Houdini Python开发实战 课程笔记
P2 + P3 + P4 + P5 - 基础:
1. Houdini中使用Python的地方
2. Textport:可使用cd、ls等路径操作的命令(命令前加%,可在python中使用)
3. Source Editor
在Source Editor中定义函数
在其他地方调用
hou.session.getChildren(hou.node("/"))
4. Python Shell
示例
p2
obj = hou.node("/obj")
obj.createNode("geo") hou.cd("/obj/geo") # 返回当前路径 hou.pwd() file1 = hou.node("./file1") file1.destory() hou.pwd().createNode("shpere") shpere = hou.node("shpere1") hou.pwd().createNode("box1") box = hou.node("box") hou.pwd().createNode("merge") merge = hou.node("merge1") # 将box和shpere联合起来 merge.setFirstInput(sphere, 0) merge.setNextInput(box)
p3
# 返回merge联合的节点 merge.inputs() # 将merge联合的box去除 merge.setInput(1,None) # 返回父节点及子节点 merge.parent() obj.children() # 返回子节点元组的函数 def getChildren(node): childList = [] for n in node.children(): childList.append(n) return childList # 调用函数 getChildren("/obj/geo1") getChildren("/") # 返回场景中所有节点的元组的函数 def getChildren(node): childList = [] for n in node.children(): childList.append(n) if n.children(): childList += getChildren(n) return childList
p4
# 操作节点的参数 # 获得参数 parm = hou.parm("./shpere1/radx") # 取参数值 parm.eval() # 修改值 parm.set(5.0) parmtuple = hou.parmTuple("./shpere1/rad") parmtuple.eval() parmtuple.set((5.0, 5.0, 5.0))
p5
可通过将界面元素(节点、参数、工具)拖进Python Shell获得其代码定义
# 取得节点的name hou.pwd().name() # 取得帮助 help(hou.pwd())
Python文档:Houdini - Help
# 将多个节点布局好 hou.pwd().layoutChildren() sphere.setParms({"radx": 3.0 , "tx": 2.0})
P6 - 创建工具栏工具:
1. New Shelf
Name - 小写 加 下划线
Label - 首字母大写
2. New Tool
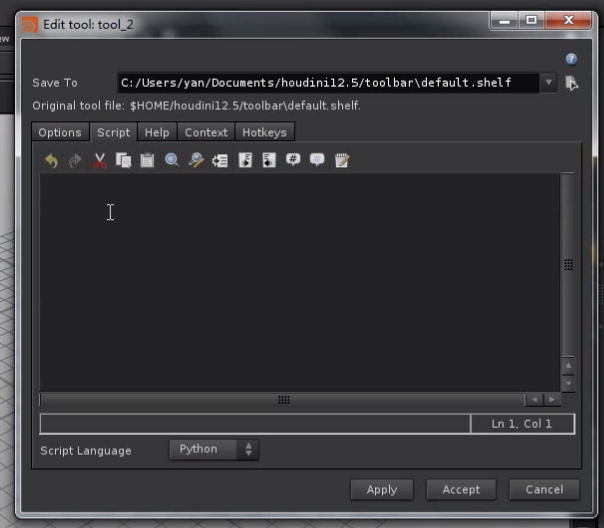
Options中指定Name和Label
Script中写代码
# 点击工具得到对话框 hou.ui.displayMessage("Hello Houdini !") # box_tool 创建一个box节点 geoNet = hou.ui.paneTabOfType(hou.paneTabType.NetworkEditor) position = geoNet.selectPosition() box = geoNet.pwd().createNode("box") box.setPosition(position)
P7 + P8 - 创建螺旋线工具:
1. 工具栏 kwargs参数(世界列表)
包含:按键信息、pane信息、View信息
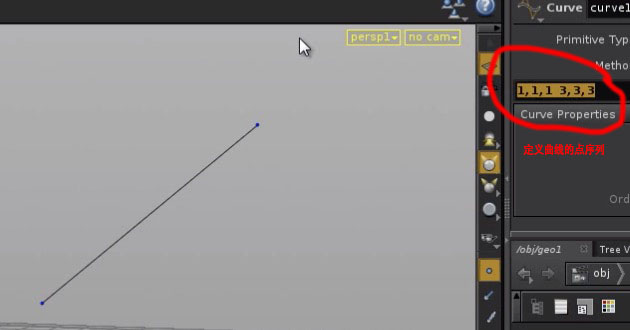
2. 自定义工具-螺旋线
from math import sin, cos geoNet = hou.ui.paneTabOfType(hou.paneTabType.NetworkEditor) spiral = geoNet.pwd().createNode("curve") coordsParm = spiral.parm("coords") inputParms = readMultiInput(message = "Enter parameters:" , input_labels = ["height", "lRadius", "uRadius", "frequency"], initial_contents = ["20", "10", "5", "3"]) height = float(inputParms[1][0]) lRadius = float(inputParms[1][1]) uRadius = float(inputParms[1][2]) frequency = float(inputParms[1][3]) coordsStr = "" radius = lRadius step = (lRadius - uRadius) / (height * frequency) for i in range(int(height * frequency)): px = str(radius * sin(i)) py = str(i / frequency) pz = str(radius * cos(i)) coordsStr += px + ", " + py + ", " + pz + " " radius -= step coordsParm.set(coordsStr)
