Tomcat启动流程
1. 首先去Tomcat的目录下载它的源码包
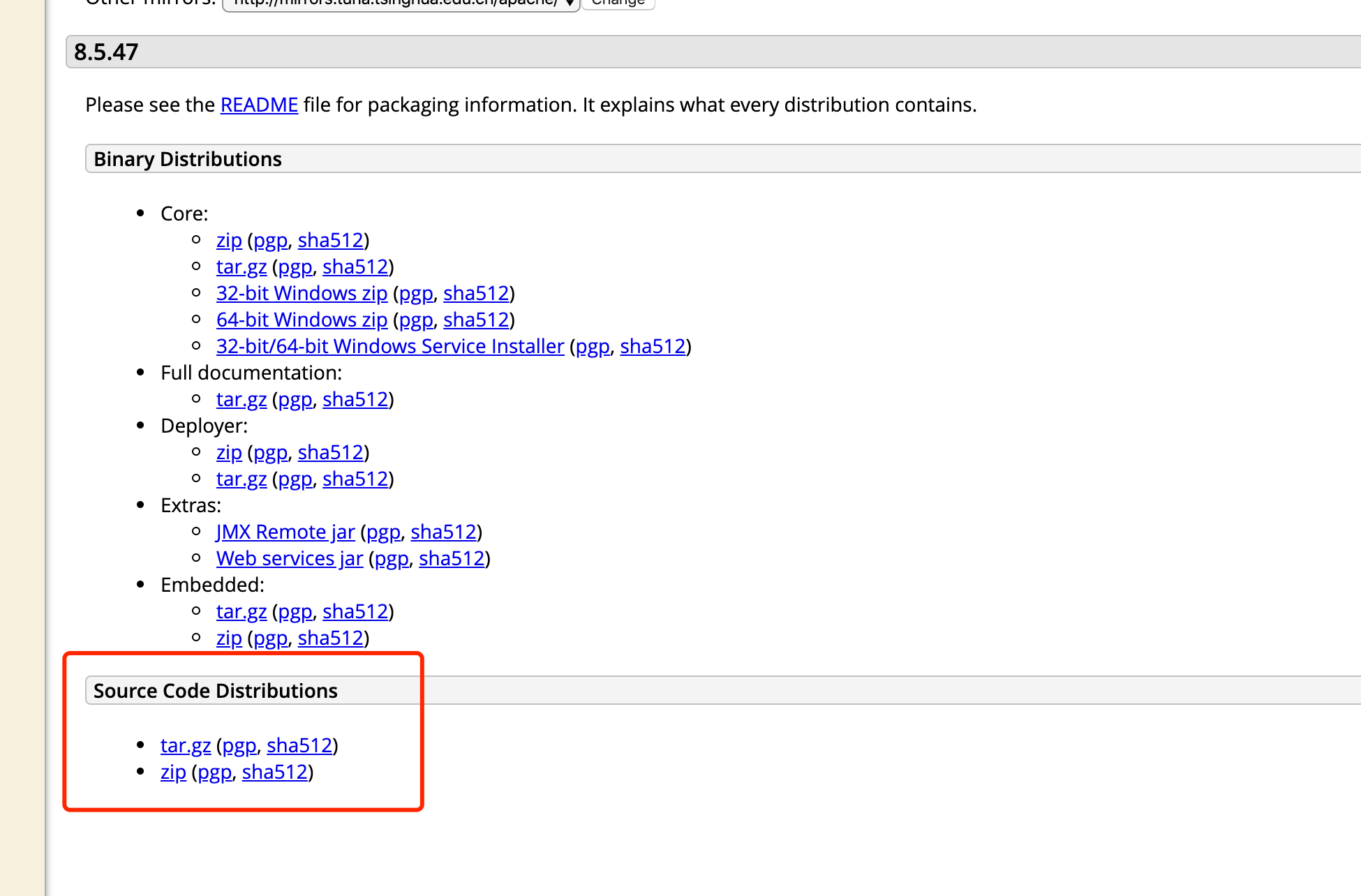
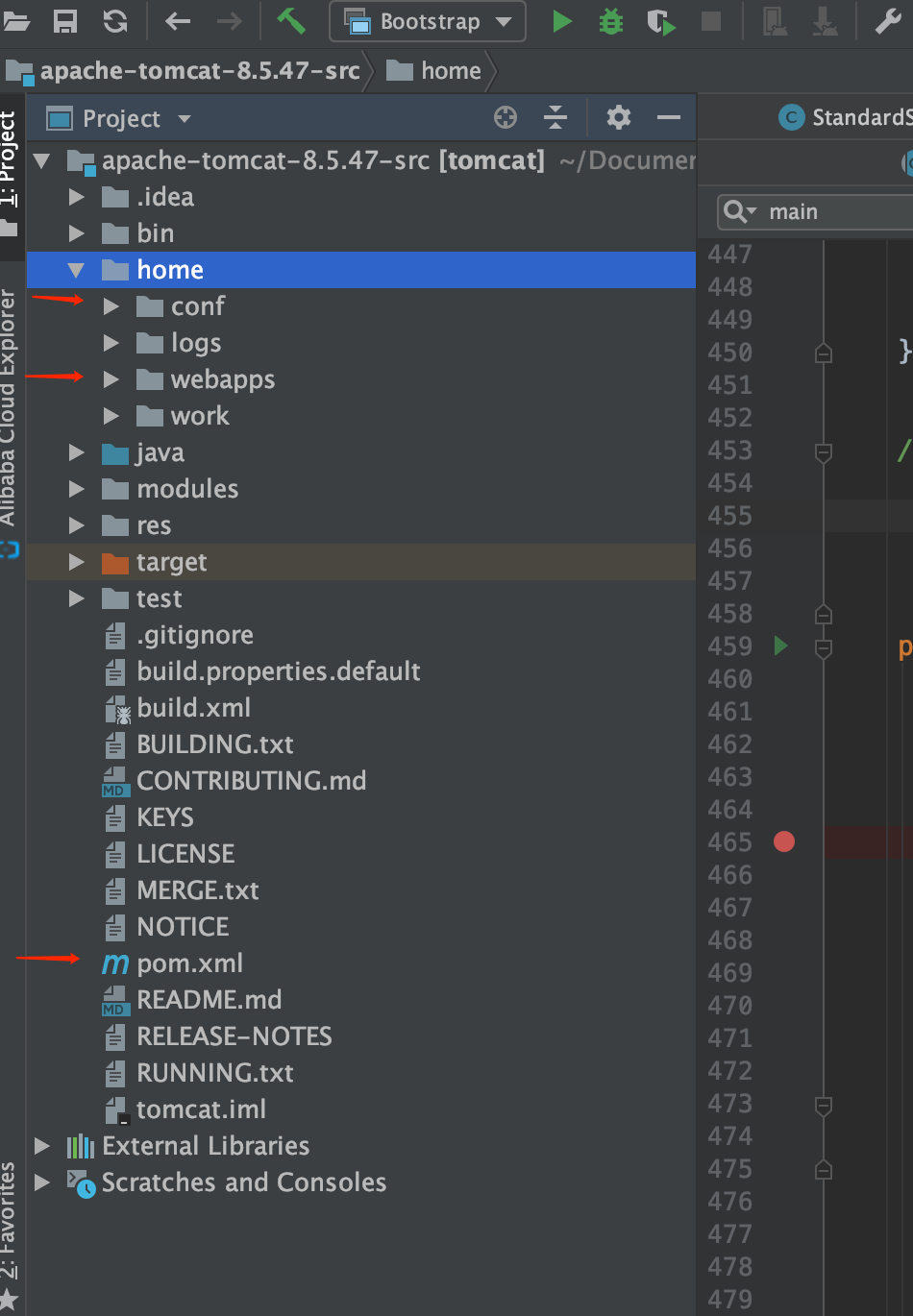
2. 把此项目解压之后,转换成maven的项目。创建pom.xml文件,以及创建home的目录,再把原先存在的conf目录和webapps目录拷贝至home目录下
3. pom.xml加入必要的Tomcat的依赖
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 3 xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd"> 4 5 <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> 6 <packaging>war</packaging> 7 8 <groupId>com.foreign</groupId> 9 <artifactId>tomcat</artifactId> 10 11 <name>Tomcat8.5</name> 12 <version>8.5</version> 13 14 15 <build> 16 <finalName>Tomcat8.5</finalName> 17 <sourceDirectory>java</sourceDirectory> 18 <resources> 19 <resource> 20 <directory>java</directory> 21 </resource> 22 </resources> 23 <plugins> 24 <plugin> 25 <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> 26 <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> 27 <version>2.3</version> 28 <configuration> 29 <encoding>UTF-8</encoding> 30 <source>1.8</source> 31 <target>1.8</target> 32 </configuration> 33 </plugin> 34 </plugins> 35 </build> 36 <dependencies> 37 <dependency> 38 <groupId>junit</groupId> 39 <artifactId>junit</artifactId> 40 <version>4.12</version> 41 <scope>test</scope> 42 </dependency> 43 <dependency> 44 <groupId>org.easymock</groupId> 45 <artifactId>easymock</artifactId> 46 <version>3.4</version> 47 </dependency> 48 <dependency> 49 <groupId>ant</groupId> 50 <artifactId>ant</artifactId> 51 <version>1.7.0</version> 52 </dependency> 53 <dependency> 54 <groupId>wsdl4j</groupId> 55 <artifactId>wsdl4j</artifactId> 