绝对定位元素水平居中和垂直居中的原理
通常在设置绝对定位元素相对于其定位的祖先元素水平垂直居中时,通过绝对定位元素设置margin:auto; top:0; bottom:0; right:0; left:0;就可以实现。下面简单探索一下绝对定位元素这么设置就可以实现水平居中和垂直居中的原理。
核心CSS代码:
position:absolute; margin:auto; top:0; bottom:0; right:0; left:0;
绝对定位元素的布局由元素的三个因素决定:位置(top、bottom、left、right)、元素尺寸和margin。绝对定位元素在布局上呈现自适应的特点——位置和尺寸固定,则自适应margin值;位置和margin固定,则自适应尺寸。
(1)位置和尺寸固定,margin:auto;
<div id='wrap'>
<div id='item1'></div>
</div>
#wrap {
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
border: 1px dotted black;
margin: 0 auto;
position: relative;
}
#item1 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: purple;
/* 核心代码 */
position: absolute;
margin: auto;
top: 0;
bottom: 0;
left: 0;
right: 0;
}
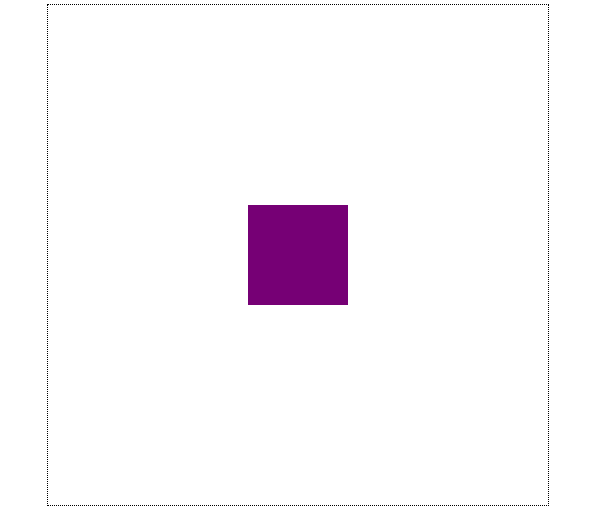
布局效果:
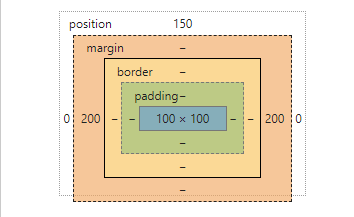
计算样式:
水平方向:
width(wrap)=margin(item)+width(item)+padding(item)+left(item)+right(item)
由于位置设置为 top: 0;bottom: 0;left: 0;right: 0; ,尺寸固定为 width: 100px;
height: 100px;,margin:auto;自适应,实际水平方向margin值为500-100 =400px,平均分配左右两侧,即为margin-left:200px;margin-right:200px;。垂直方向同理可得。可以看到在绝对定位元素中,若水平方向位置left与right值相等,那么margin-left: auto;margin-right:auto;可以让其相对于定位的祖先元素水平居中。
(2)位置和margin固定
<div id='wrap'>
<div id='item1'></div>
</div>
#wrap {
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
border: 1px dotted black;
margin: 0 auto;
position: relative;
}
#item1 {
background-color: purple;
/* 核心代码 */
position: absolute;
margin: 20px;
top:0;
bottom: 0;
left: 0;
right: 0;
}
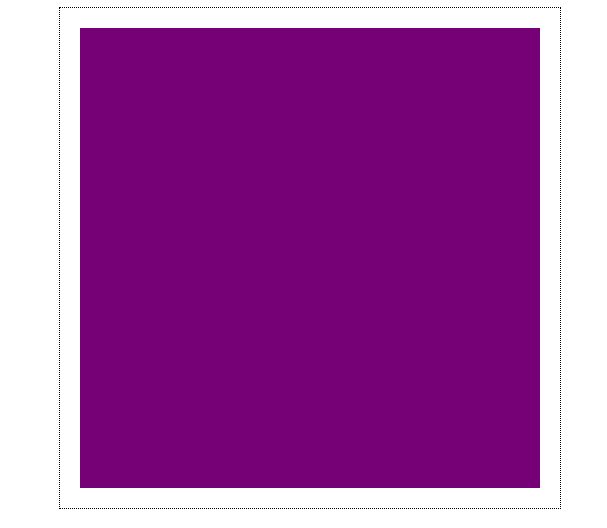
布局效果
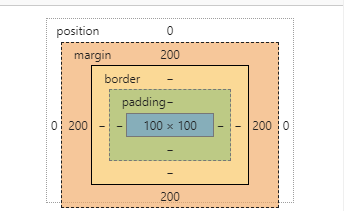
计算样式

在水平方向,由于right:0;left:0;并且margin-left:20px;margin-right:20px;各项相加和等于定位的祖先元素宽度,因此width的值为460px。
其他情况:
如果同时设置top、bottom、left、right,margin设置值中没有auto,那么位置top值优先于bottom值,left值优先于right值。
如果不设置位置,只设置margin:auto;那么布局中相当于margin:0;。
绝对定位元素和静态定位元素的相互作用:
如果绝对定位元素存在静态定位的兄弟元素,如果该元素没有设置垂直位置,那么其垂直位置将以静态定位的兄弟元素占位计算。
<div id='wrap'>
<div class='item2'>
</div>
<div id='item1'></div>
</div>
#wrap {
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
border: 1px dotted black;
margin: 0 auto;
position: relative;
}
#item1 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: purple;
/* 核心代码 */
position: absolute;
margin: auto;
/* top: 0px;
bottom: 0; */
left: 0;
right: 0;
}
.item2 {
width: 150px;
height: 150px;
background-color: green;
position: static;
}