【ASP.NET Core】参数绑定 & 验证
模型绑定
什么是模型绑定?简单说就是将HTTP请求参数绑定到程序方法入参上,该变量可以是简单类型,也可以是复杂类。
绑定源
所谓绑定源,是指用于模型绑定的值来源。
- [FromQuery]:从Url的查询字符串中获取值。查询字符串就是Url中问号(?)后面拼接的参数
- [FromRoute]:从路由数据中获取值。例如上例中的
- [FromForm]:从表单中获取值。
- [FromBody]:从请求正文中获取值。
- [FromHeader]:从请求标头中获取值。
建议大家在编写接口时,尽量显式指明绑定源。
模型属性默认值
默认的,若模型属性在绑定源中不存在,且不加任何验证条件时,不会将其标记为模型状态错误,而是会将该属性设置为null或默认值:
- 可以为Null的简单类型设置为null
- 不可为Null的值类型设置为default
- 如果是复杂类型,则通过默认构造函数创建该实例。
- 数组则设置为Array.Empty
(),不过byte[]数组设置为null。
绑定源无法转换为模型中的目标类型
比如,当尝试将绑定源中的字符串abc转换为模型中的值类型int时,会发生类型转换错误,此时,会将该模型状态标记为无效。
绑定格式
int、string、模型类等绑定格式大家已经很熟悉了,我就不再赘述了。这次,只给大家介绍一些比较特殊的绑定格式。
集合绑定格式
假设存在以下接口,接口参数是一个数组:
public string[] Post([FromQuery] string[] ids)
public string[] Post([FromForm] string[] ids)
参数为:[1,2]
为了将参数绑定到数组ids上,你可以通过表单或查询字符串传入,可以采用以下格式之一:
ids=1&ids=2
ids[0]=1&ids[1]=2
[0]=1&[1]=2
ids[a]=1&ids[b]=2&ids.index=a&ids.index=b
[a]=1&[b]=2&index=a&index=b
此外,表单还可以支持一种格式:ids[]=1&ids[]=2
字典绑定格式
假设存在以下接口,接口参数是一个字典:
public Dictionary<int, string> Post([FromQuery] Dictionary<int, string> idNames)
参数为:{ [1] = "j", [2] = "k" }
为了将参数绑定到字典idNames上,你可以通过表单或查询字符串传入,可以采用以下格式之一:
idNames[1]=j&idNames[2]=k,注意:方括号中的数字是字典的key
[1]=j&[2]=k
idNames[0].key=1&idNames[0].value=j&idNames[1].key=2&idNames[1].value=k,注意:方括号中的数字是索引,不是字典的key
[0].key=1&[0].value=j&[1].key=2&[1].value=k
参数绑定案例
Query请求
GET http://localhost:5000/weatherforecast?id=1&description=aaa
[HttpGet]
public ActionResult<Entity> Get([FromQuery] Entity entity,string description)
{
return entity;
}
public class Entity
{
[FromQuery(Name ="id")]
public int EntityID { get; set; }
}
表单提交
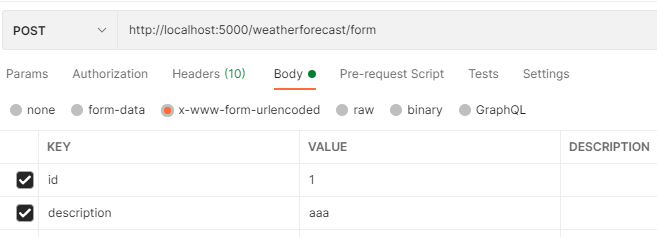
[HttpPost("form")]
public ActionResult Post([FromForm] FormData form,[FromForm]string description)
{
return Content("ok");
}
public class FormData
{
[FromForm(Name ="id")]
public int FormDataID { get; set; }
}
Json提交
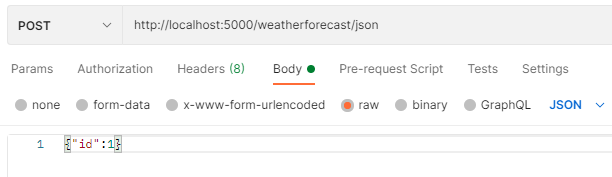
[HttpPost("json")]
public ActionResult Post2(JsonData form)
{
return Content("ok");
}
public class JsonData
{
[JsonProperty("id")]
public int JsonDataID { get; set; }
}
记得startup中设置:services.AddControllers().AddNewtonsoftJson();
Route请求
[HttpGet("user/{user_id}")]
public void GetUser([FromRoute(Name = "user_id")] long userId)
{
}
//加问号表示可选参数,可传可不传
[HttpGet("{order_id?}")]
public JsonModel<ApiOrderInfoSelectModel> GetOne([FromRoute(Name = "order_id")] long orderID)
{
}
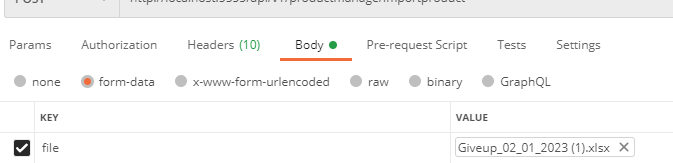
文件上传
public async Task<JsonModel<object>> ImportProduct(IFormFile file)
{
//file = file != null ? file : Request.Form.Files[0];
}
模型验证
聊完了模型绑定,那接下来就是要验证绑定的模型是否有效。
[HttpPost]
public string Post([FromBody] CreateUserDto input)
{
// 模型状态无效,返回错误消息
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return "模型状态无效:"
+ string.Join(Environment.NewLine,
ModelState.Values.SelectMany(v => v.Errors.Select(e => e.ErrorMessage)));
}
return JsonSerializer.Serialize(input);
}
