()函数,具有特定的参数timeout,设置后可以在其运行超过一定时间还没运行完成时抛出超时错误。
而如果我们想为自定义函数也添加类似的“闹钟”超时检查功能,最简单的方式是使用第三方库wrapt_timeout_decorator中的timeout()装饰器,通过参数传递超时时长(单位:秒)即可,下面是一个简单的例子:
from wrapt_timeout_decorator import timeout
@timeout(5) # 设置超时时长为5秒
def demo_func(seconds: float) -> float:
# 此处time在函数中导入是为了绕开jupyter中wrapt_timeout_decorator与time模块的特殊错误
# 详见https://github.com/bitranox/wrapt_timeout_decorator/issues/24
import time
time.sleep(seconds)
return seconds
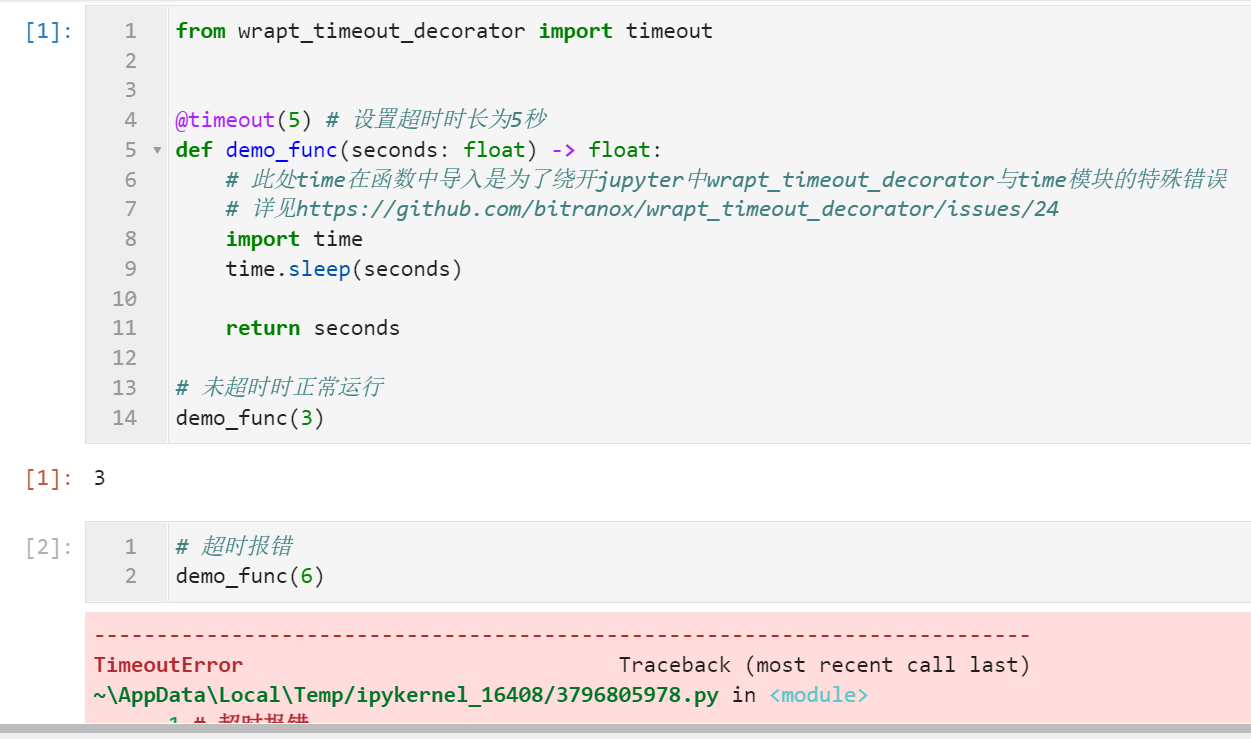
# 未超时时正常运行
demo_func(3)
# 超时报错
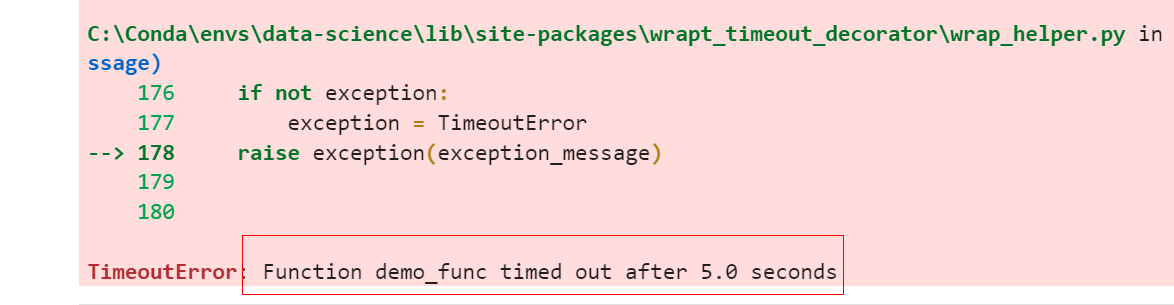
demo_func(6)
并且不只是函数,类中的静态方法亦可使用:
class Demo:
@timeout(5) # 设置超时时长为5秒
@staticmethod
def demo_func(seconds: float) -> float:
# 此处time在函数中导入是为了绕开jupyter中wrapt_timeout_decorator与time模块的特殊错误
# 详见https://github.com/bitranox/wrapt_timeout_decorator/issues/24
import time
time.sleep(seconds)
return seconds
demo = Demo()
demo.demo_func(3)
Demo().demo_func(6)
使用场景非常之多,譬如前不久笔者就用它来解决fabric模拟执行nohup命令时的持续阻塞问题。
本期分享结束,咱们下回见~👋


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号