JavaWeb阶段性项目1:Servlet-api、mvc-service引入、IOC和DI
Servlet-api
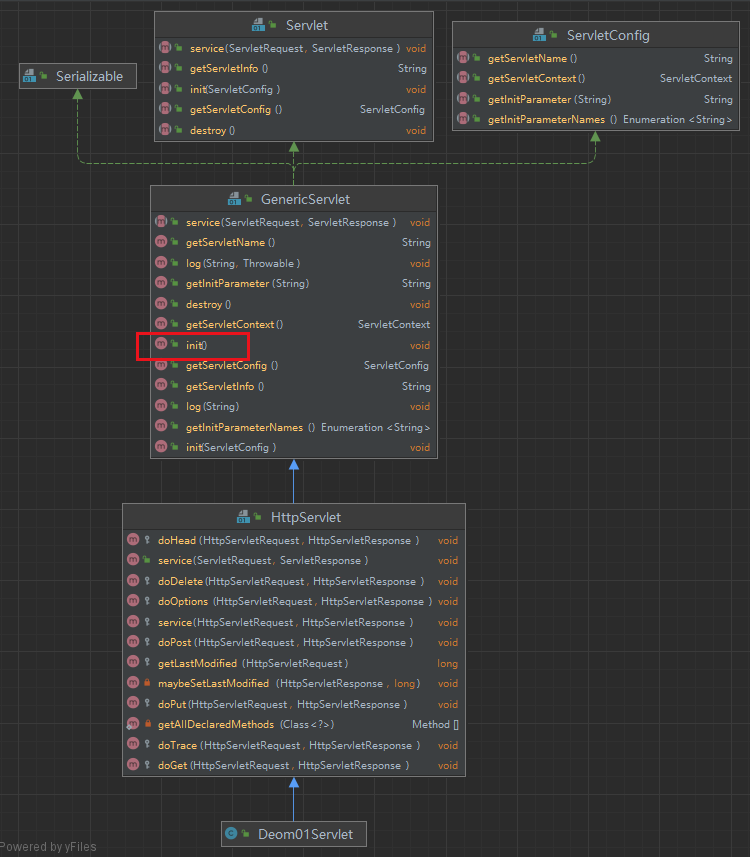
servlet类的继承与实现结构
-
Servlet生命周期:实例化、初始化、服务、销毁
init()方法
抽象类GenericServlet实现了Servlet接口中的init方法,初始化Servlet
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
this.config = config;
this.init();
}
public void init() throws ServletException {
}
public class Demo01Servlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
public void init() throws ServletException {
ServletConfig config = getServletConfig();
String initValue = config.getInitParameter("hello");
System.out.println("initValue = " + initValue);
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
String contextConfigLocation = servletContext.getInitParameter("contextConfigLocation");
System.out.println("contextConfigLocation = " + contextConfigLocation);
}
}web.xml
也可以通过注解的方式进行配置: @WebServlet(urlPatterns = {"/demo01"} , initParams = { @WebInitParam(name="hello",value="world"), @WebInitParam(name="uname",value="jim") })
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>Demo01Servlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.atguigu.servlet.Demo01Servlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>hello</param-name>
<param-value>world</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>uname</param-name>
<param-value>jim</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>Demo01Servlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/demo01</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>该方法可以解析web.xml,以此来获取我们初始化设置的数据,将解析的数据放入共享变量中(此知识点在框架技术中有所涉及)
-
获取config对象:ServletConfig config = getServletConfig();
-
获取初始化参数值: config.getInitParameter(key);.