56 <version>1.6.2</version> 57 </dependency> 58 <dependency> 59 <groupId>javax.xml</groupId> 60 <artifactId>jaxrpc</artifactId> 61 <version>1.1</version> 62 </dependency> 63 <dependency> 64 <groupId>org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler</groupId> 65 <artifactId>ecj</artifactId> 66 <version>4.5.1</version> 67 </dependency> 68 </dependencies> 69 </project>
4. 在ContextConfig类下加入解析jsp的代码

1 context.addServletContainerInitializer(new JasperInitializer(), null);
5. 创建java的应用程序启动
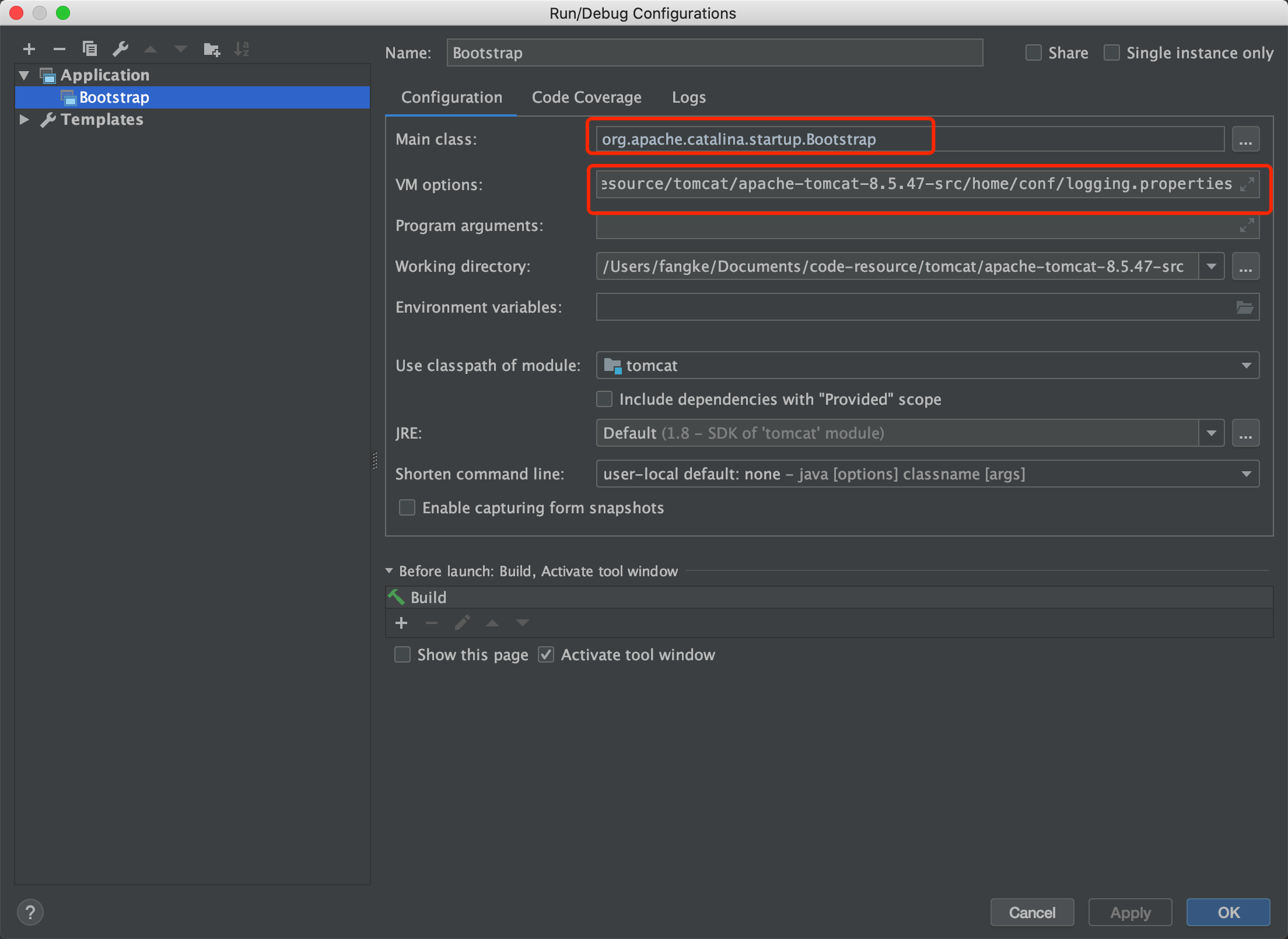
6. VM options
1 -Dcatalina.home=/Users/fangke/Documents/code-resource/tomcat/apache-tomcat-8.5.47-src/home 2 -Dcatalina.base=/Users/fangke/Documents/code-resource/tomcat/apache-tomcat-8.5.47-src/home 3 -Djava.util.logging.manager=org.apache.juli.ClassLoaderLogManager
4 -Djava.util.logging.config.file=/Users/fangke/Documents/code-resource/tomcat/apache-tomcat-8.5.47-src/home/conf/logging.properties
7. 分析下tomcat的启动流程
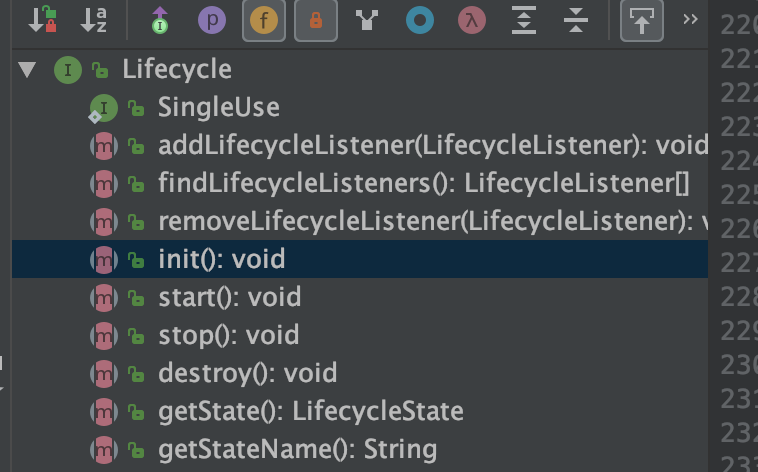
8. 其实tomcat采用了模版方法的设计模式,把公共的方法init,start,destory,stop等方法抽取到了Lifecycle的接口中,这样就能确定执行流程
9. Bootstrap类的main方法会创建一个init方法
1 public static void main(String args[]) { 2 3 if (daemon == null) { 4 // Don't set daemon until init() has completed 5 Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap(); 6 try { 7 bootstrap.init(); 8 } catch (Throwable t) { 9 handleThrowable(t); 10 t.printStackTrace(); 11 return; 12 } 13 daemon = bootstrap;
10. 该方法会通过反射创建出一个Catalina的load方法
