Spring 事务源码学习
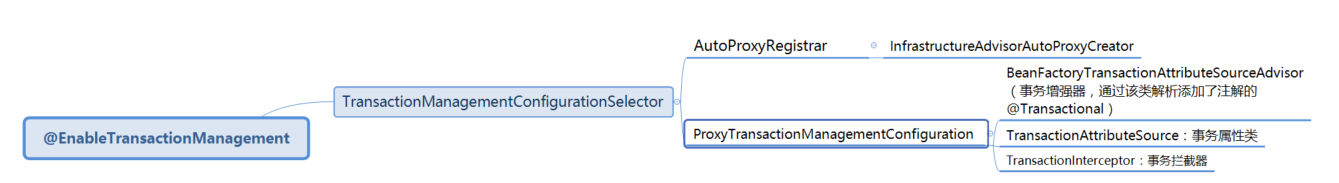
@EnableTransactionManagement
@Import({TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector.class}组件导入了两个组件
- AutoProxyRegistrar
- ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration
在ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration里面主要创建了
- BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor
- AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource
- TransactionInterceptor
TransactionInterceptor类图
事务拦截器,实现MethodInterceptor

事务增强器BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor类图

Spring 是如何管理事务的?
1. PlatformTransactionManager:事务管理器--主要用于平台相关事务的管理
主要有三个方法:
-
commit 事务提交;
-
rollback 事务回滚;
-
getTransaction 获取事务状态。
2. TransactionDefinition:事务定义信息--用来定义事务相关的属性,给事务管理器PlatformTransactionManager使用
这个接口有下面四个主要方法:
-
getIsolationLevel:获取隔离级别;
-
getPropagationBehavior:获取传播行为;
-
getTimeout:获取超时时间;
-
isReadOnly:是否只读(保存、更新、删除时属性变为false--可读写,查询时为true--只读)
事务管理器能够根据这个返回值进行优化,这些事务的配置信息,都可以通过配置文件进行配置。
3. TransactionStatus:事务具体运行状态--事务管理过程中,每个时间点事务的状态信息。
例如它的几个方法:
-
hasSavepoint():返回这个事务内部是否包含一个保存点,
-
isCompleted():返回该事务是否已完成,也就是说,是否已经提交或回滚
-
isNewTransaction():判断当前事务是否是一个新事务
声明式事务的优缺点:
-
优点:不需要在业务逻辑代码中编写事务相关代码,只需要在配置文件配置或使用注解(@Transaction),这种方式没有侵入性。
-
缺点:声明式事务的最细粒度作用于方法上,如果像代码块也有事务需求,只能变通下,将代码块变为方法。
事务实现原理
1.创建代理对象
代理对象生成入口图
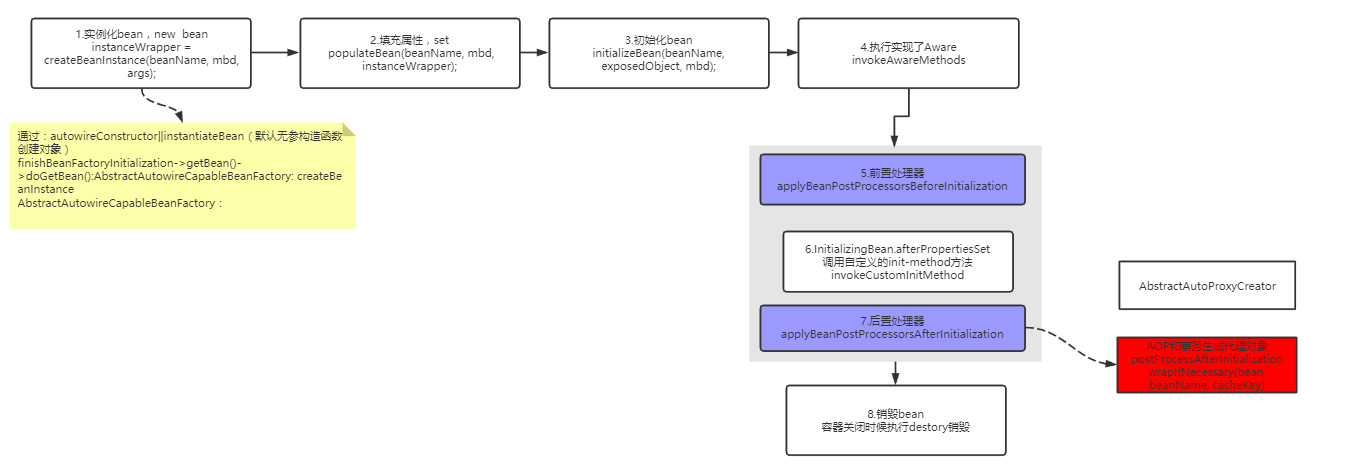

@Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { if (bean != null) { Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName); if (!this.earlyProxyReferences.contains(cacheKey)) { //生成AOP代理对象 事务和AOP 都会生成代理对象 return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey); } } return bean; } protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) { if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) { return bean; } //不需要增强的 if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) { return bean; } //是否是基础bean,是否需要跳过 //shouldSkip 事务 跳过,AOP根据条件判断是否要跳过 if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) { this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE); return bean; } // Create proxy if we have advice. //如果有通知就创建代理对象 添加@aspect 或者实现Advice接口的 就是有通知 //getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean 事务增强器对象 //事务找到:BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor //得到Advisors 通知类 这里是区分aop和事务的 事务找到 Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null); //找到合适的通知器不为空 if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) { this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE); //创建代理类 Object proxy = createProxy( bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean)); this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass()); return proxy; } this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE); return bean; }
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);

//AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) { //找到IOC容器中候选的通知 BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors(); //debug aop和事务的区别?? //事务找到:BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName); extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors); if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) { eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors); } return eligibleAdvisors; }

public List<Advisor> findAdvisorBeans() { // Determine list of advisor bean names, if not cached already. String[] advisorNames = null; synchronized (this) { advisorNames = this.cachedAdvisorBeanNames; if (advisorNames == null) { // Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans // uninitialized to let the auto-proxy creator apply to them! //去容器中找实现了 Advisor接口的实现类 /** * 二我们的事务注解@EnableTransactionManagement 导入了一个叫ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration * 在这个配置类中配置了 * @Bean(name = TransactionManagementConfigUtils.TRANSACTION_ADVISOR_BEAN_NAME) *@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE) *public BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor transactionAdvisor() { TRANSACTION_ADVISOR_BEAN_NAME 把他的名字取出来放入到cachedAdvisorBeanNames中 */ advisorNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors( this.beanFactory, Advisor.class, true, false); this.cachedAdvisorBeanNames = advisorNames; } } if (advisorNames.length == 0) { return new LinkedList<>(); } List<Advisor> advisors = new LinkedList<>(); for (String name : advisorNames) { if (isEligibleBean(name)) { if (this.beanFactory.isCurrentlyInCreation(name)) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Skipping currently created advisor '" + name + "'"); } } return advisors; } //findAdvisorsThatCanApply protected List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply( List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) { ProxyCreationContext.setCurrentProxiedBeanName(beanName); try { //查找增强器 return AopUtils.findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass); } finally { ProxyCreationContext.setCurrentProxiedBeanName(null); } } //AopUtils public static List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> clazz) { if (candidateAdvisors.isEmpty()) { return candidateAdvisors; } List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = new LinkedList<>(); for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) { if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor && canApply(candidate, clazz)) { eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate); } } boolean hasIntroductions = !eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty(); for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) { if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) { // already processed continue; } if (canApply(candidate, clazz, hasIntroductions)) { eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate); } } return eligibleAdvisors; } public static boolean canApply(Advisor advisor, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) { if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) { return ((IntroductionAdvisor) advisor).getClassFilter().matches(targetClass); } else if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) { //判断事务增强器 BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor 是否实现了 PointcutAdvisor pca = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor; //找到真正能用的增强器 return canApply(pca.getPointcut(), targetClass, hasIntroductions); } else { // It doesn't have a pointcut so we assume it applies. return true; } } public static boolean canApply(Pointcut pc, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) { Assert.notNull(pc, "Pointcut must not be null"); if (!pc.getClassFilter().matches(targetClass)) { return false; } MethodMatcher methodMatcher = pc.getMethodMatcher(); if (methodMatcher == MethodMatcher.TRUE) { // No need to iterate the methods if we're matching any method anyway... return true; } IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher introductionAwareMethodMatcher = null; if (methodMatcher instanceof IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) { introductionAwareMethodMatcher = (IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) methodMatcher; } Set<Class<?>> classes = new LinkedHashSet<>(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(targetClass)); classes.add(targetClass); //循环所有的class对象 for (Class<?> clazz : classes) { //通过class获取到所有的 方法 Method[] methods = ReflectionUtils.getAllDeclaredMethods(clazz); //循环方法 for (Method method : methods) { if ((introductionAwareMethodMatcher != null && introductionAwareMethodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass, hasIntroductions)) || //事务: 查找对应添加注解的方法 查找添加注解的方法 //TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut,AbstractFallbackTransactionAttributeSource //AOP :AbstractRegexpMethodPointcut methodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass)) { return true; } } } return false; }
TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut .matches 解析事务注解生成事务

@Override @Nullable public TransactionAttribute getTransactionAttribute(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass) { if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) { return null; } // First, see if we have a cached value. Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(method, targetClass); Object cached = this.attributeCache.get(cacheKey); if (cached != null) { // Value will either be canonical value indicating there is no transaction attribute, // or an actual transaction attribute. if (cached == NULL_TRANSACTION_ATTRIBUTE) { return null; } else { return (TransactionAttribute) cached; } } else { // We need to work it out. //重点 :查找事务注解 根据方法查找添加事务 并且解析为TransactionAttribute TransactionAttribute txAttr = computeTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass); // Put it in the cache. //解析出来的事务注解属性为空 if (txAttr == null) { //存放空事务注解属性 this.attributeCache.put(cacheKey, NULL_TRANSACTION_ATTRIBUTE); } else { //方法的描述符 包名+类名+方法名 String methodIdentification = ClassUtils.getQualifiedMethodName(method, targetClass); //把方法描述设置到事务属性上去 if (txAttr instanceof DefaultTransactionAttribute) { ((DefaultTransactionAttribute) txAttr).setDescriptor(methodIdentification); } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Adding transactional method '" + methodIdentification + "' with attribute: " + txAttr); } //加入到缓存中 this.attributeCache.put(cacheKey, txAttr); } return txAttr; } }

//AbstractFallbackTransactionAttributeSource @Nullable protected TransactionAttribute computeTransactionAttribute(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass) { // Don't allow no-public methods as required. //添加事务的方法必须是 public的 ,非public 直接返回空 不处理 if (allowPublicMethodsOnly() && !Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) { return null; } // Ignore CGLIB subclasses - introspect the actual user class. Class<?> userClass = (targetClass != null ? ClassUtils.getUserClass(targetClass) : null); // The method may be on an interface, but we need attributes from the target class. // If the target class is null, the method will be unchanged. Method specificMethod = ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, userClass); // If we are dealing with method with generic parameters, find the original method. specificMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(specificMethod); //第一步 在实现类的方法上面找: 在目标class方法找事务注解 @Transactional,并且解析注解相关属性封装为TransactionAttribute类 //findTransactionAttribute 找到添加注解的类或者方法 解析注解的值封装为 RuleBasedTransactionAttribute 类 //RuleBasedTransactionAttribute // First try is the method in the target class. TransactionAttribute txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(specificMethod); if (txAttr != null) { return txAttr; } // Second try is the transaction attribute on the target class. //第二步:在实现类上面找 注解 txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(specificMethod.getDeclaringClass()); if (txAttr != null && ClassUtils.isUserLevelMethod(method)) { return txAttr; } if (specificMethod != method) { // Fallback is to look at the original method. //去实现类的接口的方法上找注解 txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(method); if (txAttr != null) { return txAttr; } // Last fallback is the class of the original method. //去实现类接口上找注解 txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(method.getDeclaringClass()); if (txAttr != null && ClassUtils.isUserLevelMethod(method)) { return txAttr; } } return null; } //AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource @Override @Nullable protected TransactionAttribute findTransactionAttribute(Method method) { return determineTransactionAttribute(method); } @Nullable protected TransactionAttribute determineTransactionAttribute(AnnotatedElement ae) { //获取注解解析器 for (TransactionAnnotationParser annotationParser : this.annotationParsers) { //通过注解解析器去解析方法上的注解 TransactionAttribute attr = annotationParser.parseTransactionAnnotation(ae); if (attr != null) { return attr; } } return null; } //SpringTransactionAnnotationParser @Override @Nullable public TransactionAttribute parseTransactionAnnotation(AnnotatedElement ae) { AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotationAttributes( ae, Transactional.class, false, false); if (attributes != null) { //解析出真正的事务属性对象 return parseTransactionAnnotation(attributes); } else { return null; } } //SpringTransactionAnnotationParser protected TransactionAttribute parseTransactionAnnotation(AnnotationAttributes attributes) { RuleBasedTransactionAttribute rbta = new RuleBasedTransactionAttribute(); Propagation propagation = attributes.getEnum("propagation"); rbta.setPropagationBehavior(propagation.value()); Isolation isolation = attributes.getEnum("isolation"); rbta.setIsolationLevel(isolation.value()); rbta.setTimeout(attributes.getNumber("timeout").intValue()); rbta.setReadOnly(attributes.getBoolean("readOnly")); rbta.setQualifier(attributes.getString("value")); ArrayList<RollbackRuleAttribute> rollBackRules = new ArrayList<>(); Class<?>[] rbf = attributes.getClassArray("rollbackFor"); //事务回滚类属性 for (Class<?> rbRule : rbf) { //可以指定多个异常回滚类 RollbackRuleAttribute rule = new RollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule); rollBackRules.add(rule); } String[] rbfc = attributes.getStringArray("rollbackForClassName"); for (String rbRule : rbfc) { RollbackRuleAttribute rule = new RollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule); rollBackRules.add(rule); } //不回滚类属性 Class<?>[] nrbf = attributes.getClassArray("noRollbackFor"); for (Class<?> rbRule : nrbf) { NoRollbackRuleAttribute rule = new NoRollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule); rollBackRules.add(rule); } String[] nrbfc = attributes.getStringArray("noRollbackForClassName"); for (String rbRule : nrbfc) { NoRollbackRuleAttribute rule = new NoRollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule); rollBackRules.add(rule); } rbta.getRollbackRules().addAll(rollBackRules); return rbta; }

AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource 主要用于解析事务注解如回滚策略,事务隔离级别等

//解析事务注解 AbstractFallbackTransactionAttributeSource @Override @Nullable public TransactionAttribute getTransactionAttribute(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass) { if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) { return null; } // First, see if we have a cached value. Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(method, targetClass); Object cached = this.attributeCache.get(cacheKey); if (cached != null) { // Value will either be canonical value indicating there is no transaction attribute, // or an actual transaction attribute. if (cached == NULL_TRANSACTION_ATTRIBUTE) { return null; } else { return (TransactionAttribute) cached; } } else { // We need to work it out. //重点 :查找事务注解 根据方法查找添加事务 并且解析为TransactionAttribute TransactionAttribute txAttr = computeTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass); // Put it in the cache. //解析出来的事务注解属性为空 if (txAttr == null) { //存放空事务注解属性 this.attributeCache.put(cacheKey, NULL_TRANSACTION_ATTRIBUTE); } else { //方法的描述符 包名+类名+方法名 String methodIdentification = ClassUtils.getQualifiedMethodName(method, targetClass); //把方法描述设置到事务属性上去 if (txAttr instanceof DefaultTransactionAttribute) { ((DefaultTransactionAttribute) txAttr).setDescriptor(methodIdentification); } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Adding transactional method '" + methodIdentification + "' with attribute: " + txAttr); } //加入到缓存中 this.attributeCache.put(cacheKey, txAttr); } return txAttr; } } //AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource @Nullable protected TransactionAttribute findTransactionAttribute(Method method) { return this.determineTransactionAttribute(method); }
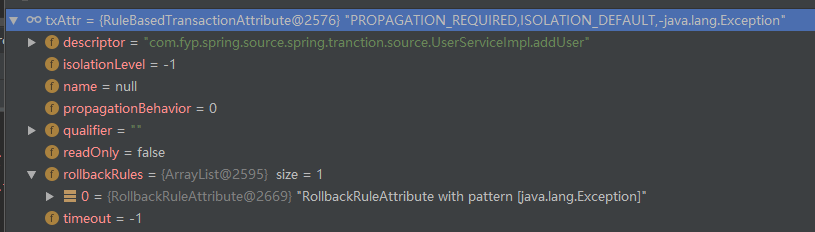

