线性插值编写可视化代码

线性插值
处于创意编码,游戏开发,数据可视化和生成创意的功能
[start,end] 在范围内插值,t通常在[0,1] 范围内
function lerp (start, end, t) {
return start * (1 - t) + end * t;
}
//虽然这样,但是我感觉现在这样,更容易理解
start+(end-start)*t
// 当 t 为 50%的时候,结果为50
lerp(0, 100, 0.5); // 50
// 当 t 为 0% 的时候,结果20
lerp(20, 80, 0); // 20
// 当t 为1 的时候,结果为5
lerp(30, 5, 1); // 5
lerp(-1, 1, 0.5); // 0
lerp(0.5, 1, 0.5); // 0.75
案例
lerp(20, 50, t)逐渐增大圆的半径或lerp(20, 10, t)逐渐减小其线的粗细
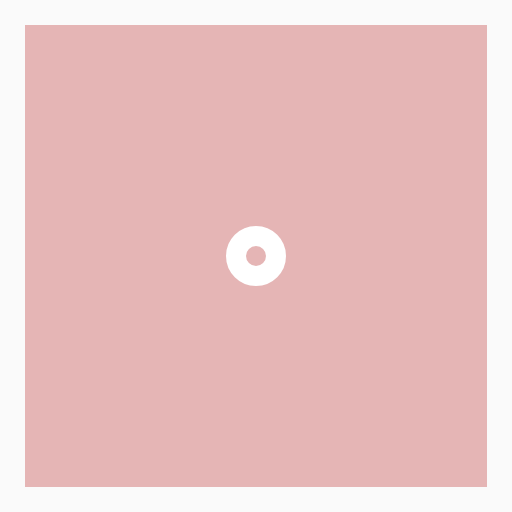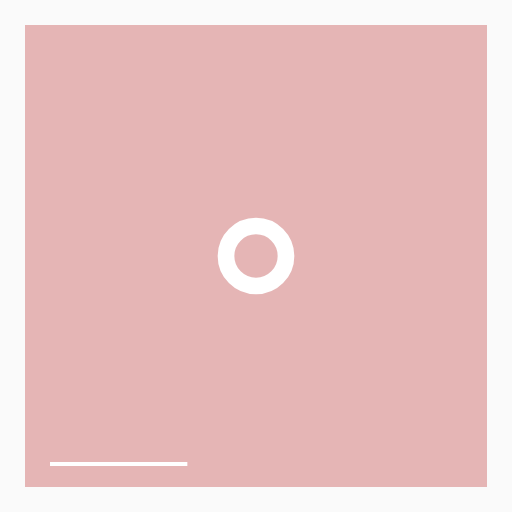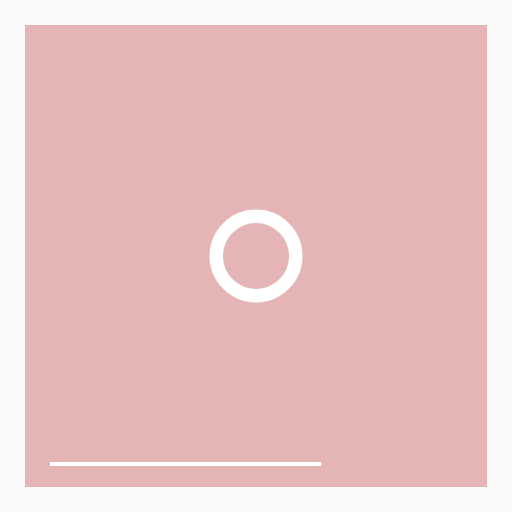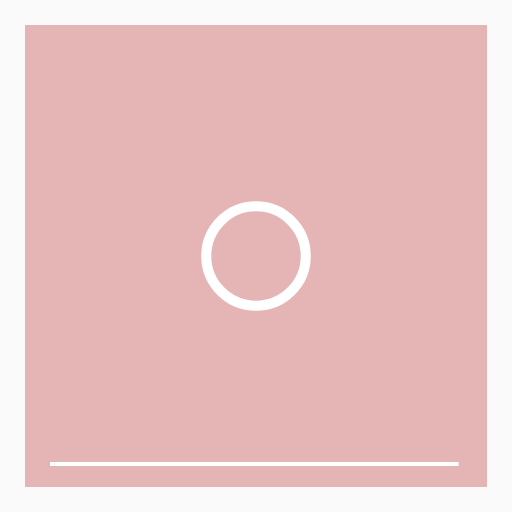
关键代码
// 半径20-50
const radius = lerp(20, 50, t);
// 线宽 20-10
const lineWidth = lerp(20, 10, t);
const canvasSketch = require('canvas-sketch');
function lerp (start, end, t) {
return start * (1 - t) + end * t;
}
const settings = {
dimensions: [ 512, 512 ],
animate: true,
duration: 5
};
const rect = (context, x, y, width, height, color) => {
context.fillStyle = color;
context.fillRect(x, y, width, height);
};
const circle = (context, x, y, radius, color, lineWidth) => {
context.strokeStyle = context.fillStyle = color;
context.beginPath();
context.arc(x, y, radius, 0, Math.PI * 2, false);
context.lineWidth = lineWidth;
if (lineWidth != null) context.stroke();
else context.fill();
};
const progress = (context, time, width, height, margin = 0) => {
context.fillStyle = 'white';
context.fillRect(
margin * 2,
height - margin * 2,
(width - margin * 4) * time,
4
);
};
const sketch = ({ width, height }) => {
const margin = 25;
return props => {
// 拿到我们需要的属性
const { context, width, height, playhead } = props;
// 设置距离margin的背景
rect(context, margin, margin, width - margin * 2, height - margin * 2, '#e5b5b5');
// 画出场景
draw(props);
// 在下面画一个时间轴
progress(context, playhead, width, height, margin);
};
function draw ({ context, width, height, playhead, deltaTime }) {
// Get our 0..1 range value
const t = playhead;
// 半径20-50
const radius = lerp(20, 50, t);
// 线宽 20-10
const lineWidth = lerp(20, 10, t);
// 画圆
circle(context, width / 2, height / 2, radius, 'white', lineWidth);
}
};
canvasSketch(sketch, settings);
逆线性插值

我们需要20过渡到40的比例是50%,值设置了30
假设您要对0到100像素之间的滚动位置做出反应。我们称它们为a和b。用下面的逆线性插值,你在传递a,b以及滚动位置v
function invlerp(a, b, v) {
return ( v - a ) / ( b - a )
}
但是我们会发现返回的值可能会大于1,超过两个极限
const lerp = (x, y, a) => x * (1 - a) + y * a
const invlerp = (a, b, v) => clamp(( v - a ) / ( b - a ))
const clamp = (v, min = 0, max = 1) => Math.min(max, Math.max(min, v))
我自己也是很蒙蔽,直接上案例
invlerp(20, 40, 20) // 0
invlerp(20, 40, 30) // 0.5
结果范围20-40结果返回的是0-1
在小于等于20的时候都是0
大于等于40的时候都是1
demo
决定自己的高度的是你的态度,而不是你的才能
记得我们是终身初学者和学习者
总有一天我也能成为大佬





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 探究高空视频全景AR技术的实现原理
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· AI编程工具终极对决:字节Trae VS Cursor,谁才是开发者新宠?
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!