python Django ORM相关
- ORM快速使用
# 1 获取数据库信息,放回queryset到前端模板
from report.models import ReportInfo
def reportDetail(request):
return render(request, "app/report.html", {"report": ReportInfo.objects.order_by("-id")})
# 2 允许字段为空
https://www.cnblogs.com/MacoLee/p/5610989.html
# orm 反向查找
report_info_obj = ReportInfo.objects.filter(report_uuid='2d3c510b-6a37-45af-9fba-b0a204b2aafb').get() # ReportInfo object
report_info_obj = ReportInfo.objects.get(report_uuid='2d3c510b-6a37-45af-9fba-b0a204b2aafb') # ReportInfo object
reportdetail_qset = report_info_obj.reportdetail_set.all() #report_info_obj 中没有reportdetail相关字段,叫反向查找
# filter 与或非 查找
from django.db.models import Q
Item.objects.filter(Q(creator=owner) | Q(moderated=False))
report_details_by_casename = ReportDetail.objects.filter(Q(case_name=case_name) & (~Q(platform_name='null')) )
# orm 模板语言反向查找
< td > {{r.reportdetail_set.first.bbu_vesion}} < / td >
< td > {{r.reportdetail_set.first.rru_vesion}} < / td >
- ORM的返回值
#1、返回QuerySet对象的方法有:
all()、filter()、exelude()、order_by()、reverse()、distinct()
QuerySet可以直接用delete()
TestCaseInfo.objects.filter(belong_module__module_name=module_name).delete()
ret2 = get_objects_for_user(user,'app.view_project').all().all() #这里多少个all都是返回QuerySet
ret3 = get_objects_for_user(user,'app.view_project').first()
#2、特殊的QuerySet:
values() :返回一个可迭代的字典序列
values_list() 返回一个可迭代的元祖序列
#3、返回具体对象的
get()、first()、last()
#4、返回布尔值的方法有:
exists()
#5、返回数字的方法有:
count()
- ORM的正向查询和反向查询
https://www.cnblogs.com/aaronthon/p/9520832.html
- Django ORM的log配置
##### 配置显示**sql**的log
LOGGING = {
'version': 1,
'disable_existing_loggers': False,
'handlers': {
'console':{
'level':'DEBUG',
'class':'logging.StreamHandler',
},
},
'loggers': {
'django.db.backends': {
'handlers': ['console'],
'propagate': True,
'level':'DEBUG',
},
}
}
- ORM查询命令
- 基于obj对象查询(子查询)
# 对应sql:
select publish_id from Book where title="python"
select email from Publish where nid = 1
##### 一对多
```python
# 按字段(publish)
# 一对多 book -----------------> publish
# <----------------
# book_set.all()
# 正向查询按字段:
# 查询python这本书籍的出版社的邮箱
python=models.Book.objects.filter(title="python").first()
print(python.publish.email)
# 反向查询按 表名小写_set.all()
# xx出版社出版的书籍名称
publish_obj=models.Publish.objects.filter(name="xx出版社").first()
for obj in publish_obj.book_set.all():
print(obj.title)
多对多
# 按字段(authors.all())
# 多对多 book -----------------------> author
# <----------------
# book_set.all()
# 正向查询
# 查询python作者的年龄
python = models.Book.objects.filter(title="python").first()
for author in python.authors.all():
print(author.name ,author.age)
# 反向查询
# 查询hehe出版过的书籍名称
alex=models.Author.objects.filter(name="hehe").first()
