LinkedList源码浅析
一、LinkedList简介
LinkedList是List接口的另外一个常用实现类,其底层是双向链表。
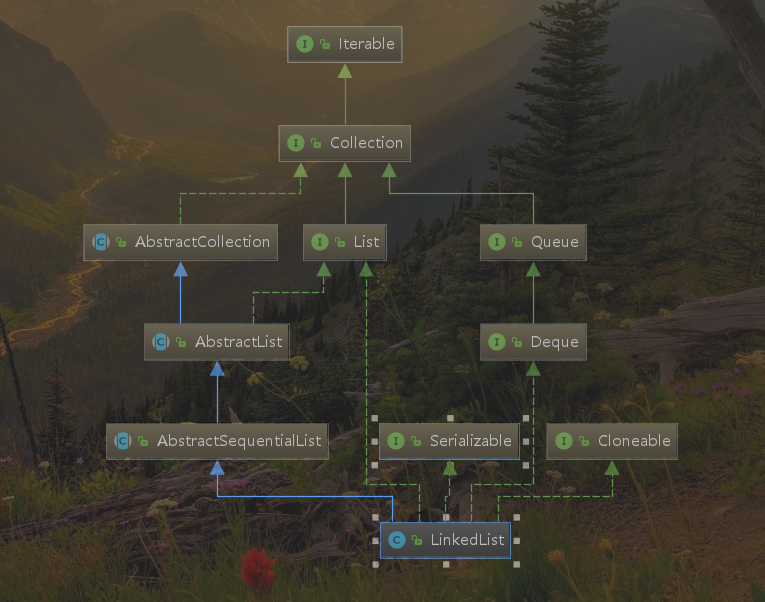
可以看到LinkedList的顶层集合类为Collection,实现了List接口,继承了AbstracList类,提供了数组集合相关的增、删、改、查和遍历等功能;实现了Queue接口,具备队列的性质。
与ArrayList不同的是,LinkedList的底层实现不是数组,没有实现RandomAccess接口,不具备随机访问的功能。但是,LinkedList的底层是基于链表结构的,元素的增删只需要改动节点之间的引用关系,而元素的位置不需要改变,因此其在执行插入、删除操作时具有较好的性能,而查询和修改都必须通过迭代定位元素的位置,性能很差。
二、源码浅析
和上篇一样,也是按照LinkedList源码中的属性、增删改查的方法向下阅读整理:
1、属性和构造方法
transient int size = 0; /** * 指向首节点 * Node是LinkedList的静态内部类 */ transient Node<E> first; /** * 指向尾节点 */ transient Node<E> last;
LinkedList只有三个属性,分别是size:当前LinkedList实例对象中有几个元素节点,还有指向链表首尾元素位置的引用,Node是LinkedList的内部类。
/** * 无参构造
* 无参构造什么都没有做,初始化size为0,first和last也都为空; */ public LinkedList() { }
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) { this(); addAll(c); }
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) { return addAll(size, c); } public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { checkPositionIndex(index); //判断是否越界 Object[] a = c.toArray();//将入参集合c转换为数组对象a int numNew = a.length; if (numNew == 0) return false; Node<E> pred, succ; if (index == size) { //将当前实例的size作为入参,所以这里index和size的值始终一致 succ = null; pred = last; //last引用指向pred } else { succ = node(index); pred = succ.prev; } for (Object o : a) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o; Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null); //遍历数组,将每个元素依次加入到链表的末尾 if (pred == null) first = newNode; //如果原链表末尾为null,那么newNode就作为链表的第一个节点 else pred.next = newNode; pred = newNode; //pred依次指向数组当前迭代的元素,直至最后一个元素 } if (succ == null) { last = pred; //最后一个元素作为链表的末尾 } else { pred.next = succ; succ.prev = pred; } size += numNew; //修改当前实例的size modCount++; return true; }
2、新增及插入元素
/** * * 将指定元素添加到此列表的结尾。 */ public boolean add(E e) { linkLast(e); return true; } /** * Links e as first element. * 将元素插入到链的首节点 */ private void linkFirst(E e) { final Node<E> f = first; final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f); first = newNode; if (f == null) last = newNode; //如果以前的第一个节点是null,那么newNode就是last节点 else f.prev = newNode; //否则就将以前的首节点(当前第二节点)的前节点指向newNode size++; modCount++; } /** * Links e as last element. * 将元素插入到链的尾节点 */ void linkLast(E e) { final Node<E> l = last; final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); last = newNode; if (l == null) first = newNode; //如果以前的尾节点是null,那么newNode也就是首节点 else l.next = newNode; size++; modCount++; } /** * 在指定索引位置之后,插入新的元素*/ public void add(int index, E element) { checkPositionIndex(index); //如果index == size,就直接在尾节点后插入节点element if (index == size) linkLast(element); else //否则就在指定节点node(index)前插入节点element linkBefore(element, node(index)); } /** * Inserts element e before non-null Node succ. * 在指定节点succ之前插入新的节点E */ void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) { // assert succ != null; //源码就是插入一个Node节点,前后连接变一下。但是succ不能为null吗?这是在哪里判断的 final Node<E> pred = succ.prev; final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ); succ.prev = newNode; if (pred == null) first = newNode; else pred.next = newNode; size++; modCount++; }
3、删除链表元素