ServletContext和<context-param>
ServletContext
保存了共享数据
在服务方法中获取:
@WebServlet("/demo05")
public class Demo05Servlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//1.向request保存作用域保存数据
//Servlet上下文
ServletContext application = req.getServletContext();
application.setAttribute("uname","keke");
//2.客户端重定向
resp.sendRedirect("demo06");
/*//服务器内部转发
req.getRequestDispatcher("demo06").forward(req,resp);*/
}
}在初始化方法中获取
ServletContxt servletContext = getServletContext();
获取初始化值: servletContext.getInitParameter();
<context-param>
在web.xml文件中使用<context-param>配置ServletContext的公共初始化参数来创建公共信息
<!-- 配置上下文参数 -->
<context-param>
<param-name>key</param-name>
<param-value>value</param-value>
</context-param>获取初始化值
servletContext.getInitParameter("key");
servletContext.getInitParameter();
mvc-service引入
引入前结构

引入后
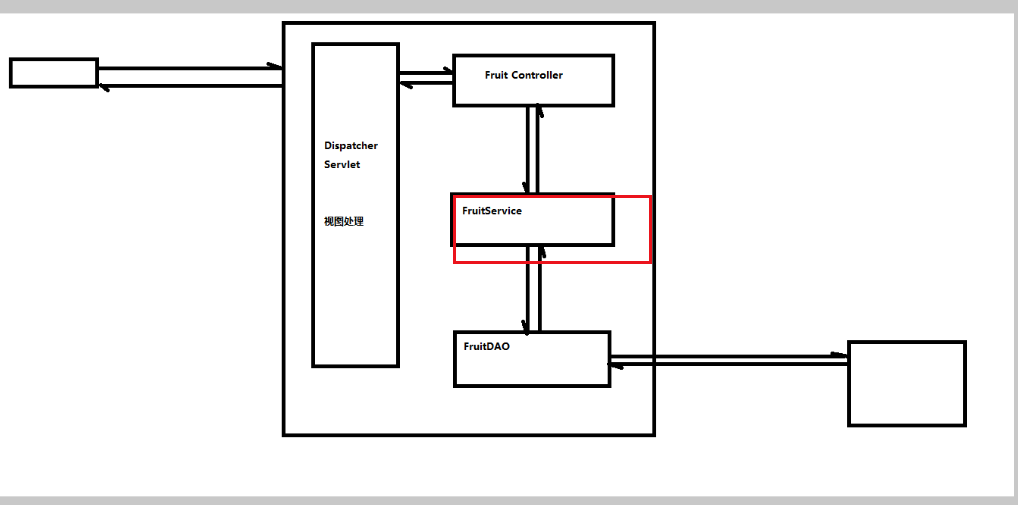
service就是多个DAO的组合调用,只不过这里的service比较简单,和普通DAO没有区别
MVC模式
MVC : V:view 视图 ; C:Controller 控制器 ; M:Model 模型 模型有很多种类:数据访问模型(DAO);业务逻辑模型(BO);值对象模型(POJO);数据传输对象(DTO)
package com.fancy.fruit.biz;
import com.fancy.fruit.pojo.Fruit;
import java.util.List;
public interface FruitService {
//获取指定页面的库存列表信息
List<Fruit> getFruitList(String keyword, Integer pageNo);
//添加库存记录信息
void addFruit(Fruit fruit);
//根据id查看制定库存记录
Fruit getFruitByFid(Integer fid);
//删除特定库存记录
void delFruit(Integer fid);
//获取总页数
Integer getPageCount(String keyword);
//修改特定库存记录
void updateFruit(Fruit fruit);
}注意:运行失败的看看是不是DispatcherServlet运行时把获取的方法参数给自动抹除了
package com.fancy.fruit.biz.impl;
import com.fancy.fruit.biz.FruitService;
import com.fancy.fruit.dao.FruitDAO;
import com.fancy.fruit.dao.impl.FruitDAOImpl;
import com.fancy.fruit.pojo.Fruit;
import java.util.List;
public class FruitServiceImpl implements FruitService {
private FruitDAO fruitDAO = new FruitDAOImpl();
@Override
public List<Fruit> getFruitList(String keyword, Integer pageNo) {
return fruitDAO.getFruitList(keyword, pageNo);
}
@Override
public void addFruit(Fruit fruit) {
fruitDAO.addFruit(fruit);
}
@Override
public Fruit getFruitByFid(Integer fid) {
return fruitDAO.getFruitByFid(fid);
}
@Override
public void delFruit(Integer fid) {
fruitDAO.delFruit(fid);
}
@Override
public Integer getPageCount(String keyword) {
int count = fruitDAO.getFruitCount(keyword);
int pageCount = (count + 5 - 1) / 5;
return pageCount;
}
@Override
public void updateFruit(Fruit fruit) {
fruitDAO.updateFruit(fruit);
}
}改FruitController
package com.fancy.fruit.controllers;
import com.fancy.fruit.dao.FruitDAO;
import com.fancy.fruit.dao.impl.FruitDAOImpl;
import com.fancy.fruit.pojo.Fruit;
import com.fancy.myssm.basedao.myspringmvc.ViewBaseServlet;
import com.fancy.myssm.basedao.util.StringUtil;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.List;
public class FruitController extends ViewBaseServlet {
private FruitDAO fruitDAO = new FruitDAOImpl();
private String update(Integer fid, String fname, Integer price, Integer fcount, String remark) {
//2.获取参数
//3.执行更新
fruitDAO.updateFruit(new Fruit(fid, fname, price, fcount, remark));
//4.资源跳转
//super.processTemplate("index",req,resp);
//此处需要重定向,目的是重新给IndexServlet发请求,然后覆盖到session中,这样index页面上显示的数据才是最新的
//resp.sendRedirect("fruit.do");//重定向,重新给fruit.do,给session重新给fruit更改后的数据
return "redirect:fruit.do";
}
private String edit(Integer fid, HttpServletRequest req) {
//HTML是模板,thymeleaf是引擎,我们在servlet中调用了引擎并且给了引擎需要的模板和参数
if (fid != null) {
Fruit fruit = fruitDAO.getFruitByFid(fid);
//获取到fruit对象后将之放置在session作用域
req.setAttribute("fruit", fruit);
//thymeleaf的viewBaseServlet中的方法,处理模板数据
//super.processTemplate("edit",req,resp);
return "edit";
}
return "error";
}
private String del(Integer fid) {
if (fid != null) {
fruitDAO.delFruit(fid);
return "redirect:fruit.do";
}
return "error";
}
private String add(String fname, Integer price, Integer fcount, String remark) {
Fruit fruit = new Fruit(0, fname, price, fcount, remark);
fruitDAO.addFruit(fruit);
return "redirect:fruit.do";
}
private String index(String oper, String keyword, Integer pageNo, HttpServletRequest req) {
//添加关键词查询功能
HttpSession session = req.getSession();
if (pageNo == null) {
pageNo = 1;
}
if (StringUtil.isNotEmpty(oper) && "search".equals(oper)) {
pageNo = 1;
if (StringUtil.isEmpty(keyword)) {
keyword = "";
}
session.setAttribute("keyword", keyword);
} else {
Object keywordObj = session.getAttribute("keyword");
if (keywordObj != null) {
keyword = (String) keywordObj;
} else {
keyword = "";
}
}
// 重新更新当前页的值
session.setAttribute("pageNo", pageNo);
FruitDAO fruitDAO = new FruitDAOImpl();
List<Fruit> fruitList = fruitDAO.getFruitList(keyword, pageNo);
session.setAttribute("fruitList", fruitList);
//总记录条数
int fruitCount = fruitDAO.getFruitCount(keyword);
//总页数
int pageCount = (fruitCount + 5 - 1) / 5;
session.setAttribute("pageCount", pageCount);
return "index";
}
}改之后
package com.fancy.fruit.controllers;
import com.fancy.fruit.biz.FruitService;
import com.fancy.fruit.biz.impl.FruitServiceImpl;
import com.fancy.fruit.dao.FruitDAO;
import com.fancy.fruit.dao.impl.FruitDAOImpl;
import com.fancy.fruit.pojo.Fruit;
import com.fancy.myssm.basedao.myspringmvc.ViewBaseServlet;
import com.fancy.myssm.basedao.util.StringUtil;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.List;
public class FruitController extends ViewBaseServlet {
private FruitService fruitService = new FruitServiceImpl();
private String update(Integer fid, String fname, Integer price, Integer fcount, String remark) {
//2.获取参数
//3.执行更新
fruitService.updateFruit(new Fruit(fid, fname, price, fcount, remark));
//4.资源跳转
//super.processTemplate("index",req,resp);
//此处需要重定向,目的是重新给IndexServlet发请求,然后覆盖到session中,这样index页面上显示的数据才是最新的
//resp.sendRedirect("fruit.do");//重定向,重新给fruit.do,给session重新给fruit更改后的数据
return "redirect:fruit.do";
}
private String edit(Integer fid, HttpServletRequest req) {
//HTML是模板,thymeleaf是引擎,我们在servlet中调用了引擎并且给了引擎需要的模板和参数
if (fid != null) {
Fruit fruit = fruitService.getFruitByFid(fid);
//获取到fruit对象后将之放置在session作用域
req.setAttribute("fruit", fruit);
//thymeleaf的viewBaseServlet中的方法,处理模板数据
//super.processTemplate("edit",req,resp);
return "edit";
}
return "error";
}
private String del(Integer fid) {
if (fid != null) {
fruitService.delFruit(fid);
return "redirect:fruit.do";
}
return "error";
}
private String add(String fname, Integer price, Integer fcount, String remark) {
Fruit fruit = new Fruit(0, fname, price, fcount, remark);
fruitService.addFruit(fruit);
return "redirect:fruit.do";
}
private String index(String oper, String keyword, Integer pageNo, HttpServletRequest req) {
//添加关键词查询功能
HttpSession session = req.getSession();
if (pageNo == null) {
pageNo = 1;
}
if (StringUtil.isNotEmpty(oper) && "search".equals(oper)) {
pageNo = 1;
if (StringUtil.isEmpty(keyword)) {
keyword = "";
}
session.setAttribute("keyword", keyword);
} else {
Object keywordObj = session.getAttribute("keyword");
if (keywordObj != null) {
keyword = (String) keywordObj;
} else {
keyword = "";
}
}
// 重新更新当前页的值
session.setAttribute("pageNo", pageNo);
List<Fruit> fruitList = fruitService.getFruitList(keyword, pageNo);
session.setAttribute("fruitList", fruitList);
//总记录条数
int pageCount = fruitService.getPageCount(keyword);
//总页数
session.setAttribute("pageCount", pageCount);
return "index";
}
}为什么引入service
什么是业务层
-
Model1和Model2 MVC : Model(模型)、View(视图)、Controller(控制器) 视图层:用于做数据展示以及和用户交互的一个界面 控制层:能够接受客户端的请求,具体的业务功能还是需要借助于模型组件来完成 模型层:模型分为很多种:有比较简单的pojo/vo(value object),有业务模型组件,有数据访问层组件
-
pojo/vo : 值对象
-
DAO : 数据访问对象
-
BO : 业务对象
-
区分业务对象和数据访问对象
1) DAO中的方法都是单精度方法或者称之为细粒度方法。什么叫单精度?一个方法只考虑一个操作,比如添加,那就是insert操作、查询那就是select操作.... 2) BO中的方法属于业务方法,也实际的业务是比较复杂的,因此业务方法的粒度是比较粗的 注册这个功能属于业务功能,也就是说注册这个方法属于业务方法。 那么这个业务方法中包含了多个DAO方法。也就是说注册这个业务功能需要通过多个DAO方法的组合调用,从而完成注册功能的开发。 注册:
-
检查用户名是否已经被注册 - DAO中的select操作 向用户表新增一条新用户记录 - DAO中的insert操作
-
向用户积分表新增一条记录(新用户默认初始化积分100分) - DAO中的insert操作 向系统消息表新增一条记录(某某某新用户注册了,需要根据通讯录信息向他的联系人推送消息) - DAO中的insert操作
-
向系统日志表新增一条记录(某用户在某IP在某年某月某日某时某分某秒某毫秒注册) - DAO中的insert操作 ....
-
-
所以我们在库存系统中添加业务层组件FruitService来专门处理复杂的业务,Controller专门用来处理客户端的请求
IOC实现
理解IOC
IOC—Inversion of Control,即“控制反转”,是一种设计思想。
-
之前在Servlet中,我们创建service对象 , FruitService fruitService = new FruitServiceImpl(); 这句话如果出现在servlet中的某个方法内部,那么这个fruitService的作用域(生命周期)应该就是这个方法级别; 如果这句话出现在servlet的类中,也就是说fruitService是一个成员变量,那么这个fruitService的作用域(生命周期)应该就是这个servlet实例级别
-
之后我们在applicationContext.xml中定义了这个fruitService。然后通过解析XML,产生fruitService实例,存放在beanMap中,这个beanMap在一个BeanFactory中 因此,我们转移(改变)了之前的service实例、dao实例等等他们的生命周期。控制权从程序员转移到BeanFactory。这个现象我们称之为控制反转
在软件系统中,层与层之间是存在依赖的。我们也称之为耦合。 我们系统架构或者是设计的一个原则是: 高内聚低耦合。 层内部的组成应该是高度聚合的,而层与层之间的关系应该是低耦合的,最理想的情况0耦合(就是没有耦合)
public class FruitServiceImpl implements FruitService {
private FruitDAO fruitDAO = new FruitDAOImpl();public class FruitController extends ViewBaseServlet {
private FruitService fruitService = new FruitServiceImpl();所谓的解耦,不是说完全没关系,而是在代码层面解除锁定,打个比方就是用胶水黏在一起,还是像乐高那样拼接,以上代码可以看出我们目前的系统各层之前耦合度较高
实现IOC
①修改配置文件applicationContext
配置好三个bean、对应三个组件,下次在Tomcat启动时,就会将三个组件准备好放置在一个容器里。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<beans>
<bean id="fruitDAO" class="com.fancy.fruit.dao.impl.FruitDAOImpl" />
<bean id="fruitService" class="com.fancy.fruit.service.impl.FruitServiceImpl" />
<!-- 这个bean标签的作用是将来servletpath中涉及的名字对应的fruit,那么就要FruitController这个类来处理-->
<bean id="fruit" class="com.fancy.fruit.controllers.FruitController"></bean>
</beans>不光如此,以后添加一些Controller和service只需要到xml里面配置,然后beanfactory就会自动放到map里面
②添加BeanFactory接口
package com.fancy.myssm.io;
public interface BeanFactory {
//根据id获取到某一个bean对象
Object getBean(String id);
}③添加ClassPathXmlApplicationContext实现BeanFactory
package com.fancy.myssm.io;
import org.w3c.dom.Document;
import org.w3c.dom.Element;
import org.w3c.dom.Node;
import org.w3c.dom.NodeList;
import org.xml.sax.SAXException;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory;
import javax.xml.parsers.ParserConfigurationException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class ClassPathXmlApplicationContext implements BeanFactory{
private Map<String,Object> beanMap = new HashMap<>();
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(){
try {
InputStream inputStream = getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("applicationContext.xml");
DocumentBuilderFactory documentBuilderFactory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
DocumentBuilder documentBuilder = documentBuilderFactory.newDocumentBuilder();
//创建document对象
Document document = documentBuilder.parse(inputStream);
//获取所有的bean节点
NodeList beanNodeList = document.getElementsByTagName("bean");
for (int i = 0; i < beanNodeList.getLength(); i++) {
Node beanNode = beanNodeList.item(i);
//如果是一个元素节点,就强转为元素节点
if (beanNode.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) {
Element beanElement = (Element) beanNode;
//获取了bean中的id属性、class属性
String beanId = beanElement.getAttribute("id");
String className = beanElement.getAttribute("class");
//获取全类名后,要获取它的实例对象
Class beanClass = Class.forName(className);
Object beanObj = beanClass.newInstance();
//将beanId、beanObj放入Map中
beanMap.put(beanId, beanObj);
}
}
for(int i = 0 ; i<beanNodeList.getLength() ; i++){
Node beanNode = beanNodeList.item(i);
if(beanNode.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) {
Element beanElement = (Element) beanNode;
String beanId = beanElement.getAttribute("id");
NodeList beanChildNodeList = beanElement.getChildNodes();
for (int j = 0; j < beanChildNodeList.getLength() ; j++) {
Node beanChildNode = beanChildNodeList.item(j);
if(beanChildNode.getNodeType()==Node.ELEMENT_NODE && "property".equals(beanChildNode.getNodeName())){
Element propertyElement = (Element) beanChildNode;
String propertyName = propertyElement.getAttribute("name");
String propertyRef = propertyElement.getAttribute("ref");
//1) 找到propertyRef对应的实例
Object refObj = beanMap.get(propertyRef);
//2) 将refObj设置到当前bean对应的实例的property属性上去
Object beanObj = beanMap.get(beanId);
Class beanClazz = beanObj.getClass();
Field propertyField = beanClazz.getDeclaredField(propertyName);
propertyField.setAccessible(true);
propertyField.set(beanObj,refObj);
}
}
}
}
} catch (ParserConfigurationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SAXException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public Object getBean(String id) {
//根据id获取到beanMap容器中某一个bean对象
return beanMap.get(id);
}
}④改原先在DispatcherServlet的init方法中的获取对应Controller的方法体
try {
InputStream inputStream = getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("applicationContext.xml");
DocumentBuilderFactory documentBuilderFactory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
DocumentBuilder documentBuilder = documentBuilderFactory.newDocumentBuilder();
//创建document对象
Document document = documentBuilder.parse(inputStream);
//获取所有的bean节点
NodeList beanNodeList = document.getElementsByTagName("bean");
for (int i = 0; i < beanNodeList.getLength(); i++) {
Node beanNode = beanNodeList.item(i);
//如果是一个元素节点,就强转为元素节点
if (beanNode.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) {
Element beanElement = (Element) beanNode;
//获取了bean中的id属性、class属性
String beanId = beanElement.getAttribute("id");
String className = beanElement.getAttribute("class");
//获取全类名后,要获取它的实例对象
Class controllerBeanClass = Class.forName(className);
Object beanObj = controllerBeanClass.newInstance();
//将beanId、beanObj放入Map中
beanMap.put(beanId, beanObj);
}
}
} catch (ParserConfigurationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SAXException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}获取全类名后,要获取它的实例对象不再只是对应的Controller,而是三个模型controller、service、DAO
添加到ClassPathXmlApplicationContext构造器中
⑤修改中央控制器DispatcherServlet中的代码
@WebServlet("*.do")
public class DispatcherServlet extends ViewBaseServlet {
private BeanFactory beanFactory ;⭕⭕⭕
//servlet有加载-实例化-服务-销毁的生命周期,所以先在实例化阶段的构造器中解析xml配置文件
public DispatcherServlet() {
}
//应该使用init方法加载而不是构造器
public void init() throws ServletException {
super.init();
beanFactory = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext();⭕⭕⭕
}
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
req.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
String servletPath = req.getServletPath();
servletPath = servletPath.substring(1);
int lastDotIndex = servletPath.lastIndexOf(".do");
servletPath = servletPath.substring(0, lastDotIndex);
Object controllerBeanObj = beanFactory⭕⭕⭕.getBean(servletPath);
String operate = req.getParameter("operate");思考:此处为什么声明的是一个接口BeanFactory类型的变量?为什么new 一个ClassPathXmlApplicationContext?
