算法竞赛入门 (一)语言篇 顺序与分支结构
1.1 算术表达式
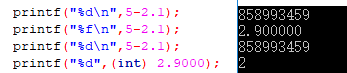
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main() { printf("%d\n",3+2); printf("%d\n",3*2); printf("%d\n",3/2); printf("%d\n",3-2); return 0; }
结果:
5 6 1 1
3/2指3处以2所得商值的整数部分
输出3/2的值,并保留小数点后一位
【整数用 %d 输出,浮点数用 %f输出】
【整数 / 整数 = 整数 浮点数 / 浮点数 = 浮点数】
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main() { printf("%d\n",3/2);
printf("%.1f\n",3/2); printf("%.1f\n",3.0/2.0); return 0; }
结果:
1 0.0 1.5
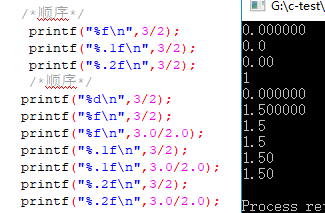
整数 - 浮点数 时,整数先变成浮点数,再减去浮点数
1.2 变量及其输入
例题:输入半径r 高h 求圆柱表面积
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <math.h> int main() { const double pi = acos(-1.0); //math.h中定义的常量M_PI,但这个常数不是ANSI C标准的,而此处的pi是一个真正的数学常数 double r,h,s1,s2,s; scanf("%lf%lf",&r,&h); //输入采用的 %lf 目前先跳过,后续补 s1 = pi*r*r; s2 = 2*pi*r*h; s = s1*2.0 + s2; printf("Area = %.3f\n",s); return 0; }
const 是 constant 的缩写,本意是不变的,不易改变的意思。在 C++ 中是用来修饰内置类型变量,自定义对象,成员函数,返回值,函数参数
算法竞赛中注意事项:
- 不要在输入前打印提示信息
- 不要让程序“按任意键退出” ,输出完毕后立即终止程序————例如,调用 system("pause"); 或 添加一个多余的 getchar()
- 不要使用 getch() getche() gotoxy() clrscr()
- 不要使用头文件conio.h,包括getch() clrscr()等函数
- 输出格式非常严格:
- 每行输出均以回车符结束,包括最后一行
- 每行行首不应有空格,行末可以有
- 输出的每两个数或字符串之间应以单个空格隔开
- 尽量使用const 关键字声明常数
1.3 顺序结构程序设计

此处有个问题,如果个位是0,反转后应该输出吗?
算法竞赛的题目非常严密,如有题目漏洞,可向监考人员询问,不可随意假定
但此处要学会两种处理方法:
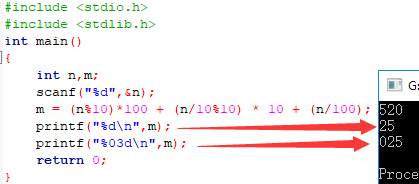
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main() { int n; scanf("%d",&n); printf("%d%d%d\n",n%10,n/10%10,n/100); return 0; }

三变量法————新加一个新的变量
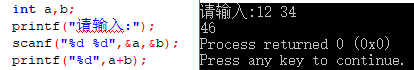
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main() { int a,b,c; scanf("%d %d",&a,&b); c = a; a = b; b = c; printf("%d %d",a,b); return 0; }
1.4 分支结构程序设计
例题1-4 鸡兔同笼子 鸡兔总数量n,总腿数m,求依次输出鸡兔的数目
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main() { int m,n,x,y; scanf("%d %d",&n,&m); x = (4 * n - m) / 2; y = n - x; if(m %2 == 1 || x < 0 || y < 0) printf("No answer"); else printf("%d %d",x,y); return 0; }
C语言中的短路:
如果a || b 中,a为真,就不会计算b的值 【速度更快】
C语言中的逻辑运算符都是短路运算符,一旦确定整个表达式的值,就不再计算
1-5 三整数排序
输入 a ,b,c 从大到小排序后输出
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main() { int a,b,c; scanf("%d %d %d",&a,&b,&c); if( a >= b){ if(b >= c){ printf("%d %d %d",a,b,c); }else if(a >= c){ printf("%d %d %d",a,c,b); }else{ printf("%d %d %d",c,a,b); } }else{ if(a >=c ){ printf("%d %d %d",b,a,c); }else if(b >= c ){ printf("%d %d %d",b,c,a); }else{ printf("%d %d %d",c,b,a); } } return 0; }
数据类型实验
实验一
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main() { printf("%d\n",11111*11111); printf("%d\n",111111*111111); printf("%d\n\n",1111111*1111111); printf("%f\n",11111*11111); printf("%f\n",111111*111111); printf("%f",1111111*1111111); return 0; }
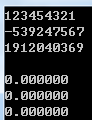
实验二
