C++模拟C#事件委托机制(二)
原文 来自于http://www.cnblogs.com/netssfy/archive/2010/02/02/1662056.html
为了解决非法地址访问的冲突,首先需要知道发生该错误的原因是什么
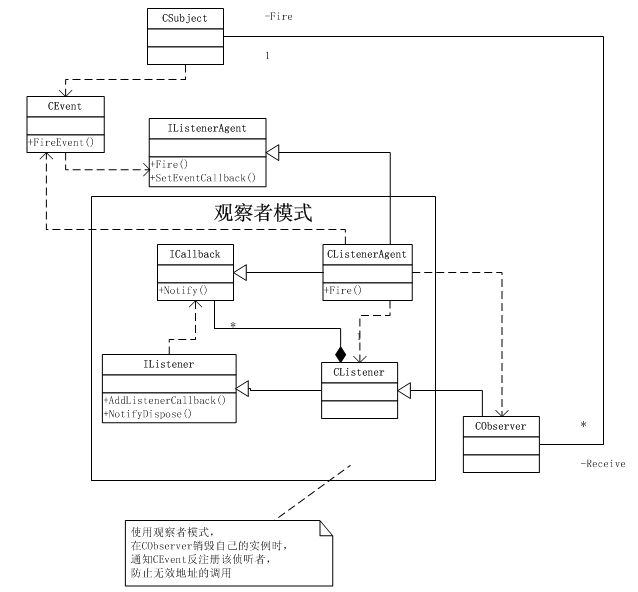
事件与委托的关系是1对多的,事件与委托对象实例的关系是多对多的,所以使用CListenerAgent将这种多对多的关系拆开。而每个CListenerAgent是事件与委托对象实例的一一对应
对于事件来说当事件本身销毁时,所有订阅的委托都应该销毁,否则存在内存泄漏。
对于委托对象实例来说,当本身销毁时,所有已经订阅的委托(可以订阅多个不同的事件)需要告知对应的事件,在事件发生时不用再通知它了,因为他已经不存在了。
所以实现这个的核心还是CListenerAgent,让CListenerAgent管理事件实例和委托对象实例,当他们销毁时可以及时的通过CListenerAgent去通知另一端。
同时,因为每个对象可以订阅多个事件,所以也需要一个类型帮助对象去管理CListenerAgent。
CListener孕育而生,所有想要订阅到CEvent类上的类型,都必须继承这个CListener,因为他会帮你去管理,所有的CListenerAgent。这样用户可以专注于自己的逻辑实现。
前面说过了一个对象可以订阅到多个事件上,那么CListenerAgent的第2个模板参数肯定会不同,那怎么让CListener管理各种不同的CListenerAgent呢?
答案还是接口。想想我们在CListener里管理CListenerAgent的作用是什么?只是为了CListener的派生类在销毁时能通过CListenerAgent去通知CEvent反订阅这个委托。
对,这里没有任何的其他类型相关的要求。所以设计一个接口
class IDispose
{
public:
/*Dispose, free memory*/
virtual void Dispose() = 0;
};
CListener 去会维护一个这个接口的LIST,而CListenerAgent则会实现这个接口。
Dispose的工作就是删除自己,并且将自己从CEvent和CListener的list中移除。
同样,CEvent也是在析构时依次调用Dispose去完成清理工作。
实现如下:
代码如下:
/*
Description:This library allow programmer use event feature like C# with C++ language
Author:SeigfriedY
Usage:
CEvent<CEventArgs> event;
CEventArgs args;
Observer* pO = new Observ er(); //Observer has a function : void Handler(CEventArgs)
CListenerAgent<Observer, CEventArgs>* agent = new CListenerAgent<Observer, CEventArgs>(pO, &Observer::Handler);
event += agent;
event(args);
event -= agent;
ps:CEventArgs is a argument type which define the type of event, it can be any type;
Note:
1.If the type would be a listener to subscribe some events on other type, it must inherit from CListener.
2.The return type of handler function must be void.
3.CListenerAgent should be create on heap(use new operator to create the instance)
4.Programmer can't and never to delete CListenerAgent's instance, the life cycle is depend on CEvent and the relative observer's instance
Design:
As one observer can subscribe on many different events, and one event can be subscribe from many different observer type, they are "N to N"
relationship.So need a class to decompose the one relationship into 2 like "1 to N" and "N to 1", this class is named CListenerAgent.