1 public void init() throws Exception { 2 3 initClassLoaders(); 4 5 Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(catalinaLoader); 6 7 SecurityClassLoad.securityClassLoad(catalinaLoader); 8 9 // Load our startup class and call its process() method 10 if (log.isDebugEnabled()) 11 log.debug("Loading startup class"); 12 Class<?> startupClass = catalinaLoader.loadClass("org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina"); 13 Object startupInstance = startupClass.getConstructor().newInstance(); 14 15 // Set the shared extensions class loader 16 if (log.isDebugEnabled()) 17 log.debug("Setting startup class properties"); 18 String methodName = "setParentClassLoader"; 19 Class<?> paramTypes[] = new Class[1]; 20 paramTypes[0] = Class.forName("java.lang.ClassLoader"); 21 Object paramValues[] = new Object[1]; 22 paramValues[0] = sharedLoader; 23 Method method = 24 startupInstance.getClass().getMethod(methodName, paramTypes); 25 //通过反射调用catalina中的load方法 26 method.invoke(startupInstance, paramValues); 27 28 catalinaDaemon = startupInstance; 29 30 }
11. Catalina的load方法先去解析Tomcat的Server.xml配置文件,然后会去调用server的init方法
1 public void load() { 2 3 if (loaded) { 4 return; 5 } 6 loaded = true; 7 8 long t1 = System.nanoTime(); 9 10 initDirs(); 11 12 // Before digester - it may be needed 13 initNaming(); 14 15 // Create and execute our Digester 16 //解析tomcat的xml文件 17 Digester digester = createStartDigester();
1 // Start the new server 2 try { 3 //调用server的init方法 4 getServer().init(); 5 } catch (LifecycleException e) { 6 if (Boolean.getBoolean("org.apache.catalina.startup.EXIT_ON_INIT_FAILURE")) { 7 throw new java.lang.Error(e); 8 } else { 9 log.error("Catalina.start", e); 10 } 11 }
