java面试:手写代码
二分查找法
/**
* 二分查找法。时间复杂度:O(log n)
* 二分查找法:给定一组有序的数组,每次都从一半中查找。直到找到要求的数据。
*
* @param nums
* @param target
* @return
*/
public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
if (nums==null) {
return -1;
}
//二分查找,left,right,mid
int left=0;
int right = nums.length -1;
int mid ;
//注意,结束循环的条件是 左边界<=右边界
while (left<=right) {
//中间节点的下标
mid = (right+left)/2 ;
//如果 nums[i]=target,则下标 i 即为要寻找的下标;
//如果 nums[i]>target,则 target 只可能在下标 i 的左侧;
//如果 nums[i]<target,则 target 只可能在下标 i 的右侧。
if (target == nums[mid]) {
return mid;
} else if (target > nums[mid]) {
left = mid+1;
} else {
right = mid-1;
}
}
return -1;
}
排序算法
1.快速排序
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* 快速排序的核心思想是分治和递归,可以平均达到类似二分查找的时间复杂度
* 解题思路:
* 1)递归的终止条件 left >= right
* 2) 选定一个靶向值,然后进行调整,大于靶向值的都移到该值右边,小于靶向值的都移到左边,靶向值移到分割位置
* 3)然后在分隔位置左右分别进行递归
* https://blog.csdn.net/tala_cai/article/details/120699636
*/
public class QuickSort {
public static void sort(int[] array, int left, int right) {
//1、递归的终止条件
if (left >= right) {
return;
}
//2、选定靶向值进行调整
int x = array[right];
int target = left - 1;
for (int j = left; j < right; j++) {
if (array[j] <= x) {
//顺序进行调整,不容易出错,统一小的都移动到左边
swap(array, ++target, j);
}
}
//靶向值放到正确位置
swap(array, target + 1, right);
//3、递归
//左递归
sort(array, left, target);
//右递归
sort(array, target + 1, right);
}
public static void swap(int[] array, int i, int j) {
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = temp;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {2,3,4,5,8,7,9,1};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
sort(array, 0, array.length-1);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
}
2.各个排序算法的时间复杂度:
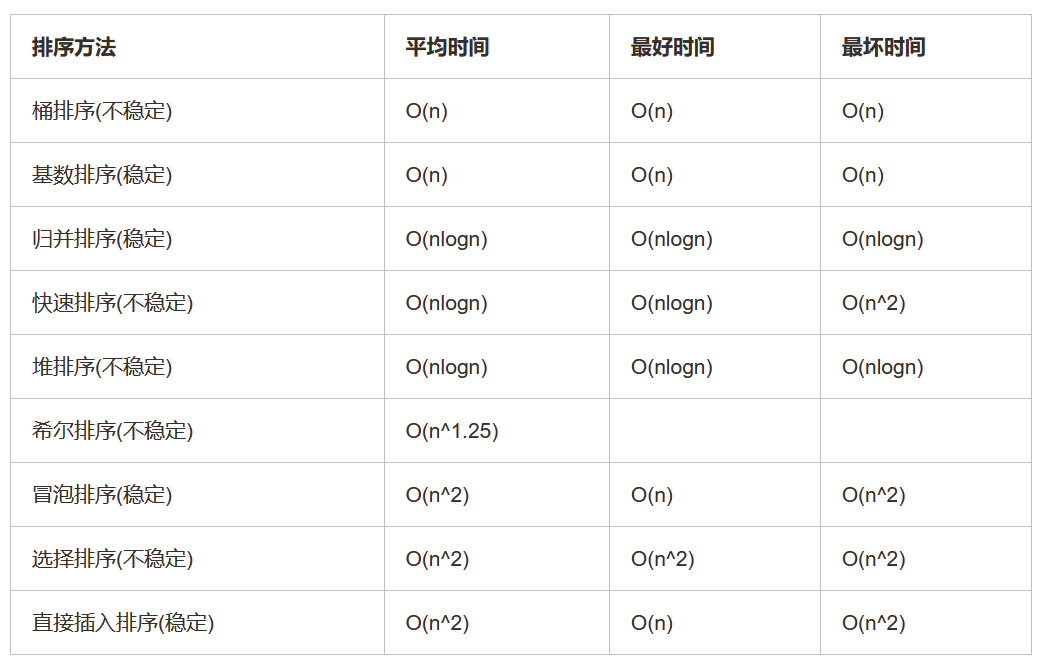
判断一个数是不是斐波那契数
斐波纳契数列,又称黄金分割数列,指的是这样一个数列:1、1、2、3、5、8、13、21、……
在数学上,斐波纳契数列以如下被以递归的方法定义:F0=1,F1=1,Fn=F(n-1)+F(n-2)(n>=2,n∈N*)。
public class Fibonacci {
/**
* 这道题挺简单的。就是要注意一些边界值。
* @param num
* @return
*/
public boolean isFibo(int num) {
//负数检查
if (num<=0) {
return false;
}
if (num == 1) {
return true;
}
int[] dp = new int[num];
dp[0] = 1;
dp[1] = 1;
for (int i=2;i<num;i++) {
dp[i]= dp[i-1] + dp[i-2];
if (dp[i] == num) {
return true;
} else if (dp[i] > num) {
//超出范围了就不再检测
