Spring Cloud核心组件:Eureka、Ribbon、Hystrix 、Feign
Spring Cloud是一个全家桶式的技术栈,包含了很多组件。本文先从其最核心的几个组件入手,来剖析一下其底层的工作原理。也就是Eureka、Ribbon、Feign、Hystrix、Zuul这几个组件。
1.Spring Cloud Netflix Eureka 服务治理
Eureka,服务注册和发现,它提供了一个服务注册中心、服务发现的客户端,还有一个方便的查看所有注册的服务的界面。 所有的服务使用Eureka的服务发现客户端来将自己注册到Eureka的服务器上。
2.Spring Cloud Ribbon 负载均衡
即负载均衡,Zuul网关将一个请求发送给某一个服务的应用的时候,如果一个服务启动了多个实例,就会通过Ribbon来通过一定的负载均衡策略来发送给某一个服务实例
3.Spring Cloud Hystrix 服务容错保护 ,监控和熔断器。我们只需要在服务接口上添加Hystrix标签,就可以实现对这个接口的监控和断路器功能。
Hystrix Dashboard,监控面板,他提供了一个界面,可以监控各个服务上的服务调用所消耗的时间等。发起请求是通过Hystrix的线程池来走的,不同的服务走不同的线程池,实现了不同服务调用的隔离,避免了服务雪崩的问题
Turbine,监控聚合,使用Hystrix监控,我们需要打开每一个服务实例的监控信息来查看。而Turbine可以帮助我们把所有的服务实例的监控信息聚合到一个地方统一查看。这样就不需要挨个打开一个个的页面一个个查看。
4.Spring Cloud Feign 声明式服务调用
服务客户端,服务之间如果需要相互访问,可以使用RestTemplate,也可以使用Feign客户端访问。它默认会使用Ribbon来实现负载均衡。基于Feign的动态代理机制,根据注解和选择的机器,拼接请求URL地址,发起请求(Hystrix的隔离策略有两种:分别是线程隔离和信号量隔离)
5.Spring Cloud Zuul API网关服务
网关,所有的客户端请求通过这个网关访问后台的服务。他可以使用一定的路由配置来判断某一个URL由哪个服务来处理。并从Eureka获取注册的服务来转发请求。
6.Spring Cloud Config 分布式配置中心类似于Apollo
7.Spring Cloud Bus 消息总线:是一种消息代理,消息验证,传输,路由的架构模式,用来接收和分发消息。支持RabbitMQ和Kafka(实现原理就是AMQP面向
消息中间件的开发室标准应用成协议)可以实现消息方向,消息队列效率路由,可靠性,安全性
Spring Cloud Sleuth分布式服务跟踪 如SkyWalking
一、业务场景介绍
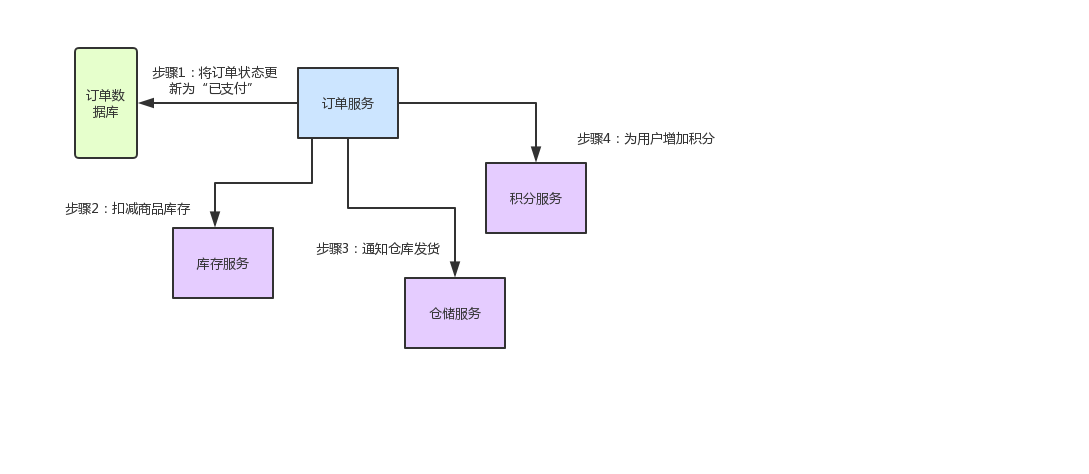
先来给大家说一个业务场景,假设咱们现在开发一个电商网站,要实现支付订单的功能,流程如下:
-
创建一个订单之后,如果用户立刻支付了这个订单,我们需要将订单状态更新为“已支付”
-
扣减相应的商品库存
-
通知仓储中心,进行发货
-
给用户的这次购物增加相应的积分
针对上述流程,我们需要有订单服务、库存服务、仓储服务、积分服务。整个流程的大体思路如下:
-
用户针对一个订单完成支付之后,就会去找订单服务,更新订单状态
-
订单服务调用库存服务,完成相应功能
-
订单服务调用仓储服务,完成相应功能
-
订单服务调用积分服务,完成相应功能
至此,整个支付订单的业务流程结束
下图这张图,清晰表明了各服务间的调用过程:
好!有了业务场景之后,咱们就一起来看看Spring Cloud微服务架构中,这几个组件如何相互协作,各自发挥的作用以及其背后的原理。
二、Spring Cloud核心组件:Eureka
咱们来考虑第一个问题:订单服务想要调用库存服务、仓储服务,或者是积分服务,怎么调用?
-
订单服务压根儿就不知道人家库存服务在哪台机器上啊!他就算想要发起一个请求,都不知道发送给谁,有心无力!
-
这时候,就轮到Spring Cloud Eureka出场了。Eureka是微服务架构中的注册中心,专门负责服务的注册与发现。
咱们来看看下面的这张图,结合图来仔细剖析一下整个流程:
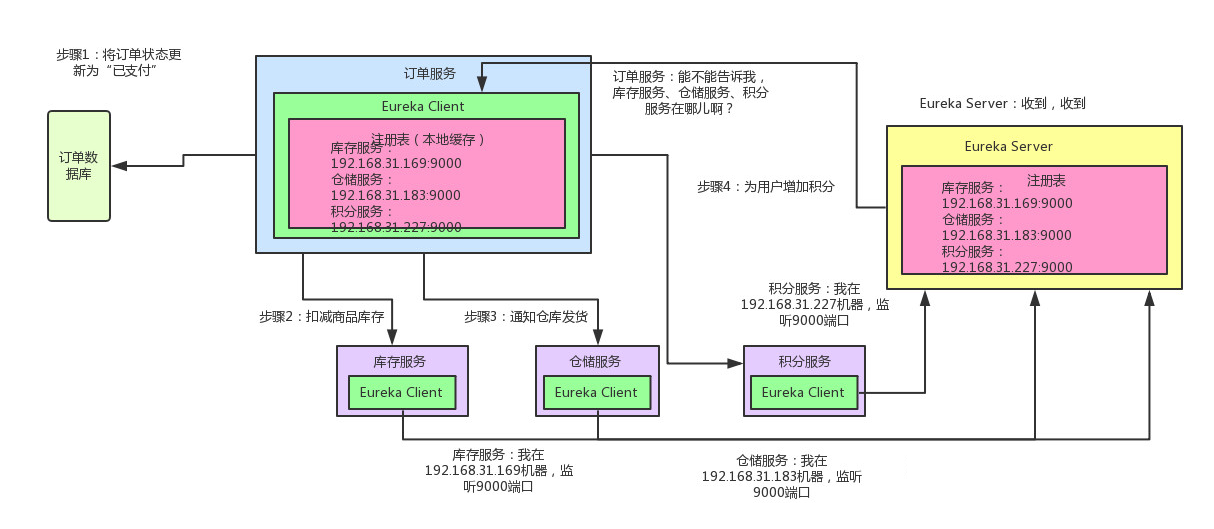
如上图所示,库存服务、仓储服务、积分服务中都有一个Eureka Client组件,这个组件专门负责将这个服务的信息注册到Eureka Server中。说白了,就是告诉Eureka Server,自己在哪台机器上,监听着哪个端口。而Eureka Server是一个注册中心,里面有一个注册表,保存了各服务所在的机器和端口号
订单服务里也有一个Eureka Client组件,这个Eureka Client组件会找Eureka Server问一下:库存服务在哪台机器啊?监听着哪个端口啊?仓储服务呢?积分服务呢?然后就可以把这些相关信息从Eureka Server的注册表中拉取到自己本地缓存起来。
这时如果订单服务想要调用库存服务,不就可以找自己本地的Eureka Client问一下库存服务在哪台机器?监听哪个端口吗?收到响应后,紧接着就可以发送一个请求过去,调用库存服务扣减库存的那个接口!同理,如果订单服务要调用仓储服务、积分服务,也是如法炮制。
总结一下:
-
Eureka Client:负责将这个服务的信息注册到Eureka Server中 ,既可以是服务提供者也可以是服务消费者