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main() { printf("%f\n",1111.1*1111.1); printf("%f\n",11111.1*11111.1); printf("%f",111111.1*111111.1); return 0; }
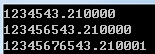
实验三
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <math.h> int main() { printf("%f\n",sqrt(-10)); printf("%d\n",sqrt(-10)); return 0; }
计算过程中,系统不会报错
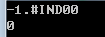
实验四
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <math.h> int main() { printf("%d\n",1.0/0.0); printf("%d\n",0.0/0.0); printf("%f\n",1.0/0.0); printf("%f\n",0.0/0.0); return 0; }
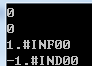
实验五
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <math.h> int main() { printf("%d\n",1/0); printf("%f\n",1/0); return 0; }
无论注释那个,都会报错
实验六:
#include<stdio.h> int main(){ //C语言中 除法 问题总结 // 整数 除以 整数 int a = 13,b = 4; printf("整数除以整数 %d\n",a/b); printf("【注意顺序 此处和 下方第二条 是完全一样的】整数除以整数 直接以float输出: %f\n",a/b); printf("整数除以整数 强制转换为 float: %f\n",(float) a/b); // printf("整数除以整数 直接以float输出: %f\n",a/b); //double 除以 double printf("\n"); printf("\n"); printf("\n"); printf("\n"); double x = 13.0,y = 4.0; printf("小数除以小数 : %f\n",x/y); printf("【注意顺序 此处和 下方第二条 是完全一样的】小数除以小数 以int输出: %d\n",x/y); printf("小数除以小数 强制转换为 int: %d\n",(int) x/y); printf("小数除以小数 以int输出: %d\n",x/y); //小数除以整数 / 整数除以小数 double i = 13.4; int j = 3; printf("\n\n\n小数除以整数 / 整数除以小数:"); printf("%f",i/j); printf("\n%f",j/i); return 0; }
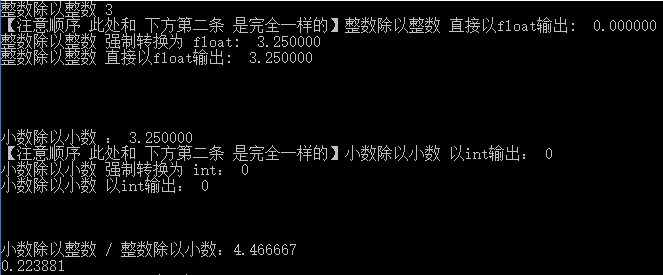
输入输出实验
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <math.h> int main() { int a,b; scanf("%d%d",&a,&b); printf("%d %d",a,b); return 0; }
- 1.同一行输入12 2 ,以空格隔开
- 2.不同行输入12 2
- 3.在1、2实验中,在12 和 2 之前加入大量的空格和水平制表符TAB,升值一些空行,重复实验1 2 3
习题:
1.输入3个整数,计算平均值,保留三位小数
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main() { int a,b,c; scanf("%d %d %d",&a,&b,&c); printf("%.3f",(a+b+c)/3.0); return 0; }
2.温度,输入华氏摄氏度f,输出对应的摄氏温度c,保留三位,c = 5 (f-32)/9
1 printf输出float和double都可以用%f,double还可以用%lf。
2 scanf输入float用%f,double输入用%lf,不能混用。
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main() { float f; scanf("%f",&f); printf("%.3f",5 *(f-32)/9.0); return 0; }
3.1+..+n
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main() { int n; scanf("%d",&n); int sum = 0,i = 0; for(i = 1;i < n+1;i++){ sum+=i; } printf("%d",sum); return 0; }
4.正弦和余弦
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <math.h> int main() { int n; scanf("%d",&n); printf("%f\n",sin(n)); printf("%f",cos(n)); return 0; }
5.判断闰年
公历纪年法中,能被 4 整除的大多是闰年,但能被 100整除而不能被 400整除的年份不是闰年,如 1900年是平年,2000 年是闰年
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
if(n % 4 != 0){
printf("N");
}else{
if(n % 100 == 0 && n%400 != 0){
printf("N");
}else{
printf("Y");
}
}
return 0;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号