R图表入门
R图表入门
R语言最强的功能就是统计和作图了,在学习了基本语法之后,博主马上体验了一下R的图表功能
条形图
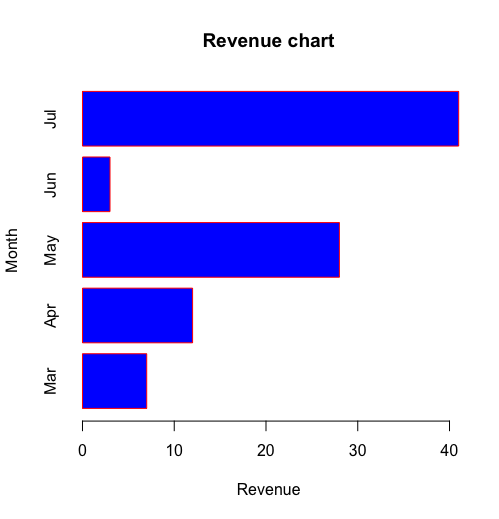
例1
H = c(7,12,28,3,41)
M = c("Mar","Apr","May","Jun","Jul")
barplot(H, #数据集
names.arg = M, #坐标项名称
xlab = "Revenue", #坐标标签
ylab = "Month", #坐标标签
col = "blue", #主体颜色
border = "red", #边缘颜色
main = "Revenue chart", #标题
horiz = TRUE) #水平方向
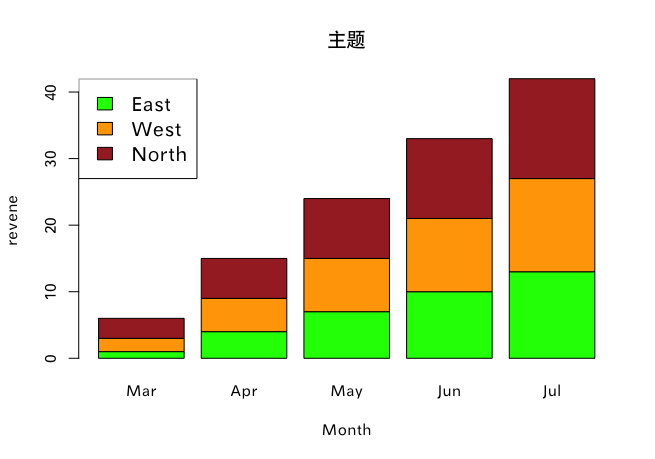
例2
colors = c("green","orange","brown")
months = c("Mar","Apr","May","Jun","Jul")
regions = c("East","West","North")
values = matrix(1:15,nrow = 3)
#调用系统字体显示中
#这里使用了黑体
par( family = 'Hei')
barplot(values, main = "主题",
names.arg = months,
xlab = "Month",
ylab = "revene",
col = colors)
legend("topleft",regions,
cex = 1.3,
fill = colors)
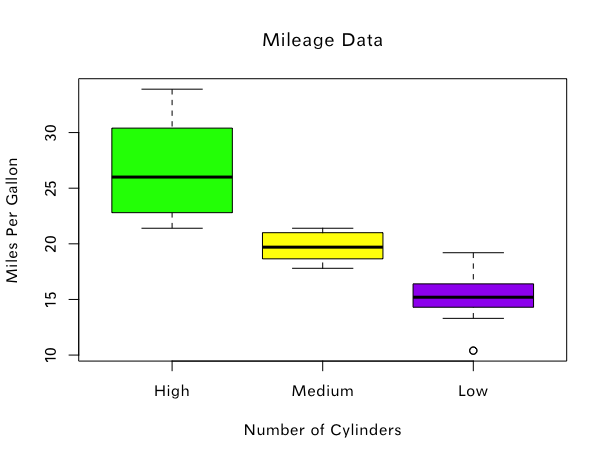
箱式图
input = mtcars[,c('mpg','cyl')] #取mtcars做测试
boxplot(mpg ~ cyl, #mpg关于不同cyl的的分布
data = mtcars,
xlab = "Number of Cylinders",
ylab = "Miles Per Gallon",
main = "Mileage Data",
# notch = TRUE, #带槽的图
# varwidth = FALSE,
col = c("green","yellow","purple"),
names = c("High","Medium","Low"))
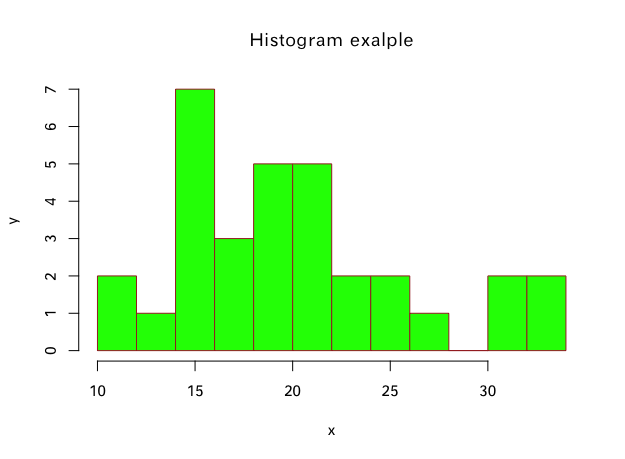
直方图
input = mtcars[,c('mpg')] #取mtcars做测试
hist(
input,
main = "Histogram exalple",
xlab = "x",
ylab = "y",
col = "green",
border = "brown",
breaks = 10 #分割10次,共11段
)
print(input)
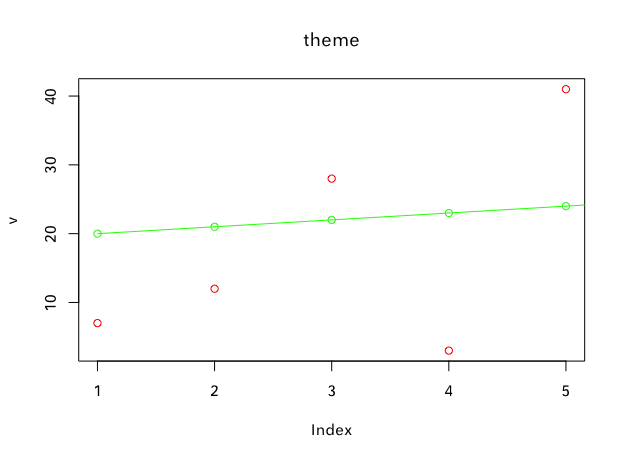
折线图&散点图
v = c(7,12,28,3,41)
#在没有y的情况下,横坐标默认为1,2,3……
#type为图像类型,p为点,l为线,o为点线
plot(v, type = "p", col = "red", main = "theme")
#lines函数可以画多条线
lines(20:50,type = "o", col = "green")
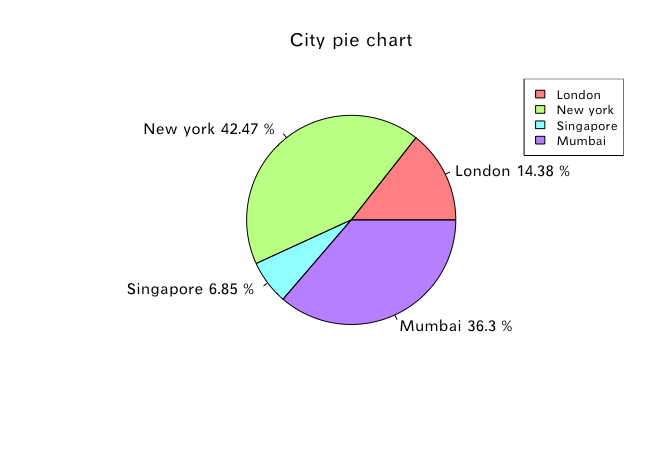
饼图
例1
x = c(21,62,10,53)
labels = c("London", "New york", "Singapore", "Mumbai")
labels = c("London", "New york", "Singapore", "Mumbai")
piepercent = paste( round(100*x/sum(x), digits = 2),'%',seq = '') #计算百分比
pie(x, paste(labels,piepercent),
main = "City pie chart",
#可以使用彩虹函数设置颜色
col = rainbow(length(x),alpha = 0.5)
)
legend("topright",
labels,
cex = 0.8, #调整大小,1为正常
fill = rainbow(length(x),alpha = 0.5))
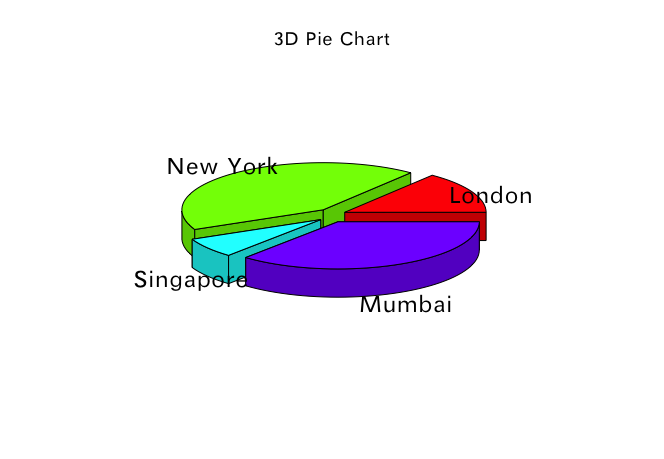
例2
3D饼图
# library(plotrix)
x = c(21,62,10,53)
lbl = c("London","New York","Singapore","Mumbai")
plotrix::pie3D(x,labels = lbl,explode = 0.1, main = "3D Pie Chart")
保存到本地
H = c(7,12,28,3,41)
# 创建一个图形的Device
png(file = "barchart.png")
# 在Device上作图
barplot(H)
# 关闭Device(保存)
dev.off()
小结
博主这里学习了R语言基础的作图方法,大体上已经够用,更高阶的应该要请大名鼎鼎的ggplot2登场,以后有机会再学习。