-
Eureka Server:注册中心,里面有一个注册表,保存了各个服务所在的机器和端口号
Eureka基础架构
服务注册中心:Eureka提供的服务端,提供服务注册与服务发现功能
服务提供者:将自身的服务注册到注册中心,以供其他应用发现
服务消费者:从注册中心获取服务列表,然后根据服务列表调用具体的服务提供者
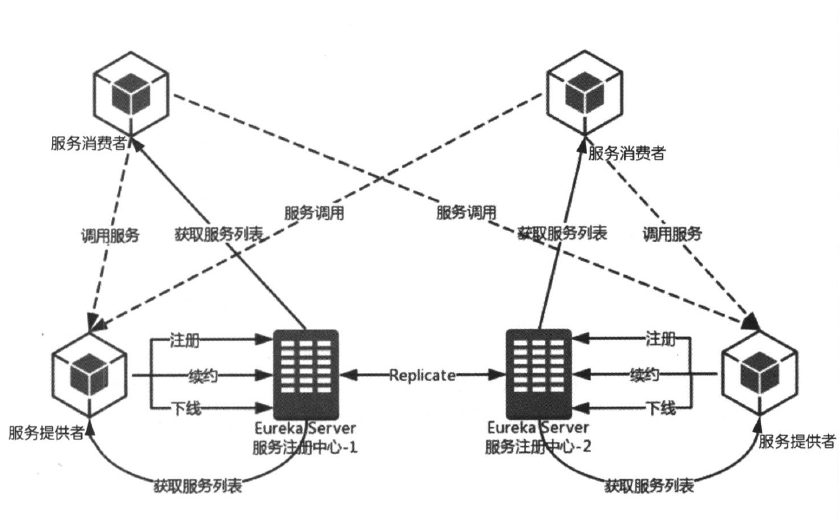
高可用eureka注册中心:(所有的节点即使是服务提供方,也是服务消费方,服务注册中心也如此) ,将自己作为服务向其他注册中心注册自己,形成一组互相注册的服务注册中心,实现服务清单的互相同步,达到高可用
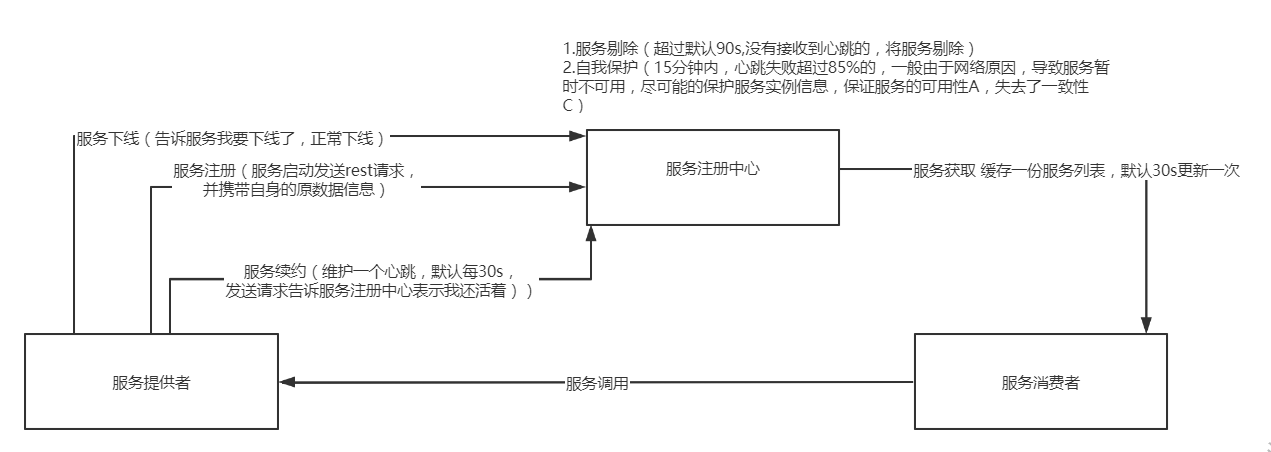
服务提供者
- 服务注册:服务启动时发送REST请求将自己注册到Eureka Server上,同时带自身的元数据信息,Eureka Server接收之后,
维护一个AbstractInstanceRegistry.ConcurrentHashMap<String, Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>>> registry 存储(可以实现保存微服务集群的信息),key=服务名 ,(Server1,实例信息,service2,实例信息),维护注册表、拉取注册表、更新心跳时间,全部发生在内存里!这是Eureka Server非常核心的一个点。实例信息包括:这个InstanceInfo就代表了服务实例的具体信息,比如机器的ip地址、hostname以及端口号,状态(up,down),Lease,里面则会维护每个服务最近一次发送心跳的时间
- 服务续约:服务提供者维护一个心跳来持续告诉Eureka Server“我还活着”,防止Eureka Server的“剔除任务”,配置: lease-renewal-interval-in-seconds: 30 #服务续约任务的调用间隔时间 默认为30秒
- 服务下线:服务实例正常关闭操作,触发服务下线的Rest请求给Eureka Server,告诉服务注册中心“我要下线了”,服务端接收到请求后,将服务状态置为down,并把下线事件传播出去。
服务注册中心
- 失效剔除:非正常下线,没有续约的服务进行剔除,当服务实例非正常下线如内存溢出,网络故障灯,服务注册中心未收到“服务下线”请求,Eureka Server在启动时候会创建一个定时任务,默认每隔60秒,将当前清单中超时(默认90秒没有需续约的服务)剔除出去 配置:lease-expiration-duration-in-seconds: 90
- 服务同步:注册中心互相注册为服务,当服务提供者发送注册请求到一个服务注册中心时,他会将改请求转发给集群中相连的其他注册中心,实现服务同步,实现高可用
- 自我保护:服务注册到Eureka Server之后,维护一个心跳连接,告诉Eureka Server 自己还活着,Eureka Server 在运行期间,统计心跳失败的比例在15分钟低于85%(实际生产环境是由于网络不稳定),Eureka Server会将当前的实例注册信息保护起来,让这些实例不会过期,尽可能保护实例信息,(可能会出现客户端会获取到实际已经不存在的服务实例,出现服务调用失败的情况,需要客户端实现容错机制,请求重试,断路器等机制)
服务消费者
- 获取服务:启动服务消费者时候,发送一个rest请求给服务注册中心,获取服务清单(服务注册中心会缓存一份服务列表(性能考虑),每30秒更新一次)Eureka Client会每隔30秒去找Eureka Server拉取最近注册表的变化,看看其他服务的地址有没有变化。
- 服务调用:根据服务名获取具体的服务实例名和实例的元数据,客户端根据需要调用具体的实例,(ribbon通过轮询方式实现客户端负载均衡)注册中心Eureka Server会缓存一份(性能考虑)只读的服务清单给客户端,每30秒更新一次服务清单
- 负载均衡:Ribbon,Ribbon(对服务实例的选择策略) :是一个与Http和TCP的客户端负载均衡器,通过客户端配置的ribbonServerList服务端列表去轮询访问已达到负载均衡的作用,DiscoveryEnabledNIWSServerList重写ribbonServerList
Eureka提供了region和zone两个概念来进行分区
这两个概念均来自于亚马逊的AWS,region一个服务只能设置一个,可用设置多个zone,他们是一对多的关系。
- region:可以简单理解为地理上的分区,比如亚洲地区,或者华北地区,再或者北京等等,没有具体大小的限制。根据项目具体的情况,可以自行合理划分region。
- zone:可以简单理解为region内的具体机房,比如说region划分为北京,然后北京有两个机房,就可以在此region之下划分出zone1,zone2两个zone
服务地址:getServiceUrlsMapFromConfig 1先获取region 在获取zone,在获取注册中心的地址 key:defaultZone,value:urlribbon:默认策略会优先访问同一个Zone中的
三、相关面试题
Jersey框架:是一个类似于Spring MVC的框架,是通过Filter实现过滤请求转发的 ,在Eureka中可以看到Jerseyt添加过滤器的Bean

