173. Binary Search Tree Iterator - Medium
Implement an iterator over a binary search tree (BST). Your iterator will be initialized with the root node of a BST.
Calling next() will return the next smallest number in the BST.
Example:
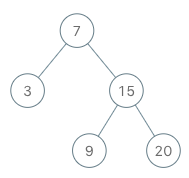
BSTIterator iterator = new BSTIterator(root); iterator.next(); // return 3 iterator.next(); // return 7 iterator.hasNext(); // return true iterator.next(); // return 9 iterator.hasNext(); // return true iterator.next(); // return 15 iterator.hasNext(); // return true iterator.next(); // return 20 iterator.hasNext(); // return false
Note:
next()andhasNext()should run in average O(1) time and uses O(h) memory, where h is the height of the tree.- You may assume that
next()call will always be valid, that is, there will be at least a next smallest number in the BST whennext()is called.
M1: 先inorder全部遍历完(慢)
time: O(n) , space: O(n)
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ class BSTIterator { List<Integer> list; int idx; public BSTIterator(TreeNode root) { list = new ArrayList<>(); idx = 0; inorder(root, list); } public void inorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list) { if(root == null) { return; } inorder(root.left, list); list.add(root.val); inorder(root.right, list); } /** @return the next smallest number */ public int next() { int tmp = idx; idx++; return list.get(tmp); } /** @return whether we have a next smallest number */ public boolean hasNext() { return idx < list.size(); } } /** * Your BSTIterator object will be instantiated and called as such: * BSTIterator obj = new BSTIterator(root); * int param_1 = obj.next(); * boolean param_2 = obj.hasNext(); */
M2: optimized,用stack,先把所有的左边的节点压进栈,当call next()时再按顺序出栈
next() -- time: O(h), space: O(h)
hasNext() -- time: O(1)
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ class BSTIterator { Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>(); public BSTIterator(TreeNode root) { getAllLeft(root); } public void getAllLeft(TreeNode root) { while(root != null) { stack.push(root); root = root.left; } } /** @return the next smallest number */ public int next() { TreeNode node = stack.pop(); getAllLeft(node.right); return node.val; } /** @return whether we have a next smallest number */ public boolean hasNext() { return !stack.isEmpty(); } } /** * Your BSTIterator object will be instantiated and called as such: * BSTIterator obj = new BSTIterator(root); * int param_1 = obj.next(); * boolean param_2 = obj.hasNext(); */


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号