HashMap对HashCode碰撞的处理
2017-12-06 13:28 faunjoe88 阅读(2504) 评论(1) 编辑 收藏 举报先说Java之外的,什么是拉链法?怎么解决冲突的:
拉链法解决冲突的做法是:将所有关键字为同义词的结点链接在同一个单链表中。
若选定的散列表长度为m,则可将散列表定义为一个由m个头指针组成的指针数组t[0..m-1]。凡是散列地址为i的结点,均插入到以t为头指针的单链表中。
t中各分量的初值均应为空指针。在拉链法中,装填因子α可以大于1,但一般均取α≤1。
换句话说:HashCode是使用Key通过Hash函数计算出来的,由于不同的Key,通过此Hash函数可能会算的同样的HashCode,
所以此时用了拉链法解决冲突,把HashCode相同的Value连成链表. 但是get的时候根据Key又去桶里找,如果是链表说明是冲突的,此时还需要检测Key是否相同
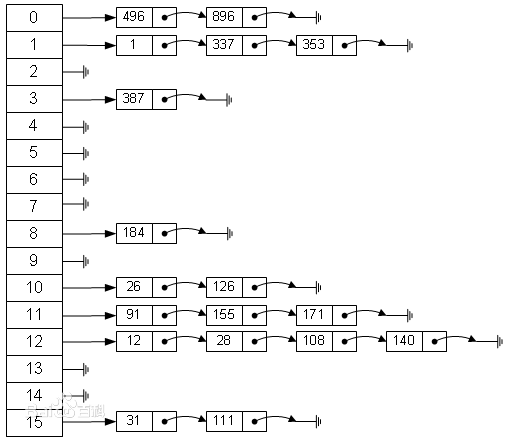
在解释下,Java中HashMap是利用“拉链法”处理HashCode的碰撞问题。
在调用HashMap的put方法或get方法时,都会首先调用hashcode方法,去查找相关的key,当有冲突时,再调用equals方法。
hashMap基于hasing原理,我们通过put和get方法存取对象。
当我们将键值对传递给put方法时,他调用键对象的hashCode()方法来计算hashCode,然后找到bucket(哈希桶)位置来存储对象。
当获取对象时,通过键对象的equals()方法找到正确的键值对,然后返回值对象。HashMap使用链表来解决碰撞问题,当碰撞发生了,对象将会存储在链表的下一个节点中。
hashMap在每个链表节点存储键值对对象。当两个不同的键却有相同的hashCode时,他们会存储在同一个bucket位置的链表中。
键对象的equals()来找到键值对。HashMap的put和get方法源码如下:
/** * Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped, * or if this map contains no mapping for the key. * * 获取key对应的value */ public V get(Object key) { if (key == null) return getForNullKey(); //获取key的hash值 int hash = hash(key.hashCode()); // 在“该hash值对应的链表”上查找“键值等于key”的元素 for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)]; e != null; e = e.next) { Object k; if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) return e.value; } return null; } /** * Offloaded version of get() to look up null keys. Null keys map * to index 0. * 获取key为null的键值对,HashMap将此键值对存储到table[0]的位置 */ private V getForNullKey() { for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) { if (e.key == null) return e.value; } return null; } /** * Returns <tt>true</tt> if this map contains a mapping for the * specified key. * * HashMap是否包含key */ public boolean containsKey(Object key) { return getEntry(key) != null; } /** * Returns the entry associated with the specified key in the * HashMap. * 返回键为key的键值对 */ final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) { //先获取哈希值。如果key为null,hash = 0;这是因为key为null的键值对存储在table[0]的位置。 int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key.hashCode()); //在该哈希值对应的链表上查找键值与key相等的元素。 for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)]; e != null; e = e.next) { Object k; if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) return e; } return null; } /** * Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map. * If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old * value is replaced. * * 将“key-value”添加到HashMap中,如果hashMap中包含了key,那么原来的值将会被新值取代 */ public V put(K key, V value) { //如果key是null,那么调用putForNullKey(),将该键值对添加到table[0]中 if (key == null) return putForNullKey(value); //如果key不为null,则计算key的哈希值,然后将其添加到哈希值对应的链表中 int hash = hash(key.hashCode()); int i = indexFor(hash, table.length); for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) { Object k; //如果这个key对应的键值对已经存在,就用新的value代替老的value。 if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) { V oldValue = e.value; e.value = value; e.recordAccess(this); return oldValue; } } modCount++; addEntry(hash, key, value, i); return null; }
从HashMap的put()和get方法实现中可以与拉链法解决hashCode冲突解决方法相互印证。
并且从put方法中可以看出HashMap是使用Entry<K,V>来存储数据。数据节点Entry的数据结构如下:
// Entry是单向链表。 // 它是 “HashMap链式存储法”对应的链表。 // 它实现了Map.Entry 接口,即实现getKey(), getValue(), setValue(V value), equals(Object o), hashCode()这些函数 static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { final K key; V value; //指向下一个节点 Entry<K,V> next; final int hash; /** * Creates new entry. * 输入参数包括"哈希值(h)", "键(k)", "值(v)", "下一节点(n)" */ Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entry<K,V> n) { value = v; next = n; key = k; hash = h; } public final K getKey() { return key; } public final V getValue() { return value; } public final V setValue(V newValue) { V oldValue = value; value = newValue; return oldValue; } // 判断两个Entry是否相等 // 若两个Entry的“key”和“value”都相等,则返回true。 // 否则,返回false public final boolean equals(Object o) { if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry)) return false; Map.Entry e = (Map.Entry)o; Object k1 = getKey(); Object k2 = e.getKey(); if (k1 == k2 || (k1 != null && k1.equals(k2))) { Object v1 = getValue(); Object v2 = e.getValue(); if (v1 == v2 || (v1 != null && v1.equals(v2))) return true; } return false; } public final int hashCode() { return (key==null ? 0 : key.hashCode()) ^ (value==null ? 0 : value.hashCode()); } public final String toString() { return getKey() + "=" + getValue(); } /** * This method is invoked whenever the value in an entry is * overwritten by an invocation of put(k,v) for a key k that's already * in the HashMap. */ void recordAccess(HashMap<K,V> m) { } /** * This method is invoked whenever the entry is * removed from the table. */ void recordRemoval(HashMap<K,V> m) { } }
从这段代码中,我们可以看出Entry是一个单向链表,这也是我们为什么说HashMap是通过拉链法解决hash冲突的原因。Entry实现了Map.Entry接口。