//EurekaServerAutoConfiguration @Bean public FilterRegistrationBean jerseyFilterRegistration(Application eurekaJerseyApp) { FilterRegistrationBean bean = new FilterRegistrationBean(); bean.setFilter(new ServletContainer(eurekaJerseyApp)); bean.setOrder(2147483647); bean.setUrlPatterns(Collections.singletonList("/eureka/*")); return bean; }
FilterRegistrationBean
如:Resource(类似于Controller)如:ApplicationResource,InstanceResource,PeerReplicationResource
1.客户端启动时如何注册到服务端?
Eureka客户端在启动时,首先会创建一个心跳的定时任务,定时向服务端发送心跳信息,服务端会对客户端心跳做出响应,如果响应状态码为404时,表示服务端没有该客户端的服务信息,那么客户端则会向服务端发送注册请求,注册信息包括服务名、ip、端口、唯一实例ID等信息。
在register方法中,向服务端的注册信息instanceInfo,它是com.netflix.appinfo.InstanceInfo,包括服务名、ip、端口、唯一实例ID等信息
com.netflix.discovery.DiscoveryClient(){
initScheduledTasks()
}

private void initScheduledTasks() { int renewalIntervalInSecs; int expBackOffBound; if (this.clientConfig.shouldFetchRegistry()) { renewalIntervalInSecs = this.clientConfig.getRegistryFetchIntervalSeconds(); expBackOffBound = this.clientConfig.getCacheRefreshExecutorExponentialBackOffBound(); this.scheduler.schedule(new TimedSupervisorTask("cacheRefresh", this.scheduler, this.cacheRefreshExecutor, renewalIntervalInSecs, TimeUnit.SECONDS, expBackOffBound, new DiscoveryClient.CacheRefreshThread()), (long)renewalIntervalInSecs, TimeUnit.SECONDS); } //服务注册 if (this.clientConfig.shouldRegisterWithEureka()) { renewalIntervalInSecs = this.instanceInfo.getLeaseInfo().getRenewalIntervalInSecs(); expBackOffBound = this.clientConfig.getHeartbeatExecutorExponentialBackOffBound(); logger.info("Starting heartbeat executor: renew interval is: {}", renewalIntervalInSecs); this.scheduler.schedule(new TimedSupervisorTask("heartbeat", this.scheduler, this.heartbeatExecutor, renewalIntervalInSecs, TimeUnit.SECONDS, expBackOffBound, new DiscoveryClient.HeartbeatThread()), (long)renewalIntervalInSecs, TimeUnit.SECONDS); //服务注册具体实现 this.instanceInfoReplicator = new InstanceInfoReplicator(this, this.instanceInfo, this.clientConfig.getInstanceInfoReplicationIntervalSeconds(), 2); this.statusChangeListener = new StatusChangeListener() { public String getId() { return "statusChangeListener"; } public void notify(StatusChangeEvent statusChangeEvent) { if (InstanceStatus.DOWN != statusChangeEvent.getStatus() && InstanceStatus.DOWN != statusChangeEvent.getPreviousStatus()) { DiscoveryClient.logger.info("Saw local status change event {}", statusChangeEvent); } else { DiscoveryClient.logger.warn("Saw local status change event {}", statusChangeEvent); } DiscoveryClient.this.instanceInfoReplicator.onDemandUpdate(); } }; if (this.clientConfig.shouldOnDemandUpdateStatusChange()) { this.applicationInfoManager.registerStatusChangeListener(this.statusChangeListener); } this.instanceInfoReplicator.start(this.clientConfig.getInitialInstanceInfoReplicationIntervalSeconds()); } else { logger.info("Not registering with Eureka server per configuration"); } } //InstanceInfoReplicator 服务注册 public void run() { boolean var6 = false; ScheduledFuture next; label53: { try { var6 = true; this.discoveryClient.refreshInstanceInfo(); Long dirtyTimestamp = this.instanceInfo.isDirtyWithTime(); if (dirtyTimestamp != null) { this.discoveryClient.register(); this.instanceInfo.unsetIsDirty(dirtyTimestamp); var6 = false; } else { var6 = false; } break label53; } finally { if (var6) { //服务续约 (renew()) ScheduledFuture next = this.scheduler.schedule(this, (long)this.replicationIntervalSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS); this.scheduledPeriodicRef.set(next); } } //服务续约 next = this.scheduler.schedule(this, (long)this.replicationIntervalSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS); this.scheduledPeriodicRef.set(next); return; } next = this.scheduler.schedule(this, (long)this.replicationIntervalSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS); this.scheduledPeriodicRef.set(next); } //具体注册代码 是发送rest请求 boolean register() throws Throwable { EurekaHttpResponse httpResponse; try { httpResponse = this.eurekaTransport.registrationClient.register(this.instanceInfo); } catch (Exception var3) { } return httpResponse.getStatusCode() == 204; } //EurekaHttpClientDecorator ->register
服务获取& 服务续约具体实现