public class CreateUserDto
{
public int Age { get; set; }
}
现在,我们请求Post,传入以下参数:
{
"age":"abc"
}
会得到如下响应:
模型状态无效:The JSON value could not be converted to System.Int32. Path: $.age | LineNumber: 1 | BytePositionInLine: 15.
我们得到了模型状态无效的错误消息,这是因为字符串“abc”无法转换为int类型。
你也看到了,我们通过ModelState.IsValid来检查模型状态是否有效。
ModelState
ModelState的类型为ModelStateDictionary,也就是一个字典,Key就是无效节点的标识,Value就是无效节点详情。
我们一起看一下ModelStateDictionary的核心类结构:
public class ModelStateDictionary : IReadOnlyDictionary<string, ModelStateEntry>
{
public static readonly int DefaultMaxAllowedErrors = 200;
public ModelStateDictionary()
: this(DefaultMaxAllowedErrors) { }
public ModelStateDictionary(int maxAllowedErrors) { ... }
public ModelStateDictionary(ModelStateDictionary dictionary)
: this(dictionary?.MaxAllowedErrors ?? DefaultMaxAllowedErrors) { ... }
public ModelStateEntry Root { get; }
// 允许的模型状态最大错误数量,默认是 200
public int MaxAllowedErrors { get; set; }
// 指示模型状态错误数量是否达到最大值
public bool HasReachedMaxErrors { get; }
// 通过`AddModelError`或`TryAddModelError`方法添加的错误数量
public int ErrorCount { get; }
// 无效节点的数量
public int Count { get; }
public KeyEnumerable Keys { get; }
IEnumerable<string> IReadOnlyDictionary<string, ModelStateEntry>.Keys => Keys;
public ValueEnumerable Values { get; }
IEnumerable<ModelStateEntry> IReadOnlyDictionary<string, ModelStateEntry>.Values => Values;
// 枚举,模型验证状态,有 Unvalidated、Invalid、Valid、Skipped 共4种
public ModelValidationState ValidationState { get; }
// 指示模型状态是否有效,当验证状态为 Valid 和 Skipped 有效
public bool IsValid { get; }
public ModelStateEntry this[string key] { get; }
}
重新验证
默认情况下,模型验证是自动进行的。不过有时,需要为模型进行一番自定义操作后,重新进行模型验证。可以先通过ModelStateDictionary.ClearValidationState方法清除验证状态,然后调用ControllerBase.TryValidateModel方法重新验证:
public class CreateUserDto
{
[Required]
public string FirstName { get; set; }
[Required]
public string LastName { get; set; }
}
[HttpPost]
public string Post([FromBody] CreateUserDto input)
{
if (input.FirstName is null)
{
input.FirstName = "first";
}
if (input.LastName is null)
{
input.LastName = "last";
}
// 先清除验证状态
ModelState.ClearValidationState(string.Empty);
// 重新进行验证
if (!TryValidateModel(input, string.Empty))
{
return "模型状态无效:"
+ string.Join(Environment.NewLine,
ModelState.Values.SelectMany(v => v.Errors.Select(e => e.ErrorMessage)));
}
return JsonSerializer.Serialize(input);
}
验证特性
针对一些常用的验证:如判断是否为null、字符串格式是否为邮箱等,为了减少大家的工作量,减少代码冗余,可以通过特性的方式在模型的属性上进行标注。
微软为我们内置了一部分验证特性,位于System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations命名空间下(只列举一部分):
[Required]:验证属性是否为null。该特性作用在可为null的数据类型上才有效
作用于字符串类型时,允许使用AllowEmptyStrings属性指示是否允许空字符串,默认false
[StringLength]:验证字符串属性的长度是否在指定范围内
[Range]:验证数值属性是否在指定范围内
[Url]:验证属性的格式是否为URL
[Phone]:验证属性的格式是否为电话号码
[EmailAddress]:验证属性的格式是否为邮箱地址
[Compare]:验证当前属性和指定的属性是否匹配
[RegularExpression]:验证属性是否和正则表达式匹配
Web Api中的模型验证
对于Web Api应用,由于标记了[ApiController]特性,其会自动执行ModelState.IsValid进行检查,若发现模型状态无效,会返回包含错误信息的指定格式的HTTP 400响应。
