蓝桥杯省赛备战笔记—— (四)使用sort排序——练习题
例题:浮点数排序


#include<stdio.h> #include<math.h> #include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #define EPSILON 1e-6 using namespace std; double s[105]; bool cmp(double a,double b){ double aa = fabs(a - round(a)); double bb = fabs(b - round(b)); if(fabs(aa - bb) < EPSILON){ return a < b; } //如果两个浮点数的与最近整数的差 相差小于指定的值,就认为两差数大小相等,当两差数大小相等时,就按原来的浮点数的值从小到大排序 return aa < bb; //否则,按照两差数 从小到大排序 } int main(){int n; double x; scanf("%d",&n); for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){ scanf("%lf",&s[i]); } sort(s,s+n,cmp); for(int i =0; i < n;i++){ if(i == 0){ printf("%.6f",s[i]); }else{ printf(" %.6f",s[i]); } } return 0; }
- fabs() —— 对浮点数求绝对值
- round() —— 四舍五入的整数,相当于是最近的整数
例题:分数线
某小学举办了一场校内的信息学竞赛选拔赛。现在
同学们的成绩都出来了,负责信息学竞赛的老师需
要确定最终选拔赛的获奖名单。
为了鼓励大家,老师希望获奖人数不少于参赛总人
数的一半。因此,老师需要确定一个获奖分数线,
所有得分在分数线及以上的同学可以获奖。在满足
.上面条件的情况下,老师希望获奖分数线越高越
好。
请同学们通过程序设计的方法来解决以上问题,确
定获奖分数线和总获奖人数。
输入格式:
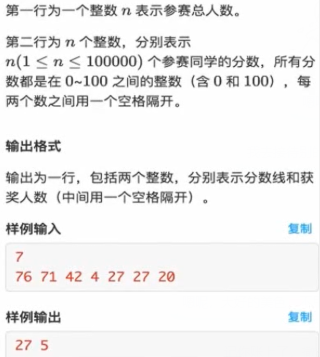
#include<stdio.h> #include<iostream> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; int s[10005]; int main(){ int n; scanf("%d",&n); for(int i= 0; i< n;i++){ scanf("%d",&s[i]); } sort(s,s+n,greater<int>()); int x= s[(n-1)/2]; printf("%d ",x); int sum = 0; for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){ if(s[i] >= x) sum++; else break; } printf("%d",sum); return 0; }
例题:交叉排序
蒜头君很无聊,他想对数组中的某些元素进行排
序。
现在我们有N个数,他想先将数组中第l1到第r1
的数字按从小到大的顺序排序。再将数组中第l2
到第r2的数字按从大到小的顺序排序。
我们帮他算一算数组排序后的结果吧~

#include<stdio.h> #include<iostream> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; int a[10005]; int main(){ int n,l1,r1,l2,r2; scanf("%d%d%d%d%d",&n,&l1,&r1,&l2,&r2); for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){ scanf("%d",&a[i]); } sort(a + l1 - 1,a + r1 ); sort(a + l2- 1, a + r2,greater<int>()); for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){ if(i == 0) printf("%d",a[i]); else printf(" %d",a[i]); } return 0; }
例题:红绿蓝
蒜头君有一个罐子,里面装着红的、绿的、蓝的玻
璃珠若干,分别用R、G、B表示。蒜头君希望
把它们排成一行,并且按照字典序排列(即B ->
G-> R的顺序)。然后以一红二绿三蓝为一-组串
成一串幸运珠,多余的放回罐子里,那么他能串成
多少串幸运珠呢?

#include<stdio.h> #include<algorithm> #include<iostream> #include<string.h> #include<math.h> using namespace std; char s[10005]; int main(){ scanf("%s",s); int len = strlen(s); sort(s,s+len); printf("%s\n",s); int r = 0; int g = 0; int b = 0; for(int i =0 ;i < len;i++){ if(s[i] == 'R') r++; else if (s[i] == 'G') g++; else b++; } int mi = min(r,min(g/2,b/3)); printf("%d",mi); return 0; }
例题:整数排序进阶
我们有N个正整数,均小于10000。现在需要将
这些正整数按照该正整数每一位数字相加的和从小
到大排序,即该正整数的每一位数字相加的和越小
排位越靠前。如果各位相加和相等,则按照正整数
的值从小到大排序。