//com.netflix.discovery.DiscoveryClient boolean renew() { try { EurekaHttpResponse<InstanceInfo> httpResponse = this.eurekaTransport.registrationClient.sendHeartBeat(this.instanceInfo.getAppName(), this.instanceInfo.getId(), this.instanceInfo, (InstanceStatus)null); logger.debug("DiscoveryClient_{} - Heartbeat status: {}", this.appPathIdentifier, httpResponse.getStatusCode()); if (httpResponse.getStatusCode() == 404) { this.REREGISTER_COUNTER.increment(); logger.info("DiscoveryClient_{} - Re-registering apps/{}", this.appPathIdentifier, this.instanceInfo.getAppName()); long timestamp = this.instanceInfo.setIsDirtyWithTime(); boolean success = this.register(); if (success) { this.instanceInfo.unsetIsDirty(timestamp); } return success; } else { return httpResponse.getStatusCode() == 200; } } catch (Throwable var5) { logger.error("DiscoveryClient_{} - was unable to send heartbeat!", this.appPathIdentifier, var5); return false; } }
注册中心相关源码
服务注册
客户端通过Jersey框架(亚马逊的一个http框架)将服务实例信息发送到服务端,服务端将客户端信息放在一个ConcurrentHashMap对象中。
服务端保存客户端实例信息:
//注册中心保存的服务注册信息 //内层map //service1:192.168.0.1 //service2:193.168.0.2 //外层map //service,内层map private final ConcurrentHashMap<String, Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>>> registry = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>>>();

public class Lease<T> { public static final int DEFAULT_DURATION_IN_SECS = 90; private T holder; private long evictionTimestamp; private long registrationTimestamp; private long serviceUpTimestamp; private volatile long lastUpdateTimestamp; private long duration; }

@POST @Consumes({"application/json", "application/xml"}) public Response addInstance(InstanceInfo info, @HeaderParam(PeerEurekaNode.HEADER_REPLICATION) String isReplication) { //入参判断 if (isBlank(info.getId())) { return Response.status(400).entity("Missing instanceId").build(); } else if (isBlank(info.getHostName())) { return Response.status(400).entity("Missing hostname").build(); } else if (isBlank(info.getIPAddr())) { return Response.status(400).entity("Missing ip address").build(); } else if (isBlank(info.getAppName())) { return Response.status(400).entity("Missing appName").build(); } else if (!appName.equals(info.getAppName())) { return Response.status(400).entity("Mismatched appName, expecting " + appName + " but was " + info.getAppName()).build(); } else if (info.getDataCenterInfo() == null) { return Response.status(400).entity("Missing dataCenterInfo").build(); } else if (info.getDataCenterInfo().getName() == null) { return Response.status(400).entity("Missing dataCenterInfo Name").build(); } // handle cases where clients may be registering with bad DataCenterInfo with missing data DataCenterInfo dataCenterInfo = info.getDataCenterInfo(); if (dataCenterInfo instanceof UniqueIdentifier) { String dataCenterInfoId = ((UniqueIdentifier) dataCenterInfo).getId(); if (isBlank(dataCenterInfoId)) { boolean experimental = "true".equalsIgnoreCase(serverConfig.getExperimental("registration.validation.dataCenterInfoId")); if (experimental) { String entity = "DataCenterInfo of type " + dataCenterInfo.getClass() + " must contain a valid id"; return Response.status(400).entity(entity).build(); } else if (dataCenterInfo instanceof AmazonInfo) { AmazonInfo amazonInfo = (AmazonInfo) dataCenterInfo; String effectiveId = amazonInfo.get(AmazonInfo.MetaDataKey.instanceId); if (effectiveId == null) { amazonInfo.getMetadata().put(AmazonInfo.MetaDataKey.instanceId.getName(), info.getId()); } } else { logger.warn("Registering DataCenterInfo of type {} without an appropriate id", dataCenterInfo.getClass()); } } } // 服务注册 registry.register(info, "true".equals(isReplication)); return Response.status(204).build(); // 204 to be backwards compatible } //PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl.register @Override public void register(final InstanceInfo info, final boolean isReplication) { int leaseDuration = Lease.DEFAULT_DURATION_IN_SECS; if (info.getLeaseInfo() != null && info.getLeaseInfo().getDurationInSecs() > 0) { leaseDuration = info.getLeaseInfo().getDurationInSecs(); } //服务注册 super.register(info, leaseDuration, isReplication); //信息同步 replicateToPeers(Action.Register, info.getAppName(), info.getId(), info, null, isReplication); } // super.register->AbstractInstanceRegistry public void register(InstanceInfo registrant, int leaseDuration, boolean isReplication) { read.lock(); try { //根据服务名称获取服务实例 Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> gMap = registry.get(registrant.getAppName()); REGISTER.increment(isReplication); if (gMap == null) { //第一次没有获取到 ,创建一个map final ConcurrentHashMap<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> gNewMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>>(); gMap = registry.putIfAbsent(registrant.getAppName(), gNewMap); if (gMap == null) { gMap = gNewMap; } } //获取集群中具体的实例信息 Lease<InstanceInfo> existingLease = gMap.get(registrant.getId()); // Retain the last dirty timestamp without overwriting it, if there is already a lease //防止发生注册冲突,根据注册时间获取最活跃的那个 if (existingLease != null && (existingLease.getHolder() != null)) { //获取已经存在实例的最新活跃时间 Long existingLastDirtyTimestamp = existingLease.getHolder().getLastDirtyTimestamp(); //获取当前注册实例的最新活跃时间 Long registrationLastDirtyTimestamp = registrant.getLastDirtyTimestamp(); logger.debug("Existing lease found (existing={}, provided={}", existingLastDirtyTimestamp, registrationLastDirtyTimestamp); // this is a > instead of a >= because if the timestamps are equal, we still take the remote transmitted // InstanceInfo instead of the server local copy. //比较时间 if (existingLastDirtyTimestamp > registrationLastDirtyTimestamp) { logger.warn("There is an existing lease and the existing lease's dirty timestamp {} is greater" + " than the one that is being registered {}", existingLastDirtyTimestamp, registrationLastDirtyTimestamp); logger.warn("Using the existing instanceInfo instead of the new instanceInfo as the registrant"); //获取最新活跃时间的实例 registrant = existingLease.getHolder(); } } else { // The lease does not exist and hence it is a new registration synchronized (lock) { if (this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews > 0) { // Since the client wants to register it, increase the number of clients sending renews this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews = this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews + 1; updateRenewsPerMinThreshold(); } } logger.debug("No previous lease information found; it is new registration"); } //心跳续约对象: 注册的节点信息,最后操作时间,注册时间,过期时间 Lease<InstanceInfo> lease = new Lease<InstanceInfo>(registrant, leaseDuration); if (existingLease != null) { lease.setServiceUpTimestamp(existingLease.getServiceUpTimestamp()); } //存到 注册表里面 gMap.put(registrant.getId(), lease); recentRegisteredQueue.add(new Pair<Long, String>( System.currentTimeMillis(), registrant.getAppName() + "(" + registrant.getId() + ")")); // This is where the initial state transfer of overridden status happens if (!InstanceStatus.UNKNOWN.equals(registrant.getOverriddenStatus())) { logger.debug("Found overridden status {} for instance {}. Checking to see if needs to be add to the " + "overrides", registrant.getOverriddenStatus(), registrant.getId()); if (!overriddenInstanceStatusMap.containsKey(registrant.getId())) { logger.info("Not found overridden id {} and hence adding it", registrant.getId()); overriddenInstanceStatusMap.put(registrant.getId(), registrant.getOverriddenStatus()); } } InstanceStatus overriddenStatusFromMap = overriddenInstanceStatusMap.get(registrant.getId()); if (overriddenStatusFromMap != null) { logger.info("Storing overridden status {} from map", overriddenStatusFromMap); registrant.setOverriddenStatus(overriddenStatusFromMap); } // Set the status based on the overridden status rules InstanceStatus overriddenInstanceStatus = getOverriddenInstanceStatus(registrant, existingLease, isReplication); registrant.setStatusWithoutDirty(overriddenInstanceStatus); // If the lease is registered with UP status, set lease service up timestamp if (InstanceStatus.UP.equals(registrant.getStatus())) { lease.serviceUp(); } registrant.setActionType(ActionType.ADDED); recentlyChangedQueue.add(new RecentlyChangedItem(lease)); registrant.setLastUpdatedTimestamp(); invalidateCache(registrant.getAppName(), registrant.getVIPAddress(), registrant.getSecureVipAddress()); logger.info("Registered instance {}/{} with status {} (replication={})", registrant.getAppName(), registrant.getId(), registrant.getStatus(), isReplication); } finally { read.unlock(); } }
服务续约
注册中心接受到客户端的服务续约请求处理源码:

