canvas基础[二]教你编写贝塞尔曲线工具

贝塞尔曲线
bezierCurveTo
在线工具
https://canvature.appspot.com/ [感觉这个好用一些]
https://blogs.sitepointstatic.com/examples/tech/canvas-curves/bezier-curve.html
三次贝塞尔曲线必须包含三个点。前两个点(cp1x,cp1y)和(cp2x,cp2y)是在三次贝塞尔曲线计算中使用的控制点,最后一个点(x,y)是曲线的终点。
bezierCurveTo(cp1x,cp1y,cp2x,cp2y,x,y)
| 参量 | 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| cp1x | number | 第一个贝塞尔控制点的x坐标。 |
| cp1y | number | 第一个贝塞尔控制点的y坐标。 |
| cp2x | number | 第二个贝塞尔控制点的x坐标。 |
| cp2y | number | 第二个贝塞尔控制点的y坐标。 |
| X | number | 要添加到当前路径的点的x坐标。 |
| y | number | 要添加到当前路径的点的y坐标。 |
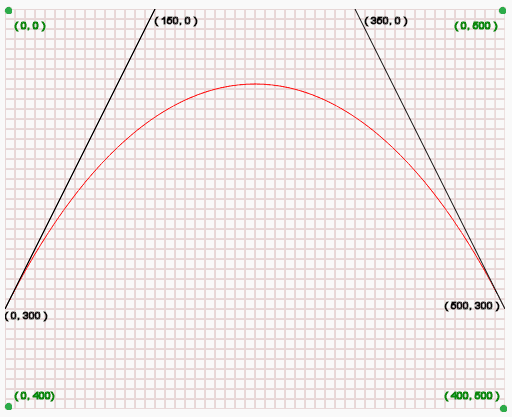
-
(0,300)是曲线的起点。[这个用
moveTo(x,y)叹气的点] -
(150,0)即(cp1x,cp1y)是曲线的第一个控制位置。
-
(350,0)即(cp2x,cp2y)是曲线的第二个控制位置。
-
(500,300),即(x,y)是曲线的终点。
quadraticCurveTo
二次贝塞尔曲线,需要两个点,控制点和曲线的终点

- (0,300)是曲线的起点。
- (250,0)即(cp1x,cp1y)是曲线的控制位置。
- (500,300),即(x,y)是曲线的终点。
绘制可视化的二次贝塞尔曲线demo
初始化
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
#app {
width: 100vw;
height: 100vh;
min-width: 1100px;
overflow: hidden;
font-family: 'Lato', sans-serif;
background-color: #ffffff;
}
#canvas {
border: 1px solid #ccc;
position: absolute;
top: 20px;
left: 20px;
}
#code{
margin-top:20px;
margin-left:520px;
display: inline-block;
padding: 0.5em;
background: #002b36;
color: #839496;
min-height: 11rem;
font-family: Consolas;
font-size: 20px;
}
</style>
<div id="app">
<canvas id="canvas" width="500" height="500"></canvas>
<pre id="code">code</pre>
</div>
let canvas = document.querySelector('#canvas')
// 代码文本
let code = document.querySelector('#code');
let ctx = canvas.getContext('2d'),
point,
style = {// 原点样式
radius: 10,
width: 2,
color: '#900',
fill: 'rgba(200,200,200,.5)',
arc1: 0,
arc2: 2 * Math.PI
},
drag = null,// 按下的时候 确认鼠标拿的那一个点
dPoint, // 拿到当前点的坐标
cpline = {
width: 1,
color: 'red'
},
curve = {
width: 6,
color: '#333'
}
// 初始化默认数据
function init() {
point = {// 鼠标的三个点
p1: { // moveTo
x: 100, y: 50
},
cp1: { // 贝塞尔第一个点
x: 100, y: 200
},
p2: {// 贝塞尔第二个点
x: 300, y: 200
}
}
}
// 代码文字
function showCode() {
if (code) {
code.firstChild.nodeValue =
"theCanvas = document.getElementById(\"canvas\");\n" +
"ctx = theCanvas.getContext(\"2d\")\n" +
"ctx.lineWidth = " + curve.width +
";\nctx.strokeStyle = \"" + curve.color +
"\";\nctx.beginPath();\n" +
"ctx.moveTo(" + point.p1.x + ", " + point.p1.y + ");\n" +
"ctx.quadraticCurveTo(" + point.cp1.x + ", " + point.cp1.y + ", " + point.p2.x + ", " + point.p2.y + ");"
+
"\nctx.stroke();"
;
}
}
画出页面
function drawScreen() {
// 清空画布
ctx.clearRect(0, 0, canvas.width, canvas.height)
ctx.lineCap = 'round';
ctx.lineJoin = 'round';
ctx.lineWidth = cpline.width;
ctx.strokeStyle = cpline.color;
ctx.beginPath()
ctx.moveTo(point.p1.x, point.p1.y)
ctx.lineTo(point.cp1.x, point.cp1.y)
ctx.lineTo(point.p2.x, point.p2.y)
ctx.stroke();
//中间的弧度
ctx.lineWidth = curve.width;
ctx.strokeStyle = curve.color;
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(point.p1.x, point.p1.y)
ctx.quadraticCurveTo(point.cp1.x, point.cp1.y, point.p2.x, point.p2.y)
ctx.stroke();
// 三个原点
for (let p in point) {
console.log(p);
ctx.lineWidth = style.width;
ctx.strokeStyle = style.color;
ctx.fillStyle = style.fill;
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.arc(point[p].x, point[p].y, style.radius, style.arc1, style.arc2, true)
ctx.fill();
ctx.stroke();
}
showCode()
}
拿到鼠标的鼠标
// 鼠标的坐标
function MousePos(event) {
event = event ? event : window.event;
return {
x: event.pageX - canvas.offsetLeft,
y: event.pageY - canvas.offsetTop
}
}
问个来了,当我们鼠标移动的时候怎么确定鼠标放在圆里面啦
这里又运用了初中数学知识圆的标准方程