#include<stdio.h> #include<iostream> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; int s[105]; bool cmp(int a,int b){ int aa = a; int bb = b; int suma = 0; int sumb = 0; while(a != 0){ suma += a % 10; a /= 10; } while(b != 0){ sumb += b % 10; b /= 10; } if(suma == sumb) return aa < bb; return suma < sumb; } int main(){ int n; scanf("%d",&n); for(int i = 0; i< n;i++){ scanf("%d",&s[i]); } sort(s,s+n,cmp); for(int i =0 ;i < n;i++){ if( i == 0) printf("%d",s[i]); else printf(" %d",s[i]); } return 0; }
例题:成绩排序
蒜头君班上一共有n个同学,每个同学依次编号为
1,2,...n,每个同学有一个分数。现在他请你帮
忙做一份全班同学的成绩排名表。
首先你需要按照分数从高到低将所有同学排序,再
输出成绩单上每个同学的编号。
保证任意两个同学的分数互不相同。

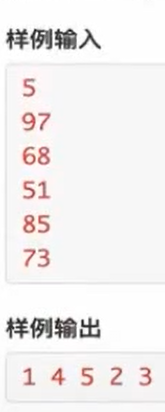
#include<stdio.h> #include<algorithm> #include<iostream> using namespace std; struct Stu{ int score; int id; }; bool cmp(Stu x,Stu y){ return x.score > y.score; } Stu stu[105]; int main(){ int n; scanf("%d",&n); for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){ int a; scanf("%d",&a); stu[i].score = a; stu[i].id = i+1; } sort(stu,stu+n,cmp); for(int i =0; i < n;i++){ if(i == 0) printf("%d",stu[i].id); else printf(" %d",stu[i].id); } return 0; }
例题:成绩排序升级版
小蒜所在的学校一开学就进行了一次摸底考试。摸
底考试考了语文、数学、英语、科学共四门课程。
小蒜的老师汇总成绩后列出了成绩单,其中包括每
个同学的姓名和四科的成绩。现在老师希望表扬一
下每门课程考试得分前四名和总分前四名的同学,
同分数的情况下,名字字典序更小的先表扬。
请你帮助老师写一个程序,快速完成这件事情吧。
输入格式
第一-行为学生人数N(4<= N ≤100)。
之后N行依次为每个学生的姓名和语文、数学、
英语、科学这四门课程的成绩,之间用一个空格隔
开(成绩都大于等于0小于等于100)
输出格式
输出第一行为语文考试要表扬前四名的同学的姓
名,之间用-一个空格隔开。
输出第二行为数学考试要表扬前四名的同学的姓
名,之间用一个空格隔开。
输出第三行为英语考试要表扬前四名的同学的姓
名,之间用一个空格隔开。
输出第四行为科学考试要表扬前四名的同学的姓
名,之间用一个空格隔开。
输出第五行为总分要表扬前四名的同学的姓名,之
间用一个空格隔开。
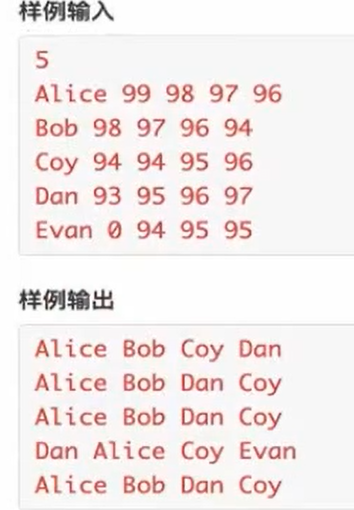
#include<stdio.h> #include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<string.h> using namespace std; struct Stu{ char name[10]; int score[4]; }; Stu stu[105]; void print(int n){ n = n - 1; for(int i = 0; i < n;i++){ if(i == 0) printf("%s",stu[i].name); else printf(" %s",stu[i].name); } printf("\n"); } bool cmp1(Stu a,Stu b){ if(a.score[0] != b.score[0]) return a.score[0] > b.score[0]; return strcmp(a.name, b.name) < 0; //strcmp(x,y). 如果字符串x 按字典序小于y,则返回小于0的值 //如果为真,则 a 排在 b 前面 } bool cmp2(Stu a,Stu b){ if(a.score[1] != b.score[1]) return a.score[1] > b.score[1]; return strcmp(a.name, b.name) < 0; } bool cmp3(Stu a,Stu b){ if(a.score[2] != b.score[2]) return a.score[2] > b.score[2]; return strcmp(a.name, b.name) < 0; //strcmp(x,y). 如果字符串x 按字典序小于y,则返回小于0的值 //如果为真,则 a 排在 b 前面 } bool cmp4(Stu a,Stu b){ if(a.score[3] != b.score[3]) return a.score[3] > b.score[3]; return strcmp(a.name, b.name) < 0; //strcmp(x,y). 如果字符串x 按字典序小于y,则返回小于0的值 //如果为真,则 a 排在 b 前面 } bool cmp_all(Stu a,Stu b){ int sum_a = 0; int sum_b = 0; for(int i = 0 ;i < 4;i++){ sum_a += a.score[i]; sum_b += b.score[i]; } if(sum_a != sum_b) return sum_a > sum_b; return strcmp(a.name, b.name) < 0; //strcmp(x,y). 如果字符串x 按字典序小于y,则返回小于0的值 //如果为真,则 a 排在 b 前面 } int main(){ int N; scanf("%d",&N); for(int i = 0;i < N;i++){ scanf("%s",stu[i].name); for(int j = 0;j < 4;j++){ scanf("%d",&stu[i].score[j]); } } sort(stu,stu+N,cmp1); print(N); sort(stu,stu+N,cmp2); print(N); sort(stu,stu+N,cmp3); print(N); sort(stu,stu+N,cmp4); print(N); sort(stu,stu+N,cmp_all); print(N); return 0; }
例题:抢气球
教室的墙上挂满了气球,五颜六色,小朋友们非常
喜欢。
刚一下课,小朋友们就打算去抢这些气球。每个气.
球在墙上都有一定的高度,只有当小朋友跳起来
时,手能够到的高度大于等于气球的高度,小朋友
才能摘到这个气球。为了公平起见,老师让跳的低
的小朋友先摘,跳的高的小朋友后摘。小朋友都很
贪心,每个小朋友在摘气球的时候都会把自己能摘
的气球都摘掉。
很巧的是,小朋友们跳起来手能够着的高度都不一
样,这样就不会有跳起来后高度相同的小朋友之间
发生争执了。