//SpringTransactionAnnotationParser protected TransactionAttribute parseTransactionAnnotation(AnnotationAttributes attributes) { RuleBasedTransactionAttribute rbta = new RuleBasedTransactionAttribute(); Propagation propagation = attributes.getEnum("propagation"); rbta.setPropagationBehavior(propagation.value()); Isolation isolation = attributes.getEnum("isolation"); rbta.setIsolationLevel(isolation.value()); rbta.setTimeout(attributes.getNumber("timeout").intValue()); rbta.setReadOnly(attributes.getBoolean("readOnly")); rbta.setQualifier(attributes.getString("value")); ArrayList<RollbackRuleAttribute> rollBackRules = new ArrayList<>(); Class<?>[] rbf = attributes.getClassArray("rollbackFor"); for (Class<?> rbRule : rbf) { RollbackRuleAttribute rule = new RollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule); rollBackRules.add(rule); } String[] rbfc = attributes.getStringArray("rollbackForClassName"); for (String rbRule : rbfc) { RollbackRuleAttribute rule = new RollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule); rollBackRules.add(rule); } Class<?>[] nrbf = attributes.getClassArray("noRollbackFor"); for (Class<?> rbRule : nrbf) { NoRollbackRuleAttribute rule = new NoRollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule); rollBackRules.add(rule); } String[] nrbfc = attributes.getStringArray("noRollbackForClassName"); for (String rbRule : nrbfc) { NoRollbackRuleAttribute rule = new NoRollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule); rollBackRules.add(rule); } rbta.getRollbackRules().addAll(rollBackRules); return rbta; }
事务通知 类org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor: advice org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionInterceptor@74c79fa2
2.添加事务注解的方法调用内部实现原理:
method.invoke()实现原理:
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class, propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED) @Override public void addUser(UserDTO userDTO) throws Exception
方法实际调用执行代理对象TransactionInterceptor.invoke()方法

//JdkDynamicAopProxy ,省略部分代码 @Override @Nullable public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { /** * 匹配目标类和方法,将通知@Before @After 。。等转换为 MethodInterceptor 链 */ List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass); // Check whether we have any advice. If we don't, we can fallback on direct // reflective invocation of the target, and avoid creating a MethodInvocation. //如果没有可以应用到此方法的通知(Interceptor),此直接反射调用 method.invoke(target, args) if (chain.isEmpty()) { // We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly // Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor so we know it does // nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot swapping or fancy proxying. Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args); retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, argsToUse); } else { /** * getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice * 这个方法执行完成后,Advised 中配置能够应用到连接点(JoinPoint)或者目标类(Target Object) * 的Advisor 全部被转化成了MethodInterceptor,接下来我们再看下得到的拦截器链是怎么起作用的。 */ // We need to create a method invocation... //创建MethodInvocation invocation = new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain); // Proceed to the joinpoint through the interceptor chain. retVal = invocation.proceed(); } }
事务这里获取的拦截执行链是 TransactionInterceptor
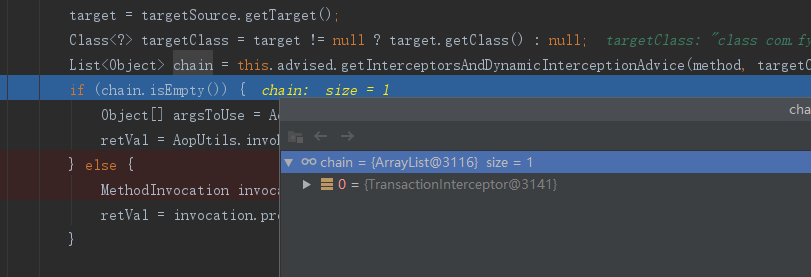
retVal = invocation.proceed();执行逻辑

