(转)从属性赋值到MVVM模式详解
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/lemontea/archive/2011/11/26/2264168.html
从属性赋值到MVVM模式详解
这两天学习了一下MVVM模式,和大家分享一下,也作为自己的学习笔记.这里不定义MVVM的概念,不用苍白的文字说它的好处,而是从简单的赋值讲起,一步步建立一个MVVM模式的Simple.通过前后对比留给读者自己去思考.我也不知道理解是否正确,有不对的地方,希望指出.
赋值VS绑定
要理解MVVM模式,最重要的是理解绑定的概念.做B/S或者对C/S理解不够的程序员可能不了解"绑定",它与赋值类似,但又"高级"一点.
一个简单的类:
public class MyClass { public MyClass() { this._Time = DateTime.Now.ToString(); } private string _Time; public string Time { get { return this._Time; } set { this._Time = value; } } }
赋值
private void UpdateTime_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { _MyClass.Time = DateTime.Now.ToString(); this.lable1.Content = _MyClass.Time; } private void Grid_Loaded(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { this.lable1.Content = _MyClass.Time; }
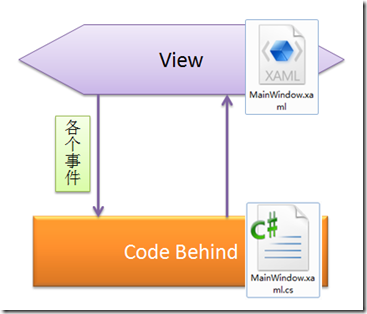
很简单的对lable1的Content属性的赋值.总结一下这种模式的流程图:
这种模式很简单,很容易理解.缺点也是很明显,View跟CodeBehind紧紧耦合在一起了(事件方法里面需要知道lable1),还有到处都是this.lable1.Content = _MyClass.Time; 这样的赋值代码,这样可维护性是很低的.于是就有了绑定.
属性绑定
绑定就是把把东西关联在一起,例如人的手脚是和整个身体绑定在一起的,手指受伤了,人会感到疼痛.属性绑定通常是把一个Model属性绑定给一个控件的属性,于是它们就有了联系,Model的属性变化了,控件的属性也会变化.
wpf的绑定.
首先把View的DataContext设为MyClass.
<Window.DataContext> <local:MyClass /> </Window.DataContext>
这样我们就可以把MyClass的属性绑定给lable1的Content.
<Label Grid.Column="1" Grid.Row="1" Content="{Binding Time}" />
WinForm也能绑定:
public Form1() { InitializeComponent(); this.label2.DataBindings.Add("Text", _MyClass, "Time", true); }
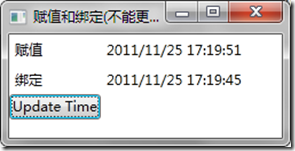
运行程序:
点击Update Time按钮,比较遗憾,绑定那一行的时间并没有更新.看来需要做更多的工作.(见源码Example1)
INotifyPropertyChanged接口
原来对于上面的那个poco类,它的属性Time发生变化时,紧紧靠<Label Grid.Column="1" Grid.Row="1" Content="{Binding Time}" />或者this.label2.DataBindings.Add("Text", _MyClass, "Time", true); 是不够的,lable不能"智能"地知道MyClass的Time变化了,需要MyClass主动去通知lable:我的Time属性变化了.INotifyPropertyChanged接口就是这样的功能.
INotifyPropertyChanged的源码:
// 摘要:向客户端发出某一属性值已更改的通知。 public interface INotifyPropertyChanged { // 摘要:在更改属性值时发生。 event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged; }
PropertyChangedEventHandler里的事件参数源码:
// 摘要:为 System.ComponentModel.INotifyPropertyChanged.PropertyChanged 事件提供数据。 public class PropertyChangedEventArgs : EventArgs { // 摘要:初始化 System.ComponentModel.PropertyChangedEventArgs 类的新实例。 // 参数:propertyName:已更改的属性名 [TargetedPatchingOptOut("Performance critical to inline this type of method across NGen image boundaries")] public PropertyChangedEventArgs(string propertyName); // 摘要:获取已更改的属性名。 // 返回结果:已更改的属性名。 public virtual string PropertyName { get; } }
接口非常简单,就一个PropertyChanged事件,而事件委托的参数也很简单,一个字符串属性名.Model继承INotifyPropertyChanged后,在这个事件中是通知者的角色(执行事件),而<Label Grid.Column="1" Grid.Row="1" Content="{Binding Time}" />和this.label2.DataBindings.Add("Text", _MyClass, "Time", true); 这里可以理解为事件的订阅.