/** * * 移除此列表中指定位置处的元素。 */ public E remove(int index) { checkElementIndex(index); return unlink(node(index)); } /** * Returns the (non-null) Node at the specified element index. * 返回指定元素索引处的(非null)节点 */ Node<E> node(int index) { // assert isElementIndex(index); //如果index索引小于size的一半,就从首节点开始遍历,否则从尾节点遍历 if (index < (size >> 1)) { Node<E> x = first; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) x = x.next; return x; //返回索引下标为index的节点 } else { Node<E> x = last; for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) x = x.prev; return x; } } /** * Unlinks non-null node x. * 释放非空的节点x。节点x为null会怎么样 */ E unlink(Node<E> x) { // assert x != null; final E element = x.item; //节点元素element final Node<E> next = x.next; final Node<E> prev = x.prev; //如果当前的前节点为null,就将后节点设置为首节点 if (prev == null) { first = next; } else { //否则就将前节点的后节点引用设置为next,并且将当前节点x的前节点引用置为null prev.next = next; x.prev = null; } //和上面同样的逻辑 if (next == null) { last = prev; } else { next.prev = prev; x.next = null; } //将当前节点元素设置为null x.item = null; size--; modCount++; return element; }
/** * 删除链表的首节点 */ public E removeFirst() { final Node<E> f = first; if (f == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return unlinkFirst(f); } /** * Unlinks non-null first node f. * 释放非空的首节点f。首节点f */ private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) { // assert f == first && f != null; final E element = f.item; final Node<E> next = f.next; //f节点的元素置为null,f节点的下个节点引用置为null f.item = null; f.next = null; // help GC //f节点的下个节点设置为首节点 first = next; if (next == null) last = null; else next.prev = null; size--; modCount++; return element; } /** * 删除链表的首节点 */ public E removeLast() { final Node<E> l = last; if (l == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return unlinkLast(l); } /** * Unlinks non-null last node l. * 释放非空的尾节点l。尾节点l */ private E unlinkLast(Node<E> l) { // assert l == last && l != null; final E element = l.item; final Node<E> prev = l.prev; //l节点的元素置为null,l节点的上个节点引用置为null l.item = null; l.prev = null; // help GC //l节点的上个节点设置为尾节点 last = prev; if (prev == null) first = null; else prev.next = null; //尾节点next引用为null size--; modCount++; return element; }
/** * * 从此列表中移除第一次出现的指定元素(从头部到尾部遍历列表时)。 */ public boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) { return remove(o); } /** * * 从此列表中移除最后一次出现的指定元素(从头部到尾部遍历列表时)。 */ public boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) { if (x.item == null) { unlink(x); return true; } } } else { for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) { if (o.equals(x.item)) { unlink(x); return true; } } } return false; }
4、修改及获取链表元素
/** * 获取指定索引下标出的元素.*/ public E get(int index) { //index >= 0 && index < size checkElementIndex(index); return node(index).item; } /** * Returns the (non-null) Node at the specified element index. * 返回指定元素索引处的(非null)节点 */ Node<E> node(int index) { // assert isElementIndex(index); //如果index索引小于size的一半,就从首节点开始遍历,否则从尾节点遍历 if (index < (size >> 1)) { Node<E> x = first; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) x = x.next; return x; //返回索引下标为index的节点 } else { Node<E> x = last; for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) x = x.prev; return x; } } /** * * 返回此列表中首次出现的指定元素的索引,如果此列表中不包含该元素,则返回 -1。 */ public int indexOf(Object o) { int index = 0; if (o == null) { //从首节点开始遍历,如果节点中存储的元素与入参元素相同,返回index索引下标 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (x.item == null) return index; index++; } } else { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { //通过equals比较,泛型元素必须重写equals方法 if (o.equals(x.item)) return index; index++; } } return -1; } /** * * 修改索引为index的节点的值 */ public E set(int index, E element) { checkElementIndex(index); Node<E> x = node(index); E oldVal = x.item; x.item = element; return oldVal; }
此外,还有一些队列相关的方法,这里就不再列出了。
三、LinkedList总结
1、LinkedList底层是双向链表,插入、删除操作比较高效(不涉及元素在内存中的移动)、迭代效率一般,随机访问效率很差(实际还是遍历到索引下标);
2、LinkedList和ArrayList一样,里面的方法都不是同步方法,非线程安全。
3、链表元素批量增加,是先将集合元素转化为数组,进行迭代依次加入到链表末尾实现的,而ArrayList是依靠System.arrayCopy实现的。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号