Tetrahedron
Problem Description
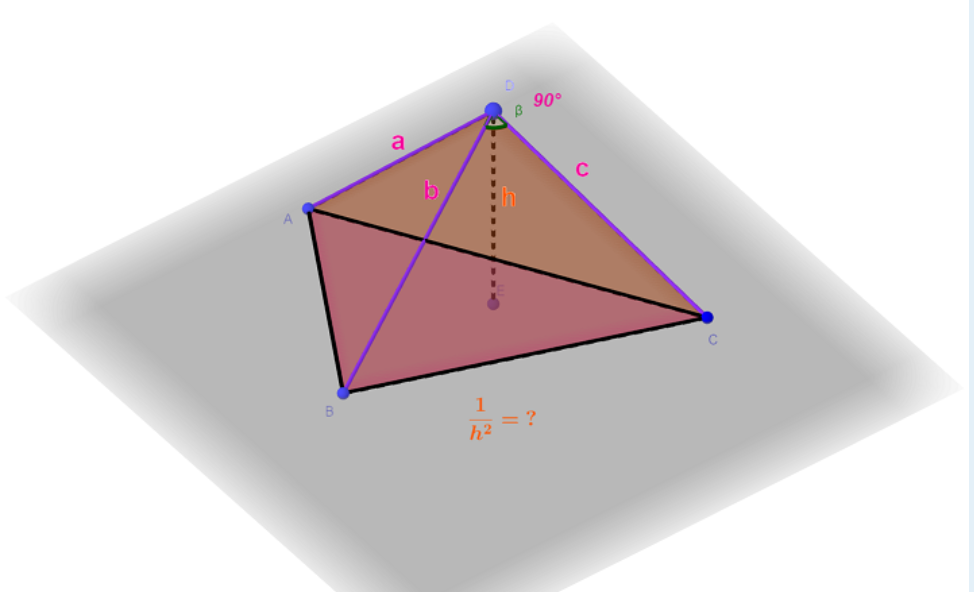
Generate three integers a,b,and c in[1,n] with equal probability independently and use them as the three right-angle side length of a right-angled tetrahedron. Find the expectation of the reciprocal square of the distance from the right-angle apex to the slope(Euclidean distance).
For each test case ,output a line containing the answer mod 998244353
Input
In the first line, you should read an integer T denoting the number of test cases.
In every test case,the only line will include an integer n.
It is guaranteed that T is no larger than \(2\times 10^{6}\) and n is no larger than \(6\times 10^{6}\) .
Output
For each test case,output the only line containing just one integer denoting the answer mod 998244353
Sample Input
3
1
2
3
Sample Output
3
124780546
194103070
题解
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
#define mod 998244353
long long F[6000005];
int T,n;
//快速幂
long long pow(long long a,long long b){
long long ans=1;
while(b){
if(b&1){
ans=ans*a%mod;
}
b>>=1;
a=a*a%mod;
}
return ans;
}
int main(){
//先打表求出逆元的前缀和
for(long long i=1;i<=6000005;i++){
F[i]=(pow(i*i%mod,mod-2)+F[i-1])%mod;
}
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--){
scanf("%d",&n);
//输出
printf("%lld\n",3*F[n]%mod*pow(n,mod-2)%mod);
}
return 0;
}
这题主要就是求期望,求\(\frac{1}{h^{2}}\) 的期望,所以在此之前,我们要求出\(\frac{1}{h^{2}}\)用a、b、c表示的式子
-
设斜面三条边长度为\(x,y,z\),面积为\(S\),四面体体积为\(V\)
-
则\(V=abc/6=Sh/3\),两边同时平方得到:
\[\frac{1}{36} a^2 b^2 c^2=\frac{h^2 S^2}{9} \] -
海伦公式
\[S=\sqrt{p(p-x)(p-y)(p-z)}, \quad p=(x+y+z)/2 \] -
代入得:
\[16 a^2 b^2 c^2=4\ h^2 2p (2 p-2 x) (2 p-2 y) (2 p-2 z) \\ 16 a^2 b^2 c^2=4 h^2 (x+y+z) (-x+y+z) (x-y+z) (x+y-z) \] -
直接化简右边计算量较大,由于其是轮换对称的,考虑含\(x\)的项:\(x^4,x^2y^2\)的系数
-
