Data Structures and Algorithm Analysis in Java-Chapter I(复习算法知识)
数学知识、Java知识的复习
一、数学知识复习
1.指数
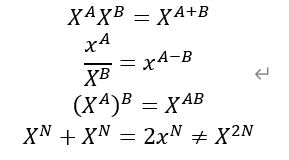
2.对数
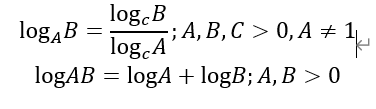
3.级数
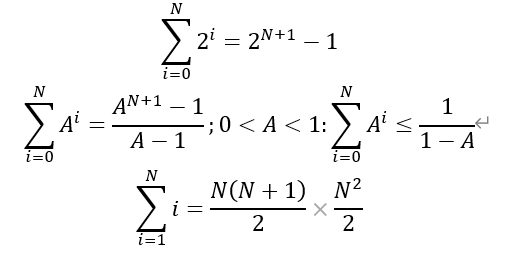
- 欧拉常数:
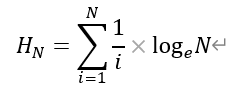
- 斐波那契数:
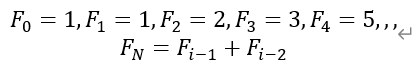
4.模运算
N整除(A-B),A与B模N同佘记为 A三B(mod N)
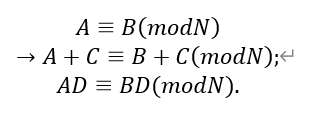
5.证明的方法
5.1归纳法证明
第一步:
确定基准情形:有限数k 成立的
第二步:
归纳假设:证明(K+1)也成立
5.2通过反例证明
5.3反证法证明
二、递归简论
打印整数的递归例程:
package www.fancy.algorithm;
public class printTest {
public int i;
public printTest(int i){
this.i = i;
}
public void PrintOut(int x){
if(x >= 10)
PrintOut(x / 10);
PrintDigit(x % 10);
}
public void PrintDigit(int x){
System.out.println(x);
}
}
class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
printTest printTest = new printTest(76234);
printTest.PrintOut(printTest.i);
}
}递归的四条基本法则:
- 基准情形。
- 不断推进。
- 设计法则。
- 合成效益法则。求解同一个问题,切勿在不同的递归调用中做重复性的工作。
三、泛型构建
如果除去对象的基本类型外,实现方法是相同的,我们就可以用 泛型实现 来描述这种基本的功能。
使用object表示泛型
package www.fancy.algorithm;
public class MemoryCell {
//Public methods
public Object read(){
return storedValue;
}
public void write(Object x){
storedValue = x;
}
//内部私有数据表示
private Object storedValue;
}
public class TestMemoryCell {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MemoryCell m = new MemoryCell();
m.write("68");
//1
//String val = (String) m.read();
//System.out.println("Number:"+val);
//2
String val = m.read().toString();
System.out.println();
}
}
基本类型的包装类
实现算法时,常常遇到语言定型问题,此时需要用到包装类。
public class TestMemoryCell {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MemoryCell m = new MemoryCell();
m.write(1);
int val = m.read();
System.out.println();
}
}使用MemoryCell直接传入基本数据类型来储存时,编译时会报错,“不兼容类型”,应当使用包装类:
package www.fancy.algorithm;
public class TestMemoryCell {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MemoryCell m = new MemoryCell();
m.write(new Integer(1));
int val = (Integer) m.read();
System.out.println("Number:"+val);
}
}
使用接口表示泛型类型
只有在使用Object类中已有的那些方法能够表示所执行的操作时,才能使用Object作为泛型类型来工作。
- 只有能够实现Comparable接口的对象才能作为Comparable数组的元素被传递;
- 如果Comparable数组有两个不相容的对象,将抛出异常ClassCastException;
- 基本类型不能作为Comparable传递,包装类可以,因为它们实现了Comparable接口;
- 接口究竟是不是标准的库接口不是必须的。
public class FindMaxDemo {
/**
* @Name FindMaxDemo
* @Description Return max item in arr.