12. StanderServer里面会去调用多个service的init方法
1 // Initialize our defined Services 2 for (int i = 0; i < services.length; i++) { 3 //调用了N个service的init方法 4 services[i].init(); 5 }
13. StanderService里面会分别去调用engine,executor,connector的init方法
1 @Override 2 protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException { 3 4 super.initInternal(); 5 6 if (engine != null) { 7 //调用engine的init方法 8 engine.init(); 9 } 10 11 // Initialize any Executors 12 for (Executor executor : findExecutors()) { 13 if (executor instanceof JmxEnabled) { 14 ((JmxEnabled) executor).setDomain(getDomain()); 15 } 16 //调用executor的init方法 17 executor.init(); 18 } 19 20 // Initialize mapper listener 21 mapperListener.init(); 22 23 // Initialize our defined Connectors 24 synchronized (connectorsLock) { 25 for (Connector connector : connectors) { 26 try { 27 //调用connector的init方法 28 connector.init(); 29 } catch (Exception e) { 30 String message = sm.getString( 31 "standardService.connector.initFailed", connector); 32 log.error(message, e); 33 34 if (Boolean.getBoolean("org.apache.catalina.startup.EXIT_ON_INIT_FAILURE")) 35 throw new LifecycleException(message); 36 } 37 } 38 } 39 }
14. 直接到connector里面会去调用ProtocolHandler的init方法
1 try { 2 //调用protocolHandler的init方法 3 protocolHandler.init(); 4 } catch (Exception e) { 5 throw new LifecycleException( 6 sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerInitializationFailed"), e); 7 }
15. 会去调用endpoint的init方法
