【趣味设计模式系列】之【策略模式】
目录
1. 简介
策略模式(strategy):定义一组算法,将每个算法都封装起来,并且使它们之间可以互换。
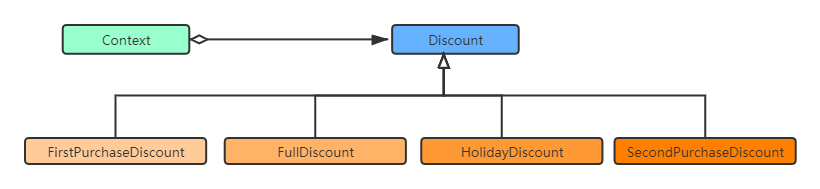
2. 图解
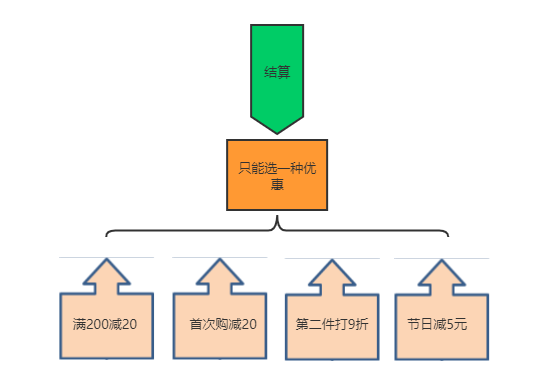
3. 案例实现
FullDistcount满200减20元;FirstPurchaseDiscount首次购买减20元;SecondPurchaseDiscount第二件打9折;HolidayDiscount节日一律减5元.
代码实现如下,环境类
折扣接口类
满减优惠
首次优惠类
第二件优惠类
节假日优惠类
测试类
结果
首次购买减20元 90
4. JDK中的策略模式-Comparable与Comparator接口
4.1 Comparable
Comparable,在jdk1.8中描述如下,实现该接口的对象的List和array,可以通过Collections.sort和Arrays.sort自动排序,该对象具备sorted map的key和sorted set的元素的特征。
源码解析
该接口实现一个抽象方法compareTo,定义两个对象的比较方式,返回值大于0、等于0、小于0,分别表示当前对象与传入对象的关系为大于、相等、小于。
4.2 Comparator
Comparator为比较器,它可以作为一个参数传递到Collections.sort和Arrays.sort方法来指定某个类对象的排序方式。同时它也能为sorted set和sorted map指定排序方式。
源码解析
JDK1.8之前,Comparator中只要两个方法,就是前两个方法,后面的所有默认方法均为1.8新增的方法,采用的是1.8新增的功能:接口可添加默认方法。即便拥有如此多方法,该接口还是函数式接口,compare用于定义比较方式
4.3 两者区别
- Comparable为可排序的,实现该接口的类的对象自动拥有可排序功能。
- Comparator为比较器,实现该接口可以定义一个针对某个类的排序方式。
- Comparator与Comparable同时存在的情况下,前者优先级高。
4.4 实例
首先定义个类,Student
定义年龄比较器
定义姓名比较器
测试类
测试结果
5. Spring源码中的策略模式
Spring Bean 实例化,是通过InstantiationStrategy接口实现的,根据创建对象情况的不同,提供了三种方法:无参构造方法、有参构造方法、工厂方法。如下
InstantiationStrategy 接口有两个实现类:SimpleInstantiationStrategy 和 CglibSubclassingInstantiationStrategy。SimpleInstantiationStrategy 对以上三个方法都做了简单的实现。
如果是工厂方法实例化,则直接使用反射创建对象,如下:
如果是构造方法实例化,则是先判断是否有 MethodOverrides,如果没有则是直接使用反射,如果有则就需要 CGLIB 实例化对象。如下:
SimpleInstantiationStrategy 对 instantiateWithMethodInjection() 的实现任务交给了子类 CglibSubclassingInstantiationStrategy。
类 CglibSubclassingInstantiationStrategy 为 Spring 实例化 bean 的默认实例化策略,其主要功能还是对父类功能进行补充:其父类将 CGLIB 的实例化策略委托其实现
CglibSubclassingInstantiationStrategy 实例化 bean 策略是通过其内部类 CglibSubclassCreator 来实现的。
6. 总结
优点
- 算法可以自由切换
- 避免使用多重条件判断
- 扩展性良好
缺点
- 策略类数量增多
- 所有的策略类都需要对外暴露
__EOF__

本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/father-of-little-pig/p/12832665.html
关于博主:不要为了技术而技术,总结分享技术,感恩点滴生活!
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
声援博主:如果您觉得文章对您有帮助,可以点击文章右下角【推荐】一下。您的鼓励是博主的最大动力!




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY