Spring Bean作用域
Bean的作用域
当在Spring中定义一个bean时,你必须声明该bean的作用域的选项。例如,为了强制Spring在每次需要时都产生一个新的bean实例,你应该申明bean的作用域属性为prototype。同理,如果你像让Spring在每次需要时都返回同一个bean实例,你应该声明bean的作用域的属性为sigleton。Spring框架支持以下五个作用域,如果你使用web-aware ApplicationContext时,其中三个是可用的。
| 作用域名称 | 描述 |
| sigleton | 该作用域将bean的定义限制在每一个SpringIoc容器中的一个单一实例 |
| prototype | 该作用域将单一bean的定义限制在任意数量的对象实例 |
| request | 该作用域将bean的定义限制为HTTP请求。只在web-awareSpringApplicationContext的上下文中有效 |
| session | 该作用域将 bean 的定义限制为 HTTP 会话。 只在web-aware Spring ApplicationContext的上下文中有效。 |
| global-session | 该作用域将 bean 的定义限制为 HTTP全局 会话。 只在web-aware Spring ApplicationContext的上下文中有效。 |
Singleton作用域:
如果作用域设置为singleton,那么Spring IoC容器刚好创建一个由该bean定义的对象的实例。该单一实例将存储在这种单例bean的高速缓存中,以及针对该bean的所有后续的请求和引用的返回缓存对象。默认的作用域始终是singleton,但是当仅仅需要bean的一个实例时,你可以在bean的配置文件中设置作用域的属性为singleton,:
<bean id="helloWorld1" class="com.tutorialspoint.HelloWorld" scope="singleton"> <property name="message" value="hello fpc!"></property> </bean>
下面是MainApp.java文件中的内容:
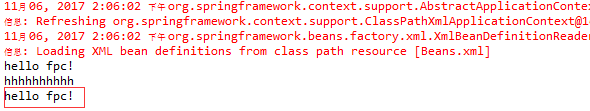
public class MainApp { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Beans.xml"); // XmlBeanFactory factory = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("Beans.xml")); // HelloWorld h = (HelloWorld) factory.getBean("helloWorld"); HelloWorld h = (HelloWorld) context.getBean("helloWorld1"); System.out.println(h.getMessage()); h.setMessage("hhhhhhhhhh"); System.out.println(h.getMessage()); HelloWorld h1 = (HelloWorld) context.getBean("helloWorld1"); System.out.println(h1.getMessage()); } }
一旦创建源码和bean配置文件完成后,我们就可以运行该应用程序。上述程序将输出以下结果:
prototype作用域
如果作用域设置为prototype,那么每次特定的bean发出请求时Spring IoC容器就创建对象的新的Bean实例。一般来说,满状态的bean使用prototype作用域和没有状态的bean使用singleton作用域。
为了定义prototype作用域,你可以在bean的配置文件中设置作用域的属性为prototype,如下图所示:
<bean id="helloWorld1" class="com.tutorialspoint.HelloWorld" scope="prototype"> <property name="message" value="hello fpc!"></property> </bean>
下面是MainApp.java文件的内容:
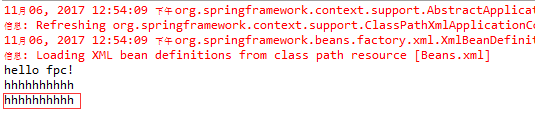
public class MainApp { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Beans.xml"); // XmlBeanFactory factory = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("Beans.xml")); // HelloWorld h = (HelloWorld) factory.getBean("helloWorld"); HelloWorld h = (HelloWorld) context.getBean("helloWorld1"); System.out.println(h.getMessage()); h.setMessage("hhhhhhhhhh"); System.out.println(h.getMessage()); HelloWorld h1 = (HelloWorld) context.getBean("helloWorld1"); System.out.println(h1.getMessage()); } }
运行的结果为: