three.js 入门学习(一)
webGl和three.js
http://webgl3d.cn/pages/aac9ab/
图形学算法
Web3D
WebGPU
下载
yarn add three @types/three
使用
import * as THREE from 'three';
onst scene = new THREE.Scene();
仅导入你所需要的部分
import { Scene } from 'three';

一个初始化的demo
场景、相机和渲染器, 设置大小, 添加到页面上
const scene = new THREE.Scene();
const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera( 75, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 0.1, 1000 );
const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer();
renderer.setSize( window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight );
document.body.appendChild( renderer.domElement );
添加一个立方体, 设置样式, 网格对象放入到我们的场景中, 物体将会添加到坐标中, 设置层级
const geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry( 1, 1, 1 );
const material = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial( { color: 0x00ff00 } );
const cube = new THREE.Mesh( geometry, material );
scene.add( cube );
camera.position.z = 5;
循环场景, 添加
function animate() {
requestAnimationFrame( animate );
renderer.render( scene, camera );
}
animate();
让立方体动起来(添加到animate()函数中renderer.render调用的上方)
cube.rotation.x += 0.01;
cube.rotation.y += 0.01;
https://github.com/pmndrs/postprocessing
后期
WebGLRenderer
渲染器
场景Scene、相机Camera、渲染器Renderer
var renderer: THREE.WebGLRenderer, scene: THREE.Scene | THREE.Object3D<THREE.Event>, camera: any, composer,
circle: THREE.Object3D<THREE.Event>, skelet: any, particle: THREE.Object3D<THREE.Event>;
window.onload = function () {
init();
animate();
// 设置相机控件轨道控制器OrbitControls
const controls = new OrbitControls(camera, renderer.domElement);
// 如果OrbitControls改变了相机参数,重新调用渲染器渲染三维场景
controls.addEventListener('change', function () {
renderer.render(scene, camera); //执行渲染操作
});//监听鼠标、键盘事件
}
function init() {
// antialias - 是否执行抗锯齿。默认为false.
// alpha 默认为false 颜色透明度
renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({antialias: true, alpha: true});
// 设置设备像素比
// window.devicePixelRatio是设备上物理像素和设备独立像素,
// 公式表示就是:window.devicePixelRatio = 物理像素 / dips
// dip或dp 与屏幕密度有关。dip可以用来辅助区分视网膜设备还是非视网膜设备。
renderer.setPixelRatio((window.devicePixelRatio) ? window.devicePixelRatio : 1);
// 设置大小
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
renderer.autoClear = false;
// 设置颜色及其透明度
renderer.setClearColor(0x000000, 0.0);
// 把渲染器的dom添加到页面上
(document.getElementById('canvas') as any).appendChild(renderer.domElement);
// 场景
scene = new THREE.Scene();
// 相机
/*
* fov — 摄像机视锥体垂直视野角度
aspect — 摄像机视锥体长宽比
near — 摄像机视锥体近端面
far — 摄像机视锥体远端面
* */
camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(75, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 1, 1000);
// 设置相机的位置
camera.position.z = 400;
// 把相机添加到场景中
scene.add(camera);
// 圆
circle = new THREE.Object3D();
skelet = new THREE.Object3D();
// 基类, 提供一些属性和方法来对三维空间中的物体进行操纵
particle = new THREE.Object3D();
scene.add(circle);
scene.add(skelet);
scene.add(particle);
// 四面缓冲几何体
var geometry = new THREE.TetrahedronGeometry(2, 0);
// 二十面缓冲几何体
// 二十面体的半径,默认为1。
// 默认值为0。将这个值设为一个大于0的数将会为它增加一些顶点,使其不再是一个二十面体。当这个值大于1的时候,实际上它将变成一个球体。
var geom = new THREE.IcosahedronGeometry(7, 1);
// 半径大一些
var geom2 = new THREE.IcosahedronGeometry(15, 1);
// 材质, 受高光影响的材质
var material = new THREE.MeshPhongMaterial({
color: 0xffffff,
flatShading: true // 定义材质是否使用平面着色进行渲染
});
for (var i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
// 网格模型, 一个几何体, 一个材质
var mesh = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material);
// 随机设置位置
mesh.position.set(Math.random() - 0.5, Math.random() - 0.5, Math.random() - 0.5).normalize();
// 将该向量与所传入的标量s进行相乘
mesh.position.multiplyScalar(70 + (Math.random() * 700));
//设置旋转角度
mesh.rotation.set(Math.random() * 2, Math.random() * 2, Math.random() * 2);
// 把物体添加到基类中, 也可以直接添加到scene 中
particle.add(mesh);
}
var mat = new THREE.MeshPhongMaterial({
color: 0xffffff,
flatShading: true
});
var mat2 = new THREE.MeshPhongMaterial({
color: 0xffffff,
wireframe: true,// 这个是设置骨架
side: THREE.DoubleSide
});
// 这个 是小的
var planet = new THREE.Mesh(geom, mat);
// 小多面体放大的倍数
planet.scale.x = planet.scale.y = planet.scale.z = 16;
circle.add(planet);
// 这个是大的骨架
var planet2 = new THREE.Mesh(geom2, mat2);
// 大多面体放大的倍数
planet2.scale.x = planet2.scale.y = planet2.scale.z = 10;
skelet.add(planet2);
// 环境光
var ambientLight = new THREE.AmbientLight(0x999999);
scene.add(ambientLight);
var lights = [];
// 加入三个不同平行光, 展示不同的颜色
// 平行光
lights[0] = new THREE.DirectionalLight(0xffffff, 1);
// 位置
lights[0].position.set(1, 0, 0);
lights[1] = new THREE.DirectionalLight(0x11E8BB, 1);
lights[1].position.set(0.75, 1, 0.5);
lights[2] = new THREE.DirectionalLight(0x8200C9, 1);
lights[2].position.set(-0.75, -1, 0.5);
scene.add(lights[0]);
scene.add(lights[1]);
scene.add(lights[2]);
window.addEventListener('resize', onWindowResize, false);
};
function onWindowResize() {
// 设置相机的长宽比
camera.aspect = window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight;
// 更新摄像机投影矩阵。在任何参数被改变以后必须被调用。
camera.updateProjectionMatrix();
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth-100, window.innerHeight-100);
}
function animate() {
requestAnimationFrame(animate);
// 设置三个网格体的旋转数据
particle.rotation.x += 0.0000;
particle.rotation.y -= 0.0040;
circle.rotation.x -= 0.0020;
circle.rotation.y -= 0.0030;
skelet.rotation.x -= 0.0010;
skelet.rotation.y += 0.0020;
// 渲染器清除颜色、深度或模板缓存
renderer.clear();
renderer.render(scene, camera)
}
outputEncoding
outputEncoding属性控制输出渲染编码。默认情况下,outputEncoding的值为THREE.LinearEncoding,看起来还行但是不真实,建议将值改为`THREE.sRGBEncoding
圆环缓冲扭结几何体
const canvas: any = document.getElementById("canvas");
let camera: any, scene: any, renderer: any, controls: any;
let geometry, material, mesh: any;
let ww, hh;
const size = 3;
ww = document.body.clientWidth / 2 / window.devicePixelRatio;
hh = ww;
// 场景
scene = new THREE.Scene();
// 渲染器
renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({
antialias: true,//抗锯齿
alpha: true // 是否透明
});
// 把渲染器的dom添加到页面上
(document.getElementById('canvas') as any).appendChild(renderer.domElement);
// // 设置设备像素比
renderer.setPixelRatio(window.devicePixelRatio);
// 设置大小
renderer.setSize(ww, hh, false);
// outputEncoding默认是LinearEncoding看起来还行但是不真实,可以设置为sRGBEncoding 会更自然
renderer.outputEncoding = THREE.sRGBEncoding;
// 摄像机
camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(40, ww / hh, 0.01, size * 30);
// 设置摄像机的位置
camera.position.set(0, size, size * 6);
// 设置网格模型对象的坐标原点
camera.lookAt(0, 0, 0);
// 环境光
const light = new THREE.AmbientLight(0x2980B9, 0.5);
scene.add(light);
// 平行光, 第二个参数光的强度
const directionalLight = new THREE.DirectionalLight(0xF8C471, 0.8);
directionalLight.position.set(0, size * 6, size * 5);
// 模拟场景中平行光 DirectionalLight 的辅助对象
const helper = new THREE.DirectionalLightHelper(directionalLight, 2, 0x239B56);
scene.add(helper);
scene.add(directionalLight);
// 几何体---- 圆环缓冲扭结几何体
/*
* radius - 圆环的半径,默认值为1。
tube — 管道的半径,默认值为0.4。
tubularSegments — 管道的分段数量,默认值为64。
radialSegments — 横截面分段数量,默认值为8。
p — 这个值决定了几何体将绕着其旋转对称轴旋转多少次,默认值是2。
q — 这个值决定了几何体将绕着其内部圆环旋转多少次,默认值是3。
* */
geometry = new THREE.TorusKnotGeometry(size, size / 3, 100, 16);
// 一种基于物理的标准材质
material = new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial({
color: new THREE.Color("#FF7F50"),
roughness: 0 // 材质的粗糙程度。0.0表示平滑的镜面反射,1.0表示完全漫反射。默认值为1.0。
});
// 几何体和材质变成网格模型
mesh = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material);
scene.add(mesh);
//轨道控制器--- 可以使得相机围绕目标进行轨道运动
controls = new OrbitControls(camera, renderer.domElement);
// 将其设为true,以自动围绕目标旋转
controls.autoRotate = false;
//阻尼惯性有多大。 Default is 0.05
controls.enableDamping = true;
// 启用或禁用摄像机平移,默认为true。
controls.enablePan = false;
// 相机向内移动多少
controls.minDistance = size * 5.5;
// 将相机向外移动多少
controls.maxDistance = size * 10;
controls.target.set(0, 0, 0);
controls.update();
window.addEventListener("resize", () => {
ww = document.body.clientWidth / 2 / window.devicePixelRatio;
hh = ww;
camera.aspect = ww / hh;
camera.updateProjectionMatrix();
renderer.setSize(ww, hh, false);
}, false);
animate();
function animate() {
requestAnimationFrame(animate);
controls.update();
mesh.rotation.x += 0.01;
mesh.rotation.z -= 0.01;
renderer.render(scene, camera);
}
指导几个概练
场景Scene、相机Camera、渲染器Renderer
写一个带箭头的辅助线
const dir = new THREE.Vector3(-2.49, 4.74, -3.01).normalize();
const origin = new THREE.Vector3(0, 0, 0);
const length = 10;
const hex = 0xffff00;
const arrowHelper = new THREE.ArrowHelper(dir, origin, length, hex);
scene.add(arrowHelper)
让天球以北极星为中心旋转
// 向量
const dir = new THREE.Vector3(-2.49, 4.74, -3.01).normalize();
// 建立四元数
const quaternion = new THREE.Quaternion();
let rotation1 = 0;
// 由dir 为轴心, rotation 为旋转弧度
quaternion.setFromAxisAngle(dir, rotation1);
function animate(){
// 不断增加弧度
rotation1 += 0.01;
// // 更新四元数
quaternion.setFromAxisAngle(dir, rotation1);
// // 增加的弧度更新到我们的天球上
sphere.rotation.setFromQuaternion(quaternion);
requestAnimationFrame(animate);
renderer.render(scene, camera);
}
Control
围绕中心点的控制镜头方式
控制镜头的方式有:
-
OrbitControls
轨道控制, 最常用, 你的镜头在一个隐形的圆形的轨道中移动,它永远面向场景中的一个点。预设原点。
-
ArcballControls
弧球控制,比轨道控制难用一点的控制,差在可以360度旋转镜头,使得你的镜头水平不平衡。
-
DragControls
用来拖拽场景中的物体,镜头不会移动
-
FirstPersonControls&FlyControls&PointerLockControls第一人称视角,没有轨道概念
-
TrackballControls跟
OrbitControls很像, 可是当用户把镜头绕过最顶端之后, 并不会绕过头,而TrackballControls则会, -
TransformControls主要是作为控制物体, 而非控制镜头的
OrbitControls
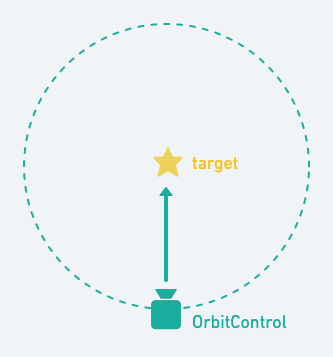
它会操控你的镜头
你会修改自己的镜头位置,它也会。控制镜头为至的方式就是修改
Camera.position
OrbitControl.target:镜头所看向的目标物件,是一个位置资讯Vecro3。
OrbitControl不會在每幀渲染時自動控制,得用OrbitControl.update()更新。
圆形轨道的镜头轨道
const scene = new THREE.Scene();
const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(50, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 0.1, 1000);
// 设置镜头位置
camera.position.set(0, 10, 15);
// 渲染器
const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer();
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
document.body.appendChild(renderer.domElement);
const geometry = new THREE.SphereGeometry(100, 50, 50);
// 加载材质
const texture = new THREE.TextureLoader().load('https://storage.googleapis.com/umas_public_assets/michaelBay/free_star_sky_hdri_spherical_map_by_kirriaa_dbw8p0w%20(1).jpg');
// 物理的标准材质
const material=new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial({map:texture, side: THREE.DoubleSide})
// 环境光
const light = new THREE.AmbientLight(0xffffff, 1);
scene.add(light);
// 星空
const sphere = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material);
scene.add(sphere);
const earthGeometry = new THREE.SphereGeometry(5, 50, 50);
// 载入材质
const earthTexture = new THREE.TextureLoader().load('https://storage.googleapis.com/umas_public_assets/michaelBay/1280px-Solarsystemscope_texture_8k_earth_daymap.jpeg')
const earthMaterial = new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial( { map: earthTexture, side: THREE.DoubleSide})
// 地球
const earth = new THREE.Mesh(earthGeometry, earthMaterial);
scene.add(earth);
// 控制镜头
const control = new OrbitControls( camera, renderer.domElement );
const axesHelper = new THREE.AxesHelper( 5 );
scene.add( axesHelper );
// 修改镜头的方式, 修改位置,让他镜头轨道更真实
control.target.set(10, 0, 0);
control.update();
function animate() {
requestAnimationFrame( animate );
renderer.render( scene, camera );
}
animate();
总结: target 跟 lookAt 的差异
使用orbitControl.target = car.position.clone() 就能移动中心点
向量
.lerp()
改成百分比的向量使用
const v1 = new THREE.Vector3(0, 0, 0);
const v2 = new THREE.Vector3(10, 10, 10);
const a = v1.lerp(v2, 0.25);
console.log(a);
// Vector3 {x: 2.5, y: 2.5, z: 2.5}
.add ( v : Vector3 )
两个向量想加
const v1 = new THREE.Vector3(20, 20, 20);
const v2 = new THREE.Vector3(10, 10, 10);
console.log(v1.add(v2));
// Vector3 {x: 30, y: 30, z: 30}
.addScalar ( s : Float )
const v1 = new THREE.Vector3(20, 20, 20);
console.log(v1.addScalar(20));
// Vector3 {x: 40, y: 40, z: 40}
.addScaledVector ( v : Vector3, s : Float )
将所传入的v与s相乘所得的乘积和这个向量相加。
const v2 = new THREE.Vector3(10, 10, 10);
const v1 = new THREE.Vector3(20, 20, 20);
console.log(v1.addScaledVector(v2, 2));
// v2 * 2 +v1
Vector3 {x: 40, y: 40, z: 40}
.addVectors ( a : Vector3, b : Vector3 ) : this
const v2 = new THREE.Vector3(10, 10, 10);
const v1 = new THREE.Vector3(20, 20, 20);
const v3 = new THREE.Vector3();
v3.addVectors(v1, v2);
v3
// Vector3 {x: 30, y: 30, z: 30}
向量归一化
向量归一化常用于进行移动和方向计算,通过归一化向量可以得到一个方向向量,并用它来对物体进行移动,而不需要关心物体的速度。此外,向量归一化还可以用于实现光线投射、碰撞检测等功能。
.applyAxisAngle ( axis : Vector3, angle : Float ) : this
axis - 一个被归一化的Vector3。
angle - 以弧度表示的角度。
将轴和角度所指定的旋转应用到该向量上。
const v2 = new THREE.Vector3(10, 10, 10).normalize();
const v1 = new THREE.Vector3(20, 20, 20);
v1.applyAxisAngle(v2, 1/4*Math.PI)
以v1的起点, v2 为轴, 然后旋转的角度, 找到新设置的旋转点
.applyEuler ( euler : Euler ) : this
通过将Euler(欧拉)对象转换为Quaternion(四元数)并应用, 将欧拉变换应用到这个向量
欧拉对象Euler
构造函数:Euler(x,y,z,order) 参数xyz分别表示绕xyz轴旋转的角度值,角度单位是弧度。参数order表示旋转顺序,默认值XYZ,也可以设置为YXZ、YZX等值
// 创建一个欧拉对象,表示绕着xyz轴分别旋转45度,0度,90度
var Euler = new THREE.Euler( Math.PI/4,0, Math.PI/2);
四元数Quaternion
四元数对象Quaternion使用x、y、z和w四个分量表示, 用四元数来处理模型旋转
Euler 类(欧拉角)与角度有关, 而Vector3 与位置有关,在实际使用中,Vector3 可用于设置位置,而 Euler 是设置对象方向的一种方式
const scene = new THREE.Scene();
const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(60, 320 / 240, 0.1, 1000);
camera.position.set(2, 2, 2);
camera.lookAt(0, 0, 0);
const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer();
renderer.setSize(640, 480, false);
(document.body).appendChild(renderer.domElement);
// 欧拉角
const euler = new THREE.Euler(Math.PI / 180 * 45, 0, 0)
// 法线网格材质(种把法向量射到RGB颜色的材质)
const meshA = new THREE.Mesh(new THREE.BoxGeometry(1, 1, 1),
new THREE.MeshNormalMaterial());
// 复制三个物体
const box1 = meshA.clone(),
box2 = meshA.clone(),
box3 = meshA.clone();
// 使用 EULER 的实例来设置状态
box2.rotation.copy(euler);
box3.rotation.copy(euler);
// 设置位置
box2.position.set(-1, 0, 0);
box3.position.set(1, 0, 0);
// 添加到视图上
scene.add(box1);
scene.add(box2);
scene.add(box3);
// 添加到渲染器上
renderer.render(scene, camera);
设置环形旋转的效果
let lt:any = new Date();
const loop = function () {
const now: any = new Date(),
secs: any = (now - lt) / 1000;
// 计算每秒消耗时间
requestAnimationFrame(loop);
if (secs >= 0.075) {
lt = now;
// USING EULER XYZ PROPS
box2.rotation.x += 1 * secs;
box2.rotation.x %= Math.PI * 2;
box3.rotation.y += 1 * secs;
box3.rotation.y %= Math.PI * 2;
renderer.render(scene, camera);
}
};
loop();
具体使用旋转的方法
let lt:any = new Date();
const state = {
x: 0,
y: 0,
z: 0
};
const loop = function () {
const now:any = new Date(),
secs:any = (now - lt) / 1000;
requestAnimationFrame(loop);
if (secs >= 0.075) {
lt = now;
state.x += 0.5 * secs;
state.y += 1.0 * secs;
state.z += 1.5 * secs;
state.x %= Math.PI * 2;
// 设置角度
box2.rotation.set(state.x, state.y, state.z);
renderer.render(scene, camera);
}
};
loop();
决定自己的高度的是你的态度,而不是你的才能
记得我们是终身初学者和学习者
总有一天我也能成为大佬





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 全程不用写代码,我用AI程序员写了一个飞机大战
· DeepSeek 开源周回顾「GitHub 热点速览」
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· MongoDB 8.0这个新功能碉堡了,比商业数据库还牛
· .NET10 - 预览版1新功能体验(一)
2019-05-03 python基础复习