MyBatis的SqlSession理解(一)
SqlSession是Mybatis最重要的构建之一,可以认为Mybatis一系列的配置目的是生成类似JDBC生成的Connection对象的statement对象,这样才能与数据库开启“沟通”,通过SqlSession可以实现增删改查(当然现在更加推荐是使用Mapper接口形式)
1 .sqlsession的创建:
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder创建SqlSessionFactory openSession,sqlSession 执行增删改查
用了注解是通过org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean该类创建sqlsession的,而mapper里面的每一个方法称为statement。
public void deleteUserTest() throws IOException { // mybatis配置文件 String resource = "SqlMapConfig.xml"; // 得到配置文件流 InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); // 创建会话工厂,传入mybatis的配置文件信息 SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder() .build(inputStream); // 通过工厂得到SqlSession SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); // 传入id删除 用户 sqlSession.delete("test.deleteUser", 39);
//更新
sqlSession.update("test.updateUser", user);
//插入
sqlSession.insert("test.insertUser", user);
//查询
List<User> list = sqlSession.selectOne("test.findUserByName", "小明"); // 提交事务 增删改 需要commit,查询无需commit sqlSession.commit(); // 关闭会话 sqlSession.close(); }
2.SqlSession原理
SqlSession提供select/insert/update/delete方法,在旧版本中使用使用SqlSession接口的这些方法,但是新版的Mybatis中就会建议使用Mapper接口的方法。
映射器其实就是一个动态代理对象,进入到MapperMethod的execute方法就能简单找到SqlSession的删除、更新、查询、选择方法,从底层实现来说:通过动态代理技术,让接口跑起来,之后采用命令模式,最后还是采用了SqlSession的接口方法(getMapper()方法等到Mapper)执行SQL查询(也就是说Mapper接口方法的实现底层还是采用SqlSession接口方法实现的)。
3.SqlSession重要的四个对象
1)Execute:调度执行StatementHandler、ParmmeterHandler、ResultHandler执行相应的SQL语句;
2)StatementHandler:使用数据库中Statement(PrepareStatement)执行操作,即底层是封装好了的prepareStatement;
3)ParammeterHandler:处理SQL参数;
4)ResultHandler:结果集ResultSet封装处理返回。
1 Execute执行器
execute接口有以下方法

执行器起到至关重要的作用,它是真正执行Java与数据库交互的东西,参与了整个SQL查询执行过程中。
1)主要有三种执行器:简易执行器SIMPLE(不配置就是默认执行器)、REUSE是一种重用预处理语句、BATCH批量更新、批量专用处理器
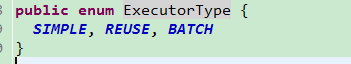
2)执行器作用:Executor会先调用StatementHandler的prepare()方法预编译SQL语句,同时设置一些基本的运行参数,然后调用StatementHandler的parameterize()方法(实际上是启用了ParameterHandler设置参数)设置参数,resultHandler再组装查询结果返回调用者完成一次查询完成预编译,简单总结起来就是即先预编译SQL语句,之后设置参数(跟JDBC的prepareStatement过程类似)最后如果有查询结果就会组装返回。
StatementHandler 接口方法
public interface StatementHandler { //预编译SQL语句 Statement prepare(Connection connection) throws SQLException; //设置一些基本的运行参数 void parameterize(Statement statement) throws SQLException; void batch(Statement statement) throws SQLException; int update(Statement statement) throws SQLException; <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException; BoundSql getBoundSql(); ParameterHandler getParameterHandler(); }
第一:Executor通过Configuration对象中newExecutor()方法中选择相应的执行器生成
//Configuration 类
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType, boolean autoCommit) { executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType; executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType; Executor executor; if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) { executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction); } else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) { executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction); } else { executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction); } if (cacheEnabled) { executor = new CachingExecutor(executor, autoCommit); }
//最后在可以在调用真正的Executor前可以修改插件代码,执行拦截器 executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor); return executor; }
//InterceptorChain 类中pluginAll 方法:
public Object pluginAll(Object target) { for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) { target = interceptor.plugin(target); } return target; }
第二:在执行器中StatementHandler是根据Configuration构建的
public class SimpleExecutor extends BaseExecutor { public SimpleExecutor(Configuration configuration, Transaction transaction) { super(configuration, transaction); } public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException { Statement stmt = null; try { Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); //获取StatementHandler 对象 StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, null, null);