* Precondition:arr.length > 0
* @Author Weiss(The author of <Data Structures and Algorithm Analysis in Java>)
* @return 2022/2/9
* @Version 1.0
*/
public static Comparable findMax(Comparable [] arr){
int maxIndex = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if(arr[i].compareTo(arr[maxIndex])>0){
maxIndex = i;
}
}
return arr[maxIndex];
}
/**
* Test findMax on Shape and String objects
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Shape[] sh1 = {new Circle(2.0), new Rectangle(3,4)};
String[] str1 = {"keke","baobao","fengfeng","maodou"};
System.out.println(findMax(sh1);
System.out.println(findMax(str1));
}
}
数组类型的兼容性
Person[] arr = new Employee[5]; //arrays are compatible
arr[0] = new Student(...);// Student IS-A Person
arr[0] 实际上引用的是一个Employee,可是Student IS-NOT-A Employee
可以指定这些数组不是类型兼容的。在Java中数组类型时兼容的,这叫作协变数组类型。
四、Java5泛型类型特性实现泛型构件
简单的泛型类和接口
package www.fancy.algorithm;
public class GenericMemory<T>{
//Public methods
public T read(){
return storedValue;
}
public void write(T x){
storedValue = x;
}
//内部私有数据表示
private T storedValue;
}public interface Comparable<T> {
public int compareTo(T o);
}
自动装拆箱
自动拆:int型量被传递到一个Integer对象的地方,编译器将在幕后插入一个Integer的构造方法。
自动装:一个Integer对象被放到需要int型量的地方,编译器将调用intValue方法。
代码:
class BoxingDemo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
GenericMemory<Integer> m = new GenericMemory<Integer>();
m.write(37);//自动装箱
int val = m.read();//自动拆箱
System.out.println("Number:"+val);
}
}
菱形运算符
作为简化代码使用,Java7新特性。
class BoxingDemo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
GenericMemory<Integer> m = new GenericMemory<>();//菱形运算符改写
m.write(37);
int val = m.read();
System.out.println("Number:"+val);
}
}
带有限制的通配符
泛型集合不是协变的。使用泛型的原因在于产生编译器错误而不是类型不匹配的运行时异常(ArrayStoreException)
为了避免因失去协变性会避免使用集合,导致代码缺少灵活性,便引入了通配符。
/**
* 计算Shape数组的总面积,传入的是一个Collection<Shape>集合
*/
public static double totalArea(Collection<? extends Shape> arr){
double total = 0;
for(Shape s : arr)
if(s != null)
total += s.area();
return total;
}
}使用带有限制的通配符后此时再传入一个Collection<Square>(Square extends Shape),方法可以正常运行。
泛型static方法
totalArea是泛型方法,但是其没有特定类型的参数表。为了特定类型,我们必须声明一种带有若干类型参数的显式泛型方法。如:
public static <T> boolean contains(T [] arr, T x){
for(T val: arr)
if(x.equals(val))
return true;
return false;
}
}该方法是泛型static方法,对值x在数组arr中进行查找。
泛型方法中的类型参数位于返回类型之前。
类型界限
需要在泛型方法中调用compareTo方法时,只有保证 T 是Comparable的情况下调用才是合法的,此时需要用到类型界限。
public static <T> T findMax(T [] arr){
int maxIndex = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if(arr[i].compareTo(arr[maxIndex])>0)
maxIndex = i;
}
return arr[maxIndex];
}
//编译时报错:Cannot resolve method 'compareTo' in 'T'
}
但是Comparable接口也是泛型的,所以类型界限的写法如下:
public static <T extends Comparable<? super T>> T findMax(T [] arr){
int maxIndex = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if(arr[i].compareTo(arr[maxIndex])>0)
maxIndex = i;
}
return arr[maxIndex];
}
类型擦除
泛型类可由编译器通过类型擦除过程变为非泛型类,编译器生成一种与泛型类同名的原始类。
类型变量由他们的类型界限代替
对于泛型的限制
①基本类型不能用做类型参数
②instanceof检测:和类型转换工作只对原始类型进行
class BoxingDemo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
GenericMemory<Integer> m1 = new GenericMemory<>();//菱形运算符改写
m1.write(37);
Object m = m1;
GenericMemory<String> m2 =(GenericMemory<String>) m;
System.out.println(m2.read());
/*System.out.println(((GenericMemory<?>) m2).read());*/
}
}以上代码会报ClassCastException异常。
③static的语境
static方法和static域均不可引用类的类型变量,因为在类型擦除后类型变量就不存在了。
④泛型类型的实例化
不能创建一个泛型类型的实例。
⑤泛型数组对象
也不能创建一个泛型的数组。
⑥参数化类型的数组
参数化类型的数组的实例化是非法的。
五、函数对象
public static <T extends Comparable<? super T>> T findMax(T [] arr){
int maxIndex = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if(arr[i].compareTo(arr[maxIndex])>0)
maxIndex = i;
}
return arr[maxIndex];
}"类型界限"中的findMax方法,找出一个T[ ] 数组的最大项,这种方法的局限性是它只对实现Comparable接口的对象有效,因为它使用CompareTo作为所有比较决策的基础。
public static Comparable findMax(Comparable[] arr) {
int maxIndex = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i].compareTo(arr[maxIndex]) > 0) {
maxIndex = i;
}
}
return arr[maxIndex];
}
//Generic findMax,with a function object.
//Precondition: a.size() > 0
public static <T>
T findMax(T[] arr, Comparator<? super T> cmp) {
int maxIndex = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (cmp.compare(arr[i], arr[maxIndex]) > 0)
maxIndex = i;
}
return arr[maxIndex];
}
class CaseInsensitiveCompare implements Comparator<String> {
public int compare(String lhs, String rhs) {
return lhs.compareToIgnoreCase(rhs);
}
}
class TestProgram {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] arr = {"AA", "BB", "CC"};
System.out.println(findMax(arr, new FindMaxDemo.CaseInsensitiveCompare()));
}
}我们可以定义一个没有数据而只有一个方法的类,并传递给一个实例。一个函数通过将其放在一个对象内部而被传递,这样的对象通常叫做函数对象。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号