继承INotifyPropertyChanged后的MyClass:
public class MyClass : INotifyPropertyChanged { public MyClass() { this._Time = DateTime.Now.ToString(); } private string _Time; public string Time { get { return this._Time; } set { if (this._Time != value) { this._Time = value; if (PropertyChanged != null) { PropertyChanged(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs("Time")); } } } } public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged; }
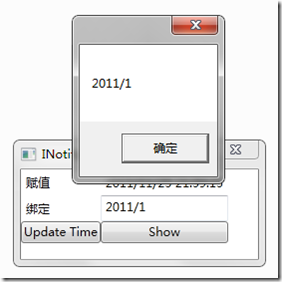
重点是Set值时执行事件,运行程序发现,lable终于知道MyClass的属性变化了,它们绑定了.而且可以发现绑定是双向的,即控件的值更新,model的属性值也会更新,添加一个按钮显示model的属性值:
private void Show_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { MessageBox.Show(_MyClass.Time); }
这里做到了把Model的属性绑定给View的控件的属性中,下面看看集合的绑定.
集合绑定
跟上面一样,普通的集合控件们是不认的,要用特殊的集合,它就是ObservableCollection<T>,它继承了INotifyCollectionChanged和INotifyPropertyChanged.部分源码:
[Serializable] public class ObservableCollection<T> : Collection<T>, INotifyCollectionChanged, INotifyPropertyChanged 一个简单的类:
public class Employe { public ObservableCollection<string> Employees { get; set; } public Employe() { Employees = new ObservableCollection<string>() { "肥猫", "大牛", "猪头" }; } }
把它绑定到一个ComboBox中:
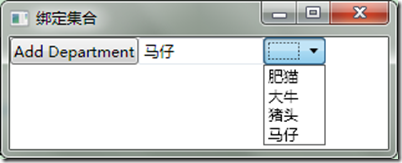
<ComboBox Grid.Column="2" Grid.Row="0" ItemsSource="{Binding Employees}" Width="50px"/>另外做一个按钮添加来Employees
private void AddDepartment_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { _MyClass.Employees.Add(this.textBox1.Text); }
运行程序,添加一个Employee,发现ComboBox也更新了(见源码Example3).
命令绑定
还有一个绑定就是命令绑定.实际解决的是要把View完全解耦,不用再写控件事件,因为AddDepartment_Click这样的写法就会把View和CodeBehind的耦合在一起,跟上面属性赋值类似.
ICommand
// 摘要:定义一个命令 [TypeConverter("System.Windows.Input.CommandConverter, PresentationFramework, Version=4.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31bf3856ad364e35, Custom=null")] [ValueSerializer("System.Windows.Input.CommandValueSerializer, PresentationFramework, Version=4.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31bf3856ad364e35, Custom=null")] public interface ICommand { // 摘要: 当出现影响是否应执行该命令的更改时发生。 event EventHandler CanExecuteChanged; // 摘要:定义用于确定此命令是否可以在其当前状态下执行的方法。 // 参数:parameter:此命令使用的数据。如果此命令不需要传递数据,则该对象可以设置为null。 // 返回结果:如果可以执行此命令,则为true;否则为false。 bool CanExecute(object parameter); // // 摘要:定义在调用此命令时调用的方法。 // 参数:parameter:此命令使用的数据。如果此命令不需要传递数据,则该对象可以设置为 null。 void Execute(object parameter); }
最主要需要实现的是Execute方法.即事件发生时要执行的方法.下面把Add Department的按钮事件去掉,改为绑定一个命令.实现这个命令首先要得到的是textbox上的值.要在命令里得到View控件的值,可以在model里新建一个属性值与这个控件绑定,因为绑定是双向的,所以属性值就是控件的值.根据上面的Employe类添加如下代码:
private string _NewEmployee; public string NewEmployee { get { return this._NewEmployee; } set { if (this._NewEmployee != value) { this._NewEmployee = value; if (PropertyChanged != null) PropertyChanged(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs("NewEmployee")); } } }
每个命令要实现为一个单独的类,继承ICommand,这里用一个委托把添加部门的逻辑转移到Employe中:
public class AddEmployeeCommand : ICommand { Action<object> _Execute; public AddEmployeeCommand(Action<object> execute) { _Execute = execute; } public bool CanExecute(object parameter) { return true; } public event EventHandler CanExecuteChanged { add { CommandManager.RequerySuggested += value; } remove { CommandManager.RequerySuggested -= value; } } public void Execute(object parameter) { _Execute(parameter); } }
Employe类再添加一个ICommand用作绑定:
private ICommand _AddEmployee; public ICommand AddEmployee { get { if (_AddEmployee == null) { _AddEmployee = new AddEmployeeCommand((p) => { Employees.Add(NewEmployee); }); } return _AddEmployee; } } 有了AddEmployee 我们就可以绑定到按钮中:
<Button Grid.Column="0" Grid.Row="0" Content="Add Department" Command="{Binding AddEmployee}" />
到这里,我们可以得到跟上面一样的功能,但成功把按钮事件改为了命令绑定.(见源码Example4)
完成上面所有工作,我们解决了一个问题,即View"后面"的模块(Code Behind也好,Model也好)完全没了view的影子,"后面"的模块不用管textbox还是Label来显示一个Name,只管把Name赋值就好了,也不用关心一个button还是一个picturebutton来点击,只管实现逻辑.但细心观察,代码还是有不少问题.