canvas.addEventListener('mousedown', dragStart, false);
canvas.addEventListener('mousemove', dragging, false);
canvas.addEventListener('mouseup', dragEnd, false);
canvas.addEventListener('mouseout', dragEnd, false);
这里我们需要知道点应该在圆内
鼠标按下的时候
function dragStart(e) {
e = MousePos(e)
let dx, dy;
// 找到鼠标拿到哪一个点
for (let p in point) {
dx = point[p].x - e.x;
dy = point[p].y - e.y;
if ((dx ** 2) + (dy ** 2) < style.radius ** 2) {
// 确定了拿到那个点
drag = p;
// 确定了拿到点的鼠标
dPoint=e;
canvas.style.cursor = 'move';
return;
}
}
}
鼠标移动
function dragging(e) {
// 这个是用来判断有按下的参数的时候触发
if (drag) {
e = MousePos(e);
// 鼠标的x - 开始鼠标的点
point[drag].x += e.x - dPoint.x;
point[drag].y += e.y - dPoint.y;
dPoint = e;
drawScreen();
}
}
鼠标离开
function dragEnd(e) {
drag = null;
canvas.style.cursor = 'default';
drawScreen();
}
再二次贝塞尔曲线的基础上绘制三次贝塞尔曲线
修改1,给html添加一个class
<canvas id="canvasOne" width="500" height="500" class="bezier"></canvas>
在初始化数据的时候,添加第二个点
// 初始化默认数据,默认不传参数三次贝塞尔曲线,不默认二次
function init(quadratic) {
....
if (quadratic) {
point.cp1={
x:250,y:100
}
}else{
point.cp1={
x:150,y:100
}
point.cp2={
x:350,y:100
}
}
画出屏幕的时候
function drawScreen() {
...
ctx.lineTo(point.cp1.x, point.cp1.y)
// 判断是否有第二个点
if (point.cp2) {
ctx.moveTo(point.p2.x,point.p2.y)
ctx.lineTo(point.cp2.x,point.cp2.y)
}else{
ctx.lineTo(point.p2.x, point.p2.y);
}
...
ctx.moveTo(point.p1.x, point.p1.y)
// 确认二次还是三次
if (point.cp2) {
ctx.bezierCurveTo(point.cp1.x, point.cp1.y, point.cp2.x, point.cp2.y, point.p2.x, point.p2.y)
}else{
ctx.quadraticCurveTo(point.cp1.x, point.cp1.y, point.p2.x, point.p2.y);
}
...
}
修改代码显示的部分
+(point.cp2 ?
"ctx.bezierCurveTo("+point.cp1.x+", "+point.cp1.y+", "+point.cp2.x+", "+point.cp2.y+", "+point.p2.x+", "+point.p2.y+");" :
"ctx.quadraticCurveTo("+point.cp1.x+", "+point.cp1.y+", "+point.p2.x+", "+point.p2.y+");"
) +
决定自己的高度的是你的态度,而不是你的才能
记得我们是终身初学者和学习者
总有一天我也能成为大佬





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 探究高空视频全景AR技术的实现原理
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· AI编程工具终极对决:字节Trae VS Cursor,谁才是开发者新宠?
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!