可能是使用多态,增加了代码的可扩展性。new一个ClassPathXmlApplicationContext就可以使用ClassPathXmlApplicationContext中实现的getBean的具体方法(根据id获取到beanMap容器中某一个bean对象),new一个别的实现了BeanFactory接口的类就可以实现其它类的方法,就可以很方便地调用不同的方法获得bean对象。
相反如果此处直接定义一个ClassPathXmlApplicationContext类型的变量,之后调用其它实现了BeanFactory接口的对象中的方法时就要重新改这个定义的变量了。
⑥去掉FruitServiceImpl和FruitController中的耦合
import com.fancy.fruit.service.FruitService;
import com.fancy.fruit.service.impl.FruitServiceImpl;
import com.fancy.fruit.pojo.Fruit;
import com.fancy.myssm.myspringmvc.ViewBaseServlet;
import com.fancy.myssm.util.StringUtil;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.util.List;
public class FruitController {
private FruitService fruitService = null;import com.fancy.fruit.service.FruitService;
import com.fancy.fruit.dao.FruitDAO;
import com.fancy.fruit.pojo.Fruit;
import java.util.List;
public class FruitServiceImpl implements FruitService {
private FruitDAO fruitDAO = null;所以,接下来我们不仅要描述DispatcherServlet需要哪些组件,还需要说明组件与组件之间的依赖关系
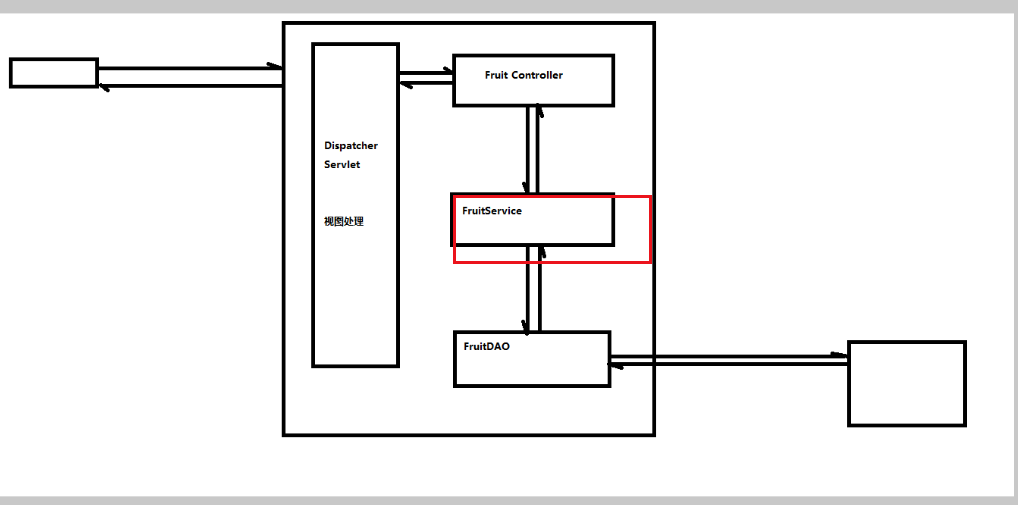
fruitservice需要fruitDAO组件,FruitController需要fruitService组件(依赖注入?)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<beans>
<bean id="fruitDAO" class="com.fancy.fruit.dao.impl.FruitDAOImpl" />
<bean id="fruitService" class="com.fancy.fruit.service.impl.FruitServiceImpl" >
<!-- property标签用来表示属性;name表示属性名;ref表示引用其他bean的id值-->
<property name="fruitDAO" ref="fruitDAO"/>
</bean>
<!-- 这个bean标签的作用是将来servletpath中涉及的名字对应的fruit,那么就要FruitController这个类来处理-->
<bean id="fruit" class="com.fancy.fruit.controllers.FruitController">
<property name="fruitService" ref="fruitService"/>
</bean>
</beans>此XML文件不仅描述了需要几个bean,还描述了他们之间依赖关系
*框架是通过dom 4j解析成beanDefinition然后挨个循环遍历创建对象,放进名为singObjects的map里
⑦改ClassPathXmlApplicationContext的构造器
之前只向map容器中保存了bean,还没有保存他们之间依赖关系
for(int i = 0 ; i<beanNodeList.getLength() ; i++){
Node beanNode = beanNodeList.item(i);
if(beanNode.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) {
Element beanElement = (Element) beanNode;
String beanId = beanElement.getAttribute("id");
NodeList beanChildNodeList = beanElement.getChildNodes();
for (int j = 0; j < beanChildNodeList.getLength() ; j++) {
Node beanChildNode = beanChildNodeList.item(j);
if(beanChildNode.getNodeType()==Node.ELEMENT_NODE && "property".equals(beanChildNode.getNodeName())){
Element propertyElement = (Element) beanChildNode;
String propertyName = propertyElement.getAttribute("name");
String propertyRef = propertyElement.getAttribute("ref");
//1) 找到propertyRef对应的实例
Object refObj = beanMap.get(propertyRef);
//2) 将refObj设置到当前bean对应的实例的property属性上去
Object beanObj = beanMap.get(beanId);
Class beanClazz = beanObj.getClass();
Field propertyField = beanClazz.getDeclaredField(propertyName);
propertyField.setAccessible(true);
propertyField.set(beanObj,refObj);
}
}
}
}Node 节点
Element 元素节点
Text 文本节点
<sname>jim</sname>
视频48可以之后学了spring再过来听一遍
DI - 依赖注入
依赖注入:
-
之前我们在控制层出现代码:FruitService fruitService = new FruitServiceImpl(); 那么,控制层和service层存在耦合。
-
之后,我们将代码修改成FruitService fruitService = null ; 然后,在配置文件中配置:
<bean id="fruit" class="FruitController"><property name="fruitService" ref="fruitService"/></bean>


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号