P9 - P15 - 创建sop节点:
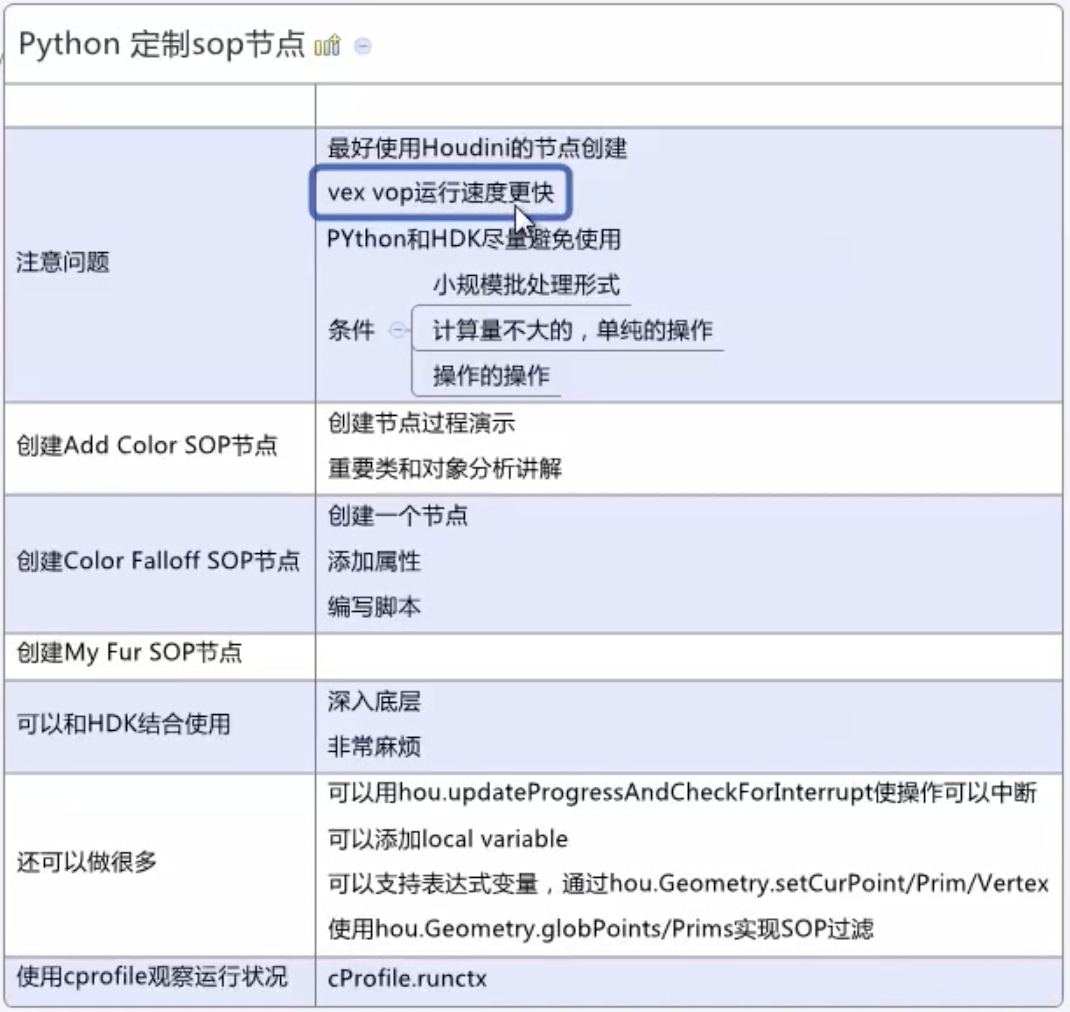
创建 “Add Color SOP” 节点
1. New Operator Type
2. 代码
import hou import random node = hou.pwd() geo = node.geometry() # 给定种子 保证每次运行otl得到的结果相同 random.seed(123) colorAttrib = geo.addAttrib(hou.attribTypr.Point, "Cd", (1.0, 1.0, 1.0)) color = hou.Color() pointsNum = len(geo.points()) for point in geo.points(): pos = point.position() px = pos[0] py = pos[1] + random.random() * random.choice([-1,1]) pz = pos[2] point.setPosition((px, py, pz)) value = float(point.number()) / pointsNum color.setHSV((value * 255, 1.0, 1.0)) point.setAttribValue(colorAttrib, color.rgb())
创建 “Color Falloff SOP” 节点
1. 添加节点,并为节点添加两个参数
2. Color Falloff 效果 - 代码
import hou import random node = hou.pwd() geo = node.geometry() # 给定种子 保证每次运行otl得到的结果相同 random.seed(123) colorAttrib = geo.addAttrib(hou.attribTypr.Point, "Cd", (1.0, 1.0, 1.0)) color = hou.Color() position = hou.Vector3(node.parmTuple("position").eval()) falloff = max( node.parm("falloff").eval(), 0.0001) for point in geo.points(): pos = point.position() px = pos[0] py = pos[1] # + random.random() * random.choice([-1,1]) pz = pos[2] point.setPosition((px, py, pz)) distance = (pos - position) value = min(distance / falloff , 1.0) color.setHSV((value * 255, 1.0, 1.0)) point.setAttribValue(colorAttrib, color.rgb())
3. Color Wave 效果 - 代码
import hou import random node = hou.pwd() geo = node.geometry() # 给定种子 保证每次运行otl得到的结果相同 random.seed(123) colorAttrib = geo.addAttrib(hou.attribTypr.Point, "Cd", (1.0, 1.0, 1.0)) color = hou.Color() position = hou.Vector3(node.parmTuple("position").eval()) falloff = max( node.parm("falloff").eval(), 0.0001) frequency = max( node.parm("frequency").eval(), 0.0001) height = node.parm("height").eval() for point in geo.points(): pos = point.position() distance = (pos - position) value = abs(sin( min(distance / falloff , 1.0) ) * frequency) color.setHSV((value * 255, 1.0, 1.0)) point.setAttribValue(colorAttrib, color.rgb()) px = pos[0] py = pos[1] + height * color.rgb()[1] pz = pos[2] point.setPosition((px, py, pz))
P13 动画
4. Color Falloff基础上 添加 法线 - 代码
