自己手动写一个RPC框架
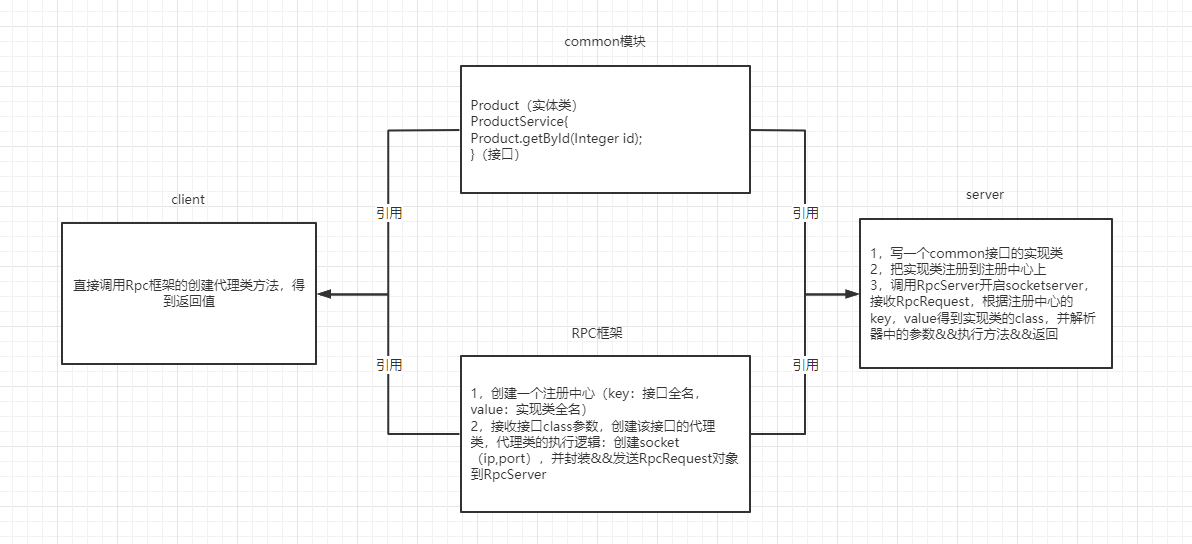
一,简单一点的过程解说图(不太清晰,凑合看吧)
Gitee仓库源码:https://gitee.com/fanjiangfeng/write-rpc-framwork
-
common模块
- 创建商品实体类和查询接口
-
RPC框架
- 创建一个注册中心(key:接口全名,value:实现类全名)
- 创建RpcRequest,装载信息,也要序列化,也是网络传输的一员
- 创建RpcServer,用来创建serversocket,接收client发来的内容【RpcRequest对象,从注册中心中根据key取出实现类class,然后根据参数和方法名利用反射来执行,返回执行结果】
-
client端
- 直接调用Rpc框架的创建代理类方法,得到返回值
-
server端
- 写一个common接口的实现类
- 把实现类注册到注册中心上
- 调用RpcServer开启socketserver,接收RpcRequest,根据注册中心的key,value得到实现类的class,并解析器中的参数&&执行方法&&返回
二,代码实现
1,rpc-common模块
新建Product类,记得实现序列化,因为要在网络中进行传输。
public class Product implements Serializable {
private String name;
private Integer price;
//...
}
新建查询的接口
public interface ProductService {
Product getById(Integer id);
}
2,rpc-framwork框架
首先一个注册中心,简单点,一个Map搞定
public class Registry {
public static HashMap<String,Class> map = new HashMap<String,Class>();
}
创建RpcRequest,装载信息,也要序列化,也是网络传输的一员。
public class RpcRequest implements Serializable {
private String className;
private String methodName;
private Class[] types;
private Object[] params;
//...