@Override @Nullable public Object invoke(final MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable { // Work out the target class: may be {@code null}. // The TransactionAttributeSource should be passed the target class // as well as the method, which may be from an interface. Class<?> targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null); // Adapt to TransactionAspectSupport's invokeWithinTransaction... //事务执行 return invokeWithinTransaction(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass, invocation::proceed); }

@Nullable protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass, final InvocationCallback invocation) throws Throwable { // If the transaction attribute is null, the method is non-transactional. //从缓存里面获取 前面(后置处理器里面解析的)事务属性 TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource(); final TransactionAttribute txAttr = (tas != null ? tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) : null); //事务管理 final PlatformTransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr); //添加事务注解的方法 final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr); if (txAttr == null || !(tm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) { // Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls. //创建事务 TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification); Object retVal = null; try { // This is an around advice: Invoke the next interceptor in the chain. // This will normally result in a target object being invoked. //这里执行的是 /** * ReflectiveMethodInvocation.proceed() * if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) { * 执行这个方法 * return this.invokeJoinpoint(); * 调用 invokeJoinpointUsingReflection, 在这个方法里面调用目标方法 * 即: * @Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class, propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED) * @Override * public void addUser(UserDTO userDTO) * } */ retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation(); } catch (Throwable ex) { // target invocation exception // 异常 如果有异常判断 根据异常类型判断是否需要回滚 completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex); throw ex; } finally { cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo); } commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo); return retVal; } else { final ThrowableHolder throwableHolder = new ThrowableHolder(); try { Object result = ((CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager) tm).execute(txAttr, status -> { TransactionInfo txInfo = prepareTransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status); try { return invocation.proceedWithInvocation(); } catch (Throwable ex) { if (txAttr.rollbackOn(ex)) { // A RuntimeException: will lead to a rollback. if (ex instanceof RuntimeException) { throw (RuntimeException) ex; } else { throw new ThrowableHolderException(ex); } } else { // A normal return value: will lead to a commit. throwableHolder.throwable = ex; return null; } } finally { cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo); } }); // Check result state: It might indicate a Throwable to rethrow. if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) { throw throwableHolder.throwable; } return result; } catch (ThrowableHolderException ex) { throw ex.getCause(); } catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) { throw ex2; } catch (Throwable ex2) { throw ex2; } } }

@Nullable protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass, final InvocationCallback invocation) throws Throwable { // If the transaction attribute is null, the method is non-transactional. //从缓存里面获取 前面(后置处理器里面解析的)事务属性 TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource(); final TransactionAttribute txAttr = (tas != null ? tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) : null); //事务管理 final PlatformTransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr); //添加事务注解的方法 final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr); if (txAttr == null || !(tm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) { // Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls. //创建事务 TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification); Object retVal = null; try { // This is an around advice: Invoke the next interceptor in the chain. // This will normally result in a target object being invoked. //这里执行的是 /** * ReflectiveMethodInvocation.proceed() * if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) { * 执行这个方法 * return this.invokeJoinpoint(); * 调用 invokeJoinpointUsingReflection, 在这个方法里面调用目标方法 * 即: * @Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class, propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED) * @Override * public void addUser(UserDTO userDTO) * } */ retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation(); } catch (Throwable ex) { // target invocation exception // 异常 如果有异常判断 根据异常类型判断是否需要回滚 completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex); throw ex; } finally { //ThreadLocal 清除 创建事务时是设置的值 cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo); } //提交事务 commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo); return retVal; } }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号