该格式默认类型为ValidationProblemDetails,在Action中可以通过调用ValidationProblem方法返回该类型。
其实现的根本原理是使用了ModelStateInvalidFilter过滤器,该过滤器会附加在所有被标注了ApiControllerAttribute的类型上。
public class ModelStateInvalidFilter : IActionFilter, IOrderedFilter
{
internal const int FilterOrder = -2000;
private readonly ApiBehaviorOptions _apiBehaviorOptions;
private readonly ILogger _logger;
// 默认 -2000
public int Order => FilterOrder;
public bool IsReusable => true;
public void OnActionExecuted(ActionExecutedContext context) { }
public void OnActionExecuting(ActionExecutingContext context)
{
if (context.Result == null && !context.ModelState.IsValid)
{
_logger.ModelStateInvalidFilterExecuting();
context.Result = _apiBehaviorOptions.InvalidModelStateResponseFactory(context);
}
}
}
如何修改API模型验证返回格式
第一种方式
builder.Services.AddControllers().ConfigureApiBehaviorOptions(
option => {
//关闭模型验证
//option.SuppressModelStateInvalidFilter = true;
option.InvalidModelStateResponseFactory = action => {//模型校验失败才会执行此委托
var IsValid = action.ModelState.IsValid;
//var Context = action.HttpContext;
if (!IsValid)
{
var message = string.Join("", action.ModelState.Values
.SelectMany(e => e.Errors)
.Select(e => e.ErrorMessage));
return new JsonResult(new { status = 500, message = message });
//return new OkObjectResult(reponse);
}
return new OkObjectResult(new { });
};
});
第二种方式
我们知道了Web Api中通过过滤器进行ModelState.IsValid检查,返回了的类型是ValidationProblemDetails,如果想自定义,就要在ModelStateInvalidFilter过滤器之前进行ModelState.IsValid检查,返回结果
过滤器:
public class ModelStateValidationFilterAttribute : ActionFilterAttribute
{
public override void OnActionExecuting(ActionExecutingContext context)
{
if (!context.ModelState.IsValid)
{
var message = string.Join("", context.ModelState.Values.SelectMany(v => v.Errors.Select(e => "<error>"+e.ErrorMessage+"</error>")));
context.Result = new JsonResult(new { status=500,message= message });
}
}
}
控制器:
[ApiController]
[Route("values")]
public class ValuesController : ControllerBase
{
[HttpGet]
[ModelStateValidationFilter(Order =-2001)]
public string Index([FromQuery]Person input)
{
return input.Id.ToString();
}
}
public class Person
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
}
注意order=-2001,因为ModelStateInvalidFilter过滤器的order是-2000,我们的过滤器要在它之前执行
调用接口http://localhost:5047/values?id=a:
{
status: 500,
message: "<error>The value 'a' is not valid for Id.</error><error>The Name field is required.</error>"
}
为Web添加自动模型验证
Web Api中有全局的自动模型验证,那Web中你是否也想整一个呢(你该不会想总在方法内写ModelState.IsValid吧)?以下给出一个简单的示例:
public class ModelStateValidationFilterAttribute : ActionFilterAttribute
{
public override void OnActionExecuting(ActionExecutingContext context)
{
if (!context.ModelState.IsValid)
{
var errorMsg = string.Join(";", context.ModelState.Values.SelectMany(v => v.Errors.Select(e => e.ErrorMessage)));
if (context.HttpContext.Request.AcceptJson())
{