#primitive type : mesh || NURBS import hou import random node = hou.pwd() geo = node.geometry() # 给定种子 保证每次运行otl得到的结果相同 random.seed(123) colorAttrib = geo.addAttrib(hou.attribTypr.Point, "Cd", (1.0, 1.0, 1.0)) color = hou.Color() position = hou.Vector3(node.parmTuple("position").eval()) falloff = max( node.parm("falloff").eval(), 0.0001) u_div = hou.evalParm("u_div") v_div = hou.evalParm("v_div") threshHold = hou.evalParm("threshHold") height = hou.evalParm("height") surface = geo.iterPrims()[0] for point in geo.iterPoints(): pos = point.position() px = pos[0] py = pos[1] pz = pos[2] point.setPosition((px, py, pz)) distance = (pos - position) value = min(distance / falloff , 1.0) color.setHSV((value * 255, 1.0, 1.0)) point.setAttribValue(colorAttrib, color.rgb()) for uNum in xrange(u_div + 1): u = float(uNum) / u_div for vNum in xrange(v_div + 1): v = float(vNum) / v_div uvColor = surface.attribValueAt("Cd", u, v) pos0 = surface.positionAt(u, v) pos1 = pos0 + surface.normalAt(u, v) * height ploy = geo.createPolygon() poly.setIsClosed(false) if uvColor[2] > threshHold: # 只给绿色的地方添加法线(0.9) for p in [pos0, pos10: point = geo.createPoint() point.setPosition(p) point.setAttribValue(colorAttrib, uvColor) poly.addVertex(point)
5. 将4完成的sop连接到 Add Color sop下
部分变量重复
修改4的代码为
#primitive type : mesh || NURBS import hou import random node = hou.pwd() geo = node.geometry() # 给定种子 保证每次运行otl得到的结果相同 random.seed(123) colorAttrib = geo.findPointAttrib("Cd") position = hou.Vector3(node.parmTuple("position").eval()) falloff = max( node.parm("falloff").eval(), 0.0001) u_div = hou.evalParm("u_div") v_div = hou.evalParm("v_div") threshHold = hou.evalParm("threshHold") height = hou.evalParm("height") surface = geo.iterPrims()[0] for uNum in xrange(u_div + 1): u = float(uNum) / u_div for vNum in xrange(v_div + 1): v = float(vNum) / v_div uvColor = surface.attribValueAt("Cd", u, v) pos0 = surface.positionAt(u, v) pos1 = pos0 + surface.normalAt(u, v) * height ploy = geo.createPolygon() poly.setIsClosed(false) if uvColor[2] > threshHold: # 只给绿色的地方添加法线(0.9) for p in [pos0, pos10: point = geo.createPoint() point.setPosition(p) point.setAttribValue(colorAttrib, uvColor) poly.addVertex(point)
再增加一个sop 来控制法线的粗细(width)
PS:
查看渲染过程中的点的信息 Details View(P12 19min)
可在Parameters中限制参数的取值范围 (P11 3min)
教程地址:https://www.bilibili.com/video/av33143116/?p=1
PS:程序员看这个教程代码的讲解过程,真的要急死。。。