}
RpcServer,用来创建serversocket,接收client发来的内容(此处线程池只是用来提高效率)
public class RPCServer {
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
public void provide(int port){
try {
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(port);
while (true){
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
service.execute(new ProcessHandler(socket));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
ProcessHandler实现Runbale,重写run方法,写核心逻辑
public class ProcessHandler implements Runnable {
private Socket socket;
public ProcessHandler(Socket socket) {
this.socket = socket;
}
@Override
public void run() {
ObjectInputStream inputStream = null;
ObjectOutputStream outputStream = null;
//核心逻辑
try {
//解析消息
inputStream = new ObjectInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
RpcRequest rpcRequest = (RpcRequest) inputStream.readObject();
//反射
Class clazz = null;
//判断注册中心是否存在接口
if(Registry.map.containsKey(rpcRequest.getClassName())){
clazz = Registry.map.get(rpcRequest.getClassName());
}
Method method = clazz.getMethod(rpcRequest.getMethodName(), rpcRequest.getTypes());
Object result = method.invoke(clazz.newInstance(),rpcRequest.getParams());
//返回结果
outputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
outputStream.writeObject(result);
outputStream.flush();
}catch (Exception e){
}finally {
//关闭流
try {
if(inputStream!=null)inputStream.close();
if(outputStream!=null)outputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
创建RpcProxy类,用于创建接口的动态代理
public class RpcProxy<T> {
public T remoteCall(String host,int port,Class interfaces){
//动态代理
return (T)Proxy.newProxyInstance(interfaces.getClassLoader(),new Class[]{interfaces},new RemoteInvocationHandler(host,port,interfaces));
}
}
创建RemoteInvocationHandler(自定义的名称),重写invoke方法,写代理类要执行的逻辑。
public class RemoteInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
private String host;
private int port;
private Class interfaces;
public RemoteInvocationHandler(String host, int port, Class interfaces) {
this.host = host;
this.port = port;
this.interfaces = interfaces;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) {
//核心逻辑
//封装消息体
RpcRequest rpcRequest = new RpcRequest();
rpcRequest.setClassName(interfaces.getName());
rpcRequest.setMethodName(method.getName());
rpcRequest.setTypes(method.getParameterTypes());
rpcRequest.setParams(args);
Object result = null;
ObjectInputStream inputStream = null;
ObjectOutputStream outputStream = null;
try {
Socket socket = new Socket(host, port);
//发送消息
outputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
outputStream.writeObject(rpcRequest);
outputStream.flush();
//接收结果
inputStream = new ObjectInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
result = inputStream.readObject();
}catch (Exception e){
}finally {
//关闭流
try {
if(inputStream!=null)inputStream.close();
if(outputStream!=null)outputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return result;
}
}
3,rpc-server模块
写一个ProductService接口的实现类的具体逻辑
public class ProductServiceImpl implements ProductService {
@Override
public Product getById(Integer id) {
Product product = new Product();
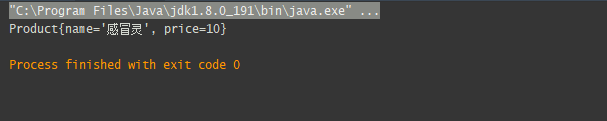
product.setName("感冒灵");
product.setPrice(10);
return product;
}
}
然后把接口和实现类注册到RPC的注册中心,然后通过RPC的RPCServer开启一个serversocket,监听某一个端口。
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Registry.map.put(ProductService.class.getName(),ProductServiceImpl.class);
new RPCServer().provide(9000);
}
}
4,rpc-client模块
直接发起对rpc-server的调用
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
RpcProxy rpcProxy = new RpcProxy();
ProductService service = (ProductService) rpcProxy.remoteCall("localhost",9000,ProductService.class);
System.out.println(service.getById(10).toString());
}
}
三,执行结果
-------------------------------------------
个性签名:独学而无友,则孤陋而寡闻。做一个灵魂有趣的人!
如果觉得这篇文章对你有小小的帮助的话,记得在右下角点个“推荐”哦,博主在此感谢!
万水千山总是情,打赏一分行不行,所以如果你心情还比较高兴,也是可以扫码打赏博主,哈哈哈(っ•̀ω•́)っ✎⁾⁾!



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 从HTTP原因短语缺失研究HTTP/2和HTTP/3的设计差异
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~
2020-03-14 手把手教你SpringBoot集成消息服务中间件RabbitMQ