第四周学习总结
一、ArrayList
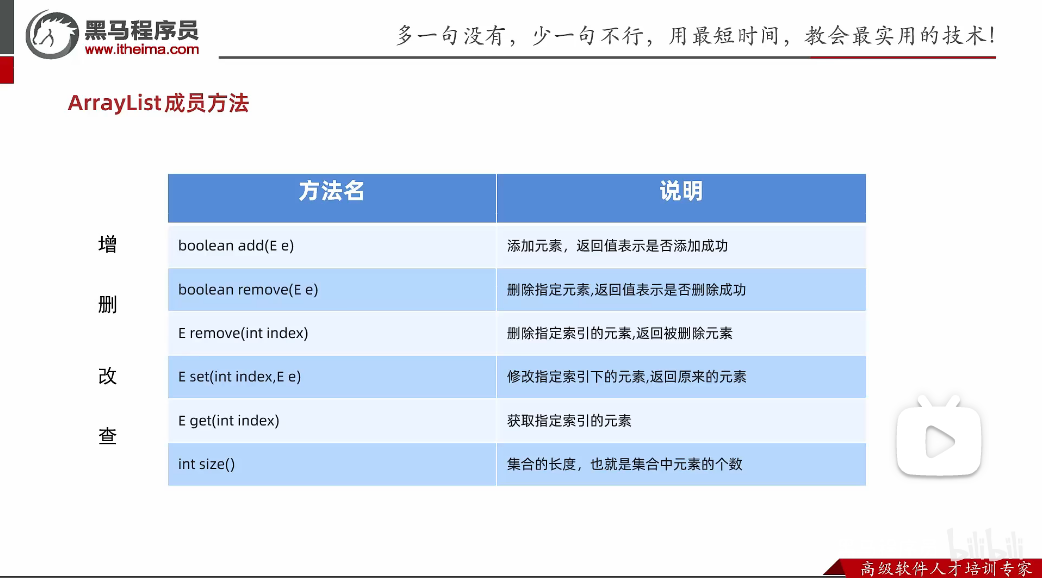
(一)基本功能
1 package com.itheima.1istdemo; 2 import java.util,Arraylist; 3 public classArrayListDemo1{ 4 public static void main(String[]args){ 5 //1.创建集合的对架 6 //泛型:限定集合中存储数据的类型 7 //ArrayList<String)list = newArrayList<String>(); 8 9 //此时我们创造的是ArrayList的对象 10 //打印对总不足地址值,而是集合中存储数据内容 11 //在长示的时候[]所有的最行过行包题 12 ArrayList<String>list = new ArrayList<>{ 13 System.out.println(list); 14 } 15 }
1 public classArrayListDemo2{ 2 public static void main(String[]args){ 3 4 ArrayList<String>list = new ArrayList<>() 5 //1.添加 6 list.add("aa"); 7 //2.删除 8 (1) 9 boolean result1 = list.remove("aa”); 10 System.out.println(result1); 11 (2) 12 boolean esult 2= list.remove("dcd"); 13 System.out,println(resul=2); 14 (3) 15 string str = list.remove(2); 16 System.out.println(str); 17 //3.修改 18 Stringresult = list.set(1, "ddd"); 19 System.out.printin(result); 20 21 //查询 22 String s = list.get(0); 23 System.out.println(s); 24 //遍历 25 for(int i = 0; i < list.size();i++) 26 String str = list.get(i); 27 28 System.out,println(str); 29 } 30 System.out.println(list); 31 } 32 }
(二)添加数字并遍历
1 public class Test2 { 2 public staticvoid main(String[] args){ 3 //1.创建 4 ArrayList<Integer> list= newArrayList<>(); 5 //2.添加 6 list_add(2); 7 list.add(3); 8 list.add(4); 9 list.add(5); 10 //3.遍历 11 System.out,print(”["); 12 for(inti m e; i< list.size(); i++) { 13 if(i== list.size() - 1){ 14 System.out.print(list.get(1));} 15 else{ 16 System.out.print(list.get(i) +", "); 17 } 18 } 19 System.out.println("]"); 20 } 21 }
(三)添加学生对象
1 public class TestS { 2 public static voidmain(String[] args){ 3 //1.创建集合 4 ArrayList<student>list = new ArrayList<>(); 5 //2.键盘入学生的信息 6 Scanner SC =new Scanner(System.in); 7 for(int i = 0;i < 3;i ++)( 8 student s =new Student(); 9 System.outorintln("请输入学生的如名"); 10 Stringname= sc.next(); 11 System.out.print1n("请输入学生的年龄”); 12 int age = sc.nextInt(); 13 //lname 和age但给学生对象 14 s.setName(name); 15 s_setAge(ege); 16 //把学生对象添加到集合当中 17 list.add(s); 18 } 19 //3.遍历 20 for (int i =0;i<list.size(); i++) 21 22 Student stu = list.get(i); 23 System.out.println(stu.getName()+",”+ stu.getAge()); 24 } 25 } 26 }
(四)查找用户
需求:
1,main方法中定义 一个集合,存入三个用户对象。
用户属性为:id, username, password
2.要求:定义一个方法,根据id查找对应的用户信息
如果存,返回1
如果不存在,返问 -1
1 public classTest7 { 2 public static voidmain(String[] args){ 3 //1.创建 4 ArrayList<User list newArrayList<>() 5 //2.创建三个用户对象 6 User ui = newUser( id heima001"username; "zhangsan", password: "123456"); 7 User u2 =newUser( id"heima602",Username: "lisi", password; “12345678"); 8 User u3 = newUser(idt heima003",username. "wangwu”, password: “1234qwer"); 9 //3.把用户对象添加到集合中 10 list.add(u1); 11 list.add(u2); 12 list.add(u3); 13 //4.台找索引 14 int index = getIndex(list, id: "helma004"); 15 //5.打印 16 System.out.println(index); 17 } 18 public static int getIndex(ArrayList<User> list, String id) (for (int i= e; i<list.size(); i++){ 19 User u = list.get(i); 20 String uid = u.getId(); 21 if(uid.equals(id)){ 22 return i; 23 } 24 } 25 return -1;
(五)返回多个数据

1 public class Test8 { 2 public static voidmain(String[] args) { 3 //1,创建集合对象 4 ArrayList<Phone>list= new ArrayList<>(); 5 //2.创建手机 6 Phone p1 = new Phone( brand“小米",price:1000); 7 Phonep2 = new Phone(brand:"苹果",price:8060); 8 Phonep3 = new Phone( brand:"华为”,price: 2999); 9 //3.添加数据 10 list.add(p1); 11 list.add(p2); 12 list.add(p3); 13 14 //4.调用方法 15 ArrayList<PhonexphoneInfoList = getPhoneInfo(list) 16 //5.运历业合 17 for (int i= 0; ikphoneInfo4stsize(); i++) 18 Phone phone= phoneIoList.get(i); 19 System.out.println(phone,getBrandi) + phone.getPrice()); 20 } 21 22 public static void getPhoneInfo(ArrayList<Phone> list){ 23 24 ArrayList<Phone> resultList = new ArrayList<>(); 2526 for (int i= 0; i< list.size() ; i++){ 27 Phone p = list.get(i); 28 int price = p.getPrice(); 29 if(price < 3000){ 30 System.out.println(phone.getBrand() +" , " + p.getPrice()); 31 } 32 } 33 } 34 }
下周学习:面向对象进阶