One observer can have multi CListenerAgent and one CEvent also can manage multi CListnerAgent.
CListenerAgent's responsibility is to build a "1 to 1" bridge between observer and CEvent.
Use interface to avoid the type-related, only the CListenerAgent need know the observer's concrete type in detail.
ClistenerAgent decrease the coupling between subject and observer.
User interface in internal to avoid type-related, So CEvent<ArgsT> only need know IListenerAgent<ArgsT> instead of CListenerAgent<ObserverT, ArgsT>.
Since CEvent only need to fire the event which contain the ArgsT, it needn't know the type of observer.This relationship is in CListenerAgent.
*/
#pragma once
#include <list>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/*Declaration*/
template<typename ArgsT>
class CEvent;
/*A sample arguments class*/
class CEventArgs
{
private:
void* _args;
public:
CEventArgs(void* args)
{
_args = args;
};
void* GetArgs()
{
return _args;
}
};
/*
The responsibility of ICallback interface is to Dispose
*/
class IDispose
{
public:
/*Dispose, free memory*/
virtual void Dispose() = 0;
};
/*The responsibility of IListener interface is to add ICallback into
CListener which implement this interface.*/
class IListener
{
public:
/*Add ICallback*/
virtual void AddListenerCallback(IDispose* agent) = 0;
/*When CListener is disposed, it will notify this event to all ICallback which has been added*/
virtual void NotifyDispose() = 0;
/*Remove the IDispose from list*/
virtual void Remove(IDispose* agent) = 0;
};
/*
The responsibility of IListenerAgent is:
1.When event has been fired, notify the listener to execute the event handler which has been subscribed
2.When CListenerAgent is being subscribed on event, set the event instance
*/
template<typename ArgsT>
class IListenerAgent : virtual public IDispose
{
public:
/*Fire the event*/
virtual void Fire(ArgsT) = 0;
/*Set the event instance*/
virtual void SetEventCallback(CEvent<ArgsT>* pEvent) = 0;
};
/*
This class help Observer class to manage the CListenerAgent class which subscribe to CEvent
Since CListener is inherited by user's observer class, so when initialize the CListenerAgent,
CListenerAgent will call IListener->AddListenerCallback(this), to register itself to CListener.
When CListener's destructor is called, it will notify all CListenerAgent that it managed to
dispose themselves
Note: User's observer class must inherit from this class if it want to be listenable.
*/
class CListener : public IListener
{
private:
list<IDispose *> _agents;
public:
CListener()
{
}
virtual ~CListener()
{
NotifyDispose();
};
private:
/*IListener*/
/*Add ICallback(CListenerAgent) and manage them*/
virtual void AddListenerCallback(IDispose* agent)
{
if (agent != NULL)
{
_agents.push_back(agent);
}
}
/*When destructor, notify all ICallback(CListenerAgent) to dispose themselves*/
virtual void NotifyDispose()
{
list<IDispose*>::iterator it, end;
IDispose* temp;
it = _agents.begin();
end = _agents.end();
for (it ; it != end ; )
{
temp = *it;
it++;
temp->Dispose();
}
}
/*Remove the agent from list*/
virtual void Remove(IDispose* agent)
{
_agents.remove(agent);
}
};
/*
The core class.This class set up a link between CEvent and CListener.