context.Result = new BadRequestObjectResult(new { status=500,message= errorMsg });
}
else
{
context.Result = new RedirectResult($"/home/error?message={errorMsg}");
}
}
}
}
public static class HttpRequestExtensions
{
public static bool AcceptJson(this HttpRequest request)
{
if (request == null) throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(request));
var regex = new Regex(@"^(\*|application)/(\*|json)$");
return request.Headers[HeaderNames.Accept].ToString()
.Split(',')
.Any(type => regex.IsMatch(type));
}
}
自定义模型绑定
Demo
public class FilterModelBinder : IModelBinder
{
private readonly IList<IInputFormatter> formatters;
private readonly IHttpRequestStreamReaderFactory readerFactory;
public FilterModelBinder(IList<IInputFormatter> formatters, IHttpRequestStreamReaderFactory readerFactory)
{
this.formatters = formatters;
this.readerFactory = readerFactory;
}
/// <inheritdoc />
public async Task BindModelAsync(ModelBindingContext bindingContext)
{
await Task.Run(() =>
{
if (bindingContext == null) throw new ArgumentNullException("bindingContext");
string filter = bindingContext.HttpContext.Request.Form["filter"];
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(filter)) return;
IFilterable t = JsonConvert.DeserializeObject(filter, bindingContext.ModelType) as IFilterable;
if (t == null) return;
if (t.Pager == null)
{
t.Pager = new Pager();
}
bindingContext.Result = ModelBindingResult.Success(t);
});
}
}
public class FilterModelBinderProvider : IModelBinderProvider
{
private readonly IList<IInputFormatter> formatters;
private readonly IHttpRequestStreamReaderFactory readerFactory;
public FilterModelBinderProvider(IList<IInputFormatter> formatters, IHttpRequestStreamReaderFactory readerFactory)
{
this.formatters = formatters;
this.readerFactory = readerFactory;
}
/// <inheritdoc />
public IModelBinder GetBinder(ModelBinderProviderContext context)
{
if (typeof(IFilterable).IsAssignableFrom(context.Metadata.ModelType))
return new FilterModelBinder(formatters, readerFactory);
return null;
}
}
public abstract class BinderAttribute : Attribute, ICustomModelBinder
{
public BinderSource BinderSource { get; protected set; }
public BinderAttribute()
{
}
public BinderAttribute(BinderSource dinderSource)
{
BinderSource = dinderSource;
}
protected string GetValue(ModelBinderContext bindingContext)
{
string vlaue = null;
switch (BinderSource)
{
case BinderSource.Form:
if (bindingContext.HttpContext.Request.Method == "POST" && bindingContext.HttpContext.Request.ContentType.ToLower().Contains("form"))
{
vlaue = bindingContext.HttpContext.Request.Form[bindingContext.ModelName];
}
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(vlaue) && BinderSource == BinderSource.Default) goto case BinderSource.Query;
break;
case BinderSource.Query:
vlaue = bindingContext.HttpContext.Request.Query[bindingContext.ModelName];
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(vlaue) && BinderSource == BinderSource.Default) goto case BinderSource.Body;
break;
case BinderSource.Body:
if (bindingContext.HttpContext.Request.Method == "POST")
{
vlaue = new StreamReader(bindingContext.HttpContext.Request.Body).ReadToEnd();
}
break;
case BinderSource.Default:
goto case BinderSource.Form;
}
return vlaue;
}
public abstract object Bind(ModelBinderContext modelBinderContext);
}
public enum BinderSource
{
Default = 0,
Body = 1,
Form = 2,
Query = 3,
Services = 4
}
/// <summary>
/// json数据绑定
/// </summary>
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Parameter)]
public class JsonBinderAttribute : BinderAttribute, ICustomModelBinder
{
public JsonBinderAttribute() : this(BinderSource.Body)
{
}
public JsonBinderAttribute(BinderSource dinderSource)
{
BinderSource = dinderSource;
}
public override object Bind(ModelBinderContext modelBinderContext)
{
if (modelBinderContext == null) throw new ArgumentNullException("bindingContext");
string json = base.GetValue(modelBinderContext);
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(json)) return null;
object t = JsonConvert.DeserializeObject(json, modelBinderContext.ModelType);
return t;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 字符串分割数组数据绑定
/// </summary>
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Parameter)]
public class ArrayBinderAttribute : BinderAttribute, ICustomModelBinder
{
private char splitChar = ',';
public ArrayBinderAttribute(char splitChar = ',', BinderSource dinderSource = BinderSource.Default)
{
this.splitChar = splitChar;
BinderSource = dinderSource;
}
public override object Bind(ModelBinderContext bindingContext)
{
if (bindingContext == null) throw new ArgumentNullException("bindingContext");
string vlaue = base.GetValue(bindingContext);
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(vlaue)) return null;
IList ids = null;
try
{
Type type = bindingContext.ModelType;
Type baseType = null;
string[] array = vlaue.Split(new[] { splitChar }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
if (bindingContext.ModelType.IsArray)
{
baseType = type.GetElementType();
ids = Activator.CreateInstance(type, array.Length) as IList;
for (int i = 0; i < array.Length; i++)
{
if (baseType == typeof(Guid))
{
ids[i] = Guid.Parse(array[i]);
}
else
{
ids[i] = Convert.ChangeType(array[i], baseType);
}
}
}
else if (typeof(IList).IsAssignableFrom(bindingContext.ModelType) || typeof(IEnumerable).IsAssignableFrom(bindingContext.ModelType))
{
baseType = type.GetGenericArguments().FirstOrDefault();
ids = Activator.CreateInstance(typeof(List<>).MakeGenericType(baseType)) as IList;
for (int i = 0; i < array.Length; i++)
{
if (baseType == typeof(Guid))
{
ids.Add( Guid.Parse(array[i]));
}
else
{
ids.Add(Convert.ChangeType(array[i], baseType));
}
}
}
}
catch
{
}
return ids;
}
}

