angular9 学习进阶(十六)
rxjs 实用
map
讲一个阵列转成另外一个阵列
of(1).pipe(
map(v => v * 20)
).subscribe(res => {
console.log(res); // 20
});
from([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]).pipe(
map(v => v * 2),
toArray()
).subscribe(res => {
console.log(res); // [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]
});
tap
不会帮助我们进行资料转化,不会影响rxjs资料流,不会都程序有什么影响
of('xxx').pipe(
tap(v=>console.log)
)
shareReplay 避免重新载入
我们会发生
shareReplay(1)只发了一次请求
public todos;
ngOnInit(): void {
this.todos = this.http.get('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/todos/').pipe(
shareReplay(1)
);
}
add() {// 点击的时候执行这个函数
this.todos.subscribe(res => {
console.log(res);
});
}
Subscription(相当于取消订阅)
someSubscriptions = new Subscription();
ngOnInit() {
this.someSubscriptions.add(xx$.subscribe(...));
this.someSubscriptions.add(yy$.subscribe(...));
}
ngOnDestroy() {
this.someSubscriptions.unsubscribe();
}
禁止使用返回键
网上的
history.pushState(null, null, document.URL);
window.addEventListener('popstate', function () {
history.pushState(null, null, document.URL);
});
实现:不能我们使用路由监听,然后调用history.pushState 方法,改变网址就不会跳转
this.router.events.subscribe((event: any) => {
if (event instanceof NavigationEnd) {
history.pushState(null, null, document.URL);
}
});
angular 动画
https://indepth.dev/in-depth-guide-into-animations-in-angular/
style在js中的命名约束
驼峰式,或者破折号
style({ backgroundColor:'green' }) style({ "background-color":"green" })
执行顺序
:enter状态更改将ngOnInit周期之后调用
:leave状态更改讲ngOnDestroy周期调用后,立即执行
设置
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { BrowserAnimationsModule } from '@angular/platform-browser/animations';
@NgModule({
imports: [
BrowserAnimationsModule
],
})
动画声明
* 通配符就是默认状态或者所有状态
void dom删除元素
自定义 特定的状态
状态变化之间的转化
import { trigger, state, style, animate, transition } from '@angular/animations';
@Component({
...
animations: [
trigger('enabledStateChange', [
state(
'default',
style({
opacity: 1,
})
),
state(
'disabled',
style({
opacity: 0.5,
})
),
transition('* => *', animate('300ms ease-out')),
])
]
})
trigger
- 接受动画接触器的名称+转换方法的数组配置
state
- 接受状态名称以及处于指定状态时应有的样式
style
- css样式
transition
- 指定在不同状态一起方向之间转化的配置
- animate 动画的属性
例子
<button (click)="clickBool()">点我</button>
<div @fadeSlideInOut *ngIf="bool" class="aaa" >
<p>1我是一个好人</p>
<p>2我是一个好人</p>
<p>3我是一个好人</p>
<p>4我是一个好人</p>
<p>5我是一个好人</p>
<p>6我是一个好人</p>
<p>7我是一个好人</p>
<p>8我是一个好人</p>
<p>9我是一个好人</p>
<p>10我是一个好人</p>
</div>
ts
public bool:boolean=false;
clickBool():void{
this.bool=!this.bool
}
@Component({
...
