【转】邻接表的DFS、BFS、两结点的全部简单路径
晚上看视频的时候一不小心把浏览器关了,所以丢失了原文链接...
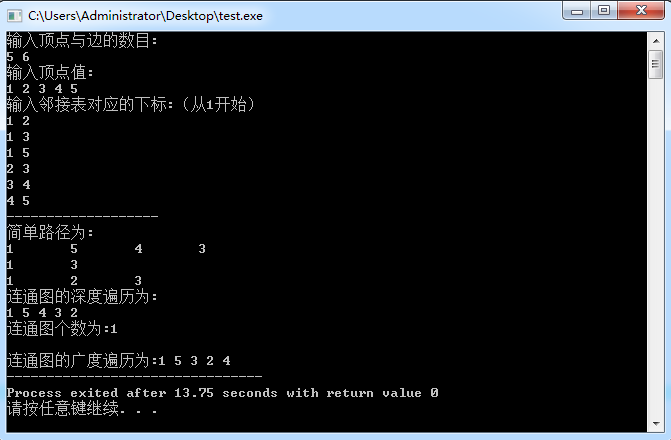
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<string.h> #define MAX_VERTEX_NUM 20 #define OVERFLOW 0 #define OK 1 #define TRUE 1 #define FALSE 0 typedef int Status ; typedef char VertexType; typedef int QElemType; typedef struct ArcNode { int adjvex; //邻接点域,存储该邻点顶点对应的下标 struct ArcNode *nextarc; //邻节点 int weight; //权值 }ArcNode; /*邻接表结构*/ typedef struct VNode { VertexType data; //顶点对应的值 ArcNode *firstarc; //边表头指针指向邻顶点 }VNode,AdjList[MAX_VERTEX_NUM]; typedef struct { AdjList vertices; int vexnum,arcnum; //顶点数,边数 }ALGraph; /*队列结构*/ typedef struct QNode { QElemType data; struct QNode *next; }QNode,*QueuePtr; typedef struct { int data[MAX_VERTEX_NUM]; int front, rear; }Queue; //队列顺序表的相关操作 //初始化 void InitQueue(Queue *Q) { Q->front = Q->rear = 0; } //入队 void EnQueue(Queue *Q, int e) { if ((Q->rear+1)%MAX_VERTEX_NUM == Q->front) return ; Q->data[Q->rear] = e; Q->rear = (Q->rear+1)%MAX_VERTEX_NUM; } //判空 int QueueEmpty(Queue *Q) { if (Q->front == Q->rear) return 1; else return 0; } //出队 void DeQueue(Queue *Q, int *e) { if (Q->front == Q->rear) return ; *e = Q->data[Q->front]; Q->front = (Q->front+1)%MAX_VERTEX_NUM; } void CreateALGraph(ALGraph *G) //构建图 { ArcNode *p; int i,j,k; printf("输入顶点与边的数目:\n"); scanf("%d%d",&G->vexnum,&G->arcnum); getchar(); printf("输入顶点值:\n"); for(i=1;i<=G->vexnum;i++) { scanf("%c",&G->vertices[i].data); getchar(); G->vertices[i].firstarc=NULL; } //建立边表 printf("输入邻接表对应的下标:(从1开始)\n"); for(k=1;k<=G->arcnum;k++) { scanf("%d%d",&i,&j); //边对应的两个顶点下标并将俩顶点联系起来 p = (ArcNode *)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode)); p->adjvex = j; p->nextarc = G->vertices[i].firstarc; G->vertices[i].firstarc = p; /*有向图只要上部分即可*/ p = (ArcNode*)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode)); p->adjvex = i; p->nextarc = G->vertices[j].firstarc; G->vertices[j].firstarc = p; } } int visited[MAX_VERTEX_NUM]; //记录是否被访问 /*邻接表的深度遍历*/ void DFS(ALGraph G,int i) { int j; ArcNode *p; visited[i]=1; //将要访问的顶点置为1 printf("%c ",G.vertices[i].data); //输出各顶点 for(p = G.vertices[i].firstarc;p!=NULL;p=p->nextarc) { j = p->adjvex; if(visited[j]==0) //深度探索 DFS(G,j); } } void Is_connected(ALGraph G) { int i; int count = 0; for(i=1;i<=G.vexnum;i++) visited[i]=0; //初始化0,未被访问 for(i=1;i<=G.vexnum;i++) { if(!visited[i]) { printf("\n"); DFS(G,i); count++; //记录连通图个数(>1)则整体是个非连通图 } } printf("\n连通图个数为:%d\n",count); } /*邻接表的广度遍历*/ void BFSTraverse(ALGraph g) { ArcNode *p; Queue Q; InitQueue(&Q); for(int i = 1; i <= g.vexnum; i++) { visited[i] = 0; } for(int j = 1; j<=g.vexnum; j++) { if(!visited[j]) { printf("%c ", g.vertices[j].data); //打印顶点,也可以其他操作 visited[j] = 1; EnQueue(&Q,j); while(!QueueEmpty(&Q)) { int m; DeQueue(&Q,&m); //访问点出队列 p = g.vertices[m].firstarc; //找到当前顶点边表链表头指针 while(p) { if(!visited[p->adjvex]) { printf("%c ", g.vertices[p->adjvex].data); visited[p->adjvex] = 1; EnQueue(&Q, p->adjvex); } p = p->nextarc; } } } } } int flag = 0; //标志探寻点置0 int top = 0; char path[MAX_VERTEX_NUM]; /*连通图的简单路径(类dfs) */ void pathdfs(ALGraph G,int i,int j) { ArcNode *p; int s,w; visited[i]=1; //将顶点i加入当前路径 path[++top] = G.vertices[i].data; if(!flag && path[top]==G.vertices[j].data) flag = 1; //存在顶点i到顶点j的路径 if(flag) //找到 { //输出当前路径上所有顶点 printf("\n"); for(s=1;s<=top;s++) printf("%c\t",path[s]); flag = 0; } else for(p=G.vertices[i].firstarc;p;p=p->nextarc) { w = p->adjvex; if(!visited[w]) pathdfs(G,w,j); } visited[i]=0; //每当顶点i回溯时,把visited[i]置为0,下次可通过顶点i寻找其他可能到达j的路径 top--; //删除顶点i } int main() { ALGraph G; CreateALGraph(&G); printf("-------------------\n"); printf("简单路径为:"); pathdfs(G,1,3); printf("\n连通图的深度遍历为:"); Is_connected(G); printf("\n连通图的广度遍历为:"); BFSTraverse(G); return 0; }
/* 样例图: 2 / \ / \ 1--------3 | | | | 5--------4
样例输入: 5 6 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 1 3 1 5 2 3 3 4 4 5 */




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号