1 public void init() throws Exception { 2 if (getLog().isInfoEnabled()) { 3 getLog().info(sm.getString("abstractProtocolHandler.init", getName())); 4 } 5 6 if (oname == null) { 7 // Component not pre-registered so register it 8 oname = createObjectName(); 9 if (oname != null) { 10 Registry.getRegistry(null, null).registerComponent(this, oname, null); 11 } 12 } 13 14 if (this.domain != null) { 15 rgOname = new ObjectName(domain + ":type=GlobalRequestProcessor,name=" + getName()); 16 Registry.getRegistry(null, null).registerComponent( 17 getHandler().getGlobal(), rgOname, null); 18 } 19 20 String endpointName = getName(); 21 endpoint.setName(endpointName.substring(1, endpointName.length()-1)); 22 endpoint.setDomain(domain); 23 24 //调用了endpoint的init方法 25 endpoint.init(); 26 }
16. endpoint里面的bind方法会去绑定8080 8089端口
1 @Override 2 public void bind() throws Exception { 3 //绑定监听的端口号InetSocketAddress 4 if (!getUseInheritedChannel()) { 5 serverSock = ServerSocketChannel.open(); 6 socketProperties.setProperties(serverSock.socket()); 7 InetSocketAddress addr = (getAddress()!=null?new InetSocketAddress(getAddress(),getPort()):new InetSocketAddress(getPort())); 8 serverSock.socket().bind(addr,getAcceptCount());
17. 至此init方法走完,会回到Bootstrap方法执行start方法,以此顺序继续执行所有的start方法
1 public void start() 2 throws Exception { 3 if( catalinaDaemon==null ) init(); 4 5 Method method = catalinaDaemon.getClass().getMethod("start", (Class [] )null); 6 //通过反射调用catalina的start方法 7 method.invoke(catalinaDaemon, (Object [])null); 8 9 }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号