//调到最后一个方法查看详细内容 stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog()); return handler.update(stmt); } finally { closeStatement(stmt); } } public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { Statement stmt = null; try { Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog()); return handler.<E>query(stmt, resultHandler); } finally { closeStatement(stmt); } } public List<BatchResult> doFlushStatements(boolean isRollback) throws SQLException { return Collections.emptyList(); } private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException { Statement stmt; Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog); stmt = handler.prepare(connection); //设置执行参数 handler.parameterize(stmt); return stmt; } }
第三:Executor会执行StatementHandler的prepare()方法进行预编译---->填入connection对象等参数---->再调用parameterize()方法设置参数---->完成预编译
//SimpleExecutor类 private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException { Statement stmt; Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog); // 执行handler.prepare()预编译sql stmt = handler.prepare(connection);
//设置执行参数 handler.parameterize(stmt); return stmt; }
2 StatementHanlder数据库会话器
1)作用:简单来说就是专门处理数据库会话。详细来说就是进行预编译并且调用ParameterHandler的setParameters()方法设置参数。
2)数据库会话器主要有三种:SimpleStatementHandler、PrepareStatementHandler、CallableStatementHandler,分别对应Executor的三种执行器(SIMPLE、REUSE、BATCH)
Executor的prepareStatement()方法中调用了StatementHandler的parameterize()
第一:StatementHandler的生成是由Configuration方法中newStatementHandler()方法生成的,但是正在创建的是实现了StatementHandler接口的RoutingStatementHandler对象
//Configuration
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) { StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler); return statementHandler; }
第二:RoutingStatementHandler的通过适配器模式找到对应(根据上下文)的StatementHandler执行的,并且有SimpleStatementHandler、PrepareStatementHandler、CallableStatementHandler,分别对应Executor的三种执行器(SIMPLE、REUSE、BATCH)
//RoutingStatementHandler public RoutingStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) { switch (ms.getStatementType()) { case STATEMENT: delegate = new SimpleStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); break; case PREPARED: delegate = new PreparedStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); break; case CALLABLE: delegate = new CallableStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); break; default: throw new ExecutorException("Unknown statement type: " + ms.getStatementType()); } }
PreparedStatementHandler , public class PreparedStatementHandler extends BaseStatementHandler , BaseStatementHandler implements StatementHandler
第三:在BaseStatementHandler中重写prepare()方法,instantiateStatement()方法完成预编译,之后设置一些基础配置(获取最大行数,超时)
//BaseStatementHandler public Statement prepare(Connection connection) throws SQLException { ErrorContext.instance().sql(boundSql.getSql()); Statement statement = null; try { statement = instantiateStatement(connection); setStatementTimeout(statement); setFetchSize(statement); return statement; } catch (SQLException e) { closeStatement(statement); throw e; } catch (Exception e) { closeStatement(statement); throw new ExecutorException("Error preparing statement. Cause: " + e, e); } }
第四:instantiateStatement()预编译实际上也是使用了JDBC的prepareStatement()完成预编译
protected Statement instantiateStatement(Connection connection) throws SQLException { String sql = boundSql.getSql(); if (mappedStatement.getKeyGenerator() instanceof Jdbc3KeyGenerator) { String[] keyColumnNames = mappedStatement.getKeyColumns(); if (keyColumnNames == null) { return connection.prepareStatement(sql, PreparedStatement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS); } else { return connection.prepareStatement(sql, keyColumnNames); } } else if (mappedStatement.getResultSetType() != null) { return connection.prepareStatement(sql, mappedStatement.getResultSetType().getValue(), ResultSet.CONCUR_READ_ONLY); } else { return connection.prepareStatement(sql); } }
第五:在prepareStatement中重写parameterize()方法。prepare()预编译完成之后,Executor会调用parameterize()方法
public void parameterize(Statement statement) throws SQLException { parameterHandler.setParameters((PreparedStatement) statement); }
(3)ParameterHandler参数处理器
作用:对预编译中参数进行设置,如果有配置typeHandler,自然会对注册的typeHandler对参数进行处理



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号