//InstanceResource @PUT public Response renewLease( @HeaderParam(PeerEurekaNode.HEADER_REPLICATION) String isReplication, @QueryParam("overriddenstatus") String overriddenStatus, @QueryParam("status") String status, @QueryParam("lastDirtyTimestamp") String lastDirtyTimestamp) { boolean isFromReplicaNode = "true".equals(isReplication); //服务续约 boolean isSuccess = registry.renew(app.getName(), id, isFromReplicaNode); // Not found in the registry, immediately ask for a register if (!isSuccess) { logger.warn("Not Found (Renew): {} - {}", app.getName(), id); return Response.status(Status.NOT_FOUND).build(); } // Check if we need to sync based on dirty time stamp, the client // instance might have changed some value Response response; if (lastDirtyTimestamp != null && serverConfig.shouldSyncWhenTimestampDiffers()) { response = this.validateDirtyTimestamp(Long.valueOf(lastDirtyTimestamp), isFromReplicaNode); // Store the overridden status since the validation found out the node that replicates wins if (response.getStatus() == Response.Status.NOT_FOUND.getStatusCode() && (overriddenStatus != null) && !(InstanceStatus.UNKNOWN.name().equals(overriddenStatus)) && isFromReplicaNode) { registry.storeOverriddenStatusIfRequired(app.getAppName(), id, InstanceStatus.valueOf(overriddenStatus)); } } else { response = Response.ok().build(); } logger.debug("Found (Renew): {} - {}; reply status={}", app.getName(), id, response.getStatus()); return response; } //具体的续约操作 public void renew() { //当前时间+过期时间(90s) lastUpdateTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis() + duration; }
服务剔除:
服务启动的时候,在初始化上下文类里面,启动了一个定时EurekaServerAutoConfiguration->EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration:start()

1 EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration->start(): 2 EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration.this.eurekaServerBootstrap.contextInitialized() 3 initEurekaServerContext() 4 this.registry.openForTraffic(this.applicationInfoManager, registryCount); 5 //PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl 6 protected void postInit() 7 // this.evictionTaskRef.set(new AbstractInstanceRegistry.EvictionTask()); 8 //创建了一个定时 9 EvictionTask():run{ 10 evict() 11 } 12 // 13 public void evict(long additionalLeaseMs) { 14 logger.debug("Running the evict task"); 15 16 //判断是否打开了自我保护机制 17 //打开就不会剔除 18 // 19 //判断是否打开了服务保护机制,打开了进行判断是否要剔除 20 //没有打开允许服务过期 21 if (!isLeaseExpirationEnabled()) { 22 logger.debug("DS: lease expiration is currently disabled."); 23 return; 24 } 25 26 // We collect first all expired items, to evict them in random order. For large eviction sets, 27 // if we do not that, we might wipe out whole apps before self preservation kicks in. By randomizing it, 28 // the impact should be evenly distributed across all applications.、 29 //保存需要剔除的服务节点 30 List<Lease<InstanceInfo>> expiredLeases = new ArrayList<>(); 31 for (Entry<String, Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>>> groupEntry : registry.entrySet()) { 32 Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> leaseMap = groupEntry.getValue(); 33 if (leaseMap != null) { 34 for (Entry<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> leaseEntry : leaseMap.entrySet()) { 35 Lease<InstanceInfo> lease = leaseEntry.getValue(); 36 //判断时是否过期 37 if (lease.isExpired(additionalLeaseMs) && lease.getHolder() != null) { 38 //存放到需要剔除的list里面 39 expiredLeases.add(lease); 40 } 41 } 42 } 43 } 44 45 // To compensate for GC pauses or drifting local time, we need to use current registry size as a base for 46 // triggering self-preservation. Without that we would wipe out full registry. 47 // 获取当前注册表的大小 48 int registrySize = (int) getLocalRegistrySize(); 49 //计算是否触发 自我保护机制 50 //计算百分之85%的节点是多少个= 注册表的大小*0.85 51 // registrySize * serverConfig.getRenewalPercentThreshold() 52 int registrySizeThreshold = (int) ( 53 registrySize * serverConfig.getRenewalPercentThreshold()); 54 // 得到剩余的数量:注册表大小- registrySizeThreshold 55 int evictionLimit = registrySize - registrySizeThreshold; 56 // 获取最小值 不会全部剔除,剔除最小值 57 //如 有 min(100 ,85) ,剔除最小值,不会全部剔除,这里就是自我保护机制的作用 58 int toEvict = Math.min(expiredLeases.size(), evictionLimit); 59 if (toEvict > 0) { 60 logger.info("Evicting {} items (expired={}, evictionLimit={})", toEvict, expiredLeases.size(), evictionLimit); 61 //随机算法剔除 why? 62 // 保证不会全部剔除 比如下单服务 期中 user有3台,库存有3台 63 //如果全部剔除 可能是把3台user,和3台库存全部剔除,这样user 和库存都不可用了 64 //采用随机算法有可能 剔除2台user,1台库存 这样 下单服务还可以继续调用user 和 库存 65 Random random = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis()); 66 for (int i = 0; i < toEvict; i++) { 67 // Pick a random item (Knuth shuffle algorithm) 68 int next = i + random.nextInt(expiredLeases.size() - i); 69 Collections.swap(expiredLeases, i, next); 70 Lease<InstanceInfo> lease = expiredLeases.get(i); 71 72 String appName = lease.getHolder().getAppName(); 73 String id = lease.getHolder().getId(); 74 EXPIRED.increment(); 75 logger.warn("DS: Registry: expired lease for {}/{}", appName, id); 76 //从map里面remove 掉,并且从缓存里面删除 77 internalCancel(appName, id, false); 78 } 79 } 80 }

//PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl @Override public boolean isLeaseExpirationEnabled() { //判断是否打开了自我保护机制 配置文件中配置 if (!isSelfPreservationModeEnabled()) { //没有打开 运行服务实例过期 // The self preservation mode is disabled, hence allowing the instances to expire. return true; } //打开了 判断 // getNumOfRenewsInLastMin getNumOfRenewsInLastMin即最后一分钟接收到的心跳总数 // numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold 表示收到一分钟内收到服务心跳数临界值(后简称临界值), // 也就是说当临界值大于0,且最后一分钟接收到的心跳总数大于临界值时,允许实例过期 // updateRenewsPerMinThreshold 计算方式如下:AbstractInstanceRegistry.updateRenewsPerMinThreshold // protected void updateRenewsPerMinThreshold() { // this.numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold = (int) (this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews // * (60.0 / serverConfig.getExpectedClientRenewalIntervalSeconds()) // * serverConfig.getRenewalPercentThreshold()); // } return numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold > 0 && getNumOfRenewsInLastMin() > numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold; }
1分钟心跳数达到多少个服务才不会被剔除?计算公式是什么?
客户端数据量*(60/30*0.85)=客户端数据量*1.7
假如有总共有10个客户端,那么表示一分钟至少需要收到17次心跳。
服务同步源码:

//ApplicationResource replicateToPeers() private void replicateToPeers(Action action, String appName, String id, InstanceInfo info /* optional */, InstanceStatus newStatus /* optional */, boolean isReplication) { Stopwatch tracer = action.getTimer().start(); try { if (isReplication) { numberOfReplicationsLastMin.increment(); } // If it is a replication already, do not replicate again as this will create a poison replication //判断 需要同步的节点是否为空 或者isReplication 为 true 就不会再次同步,防止死循环 //比如 集群中 A和B节点,本身就是节点同步,这里是true 不在进行同步 否则会A同步给B,B同步给A //造成死循环 if (peerEurekaNodes == Collections.EMPTY_LIST || isReplication) { return; } //给多个节点进行服务同步 for (final PeerEurekaNode node : peerEurekaNodes.getPeerEurekaNodes()) { // If the url represents this host, do not replicate to yourself. if (peerEurekaNodes.isThisMyUrl(node.getServiceUrl())) { continue; } //PeerEurekaNode.register 就是发送http rest 请求进行服务注册 replicateInstanceActionsToPeers(action, appName, id, info, newStatus, node); } } finally { tracer.stop(); } }
服务拉取
ApplicationsResource
private final ConcurrentMap<Key, ResponseCacheImpl.Value> readOnlyCacheMap = new ConcurrentHashMap();
private final LoadingCache<Key, ResponseCacheImpl.Value> readWriteCacheMap;

@GET public Response getContainers(@PathParam("version") String version, @HeaderParam("Accept") String acceptHeader, @HeaderParam("Accept-Encoding") String acceptEncoding, @HeaderParam("X-Eureka-Accept") String eurekaAccept, @Context UriInfo uriInfo, @Nullable @QueryParam("regions") String regionsStr) { boolean isRemoteRegionRequested = null != regionsStr && !regionsStr.isEmpty(); String[] regions = null; if (!isRemoteRegionRequested) { EurekaMonitors.GET_ALL.increment(); } else { regions = regionsStr.toLowerCase().split(","); Arrays.sort(regions); EurekaMonitors.GET_ALL_WITH_REMOTE_REGIONS.increment(); } if (!this.registry.shouldAllowAccess(isRemoteRegionRequested)) { return Response.status(Status.FORBIDDEN).build(); } else { CurrentRequestVersion.set(Version.toEnum(version)); KeyType keyType = KeyType.JSON; String returnMediaType = "application/json"; if (acceptHeader == null || !acceptHeader.contains("json")) { keyType = KeyType.XML; returnMediaType = "application/xml"; } Key cacheKey = new Key(EntityType.Application, "ALL_APPS", keyType, CurrentRequestVersion.get(), EurekaAccept.fromString(eurekaAccept), regions); Response response; if (acceptEncoding != null && acceptEncoding.contains("gzip")) { response = Response.ok(this.responseCache.getGZIP(cacheKey)).header("Content-Encoding", "gzip").header("Content-Type", returnMediaType).build(); } else { response = Response.ok(this.responseCache.get(cacheKey)).build(); } return response; } } //具体获取实例信息 @VisibleForTesting ResponseCacheImpl.Value getValue(Key key, boolean useReadOnlyCache) { ResponseCacheImpl.Value payload = null; try { if (useReadOnlyCache) { ResponseCacheImpl.Value currentPayload = (ResponseCacheImpl.Value)this.readOnlyCacheMap.get(key); if (currentPayload != null) { payload = currentPayload; } else { payload = (ResponseCacheImpl.Value)this.readWriteCacheMap.get(key); this.readOnlyCacheMap.put(key, payload); } } else { payload = (ResponseCacheImpl.Value)this.readWriteCacheMap.get(key); } } catch (Throwable var5) { logger.error("Cannot get value for key : {}", key, var5); } return payload; }

@Path("delta")
@GET
public Response getContainerDifferential(@PathParam("version") String version, @HeaderParam("Accept") String acceptHeader, @HeaderParam("Accept-Encoding") String acceptEncoding, @HeaderParam("X-Eureka-Accept") String eurekaAccept, @Context UriInfo uriInfo, @Nullable @QueryParam("regions") String regionsStr) {
boolean isRemoteRegionRequested = null != regionsStr && !regionsStr.isEmpty();
if (!this.serverConfig.shouldDisableDelta() && this.registry.shouldAllowAccess(isRemoteRegionRequested)) {
String[] regions = null;
if (!isRemoteRegionRequested) {
EurekaMonitors.GET_ALL_DELTA.increment();
} else {
regions = regionsStr.toLowerCase().split(",");
Arrays.sort(regions);
EurekaMonitors.GET_ALL_DELTA_WITH_REMOTE_REGIONS.increment();
}
CurrentRequestVersion.set(Version.toEnum(version));
KeyType keyType = KeyType.JSON;
String returnMediaType = "application/json";
if (acceptHeader == null || !acceptHeader.contains("json")) {
keyType = KeyType.XML;
returnMediaType = "application/xml";
}
Key cacheKey = new Key(EntityType.Application, "ALL_APPS_DELTA", keyType, CurrentRequestVersion.get(), EurekaAccept.fromString(eurekaAccept), regions);
return acceptEncoding != null && acceptEncoding.contains("gzip") ? Response.ok(this.responseCache.getGZIP(cacheKey)).header("Content-Encoding", "gzip").header("Content-Type", returnMediaType).build() : Response.ok(this.responseCache.get(cacheKey)).build();
} else {
return Response.status(Status.FORBIDDEN).build();
}
}
2.如何搭建高可用Eureka集群?
1.设置eureka.client.registerWithEureka: true 设置互相注册
2.设置eureka.clientservice-url.defaultZone
eureka的高可用状态下,这些注册中心是对等的,他们会互相将注册在自己的实例同步给其他的注册中心,同样是通过问题1的方式将注册在自己上的实例注册到其他注册中心去。
//同步实例信息给其他的注册中心 this.replicateToPeers(PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl.Action.Register, info.getAppName(), info.getId(), info, (InstanceStatus)null, isReplication);

