C++ 数据类型
使用编程语言进行编程时,需要用到各种变量来存储各种信息。变量保留的是它所存储的值的内存位置。这意味着,当您创建一个变量时,就会在内存中保留一些空间。
您可能需要存储各种数据类型(比如字符型、宽字符型、整型、浮点型、双浮点型、布尔型等)的信息,操作系统会根据变量的数据类型,来分配内存和决定在保留内存中存储什么
一、基本的内置类型

各种变量类型在内存中的存储空间 + 可存储的max min 请戳上方链接进入
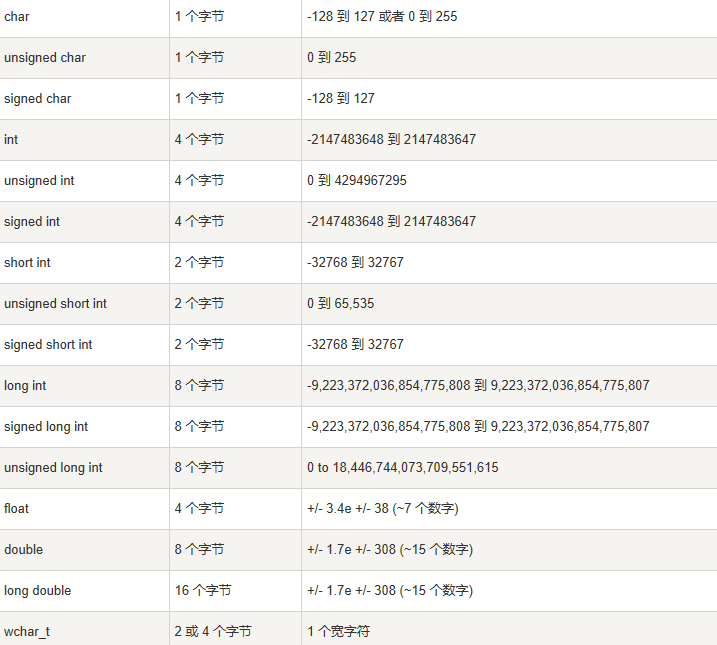
输出您电脑上各种数据类型的大小:
#include<iostream> #include<string> #include <limits> using namespace std; int main() { cout << "type: \t\t" << "************size**************"<< endl; cout << "bool: \t\t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(bool); cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<bool>::max)(); cout << "\t\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<bool>::min)() << endl; cout << "char: \t\t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(char); cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<char>::max)(); cout << "\t\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<char>::min)() << endl; cout << "signed char: \t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(signed char); cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<signed char>::max)(); cout << "\t\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<signed char>::min)() << endl; cout << "unsigned char: \t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(unsigned char); cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<unsigned char>::max)(); cout << "\t\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<unsigned char>::min)() << endl; cout << "wchar_t: \t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(wchar_t); cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<wchar_t>::max)(); cout << "\t\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<wchar_t>::min)() << endl; cout << "short: \t\t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(short); cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<short>::max)(); cout << "\t\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<short>::min)() << endl; cout << "int: \t\t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(int); cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<int>::max)(); cout << "\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<int>::min)() << endl; cout << "unsigned: \t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(unsigned); cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<unsigned>::max)(); cout << "\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<unsigned>::min)() << endl; cout << "long: \t\t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(long); cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<long>::max)(); cout << "\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<long>::min)() << endl; cout << "unsigned long: \t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(unsigned long); cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<unsigned long>::max)(); cout << "\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<unsigned long>::min)() << endl; cout << "double: \t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(double); cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<double>::max)(); cout << "\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<double>::min)() << endl; cout << "long double: \t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(long double); cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<long double>::max)(); cout << "\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<long double>::min)() << endl; cout << "float: \t\t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(float); cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<float>::max)(); cout << "\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<float>::min)() << endl; cout << "size_t: \t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(size_t); cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<size_t>::max)(); cout << "\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<size_t>::min)() << endl; cout << "string: \t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(string) << endl; // << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<string>::max)() << "\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<string>::min)() << endl; cout << "type: \t\t" << "************size**************"<< endl; return 0; }
二、typedef 声明 ———— 为一个已有的类型取一个新的名字
typedef int feet; feet x = 0;
feet 是 int 的另一个名称
三、枚举类型 ———— 是由用户定义的若干枚举常量的集合
如果一个变量只有几种可能的值,可以定义为枚举(enumeration)类型。所谓"枚举"是指将变量的值一一列举出来,变量的值只能在列举出来的值的范围内。
创建枚举,需要使用关键字 enum。枚举类型的一般形式为:
enum 枚举名{ 标识符[=整型常数], 标识符[=整型常数], ... 标识符[=整型常数] } 枚举变量;
如果枚举没有初始化, 即省掉"=整型常数"时, 则从第一个标识符开始
enum color { red, green, blue } c; c = blue;
定义了一个颜色枚举,变量 c 的类型为 color。最后,c 被赋值为 "blue“
默认情况下,第一个名称的值为 0,第二个名称的值为 1,第三个名称的值为 2,以此类推。但是,您也可以给名称赋予一个特殊的值,只需要添加一个初始值即可。例如,在下面的枚举中,green 的值为 5。
enum color { red, green=5, blue };
在这里,blue 的值为 6,因为默认情况下,每个名称都会比它前面一个名称大 1,但 red 的值依然为 0。
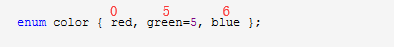
补充:
1.枚举类型实例一
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int main(){ enum days{one, two, three}day; day = one; switch(day){ case one: cout << "one" << endl; break; case two: cout << "two" << endl; break; default: cout << "three" << endl; break; } return 0; }
2.枚举类型实例二
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() { enum rank { first,second,third }; int nRank=1; switch (nRank) { case first: cout << "第一名"; break; case second: cout << "第二名"; break; case third: cout << "第三名"; break; default: break; } // system("pause"); return 0; }

