求pi方法总结
古今中外,求Pi的方法主要有三类主要的方法:
1,正多边形逼近法
2,迭代法(级数法)
3,蒙特卡洛法(随机模拟)
方法一不便用程序实现,方法二和三均可用程序语言实现,实现方法如下:
方法二(迭代法):
//求pi 使用迭代法 pi/4=1-1/3+1/5-1/7+1/9-。。。 #include<stdio.h> #include<math.h> int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) { double PI=0,term=1,n=1; int sign=1; while(fabs(term)>=pow(10,-6)){ PI+=term; n=n+2; sign=-sign; term=sign/n; } printf("PI=%10.8f\n",PI*4); return 0; }
//求pi,使用迭代法 pi/2=1+1/3+(1/3)*(2/5)+(1/3)*(2/5)*(3/7)+... //An=An-1*((n-1)/(2*n-1)) #include<stdio.h> #include<math.h> int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) { double PI=0,term=1,n=1; while(fabs(term)>=pow(10,-6)){ PI+=term; n++; term=term*((n-1)/(2*n-1)); } PI=PI*2; printf("PI=%10.8f\n",PI); return 0; }
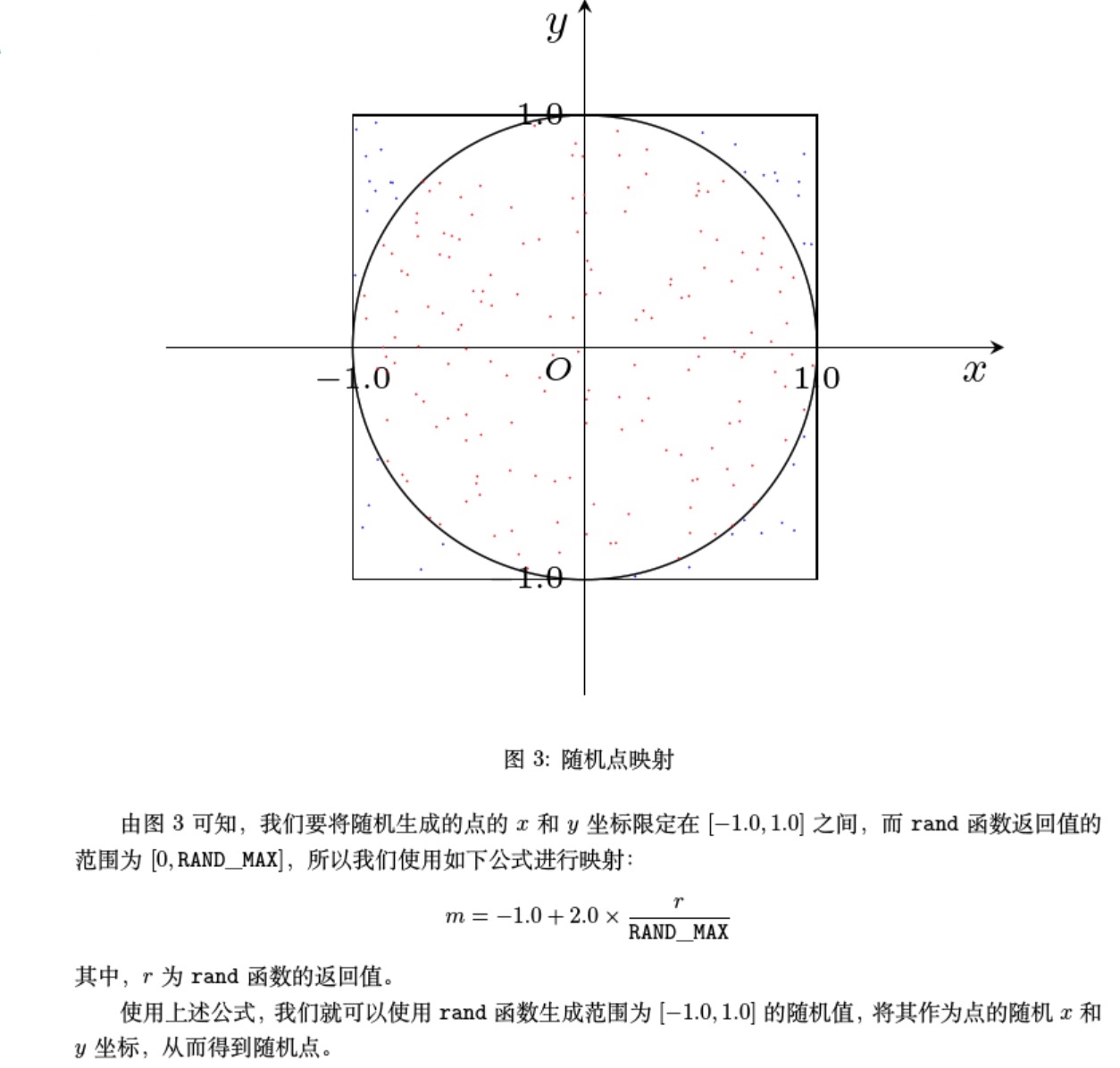
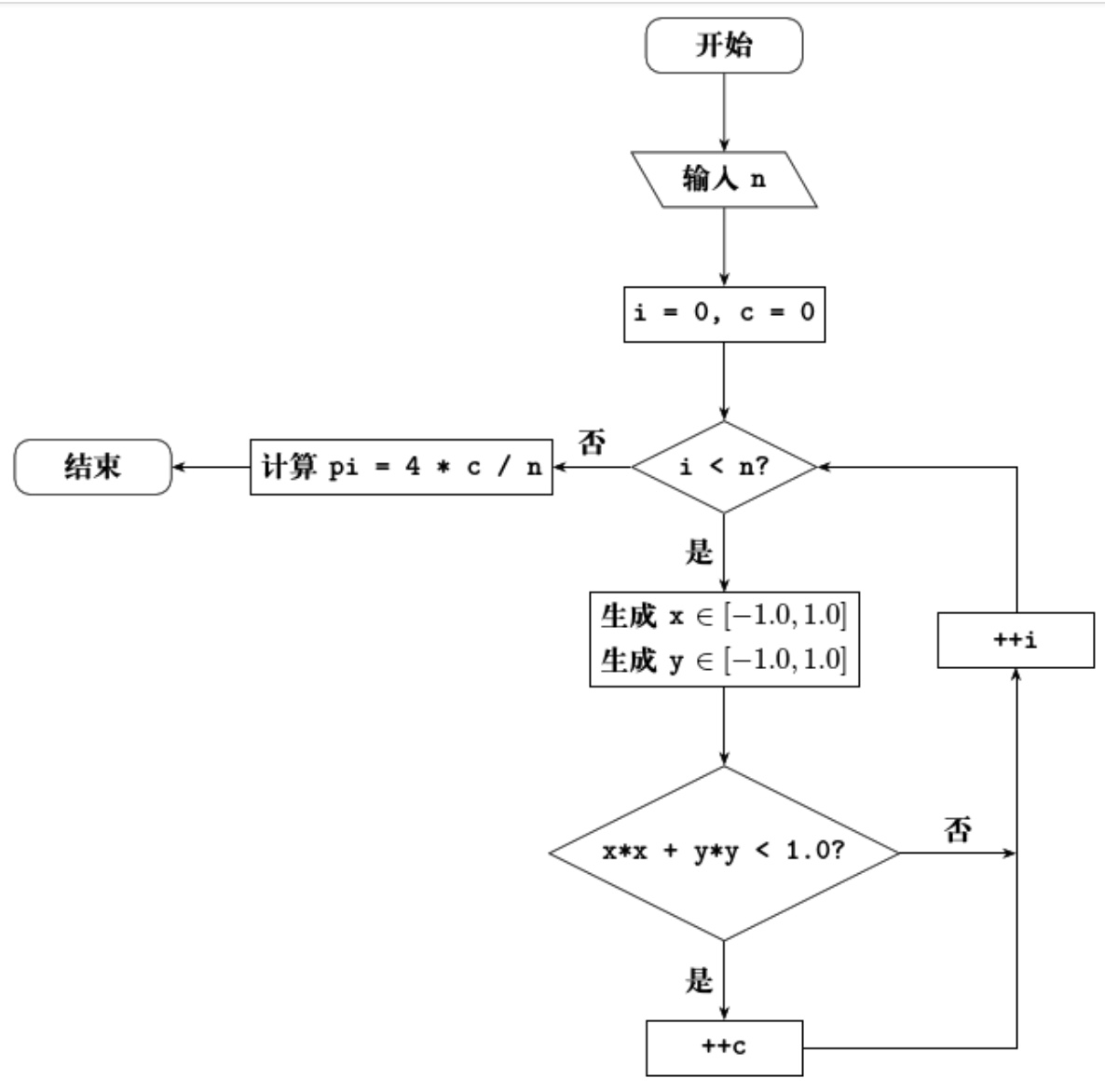
方法三(蒙特卡洛方法)【参考《算法与程序设计》一书】:
//求pi,使用蒙特卡洛法,使用随机模拟结果统计来求得pi的近似值 #include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<time.h> int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) { double n,c=0; //srand声明在stdlib.h,time声明在time.h //srand作用使用当前时间作为随机数发生器的种子值 srand(time(0)); scanf("%lf",&n); for (int i = 0; i <=n; ++i) { //RAND_MAX定义在stdlib.h中,代表rand函数返回的最大值 //rand函数定义在stdlib.h中 double x=-1.0+2.0*rand()/RAND_MAX; double y=-1.0+2.0*rand()/RAND_MAX; if (x*x+y*y<1.0) { ++c; } } double PI=(4*c)/n; printf("%f\n",PI); return 0; }