return false;
}
}
return false;
}
}
两个长字符串数字相加求和
从后往前遍历,相加之后,再倒序
如何倒序:基于 StringBuilder的reverse()方法。
注意点:两个一位数相加,>=10要进一位。
这道题,其实是 LeetCode415 。
/**
*
* 两个长字符串数字相加求和
*
* 示例 1:
* 输入:num1 = "11", num2 = "123"
* 输出:"134"
* 示例 2:
* 输入:num1 = "456", num2 = "77"
* 输出:"533"
*
*
*/
public class LeetCode415 {
public String addStrings(String num1, String num2) {
if (num1==null || num2==null) {
return null;
}
int i=num1.length()-1;
int j= num2.length()-1;
int plus=0;
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
//从后往前相加,大于等于10就进位。
while (i>=0 || j>=0 || plus!=0) {
//数字字符,减去'0',就能得到对应的数字
int first = i>=0? num1.charAt(i) - '0': 0;
int second = j>=0? num2.charAt(j) -'0': 0;
int sum = first+second+ plus;
//余数为当前位的结果
result.append(sum%10);
//进位取整
plus = sum/10;
i--;
j--;
}
//倒序
result.reverse();
return result.toString();
}
}
线程交替打印奇偶数
思路:
使用 Object类自带的 wait()和 notify()方法。
wait()休眠, notify()唤醒。
注意:wait()和 notify(),只能在 synchronized 里面使用。否则会报错: IllegalMonitorStateException
(1)打印线程编号,以及奇偶数
(2)notify()唤醒其他线程
(3)wait()休眠当前线程
public class TwoThreadNum {
private static int count = 1;
private static final Object OBJECT = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) {
printTwo();
}
public static void printTwo() {
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
//最好是设置一个范围,否则线程无休止打印。
while (count % 2 == 1 && count < 100) {
printfNum();
}
});
thread.setName("thread-1");
thread.start();
Thread thread2 = new Thread(() -> {
while (count % 2 == 0 && count < 100) {
printfNum();
}
});
thread2.setName("thread-2");
thread2.start();
}
private static void printfNum() {
//wait()和 notify(),只能在 synchronized 里面使用。否则会报错: IllegalMonitorStateException
synchronized (OBJECT) {
try {
//打印线程编号,以及奇偶数
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + count++);
//唤醒其他线程
OBJECT.notify();
//休眠当前线程
OBJECT.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
多线程
1.手写一下生产者消费者模式,不要用BlockingQueue。
思路:可以使用wait(),notify()
2.手写一个死锁。
详情见: https://www.cnblogs.com/expiator/p/9391092.html
设计模式
设计模式的代码详情见:
设计模式代码示例
1.手写一下单例模式。
单例模式示例
2.手写一下工厂模式。
3.手写一下观察者模式。
观察者模式示例
其他
其他的LeetCode算法解题思路,详情见: https://www.cnblogs.com/expiator/p/10226647.html
待补充。
参考资料:
十大排序算法全面解析-Java实现
《剑指offer》