其中最主要的是为了实现上面的功能,污染了Employe这个类.Employe应该是常见的Model层中的一个类,它应该是一个poco类,职责是定义领域模型和模型的领域(业务)逻辑.为了实现绑定,添加了各种接口和与领域(业务)无关的属性,这就是对Model的污染.所以,当想实现绑定,而又不想污染model,就得引入新的一层--ViewModel,这样就走向了MVVM模式.
MVVM模式
VM是MVVM的核心.主要作用有两个.
1.提供属性和命令供View绑定
2.还要承担MVC模式中C(Controller)的职责,作为View和业务层的中间人.
模式实践.
把上面的代码稍为修改即可以改为MVVM模式.
Model,Employee回归Poco:
public class Employee { public string Name { get; set; } public string Email { get; set; } public string Phone { get; set; } public void Add() { DataBase.AllEmployees.Add(this); } }
ViewModel提供绑定的属性和命令:
public class EmployeeViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged { public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged; /// <summary> /// 供?ComboBox绑ó定¨ /// </summary> public ObservableCollection<Employee> Employees { get; set; } public EmployeeViewModel() { Employees = new ObservableCollection<Employee>(DataBase.AllEmployees); } #region 供?textbox 绑ó定¨ private string _NewEmployeeName; public string NewEmployeeName { get { return this._NewEmployeeName; } set { if (this._NewEmployeeName != value) { this._NewEmployeeName = value; if (this.PropertyChanged != null) { PropertyChanged(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs("NewEmployeeName")); } } } } private string _NewEmployeeEmail; public string NewEmployeeEmail { get { return this._NewEmployeeEmail; } set { if (this._NewEmployeeEmail != value) { this._NewEmployeeEmail = value; if (this.PropertyChanged != null) { PropertyChanged(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs("NewEmployeeEmail")); } } } } private string _NewEmployeePhone; public string NewEmployeePhone { get { return this._NewEmployeePhone; } set { if (this._NewEmployeePhone != value) { this._NewEmployeePhone = value; if (this.PropertyChanged != null) { PropertyChanged(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs("NewEmployeePhone")); } } } } #endregion public ICommand AddEmployee { get { return new RelayCommand(new Action(() => { if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(NewEmployeeName)) { MessageBox.Show("姓名不能为空!"); return; } var newEmployee = new Employee { Name = _NewEmployeeName, Email = _NewEmployeeEmail, Phone = _NewEmployeePhone }; newEmployee.Add(); Employees.Add(newEmployee); })); } } }
代码的职责非常明确,提供5个属性(1个命令,4个普通属性)供View绑定.虽然简单,但却产生了一大堆代码,可能这就是MVVM框架出现的原因.不管怎样,一个简单的MVVM模式的Simple就完成了(参考代码Example5).
MVVM: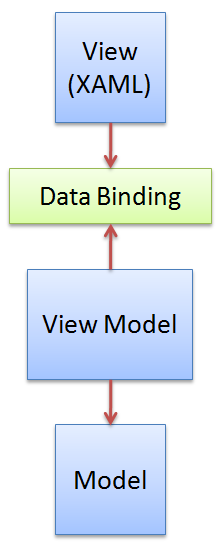
参考:链接