3.枚举类型不一定要在 main 中定义
#include <iostream> using namespace std; enum time { first,second, third,forth,fifth }; int main() { enum time a=fifth; if (a==4) { cout << "Succeed!"; } return 0; }

4.关于 typedef 的几点说明:
- typedef 可以声明各种类型名,但不能用来定义变量。用 typedef 可以声明数组类型、字符串类型,使用比较方便。
- 用typedef只是对已经存在的类型增加一个类型名,而没有创造新的类型。
- 当在不同源文件中用到同一类型数据(尤其是像数组、指针、结构体、共用体等类型数据)时,常用 typedef 声明一些数据类型,把它们单独放在一个头文件中,然后在需要用到它们的文件中用 #include 命令把它们包含进来,以提高编程效率。
- 使用 typedef 有利于程序的通用与移植。有时程序会依赖于硬件特性,用 typedef 便于移植。
5.

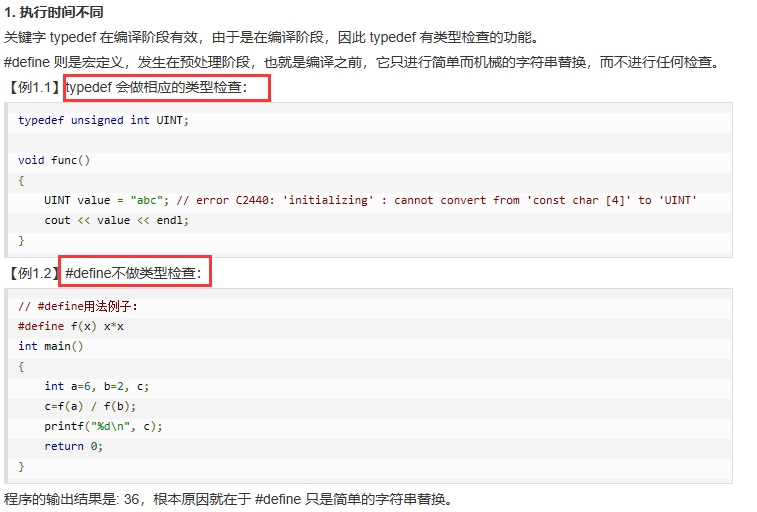
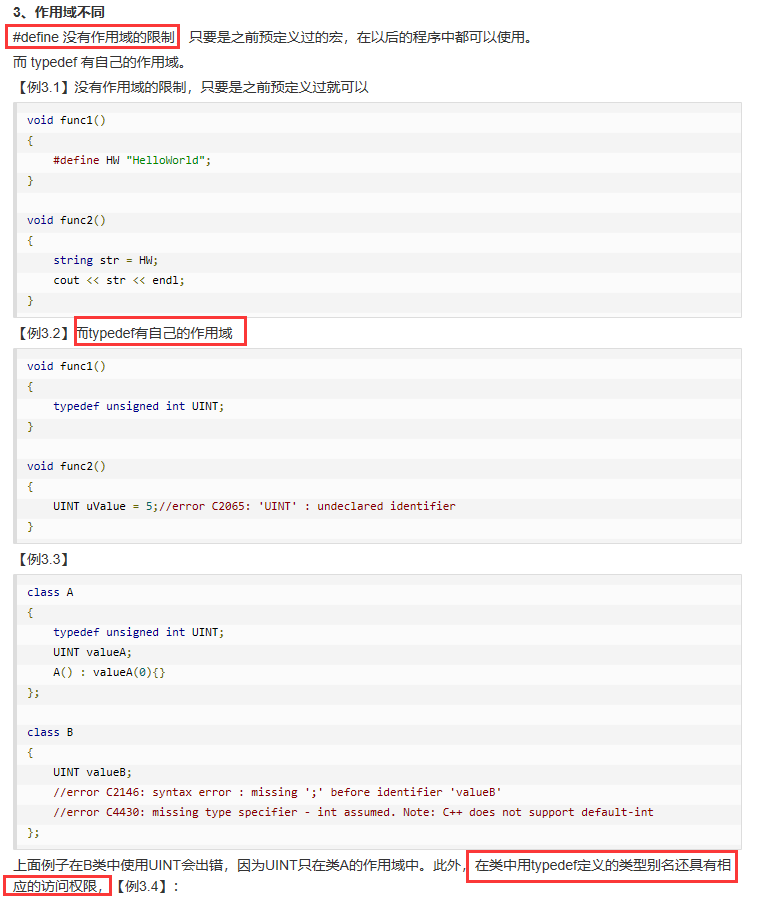
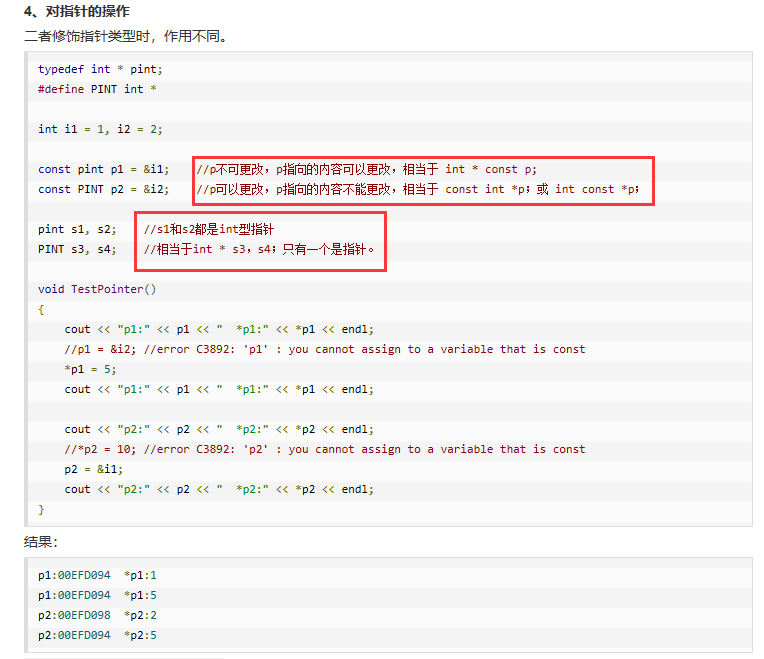
6.typedef 与 #define 的区别


7.