private void replicateToPeers(PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl.Action action, String appName, String id, InstanceInfo info, InstanceStatus newStatus, boolean isReplication) { Stopwatch tracer = action.getTimer().start(); try { if (isReplication) { this.numberOfReplicationsLastMin.increment(); } if (this.peerEurekaNodes == Collections.EMPTY_LIST || isReplication) { return; } Iterator var8 = this.peerEurekaNodes.getPeerEurekaNodes().iterator(); while(var8.hasNext()) { PeerEurekaNode node = (PeerEurekaNode)var8.next(); if (!this.peerEurekaNodes.isThisMyUrl(node.getServiceUrl())) { this.replicateInstanceActionsToPeers(action, appName, id, info, newStatus, node); } } } finally { tracer.stop(); } }
那么问题来了,一旦 其中一个eureka收到一个客户端注册实例时,既然eureka注册中心将注册在自己的实例同步到其他注册中心中的方式和客户端注册的方式相同,那么在接收的eureka注册中心一端,会不会再同步回给注册中心(或者其他注册中心),从而导致死循环。
- 注册中心收到注册信息后会判断是否是其他注册中心同步的信息还是客户端注册的信息,如果是客户端注册的信息,那么他将会将该客户端信息同步到其他注册中心去;否则收到信息后不作任何操作。通过此机制避免集群中信息同步的死循环。?
replicateToPeers方法字面意思是同步或者复制到同事(即其他对等的注册中心),最后一个参数为isReplication,是一个boolean值,表示是否同步(复制),如果是客户端注册的,那么为false,如果是其他注册中心同步的则为true,replicateToPeers方法中,如果isReplication=false时,将会发起同步
- 注册中心收到注册信息后会判断是否是其他注册中心同步的信息还是客户端注册的信息,如果是客户端注册的信息,那么他将会将该客户端信息同步到其他注册中心去;否则收到信息后不作任何操作。通过此机制避免集群中信息同步的死循环。
3.客户端是如何拉取服务端信息?是需要时才去服务端拉取,还是先拉取到本地,需要用的时候直接从本地获取?
客户端拉取服务端服务信息是通过一个定时任务定时拉取的,每次拉取后刷新本地已保存的信息,需要使用时直接从本地直接获取。

private void initScheduledTasks() { int renewalIntervalInSecs; int expBackOffBound; if (this.clientConfig.shouldFetchRegistry()) { renewalIntervalInSecs = this.clientConfig.getRegistryFetchIntervalSeconds(); expBackOffBound = this.clientConfig.getCacheRefreshExecutorExponentialBackOffBound(); this.scheduler.schedule(new TimedSupervisorTask("cacheRefresh", this.scheduler, this.cacheRefreshExecutor, renewalIntervalInSecs, TimeUnit.SECONDS, expBackOffBound, new DiscoveryClient.CacheRefreshThread()), (long)renewalIntervalInSecs, TimeUnit.SECONDS); } // new DiscoveryClient.CacheRefreshThread() 用来定时刷新服务端已保存的服务信息 @VisibleForTesting void refreshRegistry() { try { boolean success = this.fetchRegistry(remoteRegionsModified); if (success) { this.registrySize = ((Applications)this.localRegionApps.get()).size(); this.lastSuccessfulRegistryFetchTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis(); } } } catch (Throwable var9) { logger.error("Cannot fetch registry from server", var9); } }

private void initScheduledTasks() { int renewalIntervalInSecs; int expBackOffBound; if (this.clientConfig.shouldFetchRegistry()) { renewalIntervalInSecs = this.clientConfig.getRegistryFetchIntervalSeconds(); expBackOffBound = this.clientConfig.getCacheRefreshExecutorExponentialBackOffBound(); this.scheduler.schedule(new TimedSupervisorTask("cacheRefresh", this.scheduler, this.cacheRefreshExecutor, renewalIntervalInSecs, TimeUnit.SECONDS, expBackOffBound, new DiscoveryClient.CacheRefreshThread()), (long)renewalIntervalInSecs, TimeUnit.SECONDS); } //new DiscoveryClient.CacheRefreshThread()->void refreshRegistry()
4.心跳和服务剔除机制是什么?
心跳机制:
- 客户端启动后,就会启动一个定时任务,定时向服务端发送心跳数据,告知服务端自己还活着,默认的心跳时间间隔是30秒。
服务剔除机制:
- 如果开启了自我保护机制,那么所有的服务,包括长时间没有收到心跳的服务(即已过期的服务)都不会被剔除;
- 如果未开启自我保护机制,那么将判断最后一分钟收到的心跳数与一分钟收到心跳数临界值比较,如果失败率大于85%,则启用服务剔除机制;一旦服务剔除机制开启,则Eureka服务端并不会直接剔除所有已过期的服务,而是通过随机数的方式进行剔除,避免自我保护开启之前将所有的服务(包括正常的服务)给剔除。