首先\(x\)的奇数次幂系数为\(0\),因为\(-(x+y+z) (-x+y+z) (-x+y-z) (x+y-z)\),注意到前两项\(x\)加的内容是相同的,但是\(x\)本身符号不同,所以前两项中的\(x\)要么同时取,要么同时不取,否则就会被对方抵消,后两项也一样
-
\(x^2 y z\)系数为\(0\),若取前两项的\(x\),则是\(-2yz\);取后两项的\(x\),则是\(2yz\),故是\(0\)
-
\(x^4\)系数为\(-1\)
-
\(x^2y^2\)系数为\(2\),同样讨论两个\(x\)取自前两项还是后两项
-
故
\[(x+y+z) (-x+y+z) (x-y+z) (x+y-z) = -\sum_{cyc}x^4+2\sum_{cyc}x^2y^2= \sum_{cyc} x^2(2y^2-x^2) \]
-
-
勾股定理:
\[x^2=a^2+b^2 \\ y^2=a^2+c^2 \] -
代入得:
\[\sum_{cyc} x^2(2y^2-x^2)=\sum_{cyc}(a^2+b^2)(a^2-b^2+2c^2) \\ \sum_{cyc}(a^2+b^2)(a^2-b^2)+\sum_{cyc}2(a^2+b^2)c^2 \\ =2 \sum_{cyc}(c^2a^2+b^2c^2)=4\sum_{cyc}a^2b^2 \] -
\[16 a^2 b^2 c^2=16 h^2 \sum_{cyc}a^2b^2 \\ \]
-
可得到\(1/h^2=1/a^2+1/b^2+1/c^2\)。
我们可以直接记住这个公式,\(\frac{1}{h^{2}}=\frac{1}{a^{2}}+\frac{1}{b^{2}}+\frac{1}{c^{2}}\) ,下面附上一些直角四面体的性质。

得到这个公式后,我们可以得出:
\(E(\frac{1}{h^{2}})= E(\frac{1}{a^{2}}+\frac{1}{b^{2}}+{\frac{1}{c^{2}}})=3\times E(\frac{1}{x^{2}}) ,x\in [1,n]\) ,x取整数
因为a、b、c都是相互独立的,所以\(\frac{1}{a^{2}}\) 、\(\frac{1}{b^{2}}\) 和\(\frac{1}{c^{2}}\) 可以视为一个东西,我们这里用\(\frac{1}{x^{2}}\) 来代替,x是从1~n中均匀随机选择的,然后前边乘以个3就行了。
那么现在我们就是要求\(E(\frac{1}{x^{2}}),x\in [1,n]\) ,x取整数就行了。
我们要求这个离散的变量的期望,那就用相应的结果乘以对应的概率,再求和。因为它是均匀随机分布的,所以概率固定是\(\frac{1}{n}\)所以可以得出以下式子:
\(E(\frac{1}{x^{2}})=(1\times \frac{1}{n}+\frac{1}{4}\times \frac{1}{n}+...+\frac{1}{n^{2}}\times \frac{1}{n})\)
然后可以把\(\frac{1}{n}\) 提出来
\(E(\frac{1}{x^{2}})=(1+\frac{1}{4}+...+\frac{1}{n^{2}})\times \frac{1}{n}\)
由于答案是要模一个数的,我们这里记作是模mod,所以可以写成
\(E(\frac{1}{x^{2}})=[(1+\frac{1}{4}+...+\frac{1}{n^{2}})\times \frac{1}{n}]\%mod\)
\(=[(1+\frac{1}{4}+...+\frac{1}{n^{2}})\%mod\times \frac{1}{n}\%mod]\%mod\)
\(=[(1\%mod+\frac{1}{4}\%mod+...+\frac{1}{n^{2}}\%mod)\%mod\times \frac{1}{n}\%mod]\%mod\)
这个式子最后再乘一个3就是我们要求的东西了,我们可以发现这个式子中最基本的操作就是分数取模,那么也就需要求逆元,然后这个式子前边就是一个前缀和,照着这些写代码就行了。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号