animations: [
trigger('fadeSlideInOut',[
transition(':enter', [
style({ opacity: 0, transform: 'translateY(10px)' }),
animate('500ms', style({ opacity: 1, transform: 'translateY(0)' })),
]),
transition(':leave', [
animate('500ms', style({ opacity: 0, transform: 'translateY(10px)' })),
]),
])
]
})
下面这种模式是从一个状态到另一种状态
trigger('enabledState', [
state(
'default',
style({
opacity: 1,
})
),
state(
'disabled',
style({
opacity: 0.5,
})
),
transition('* => *',animate('300ms ease-out'))
]),
MergeMap
MergeMap 本质上是mergeAll 和 map 的结合
getData(param){ return of(`retrieved new data with param ${param}`).pipe( delay(1000) ) } ngOnInit(): void { from([1, 2, 3, 4]).pipe( map(val=>this.getData(val)), mergeAll() ).subscribe(res=>{ console.log(res); }) } 修改 from([1, 2, 3, 4]).pipe( mergeMap(value => of(`retrieved new data with param ${value}`).pipe(delay(1000))) ).subscribe(res=>{ console.log(res); })
concatMap
from([1, 2, 3, 4]).pipe(
concatMap(value => of(`retrieved new data with param ${value}`).pipe(delay(1000)))
).subscribe(res=>{
console.log(res);
})
两者的区别
concatMap 等待,按顺序执行任务
mergeMap 不等待,并发执行任务
延迟加载
https://stackblitz.com/edit/lazyload-images-matew17?file=src%2Fapp%2Fapp.component.html
确定分配断言
let num!:string;
!这个是告诉语法提示工具,这个已经赋值了,不需要你来判断
点击编辑文本
第一种方法
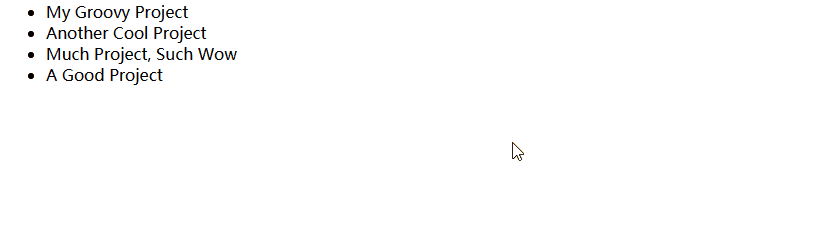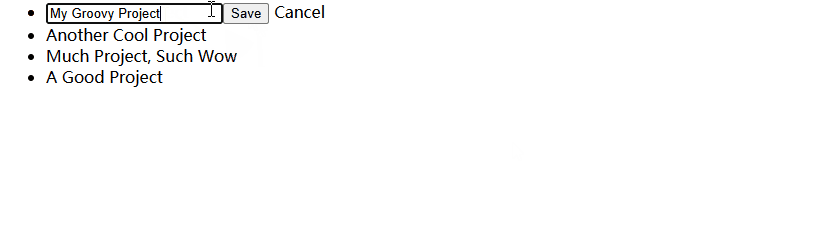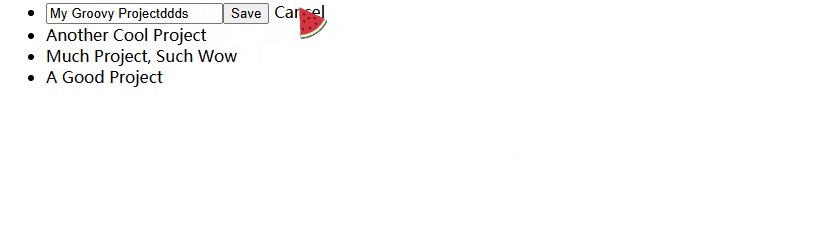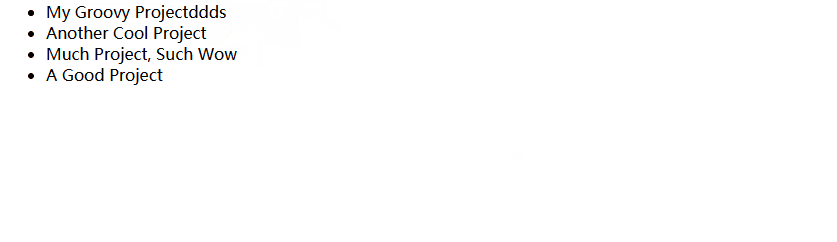
子组件
import {Component, EventEmitter, Input, OnInit, Output} from '@angular/core';
import {Observable} from 'rxjs';
import {State} from '../reducer/scoreboard/scoreboard.reducer';
import {select, Store} from '@ngrx/store';
@Component({
selector: 'app-hello-one',
templateUrl: './hello-one.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./hello-one.component.less']
})
export class HelloOneComponent implements OnInit {
public isEditing: boolean = false;
public pendingValue: string = '';
@Input('value') value!: string;
@Output('valueChange') valueChangeEvents: EventEmitter<string> = new EventEmitter();
constructor() {
}
public cancel(): void {
this.isEditing = false;
}
// 启动对值得编辑.