public void evict(long additionalLeaseMs) { logger.debug("Running the evict task"); //是否启用租约到期,即是否开启了服务过期超时机制,开启之后就会将过期的服务进行剔除 if (!this.isLeaseExpirationEnabled()) { logger.debug("DS: lease expiration is currently disabled."); } else { List<Lease<InstanceInfo>> expiredLeases = new ArrayList(); Iterator var4 = this.registry.entrySet().iterator(); while(true) { Map leaseMap; do { if (!var4.hasNext()) { int registrySize = (int)this.getLocalRegistrySize(); int registrySizeThreshold = (int)((double)registrySize * this.serverConfig.getRenewalPercentThreshold()); int evictionLimit = registrySize - registrySizeThreshold; int toEvict = Math.min(expiredLeases.size(), evictionLimit); if (toEvict > 0) { Random random = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis()); for(int i = 0; i < toEvict; ++i) { //具体的剔除功能 this.internalCancel(appName, id, false); } } return; } Entry<String, Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>>> groupEntry = (Entry)var4.next(); leaseMap = (Map)groupEntry.getValue(); } while(leaseMap == null); Iterator var7 = leaseMap.entrySet().iterator(); while(var7.hasNext()) { Entry<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> leaseEntry = (Entry)var7.next(); Lease<InstanceInfo> lease = (Lease)leaseEntry.getValue(); if (lease.isExpired(additionalLeaseMs) && lease.getHolder() != null) { expiredLeases.add(lease); } } } } } // protected boolean internalCancel(String appName, String id, boolean isReplication) { boolean var10; try { this.read.lock(); EurekaMonitors.CANCEL.increment(isReplication); Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> gMap = (Map)this.registry.get(appName); Lease<InstanceInfo> leaseToCancel = null; if (gMap != null) { leaseToCancel = (Lease)gMap.remove(id); } AbstractInstanceRegistry.CircularQueue var6 = this.recentCanceledQueue; synchronized(this.recentCanceledQueue) { //添加到取消队列 this.recentCanceledQueue.add(new Pair(System.currentTimeMillis(), appName + "(" + id + ")")); } InstanceStatus instanceStatus = (InstanceStatus)this.overriddenInstanceStatusMap.remove(id); if (leaseToCancel == null) { EurekaMonitors.CANCEL_NOT_FOUND.increment(isReplication); boolean var17 = false; return var17; } leaseToCancel.cancel(); InstanceInfo instanceInfo = (InstanceInfo)leaseToCancel.getHolder(); String vip = null; String svip = null; //设置缓存失效 this.invalidateCache(appName, vip, svip); logger.info("Cancelled instance {}/{} (replication={})", new Object[]{appName, id, isReplication}); var10 = true; } finally { this.read.unlock(); } return var10; }
5.Eureka自我保护机制是什么?
在分布式系统的CAP理论中,Eureka采用的AP,也就是Eureak保证了服务的可用性(A),而舍弃了数据的一致性(C)。当网络发生分区时,客户端和服务端的通讯将会终止,那么服务端在一定的时间内将收不到大部分的客户端的一个心跳,如果这个时候将这些收不到心跳的服务剔除,那可能会将可用的客户端剔除了,这就不符合AP理论。
为什么是AP理论?
因为自我保护是检测到心跳失败到一定的百分比,就保护注册实例信息,防止注册实例失效,保证了A,舍弃了C,所以是AP 理论。
6.Eureka Server从技术层面是如何抗住日千万级访问量的?
现在咱们假设手头有一套大型的分布式系统,一共100个服务,每个服务部署在20台机器上,机器是4核8G的标准配置。
也就是说,相当于你一共部署了100 * 20 = 2000个服务实例,有2000台机器。
每台机器上的服务实例内部都有一个Eureka Client组件,它会每隔30秒请求一次Eureka Server,拉取变化的注册表。
此外,每个服务实例上的Eureka Client都会每隔30秒发送一次心跳请求给Eureka Server。
那么大家算算,Eureka Server作为一个微服务注册中心,每秒钟要被请求多少次?一天要被请求多少次?
-
按标准的算法,每个服务实例每分钟请求2次拉取注册表,每分钟请求2次发送心跳
-
这样一个服务实例每分钟会请求4次,2000个服务实例每分钟请求8000次
-
换算到每秒,则是8000 / 60 = 133次左右,我们就大概估算为Eureka Server每秒会被请求150次
-
那一天的话,就是8000 * 60 * 24 = 1152万,也就是每天千万级访问量
按照我们的测算,一个上百个服务,几千台机器的系统,按照这样的频率请求Eureka Server,日请求量在千万级,每秒的访问量在150次左右。
即使算上其他一些额外操作,我们姑且就算每秒钟请求Eureka Server在200次~300次吧。
所以通过设置一个适当的拉取注册表以及发送心跳的频率,可以保证大规模系统里对Eureka Server的请求压力不会太大。
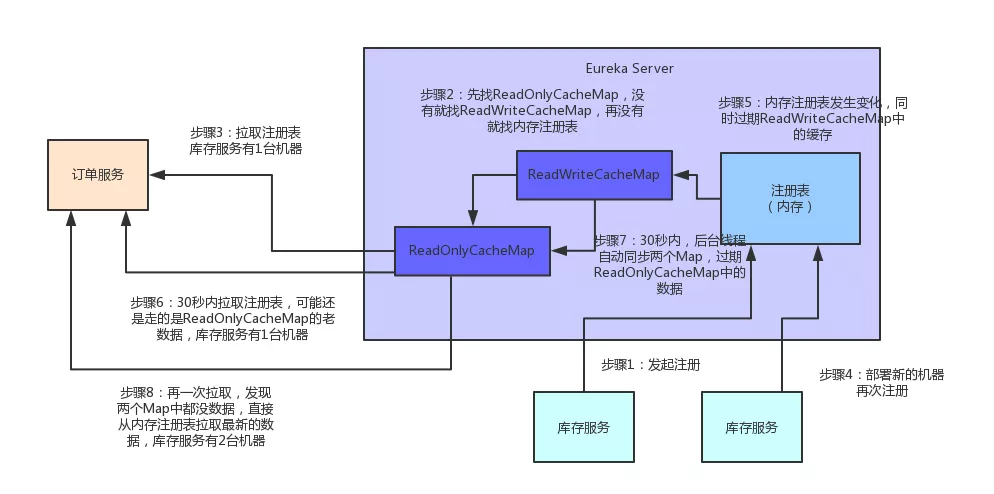
1.维护注册表、拉取注册表、更新心跳时间,全部发生在内存里,通过双层map。
2.多级缓存机制
-
Eureka Server为了避免同时读写内存数据结构造成的并发冲突问题,还采用了多级缓存机制来进一步提升服务请求的响应速度。
-
在拉取注册表的时候:
-
首先从ReadOnlyCacheMap里查缓存的注册表。 有个定时每30秒从ReadWriteCacheMap里面获取更新到自己(提升读,避免并发读不存在,然后再从读写缓存获取,相当于自己有个失效机制,每30s更新一次)
-
 readOnlyCacheMap更新
readOnlyCacheMap更新CurrentRequestVersion.set(key.getVersion()); ResponseCacheImpl.Value cacheValue = (ResponseCacheImpl.Value)ResponseCacheImpl.this.readWriteCacheMap.get(key); ResponseCacheImpl.Value currentCacheValue = (ResponseCacheImpl.Value)ResponseCacheImpl.this.readOnlyCacheMap.get(key); if (cacheValue != currentCacheValue) { ResponseCacheImpl.this.readOnlyCacheMap.put(key, cacheValue); }
-
若没有,就找ReadWriteCacheMap里缓存的注册表。 默认180s之后过期
-
 readWriteCacheMap
readWriteCacheMapthis.readWriteCacheMap = CacheBuilder.newBuilder().initialCapacity(serverConfig.getInitialCapacityOfResponseCache()).expireAfterWrite(serverConfig.getResponseCacheAutoExpirationInSeconds(), TimeUnit.SECONDS).removalListener(new RemovalListener<Key, ResponseCacheImpl.Value>() { public void onRemoval(RemovalNotification<Key, ResponseCacheImpl.Value> notification) { // serverConfig.getResponseCacheAutoExpirationInSeconds(), public long getResponseCacheAutoExpirationInSeconds() { return (long)configInstance.getIntProperty(this.namespace + "responseCacheAutoExpirationInSeconds", 180).get(); }
-
如果还没有,就从内存中获取实际的注册表数据。
-
在注册表发生变更的时候:
-
会在内存中更新变更的注册表数据,同时过期掉ReadWriteCacheMap。
-
此过程不会影响ReadOnlyCacheMap提供人家查询注册表。
-
一段时间内(默认30秒),各服务拉取注册表会直接读ReadOnlyCacheMap
-
30秒过后,Eureka Server的后台线程发现ReadWriteCacheMap已经清空了,也会清空ReadOnlyCacheMap中的缓存
-
下次有服务拉取注册表,又会从内存中获取最新的数据了,同时填充各个缓存。
7.多级缓存机制的优点是什么?
ResponseCacheImpl
private final ConcurrentMap<Key, ResponseCacheImpl.Value> readOnlyCacheMap = new ConcurrentHashMap();
private final LoadingCache<Key, ResponseCacheImpl.Value> readWriteCacheMap;
-
尽可能保证了内存注册表数据不会出现频繁的读写冲突问题。
-
并且进一步保证对Eureka Server的大量请求,都是快速从纯内存走,性能极高。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号