for book in alex.book_set.all():
print(book.title)
一对一
# 按字段 authorDetail
# 一对一 author -----------------------> authordetail
# <----------------
# 按表名 author
# 正向查询
#查询hehe的手机号
hehe=models.Author.objects.filter(name='hehe').first()
print(hehe.authorDetail.telephone)
# 反向查询
# 查询家在山东的作者名字
ad_list=models.AuthorDetail.objects.filter(addr="shandong")
for ad in ad_list:
print(ad.author.name)
- 基于queryset
#正向查询:按字段 反向查询:表名小写
# 对应sql:
select publish.email from Book left join Publish on book.publish_id=publish.nid
where book.title="python"
正向查询
# 查询python这本书籍的出版社的邮箱
models.Book.objects.filter(title="python").values("publish__email")
#查询hehe的手机号
# 方式1:
models.Author.objects.filter(name="hehe").values("authorDetail__telephone")
# 方式2:
models.AuthorDetail.objects.filter(author__name="hehe").values("telephone")
反向查询
#hehe出版社出版的书籍名称
# 方式1:
models.Publish.objects.filter(name="hehe出版社").values("book__title")
#方式2:
models.Book.objects.filter(publish__name="hehe出版社").values("title")
综合查询
# 查询手机号以151开头的作者出版过的书籍名称以及书籍对应的出版社名称
ret=models.Book.objects.filter(authors__authorDetail__telephone__startswith="151").values('title',"publish__name")
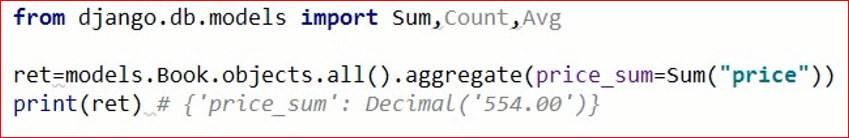
聚合
分组

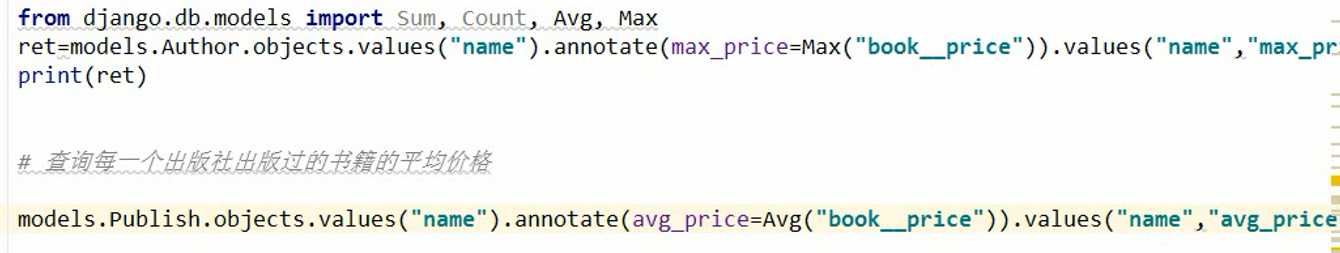
单表
models.Employee.objects.values("province").annotate(a=Avg("salary")).values("province", "a")
多表链表
models.Person.objects.values("dept_id").annotate(a=Avg("salary")).values("dept__name", "a")
原生的SQL
-
ret = models.Person.objects.all().extra( select={"gt": "salary > 2000"} )相当于
SELECT (salary > 2000) AS `gt`, `person`.`id`, `person`.`name`, `person`.`salary`, `person`.`dept_id` FROM `person` LIMIT 21; args=() -
from django.db import connection cursor = connection.cursor() # 获取光标,等待执行SQL语句 cursor.execute("""SELECT * from person where id = %s""", [1]) row = cursor.fetchone() print(row) -
# 按日期归档 archive_list = models.Article.objects.filter(user=user).extra( select={"archive_ym": "date_format(create_time,'%%Y-%%m')"} ).values("archive_ym").annotate(c=Count("nid")).values("archive_ym", "c")
Filter和values
ret = models.Article.objects.values('nid')
print(ret)
ret = models.Article.objects.filter(nid=1)
print(ret)
(0.000) SELECT `blog_article`.`nid` FROM `blog_article` LIMIT 21; args=()
(0.000) SELECT `blog_article`.`nid`, `blog_article`.`title`, `blog_article`.`desc`, `blog_article`.`create_time`, `blog_article`.`comment_count`, `blog_article`.`up_count`, `blog_article`.`down_count`, `blog_article`.`category_id`, `blog_article`.`user_id` FROM `blog_article` WHERE `blog_article`.`nid` = 1 LIMIT 21; args=(1,)

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号