This class implement IListenerAgent<ArgsT> and ICallback
*/
template<typename ObserverT, typename ArgsT>
class CListenerAgent : virtual public IListenerAgent<ArgsT>
{
private:
/*The type of observer's handler which is to handle the event when event arise*/
typedef void (ObserverT::*ObserverDelegate)(ArgsT);
/*Two function pointers*/
ObserverDelegate _pObserverDelegate;
/*CListenerAgent keep these pointer to keep the contact between CEvent and observer*/
/*These two pointers point to the same memory area, of course, their value may not be equal.*/
ObserverT* _pObserver;
IListener* _pListener;
/*This point to the event instance which subscribe on*/
CEvent<ArgsT>* _pEvent;
public:
/*Default Constructor*/
CListenerAgent()
{
_pEvent = NULL;
_pObserverDelegate = NULL;
_pObserver = NULL;
}
/*Constructor*/
CListenerAgent(ObserverT* observer, ObserverDelegate d)
{
_pObserver = observer;
_pListener = (IListener*)_pObserver;
_pObserverDelegate = d;
_pEvent = NULL;
/*Register itself to CListener,*/
_pListener->AddListenerCallback((IDispose*)this);
}
private:
/*Destructor.Notify the CEvent to remove itself from the list*/
virtual ~CListenerAgent()
{
/*remove the agent from event*/
if (_pEvent != NULL)
{
(*_pEvent) -= ((IListenerAgent<ArgsT>*)this);
}
/*remove the agent from listener*/
if (_pListener != NULL)
{
_pListener->Remove((IDispose*)this);
}
}
/*IListenerAgent*/
/*Notify the observer to handle the event*/
virtual void Fire(ArgsT args)
{
if (_pObserver != NULL)
{
(_pObserver->*_pObserverDelegate)(args);
}
}
/*Keep the CEvent instance*/
void SetEventCallback(CEvent<ArgsT>* pEvent)
{
_pEvent = pEvent;
}
/*IDispose*/
virtual void Dispose()
{
delete this;
}
};
/*
CEvent class has 3 responsibility:
1.Provide the friendly operator like C#
2.When event arise, notify all listeners
3.When disposed, notify all CListenerAgent
*/
template<typename ArgsT>
class CEvent
{
private:
/*Class member handler type, use IListenerAgent to complete the work*/
typedef IListenerAgent<ArgsT>* Listener;
/*Global or static handler type*/
typedef void (*StaticListener)(ArgsT);
/*Hold all class member handlers in a list*/
list<Listener> _listeners;
/*Hold all global or static handlers in a list*/
list<StaticListener> _staticListeners;
public:
/*Default constructor*/
CEvent()
{
}
/*Default destructor*/
virtual ~CEvent()
{
list<Listener>::iterator it, end;
Listener temp;
it = _listeners.begin();
end = _listeners.end();
for (it ; it != end ;)
{
temp = *it;
it++;
((IDispose*)temp)->Dispose();
}
_listeners.clear();
_staticListeners.clear();
}
/*Subscribe class member listener*/
void operator+=(const Listener listener)
{
Subscribe(listener);
};
/*Subscribe global or static listener*/
void operator+=(const StaticListener listener)
{
Subscribe(listener);
}
/*Unsubscribe class member listener*/
void operator-=(const Listener listener)
{
Unsubscribe(listener);
};
/*Unsubscribe class member listener*/
void operator-=(const StaticListener listener)
{
Unsubscribe(listener);
}
/*Fire the event*/
void operator()(ArgsT args)
{
FireEvent(args);
}
private:
/*Unsubscribe the listener if be found in list*/
void Unsubscribe(Listener listener)
{
_listeners.remove(listener);
}
/*Unsubscribe the listener if be found in list*/
void Unsubscribe(StaticListener listener)
{
_staticListeners.remove(listener);
}
/*Fire the event*/
void FireEvent(ArgsT args)
{
list<Listener>::iterator it, end;
it = _listeners.begin();
end = _listeners.end();
for (it ; it != end ; it++)
{
((Listener)*it)->Fire(args);
}
list<StaticListener>::iterator it2, end2;
it2 = _staticListeners.begin();
end2 = _staticListeners.end();
for (it2 ; it2 != end2 ; it2++)
{
(*it2)(args);
}
}
/*Subscribe the listener if not be found in list*/
void Subscribe(Listener listener)
{
if (listener != NULL)
{
list<Listener>::iterator it, end;
it = _listeners.begin();
end = _listeners.end();
for (it ; it != end ; it++)
{
if ((*it) == listener)
{
return;
}
}
listener->SetEventCallback(this);
_listeners.push_back(listener);
}
};
/*Subscribe the listener if not be found in list*/
void Subscribe(StaticListener listener)
{
if (listener != NULL)
{
list<StaticListener>::iterator it, end;
it = _staticListeners.begin();
end = _staticListeners.end();
for (it ; it != end ; it++)
{
if ((*it) == listener)
{
return;
}
}
_staticListeners.push_back(listener);
}
};
};


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号