public edit(): void {
this.pendingValue = this.value;
this.isEditing = true;
}
public processChanges(): void {
// 当值改变的时候才执行
if (this.pendingValue !== this.value) {
this.valueChangeEvents.emit(this.pendingValue);
}
this.isEditing = false;
}
ngOnInit(): void {
}
}
<div *ngIf="isEditing">
<input type="text"
name="value"
[(ngModel)]="pendingValue"
autofocus
(keydown.Enter)="processChanges()"
(keydown.Escape)="cancel()"
>
<button (click)="processChanges()">
Save
</button>
<a
(click)="cancel()"
(keydown.Enter)="cancel()"
tabindex="0">
Cancel
</a>
</div>
<div *ngIf="( ! isEditing )" (click)="edit()">
{{ value }}
</div>
父组件
<li *ngFor="let project of projects">
<app-hello-one [value]="project.name" (valueChange)="saveProject(project,$event)"></app-hello-one>
</li>
export interface Project {
id: string;
name: string;
}
saveProject(project: Project, newName: string) {
project.name=newName
}
public projects: Project[] = [
{ id: "p1", name: "My Groovy Project" },
{ id: "p2", name: "Another Cool Project" },
{ id: "p3", name: "Much Project, Such Wow" },
{ id: "p4", name: "A Good Project" }
];
第二种
巧妙的运行了浅拷贝,仔细思考了半小时才明白
<ul>
<li
*ngFor="let item of arr"
[ngSwitch]="(item===smg)">
<div *ngSwitchCase="true">
<label>
<input type="text"
[(ngModel)]="pendingValue"
autofocus
(keydown.enter)="processChange()"
>
</label>
<button (click)="processChange()">Save</button>
<a (click)="cancel()">Cancel</a>
</div>
<div *ngSwitchCase="false" (click)="edit(item)">
{{item.name}}
</div>
</li>
</ul>
import {Component, Input, OnInit, Output, EventEmitter} from '@angular/core';
interface ArrayId {
id: number;
name: string
}
@Component({
selector: 'app-hello-tow',
templateUrl: './hello-tow.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./hello-tow.component.less']
})
export class HelloTowComponent implements OnInit {
public pendingValue: string = '';
public smg: ArrayId | null;
public arr: ArrayId[] = [
{id: 1, name: 'xxxxxx'},
{id: 2, name: 'dddd'},
{id: 3, name: 'ccc'},
{id: 4, name: 'bbb'},
];
processChange() {
if (this.pendingValue !== this.smg!.name) {
// 浅拷贝,终于看懂了,我的天,这块代码巧妙的运用的浅拷贝的方法进行修改
this.smg!.name = this.pendingValue;
}
this.smg = null;
}
constructor() {
}
ngOnInit(): void {
}
edit(item: ArrayId): void {
this.pendingValue = item.name;
this.smg = item;
}
cancel(): void {
this.smg = null;
}
}
决定自己的高度的是你的态度,而不是你的才能
记得我们是终身初学者和学习者
总有一天我也能成为大佬





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 探究高空视频全景AR技术的实现原理
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· AI编程工具终极对决:字节Trae VS Cursor,谁才是开发者新宠?
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!