样例2:

#include<stdio.h> #include<iostream> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; struct Child{ int id; int h; }; Child ch[1005]; int flag[1005]; int child_get[1005]; int ball_h[1005]; bool cmp(Child x,Child y){ return x.h < y.h; } int main(){ int n,m; scanf("%d %d",&n,&m); for(int i = 0 ;i < n;i++){ scanf("%d",&ch[i].h); ch[i].id = i; } for(int i = 0;i < m;i++){ scanf("%d",&ball_h[i]); } sort(ch,ch+n,cmp); for(int i = 0; i < n;i++){ for(int j = 0;j < m;j++){ if(ball_h[j] <= ch[i].h && flag[j] == 0){//如果气球高度可以摘到,同时没有被摘下来 flag[j] = 1; child_get[ch[i].id]++; //排序前的顺序 } } } for(int i = 0 ;i < n;i++){ printf("%d\n",child_get[i]); } return 0; }
例题:抢气球升级版
只有n m 的规模发生了变化,增大到 10^ 5 级,时间限制1s ,显然,上方的做法会超时
#include<stdio.h> #include<iostream> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; struct Child{ int id; int h; }; Child ch[1005]; int child_get[1005]; int ball_h[1005]; bool cmp(Child x,Child y){ return x.h < y.h; } int main(){ int n,m; scanf("%d %d",&n,&m); for(int i = 0 ;i < n;i++){ scanf("%d",&ch[i].h); ch[i].id = i; } for(int i = 0;i < m;i++){ scanf("%d",&ball_h[i]); } sort(ch,ch+n,cmp); //只需要将气球也按高度排序即可,优化内部for循环,省去扫描已经被摘走的气球 sort(ball_h,ball_h + m); int p = 0; for(int i = 0; i < n;i++){ while(p < m && ball_h[p] <= ch[i].h ){ child_get[ch[i].id]++; p++; } } //时间复杂度 由O(n*m)--> O(n+m) for(int i = 0 ;i < n;i++){ printf("%d\n",child_get[i]); } return 0; }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号